Anat Cell Biol.
2023 Jun;56(2):228-235. 10.5115/acb.22.221.
Immunostaining patterns reveal potential morphogenetic role of Toll-like receptors 4 and 7 in the development of mouse respiratory system, liver and pancreas
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Health for Science, Università degli Sudi di Milano, Milano, Italy
- 2Department of Pharmacological and Biomolecular Sciences, Università degli Sudi di Milano, Milano, Italy
- 3Department of Environmental Science and Policy, Università degli Sudi di Milano, Milano, Italy
- 4Laboratory of Applied Biomechanics, Department of Biomedical Sciences for Health, University of Milan, Milano, Italy
- 5Humanitas University, Milano, Italy
- KMID: 2544085
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.22.221
Abstract
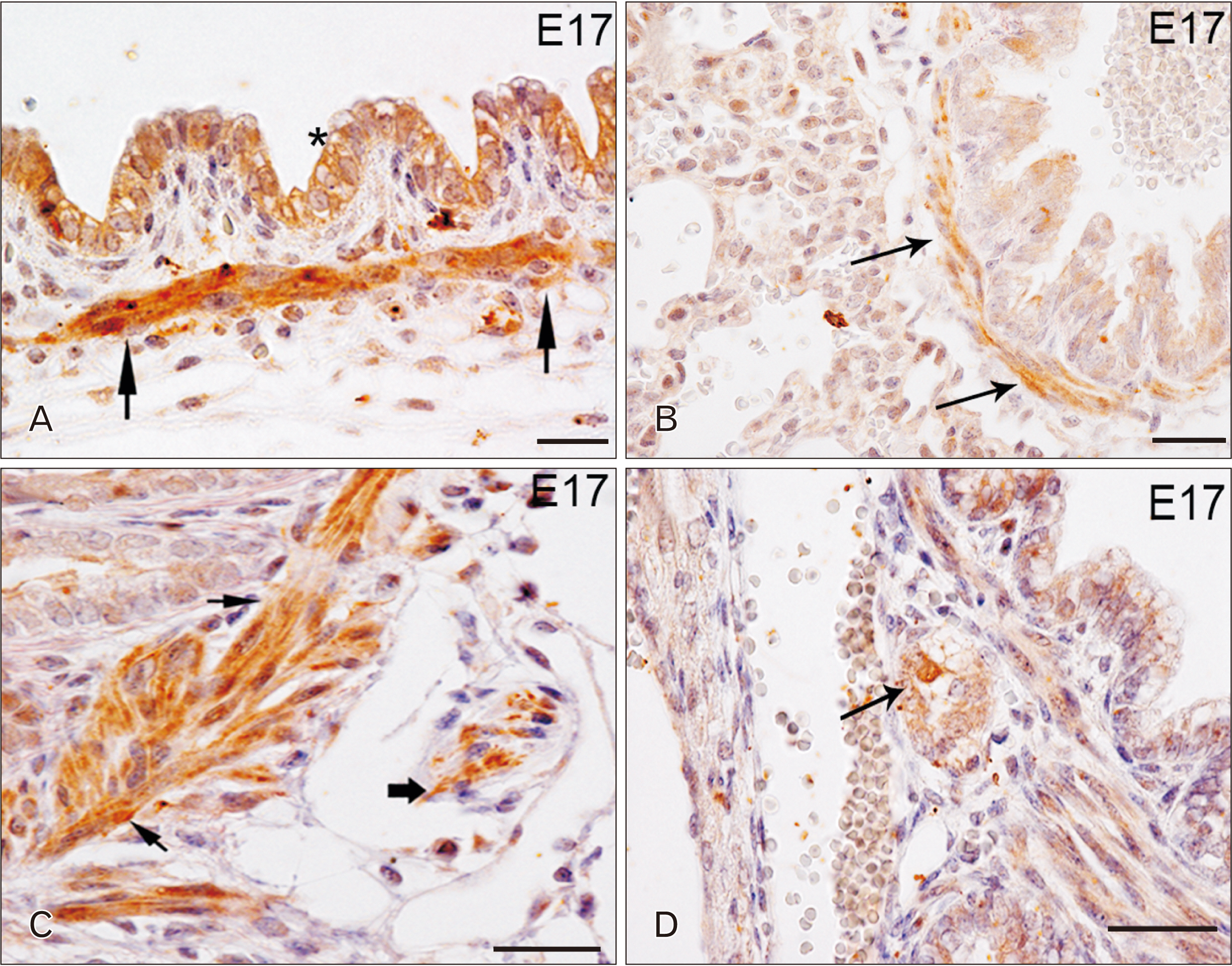
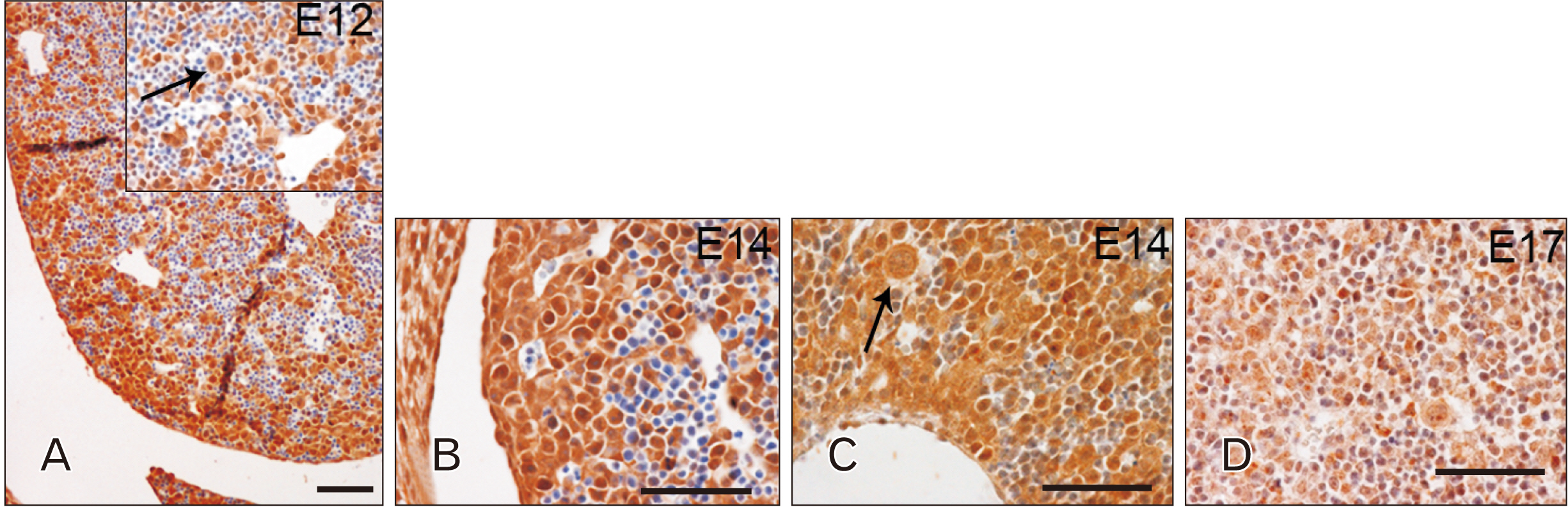
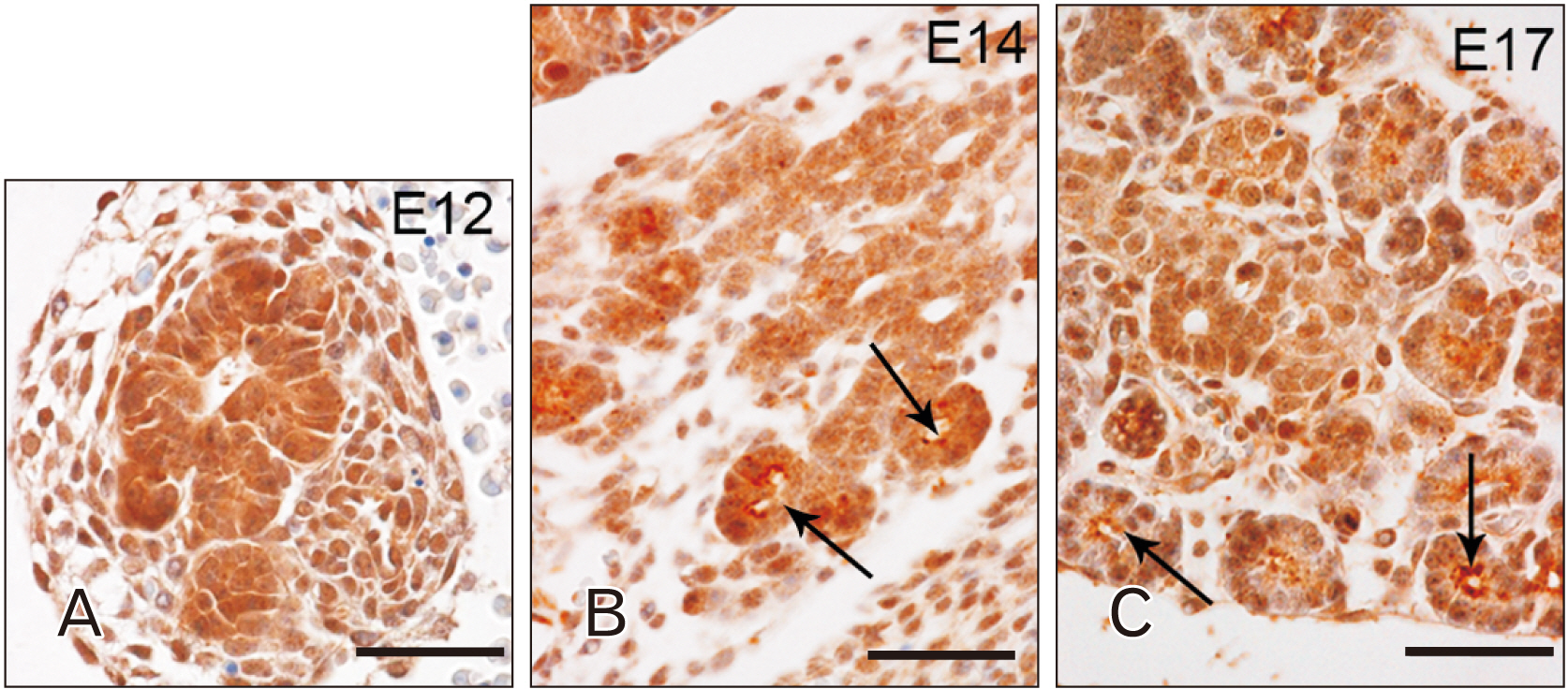
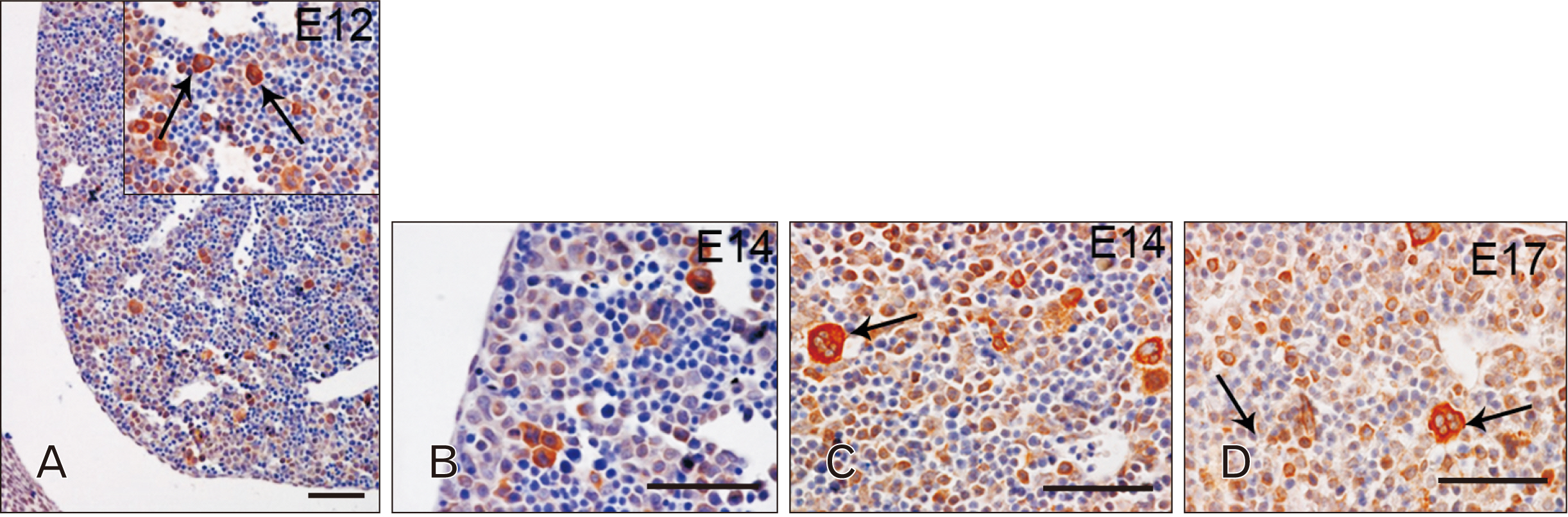
