J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2023 Jul;66(4):456-464. 10.3340/jkns.2022.0203.
Incidence and Risk Factors of Vestibular Schwannoma in Korea : A Population-Based Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Eunpyeong St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Urology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2543537
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2022.0203
Abstract
Objective
: This study aims to investigate the incidence of vestibular schwannoma (VS) and demographic characteristics in Korea using population-based National Health Insurance Service data.
Methods
: This study analyzed Korean National Health Insurance Service data from 2005 to 2020, based on the International Classification of Diseases, 10th version, Clinical Modification codes D333 and D431. Only those patients who had undergone magnetic resonance imaging and audiologic tests were considered definitive cases. Demographic variables included age, sex, treatment modality, hypertension, diabetics, dyslipidemia, smoking history, alcohol history, and income status.
Results
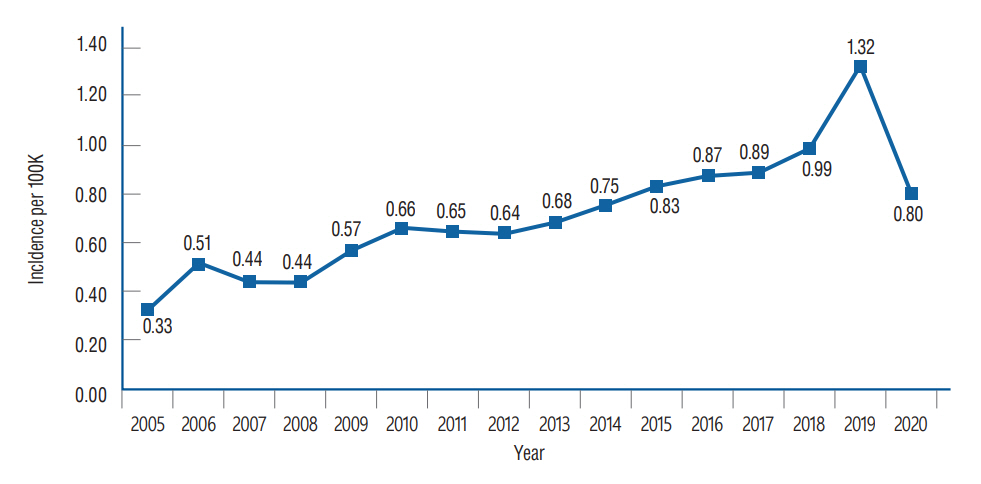
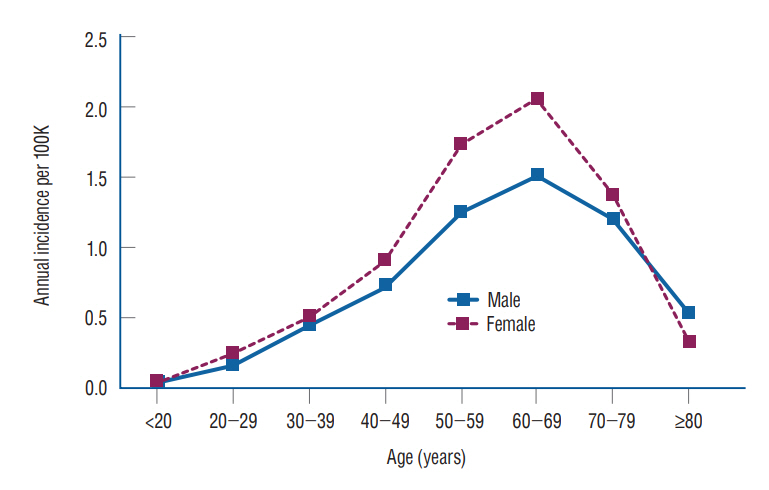
: The total number of VS patients was 5751. The average incidence rate was 0.71 per 100000 from 2005 to 2020, and the annual incidence rate increased from 0.33 in 2005 to 1.32 in 2019 but decreased to 0.80 in 2020. Incidence was highest in those aged 60–69 years (1.791) and lowest in those younger than 20 years (0.041). Incidence was higher in females, and the number of patients who received radiosurgery (46.64%) was largest compared to the wait and scan group (37.96%), microsurgery group (12.85%), or the group who received both (2.56%). Diabetes, dyslipidemia, and alcohol consumption increased the risk of VS, while cigarette smoking reduced the risk of VS.
