J Neurocrit Care.
2020 Dec;13(2):128-132. 10.18700/jnc.200014.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus after gamma knife radiosurgery in a patient with vestibular schwannoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2509945
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18700/jnc.200014
Abstract
- Background
Vestibular schwannoma is a benign, usually slow-growing tumor, which develops from Schwann cells of the eighth cranial nerve.
Case Report
The treatment options for the schwannoma are surgical removal or gamma knife radiosurgery. The treatment of choice depends on the size of the tumor and the level of hearing in the affected ear. After gamma knife radiosurgery, there may be some neurological complications including headache, dizziness, motor or cranial nerve deficits, seizure, carotid artery stenosis, and increased intracranial pressure. Hydrocephalus is a rare complication of gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma.
Conclusion
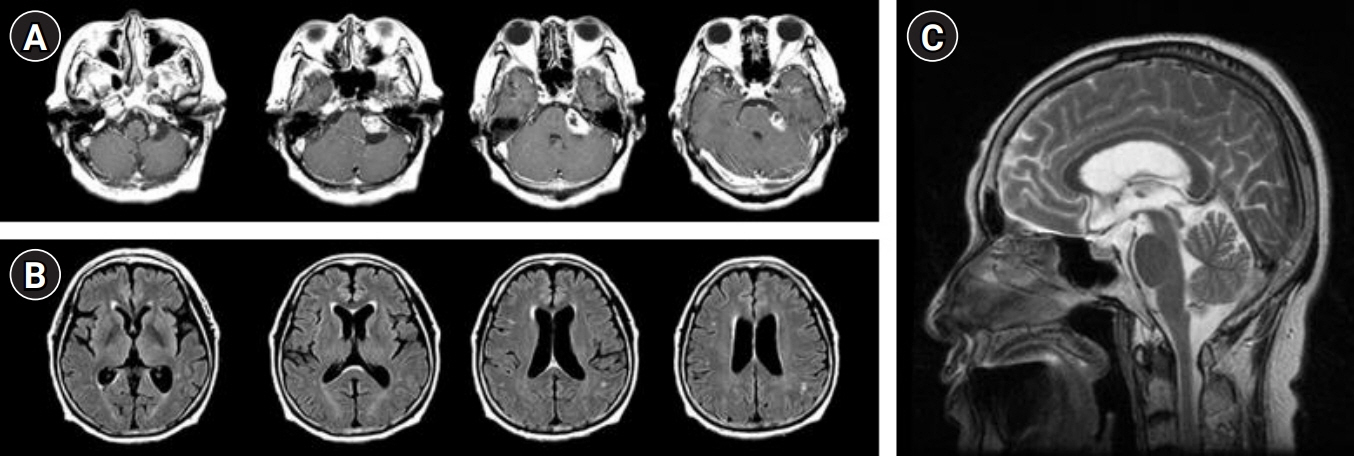
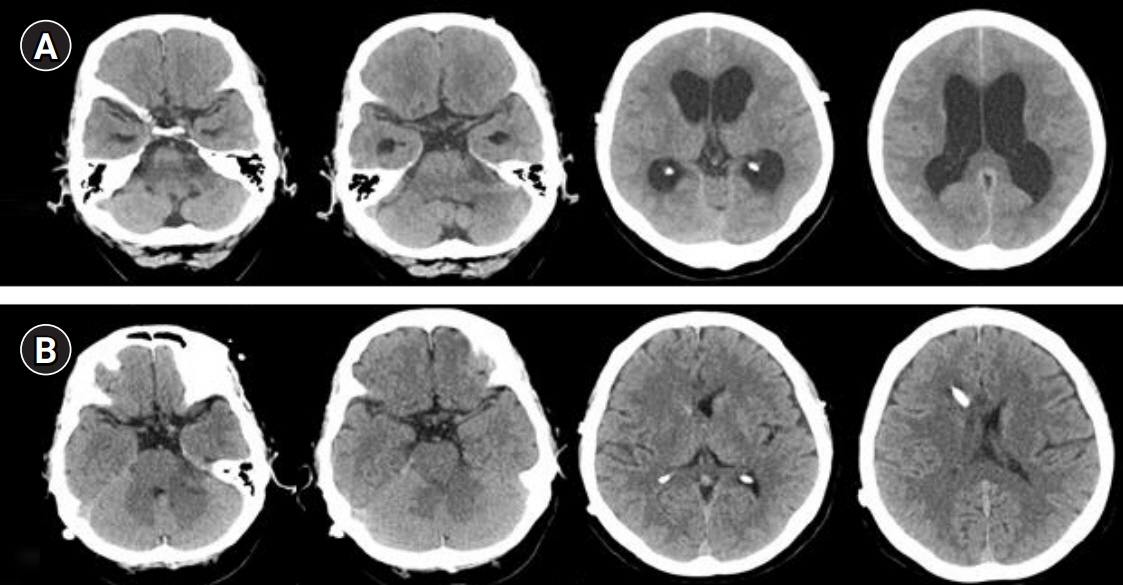
Here, we report a case of normal pressure hydrocephalus after gamma knife radiosurgery in a patient with vestibular schwannoma.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hasegawa T, Kida Y, Kato T, Iizuka H, Kuramitsu S, Yamamoto T. Long-term safety and efficacy of stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas: evaluation of 440 patients more than 10 years after treatment with Gamma Knife surgery. J Neurosurg. 2013; 118:557–65.
Article2. Cauley KA, Ratkovits B, Braff SP, Linnell G. Communicating hydrocephalus after gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma: an MR imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:992–4.
Article3. Bloch J, Vernet O, Aubé M, Villemure JG. Non-obstructive hydrocephalus associated with intracranial schwannomas: hyperproteinorrhachia as an etiopathological factor? Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2003; 145:73–8.
Article4. Rogg JM, Ahn SH, Tung GA, Reinert SE, Norén G. Prevalence of hydrocephalus in 157 patients with vestibular schwannoma. Neuroradiology. 2005; 47:344–51.
Article5. Norén G. Long-term complications following gamma knife radiosurgery of vestibular schwannomas. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1998; 70 Suppl 1:65–73.
Article6. Briggs RJ, Shelton C, Kwartler JA, Hitselberger W. Management of hydrocephalus resulting from acoustic neuromas. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993; 109:1020–4.
Article7. Steenerson RL, Payne N. Hydrocephalus in the patient with acoustic neuroma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992; 107:35–9.
Article8. Jeon CJ, Kong DS, Nam DH, Lee JI, Park K, Kim JH. Communicating hydrocephalus associated with surgery or radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma. J Clin Neurosci. 2010; 17:862–4.
Article9. Lee SH, Seol HJ, Kong DS, Nam DH, Park K, Kim JH, et al. Risk factors and tumor response associated with hydrocephalus after gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012; 154:1679–84.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hearing Preservation, Facial Nerve Dysfunction, and Tumor Control in Small Vestibular Schwannoma: A Systematic Review of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Versus Microsurgery
- Gamma-Knife Radiosurgery for Vestibular Schwannoma
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Vestibular Schwannomas
- Metachronous schwannoma in the colon with vestibular schwannoma
- How to use Leksell GammaPlan