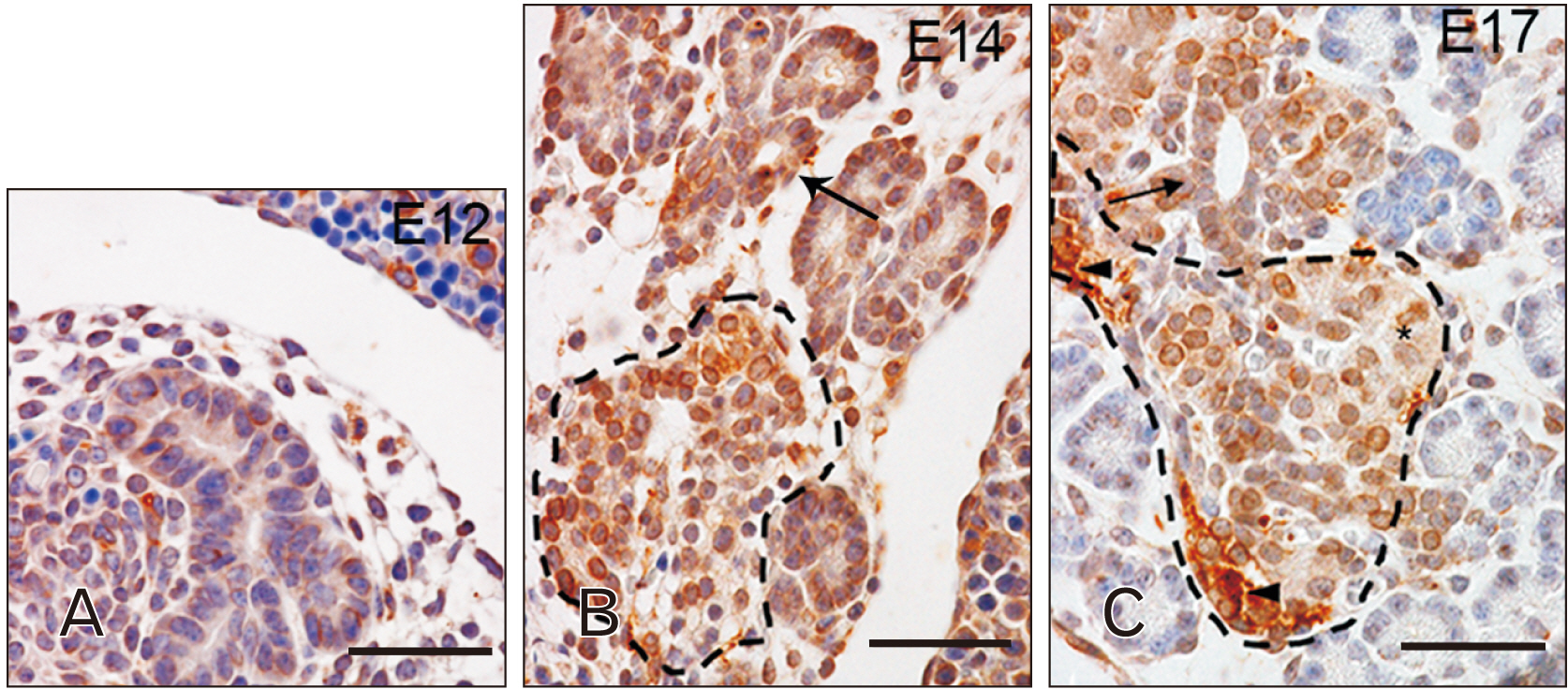
- Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are the mammalian ortholog of Drosophila melanogaster protein Toll, originally identified for its involvement in embryonic development. In mammals, TLRs are mainly known for their ability to recognize pathogen- or damage-associated molecular patterns and, consequently, to initiate the immune response. However, it is becoming clear that TLRs can play a role also in mammal embryo development. We have previously described TLR4 and TLR7 expression in developing mouse peripheral nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. In the present study, we extended the investigation of TLR4 and TLR7 to the respiratory system and to the two main accessory organs of the digestive system, the liver and pancreas. TLR4 and TLR7 immunostaining was performed on mouse conceptuses collected at different stages, from E12 to E18. TLR4 and TLR7 immunoreactivity was evident in the embryo