Conclusion
: The incidence of VS exhibited an increasing trend from 2005 to 2019. Radiosurgery (46.64%) was the most common treatment modality. Diabetes, dyslipidemia, and alcohol consumption increased the risk of VS, while cigarette smoking reduced the risk of VS.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Editor’s Pick in July 2023
Bum-Tae Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2023;66(4):341-343. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2023.0117.
Reference
-
References
1. Babu R, Sharma R, Bagley JH, Hatef J, Friedman AH, Adamson C. Vestibular schwannomas in the modern era: epidemiology, treatment trends, and disparities in management. J Neurosurg. 119:121–130. 2013.
Article2. Berkowitz O, Iyer AK, Kano H, Talbott EO, Lunsford LD. Epidemiology and environmental risk factors associated with vestibular schwannoma. World Neurosurg. 84:1674–1680. 2015.
Article3. Bernardo BM, Orellana RC, Weisband YL, Hammar N, Walldius G, Malmstrom H, et al. Association between prediagnostic glucose, triglycerides, cholesterol and meningioma, and reverse causality. Br J Cancer. 115:108–114. 2016.
Article4. Brenner AV, Linet MS, Fine HA, Shapiro WR, Selker RG, Black PM, et al. History of allergies and autoimmune diseases and risk of brain tumors in adults. Int J Cancer. 99:252–259. 2002.
Article5. Carlson ML, Habermann EB, Wagie AE, Driscoll CL, Van Gompel JJ, Jacob JT, et al. The changing landscape of vestibular schwannoma management in the United States--a shift toward conservatism. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 153:440–446. 2015.
Article6. Carlson ML, Marston AP, Glasgow AE, Habermann EB, Sweeney AD, Link MJ, et al. Racial differences in vestibular schwannoma. Laryngoscope. 126:2128–2133. 2016.
Article7. Chen M, Fan Z, Zheng X, Cao F, Wang L. Risk factors of acoustic neuroma: systematic review and meta-analysis. Yonsei Med J. 57:776–783. 2016.
Article8. Cioffi G, Yeboa DN, Kelly M, Patil N, Manzoor N, Greppin K, et al. Epidemiology of vestibular schwannoma in the United States, 2004-2016. Neurooncol Adv. 2:vdaa135. 2020.
Article9. Corona AP, Ferrite S, Lopes Mda S, Rêgo MA. Risk factors associated with vestibular nerve schwannomas. Otol Neurotol. 33:459–465. 2012.
Article10. de Vries M, van der Mey AG, Hogendoorn PC. Tumor biology of vestibular schwannoma: a review of experimental data on the determinants of tumor genesis and growth characteristics. Otol Neurotol. 36:1128–1136. 2015.11. Efird JT, Friedman GD, Sidney S, Klatsky A, Habel LA, Udaltsova NV, et al. The risk for malignant primary adult-onset glioma in a large, multiethnic, managed-care cohort: cigarette smoking and other lifestyle behaviors. J Neurooncol. 68:57–69. 2004.
Article12. Kang YJ, Baek JM, Kim YS, Jeon YW, Yoo TK, Rhu J, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the diagnosis and surgery of breast cancer: a multi-institutional study. J Breast Cancer. 24:491–503. 2021.
Article13. Kim KM, Park CK, Chung HT, Paek SH, Jung HW, Kim DG. Long-term outcomes of gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery of vestibular schwannomas. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 42:286–292. 2007.
Article14. Kleijwegt M, Ho V, Visser O, Godefroy W, van der Mey A. Real incidence of vestibular schwannoma? Estimations from a national registry. Otol Neurotol. 37:1411–1417. 2016.
Article15. Koo M, Lai JT, Yang EY, Liu TC, Hwang JH. Incidence of vestibular schwannoma in Taiwan from 2001 to 2012: a population-based national health insurance study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 127:694–697. 2018.
Article16. Kramer F, Stöver T, Warnecke A, Diensthuber M, Lenarz T, Wissel K. BDNF mRNA expression is significantly upregulated in vestibular schwannomas and correlates with proliferative activity. J Neurooncol. 98:31–39. 2010.