pancreas and liver at E12, while, in the respiratory apparatus, appeared at E14 and E17, respectively. Although further studies are required to elucidate the specific role of these TLRs in embryo development, the differential spatiotemporal TLR4 and TLR7 appearance may suggest that TLR expression in developing embryos is highly regulated for a possible their direct involvement in the formation of the organs and in the acquisition of immune-related features in preparation for the birth.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Vijay K. 2018; Toll-like receptors in immunity and inflammatory diseases: past, present, and future. Int Immunopharmacol. 59:391–412. Erratum in: Int Immunopharmacol 2018;62:338. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.06.044. PMID: 30089605. PMCID: PMC8445284.
Article2. Fitzgerald KA, Kagan JC. 2020; Toll-like receptors and the control of immunity. Cell. 180:1044–66. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.041. PMID: 32164908. PMCID: PMC9358771.
Article3. Parker LC, Prince LR, Sabroe I. 2007; Translational mini-review series on Toll-like receptors: networks regulated by Toll-like receptors mediate innate and adaptive immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 147:199–207. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03203.x. PMID: 17223959. PMCID: PMC1810480.
Article4. Zindel J, Kubes P. 2020; DAMPs, PAMPs, and LAMPs in immunity and sterile inflammation. Annu Rev Pathol. 15:493–518. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012419-032847. PMID: 31675482.
Article5. Chaturvedi A, Pierce SK. 2009; How location governs toll-like receptor signaling. Traffic. 10:621–8. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00899.x. PMID: 19302269. PMCID: PMC2741634.
Article6. Ciesielska A, Matyjek M, Kwiatkowska K. 2021; TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 78:1233–61. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-020-03656-y. PMID: 33057840. PMCID: PMC7904555.
Article7. Tojo S, Zhang Z, Matsui H, Tahara M, Ikeguchi M, Kochi M, Kamada M, Shigematsu H, Tsutsumi A, Adachi N, Shibata T, Yamamoto M, Kikkawa M, Senda T, Isobe Y, Ohto U, Shimizu T. 2020; Structural analysis reveals TLR7 dynamics underlying antagonism. Nat Commun. 11:5204. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19025-z. PMID: 33060576. PMCID: PMC7562955. PMID: be81925ea7f144b39dd225d5ffceb7a8.
Article8. Anthoney N, Foldi I, Hidalgo A. 2018; Toll and Toll-like receptor signalling in development. Development. 145:dev156018. DOI: 10.1242/dev.156018. PMID: 29695493.
Article9. Barak B, Feldman N, Okun E. 2014; Toll-like receptors as developmental tools that regulate neurogenesis during development: an update. Front Neurosci. 8:272. DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00272. PMID: 25221470. PMCID: PMC4148028. PMID: e26790cb55f24d0eb87bf717a6649a3c.
Article10. Kannaki TR, Reddy MR, Verma PC, Shanmugam M. 2015; Differential Toll-like receptor (TLR) mRNA expression patterns during chicken embryological development. Anim Biotechnol. 26:130–5. DOI: 10.1080/10495398.2014.939658. PMID: 25380465.
Article11. Awasthi S, Cropper J, Brown KM. 2008; Developmental expression of Toll-like receptors-2 and -4 in preterm baboon lung. Dev Comp Immunol. 32:1088–98. DOI: 10.1016/j.dci.2008.02.005. PMID: 18377992.
Article12. Harju K, Glumoff V, Hallman M. 2001; Ontogeny of Toll-like receptors Tlr2 and Tlr4 in mice. Pediatr Res. 49:81–3. DOI: 10.1203/00006450-200101000-00018. PMID: 11134496.
Article13. Meyerholz DK, Kawashima K, Gallup JM, Grubor B, Ackermann MR. 2006; Expression of select immune genes (surfactant proteins A and D, sheep beta defensin 1, and toll-like receptor 4) by respiratory epithelia is developmentally regulated in the preterm neonatal lamb. Dev Comp Immunol. 30:1060–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.dci.2006.01.001. PMID: 16510184. PMCID: PMC2791064.
Article14. Arnaboldi F, Sommariva M, Opizzi E, Rasile M, Camelliti S, Busnelli M, Menegola E, Di Renzo F, Menon A, Barajon I. 2020; Expression of Toll-like receptors 4 and 7 in murine peripheral nervous system development. Ann Anat. 231:151526. DOI: 10.1016/j.aanat.2020.151526. PMID: 32380196.
Article15. Vaure C, Liu Y. 2014; A comparative review of toll-like receptor 4 expression and functionality in different animal species. Front Immunol. 5:316. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00316. PMID: 25071777. PMCID: PMC4090903. PMID: 66d7b3eb90f848ce8b648d62335a7def.
Article16. Petes C, Odoardi N, Gee K. 2017; The Toll for trafficking: Toll-like receptor 7 delivery to the endosome. Front Immunol. 8:1075. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01075. PMID: 28928743. PMCID: PMC5591332. PMID: 7b044a263a8a4b2bb3394e3d5a9bb8f1.
Article17. Kaufman MH. 1992. The atlas of mouse development. Academic Press;DOI: 10.1002/mrd.1080370119.18. Barajon I, Serrao G, Arnaboldi F, Opizzi E, Ripamonti G, Balsari A, Rumio C. 2009; Toll-like receptors 3, 4, and 7 are expressed in the enteric nervous system and dorsal root ganglia. J Histochem Cytochem. 57:1013–23. DOI: 10.1369/jhc.2009.953539. PMID: 19546475. PMCID: PMC2762881.
Article19. Arnaboldi F, Menon A, Menegola E, Di Renzo F, Mirandola L, Grizzi F, Figueroa JA, Cobos E, Jenkins M, Barajon I, Chiriva-Internati M. 2014; Sperm protein 17 is an oncofetal antigen: a lesson from a murine model. Int Rev Immunol. 33:367–74. DOI: 10.3109/08830185.2014.911856. PMID: 24811209.20. Busnelli M, Manzini S, Bonacina F, Soldati S, Barbieri SS, Amadio P, Sandrini L, Arnaboldi F, Donetti E, Laaksonen R, Paltrinieri S, Scanziani E, Chiesa G. 2020; Fenretinide treatment accelerates atherosclerosis development in apoE-deficient mice in spite of beneficial metabolic effects. Br J Pharmacol. 177:328–45. DOI: 10.1111/bph.14869. PMID: 31621898. PMCID: PMC6989955.
Article21. Grapin-Botton A, Melton DA. 2000; Endoderm development: from patterning to organogenesis. Trends Genet. 16:124–30. DOI: 10.1016/S0168-9525(99)01957-5. PMID: 10689353.