Article17. Larjavaara S, Feychting M, Sankila R, Johansen C, Klaeboe L, Schüz J, et al. Incidence trends of vestibular schwannomas in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden in 1987-2007. Br J Cancer. 105:1069–1075. 2011.
Article18. Lim YJ, Choi SK. Gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 42:159–167. 2007.19. Marinelli JP, Lohse CM, Grossardt BR, Lane JI, Carlson ML. Rising incidence of sporadic vestibular schwannoma: true biological shift versus simply greater detection. Otol Neurotol. 41:813–847. 2020.
Article20. Nizri E, Irony-Tur-Sinai M, Lory O, Orr-Urtreger A, Lavi E, Brenner T. Activation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory system by nicotine attenuates neuroinflammation via suppression of Th1 and Th17 responses. J Immunol. 183:6681–6688. 2009.
Article21. OECD. OECD reviews of public health: Korea: a healthier tomorrow, OECD reviews of public health. Paris: OECD Publishing;2020.22. Palmisano S, Schwartzbaum J, Prochazka M, Pettersson D, Bergenheim T, Florentzson R, et al. Role of tobacco use in the etiology of acoustic neuroma. Am J Epidemiol. 175:1243–1251. 2012.
Article23. Preston DL, Ron E, Yonehara S, Kobuke T, Fujii H, Kishikawa M, et al. Tumors of the nervous system and pituitary gland associated with atomic bomb radiation exposure. J Natl Cancer Inst. 94:1555–1563. 2002.
Article24. Propp JM, McCarthy BJ, Davis FG, Preston-Martin S. Descriptive epidemiology of vestibular schwannomas. Neuro Oncol. 8:1–11. 2006.25. Reznitsky M, Petersen MMBS, West N, Stangerup SE, Cayé-Thomasen P. Epidemiology and diagnostic characteristics of vestibular schwannomas-does gender matter? Otol Neurotol. 41:e1372–e1378. 2020.
Article26. Schlehofer B, Blettner M, Preston-Martin S, Niehoff D, Wahrendorf J, Arslan A, et al. Role of medical history in brain tumour development. results from the international adult brain tumour study. Int J Cancer. 82:155–160. 1999.
Article27. Schneider B, Pülhorn H, Röhrig B, Rainov NG. Predisposing conditions and risk factors for development of symptomatic meningioma in adults. Cancer Detect Prev. 29:440–447. 2005.
Article28. Schoemaker MJ, Swerdlow AJ, Ahlbom A, Auvinen A, Blaasaas KG, Cardis E, et al. Mobile phone use and risk of acoustic neuroma: results of the interphone case-control study in five North European countries. Br J Cancer. 93:842–848. 2005.29. Schoemaker MJ, Swerdlow AJ, Auvinen A, Christensen HC, Feychting M, Johansen C, et al. Medical history, cigarette smoking and risk of acoustic neuroma: an international case-control study. Int J Cancer. 120:103–110. 2007.30. Seliger C, Meier CR, Becker C, Jick SS, Proescholdt M, Bogdahn U, et al. Metabolic syndrome in relation to risk of meningioma. Oncotarget. 8:2284–2292. 2017.31. Stepanidis K, Kessel M, Caye-Thomasen P, Stangerup SE. Sociodemographic distribution of vestibular schwannomas in Denmark. Acta Otolaryngol. 134:551–556. 2014.32. Zhang Z. Missing values in big data research: some basic skills. Ann Transl Med. 3:323. 2015.33. Zhu H, Li F, Yu WJ, Wang WJ, Li L, Wan LD, et al. Effect of hypoxia/reoxygenation on cell viability and expression and secretion of neurotrophic factors (NTFs) in primary cultured schwann cells. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 293:865–870. 2010.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hypervascular Vestibular Schwannoma: A Case Report
- Diagnosis and Management of Vestibular Schwannoma: Focus on Dizziness
- A Case of Intralabyrinthine Schwannoma and Literature Review of the Cases Reported Previously in Korea
- A Case of Marked Hearing Improvement after Surgical Removal of Vestibular Schwannoma with Profound Hearing Loss
- Normal pressure hydrocephalus after gamma knife radiosurgery in a patient with vestibular schwannoma