Article22. McGettrick AF, O'Neill LA. 2007; Toll-like receptors: key activators of leucocytes and regulator of haematopoiesis. Br J Haematol. 139:185–93. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06802.x. PMID: 17897294.
Article23. Sioud M, Fløisand Y, Forfang L, Lund-Johansen F. 2006; Signaling through toll-like receptor 7/8 induces the differentiation of human bone marrow CD34+ progenitor cells along the myeloid lineage. J Mol Biol. 364:945–54. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.054. PMID: 17049554.
Article24. Capitano ML. 2019; Toll-like receptor signaling in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Curr Opin Hematol. 26:207–13. DOI: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000511. PMID: 31033704.
Article25. Gittes GK. 2009; Developmental biology of the pancreas: a comprehensive review. Dev Biol. 326:4–35. DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.10.024. PMID: 19013144.
Article26. El-Zayat SR, Sibaii H, Mannaa FA. 2019; Toll-like receptors activation, signaling, and targeting: an overview. Bull Natl Res Cent. 43:187. DOI: 10.1186/s42269-019-0227-2. PMID: ea4ece1111dc45cf84eb1684e0549a98.
Article27. Lisboa RA, Andrade MV, Cunha-Melo JR. 2013; Toll-like receptor activation and mechanical force stimulation promote the secretion of matrix metalloproteinases 1, 3 and 10 of human periodontal fibroblasts via p38, JNK and NF-kB. Arch Oral Biol. 58:731–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2012.12.009. PMID: 23332208.
Article28. Li H, Xu H, Liu S. 2011; Toll-like receptors 4 induces expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Mol Biol Rep. 38:1419–23. DOI: 10.1007/s11033-010-0246-4. PMID: 20725790.
Article29. Song GG, Kim JH, Lee YH. 2013; Toll-like receptor (TLR) and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) polymorphisms and periodontitis susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 40:5129–41. DOI: 10.1007/s11033-013-2616-1. PMID: 23653009.
Article30. Iozzo RV, Schaefer L. 2010; Proteoglycans in health and disease: novel regulatory signaling mechanisms evoked by the small leucine-rich proteoglycans. FEBS J. 277:3864–75. DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07797.x. PMID: 20840584. PMCID: PMC3000440.
Article31. Kim SK, Hebrok M. 2001; Intercellular signals regulating pancreas development and function. Genes Dev. 15:111–27. DOI: 10.1101/gad.859401. PMID: 11157769.
Article32. Condon JC, Jeyasuria P, Faust JM, Mendelson CR. 2004; Surfactant protein secreted by the maturing mouse fetal lung acts as a hormone that signals the initiation of parturition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 101:4978–83. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0401124101. PMID: 15044702. PMCID: PMC387359.
Article33. Guillot L, Balloy V, McCormack FX, Golenbock DT, Chignard M, Si-Tahar M. 2002; Cutting edge: the immunostimulatory activity of the lung surfactant protein-A involves Toll-like receptor 4. J Immunol. 168:5989–92. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.12.5989. PMID: 12055204.
Article34. Valanne S, Wang JH, Rämet M. 2011; The Drosophila Toll signaling pathway. J Immunol. 186:649–56. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002302. PMID: 21209287.35. Leulier F, Lemaitre B. 2008; Toll-like receptors--taking an evolutionary approach. Nat Rev Genet. 9:165–78. DOI: 10.1038/nrg2303. PMID: 18227810.36. Rose D, Chiba A. 1999; A single growth cone is capable of integrating simultaneously presented and functionally distinct molecular cues during target recognition. J Neurosci. 19:4899–906. DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-12-04899.1999. PMID: 10366624. PMCID: PMC6782657.
Article37. Rose D, Zhu X, Kose H, Hoang B, Cho J, Chiba A. 1997; Toll, a muscle cell surface molecule, locally inhibits synaptic initiation of the RP3 motoneuron growth cone in Drosophila. Development. 124:1561–71. DOI: 10.1242/dev.124.8.1561. PMID: 9108372.38. Ritzenthaler S, Suzuki E, Chiba A. 2000; Postsynaptic filopodia in muscle cells interact with innervating motoneuron axons. Nat Neurosci. 3:1012–7. DOI: 10.1038/79833. PMID: 11017174.
Article39. Bronner ME, LeDouarin NM. 2012; Development and evolution of the neural crest: an overview. Dev Biol. 366:2–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.12.042. PMID: 22230617. PMCID: PMC3351559.
Article40. Chen CY, Shih YC, Hung YF, Hsueh YP. 2019; Beyond defense: regulation of neuronal morphogenesis and brain functions via Toll-like receptors. J Biomed Sci. 26:90. DOI: 10.1186/s12929-019-0584-z. PMID: 31684953. PMCID: PMC6827257. PMID: 2a58942071a34d878a09fdf9791a6381.
Article41. Hung YF, Chen CY, Shih YC, Liu HY, Huang CM, Hsueh YP. 2018; Endosomal TLR3, TLR7, and TLR8 control neuronal morphology through different transcriptional programs. J Cell Biol. 217:2727–42. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201712113. PMID: 29777026. PMCID: PMC6080926.
Article42. Borghi E, Massa V, Severgnini M, Fazio G, Avagliano L, Menegola E, Bulfamante GP, Morace G, Borgo F. 2019; Antenatal microbial colonization of mammalian gut. Reprod Sci. 26:1045–53. DOI: 10.1177/1933719118804411. PMID: 30309297. PMCID: PMC6661723.
Article43. La Flamme AC, Milling S. 2020; Immunological partners: the gut microbiome in homeostasis and disease. Immunology. 161:1–3. DOI: 10.1111/imm.13247. PMID: 32851647. PMCID: PMC7450166.
Article44. Zheng D, Liwinski T, Elinav E. 2020; Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. 30:492–506. DOI: 10.1038/s41422-020-0332-7. PMID: 32433595. PMCID: PMC7264227.
Article45. Sommariva M, Le Noci V, Bianchi F, Camelliti S, Balsari A, Tagliabue E, Sfondrini L. 2020; The lung microbiota: role in maintaining pulmonary immune homeostasis and its implications in cancer development and therapy. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:2739–49. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-020-03452-8. PMID: 31974656. PMCID: PMC7326824.
Article46. Le Noci V, Bernardo G, Bianchi F, Tagliabue E, Sommariva M, Sfondrini L. 2021; Toll like receptors as sensors of the tumor microbial dysbiosis: implications in cancer progression. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:732192. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.732192. PMID: 34604233. PMCID: PMC8485072. PMID: d434af675f354bdab4e7fb38cbadbdf8.
Article47. Pushalkar S, Hundeyin M, Daley D, Zambirinis CP, Kurz E, Mishra A, Mohan N, Aykut B, Usyk M, Torres LE, Werba G, Zhang K, Guo Y, Li Q, Akkad N, Lall S, Wadowski B, Gutierrez J, Kochen Rossi JA, Herzog JW, Diskin B, Torres-Hernandez A, Leinwand J, Wang W, Taunk PS, Savadkar S, Janal M, Saxena A, Li X, Cohen D, Sartor RB, Saxena D, Miller G. 2018; The pancreatic cancer microbiome promotes oncogenesis by induction of innate and adaptive immune suppression. Cancer Discov. 8:403–16. Erratum in: Cancer Discov 2020;10:1988. DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1134. PMID: 29567829. PMCID: PMC6225783.48. Spiljar M, Merkler D, Trajkovski M. 2017; The immune system bridges the gut microbiota with systemic energy homeostasis: focus on TLRs, mucosal barrier, and SCFAs. Front Immunol. 8:1353. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01353. PMID: 29163467. PMCID: PMC5670327. PMID: 999c3e93ce84434dbdd8d81ac94dbd5d.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Innate Immunity and Toll Like Receptors
- Activation of Innate Immune System During Viral Infection: Role of Pattern-recognition Receptors (PRRs) in Viral Infection
- Do Toll-like Receptors Play a New Role as a Biomarker of Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
- Toll-Like Receptors and Kidney Diseases
- From Cytokines to Toll-Like Receptors and Beyond - Current Knowledge and Future Research Needs in Irritable Bowel Syndrome