Diabetes Metab J.
2023 May;47(3):405-414. 10.4093/dmj.2022.0032.
Glycemia according to the Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring among Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Real-World Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2542517
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0032
Abstract
- Background
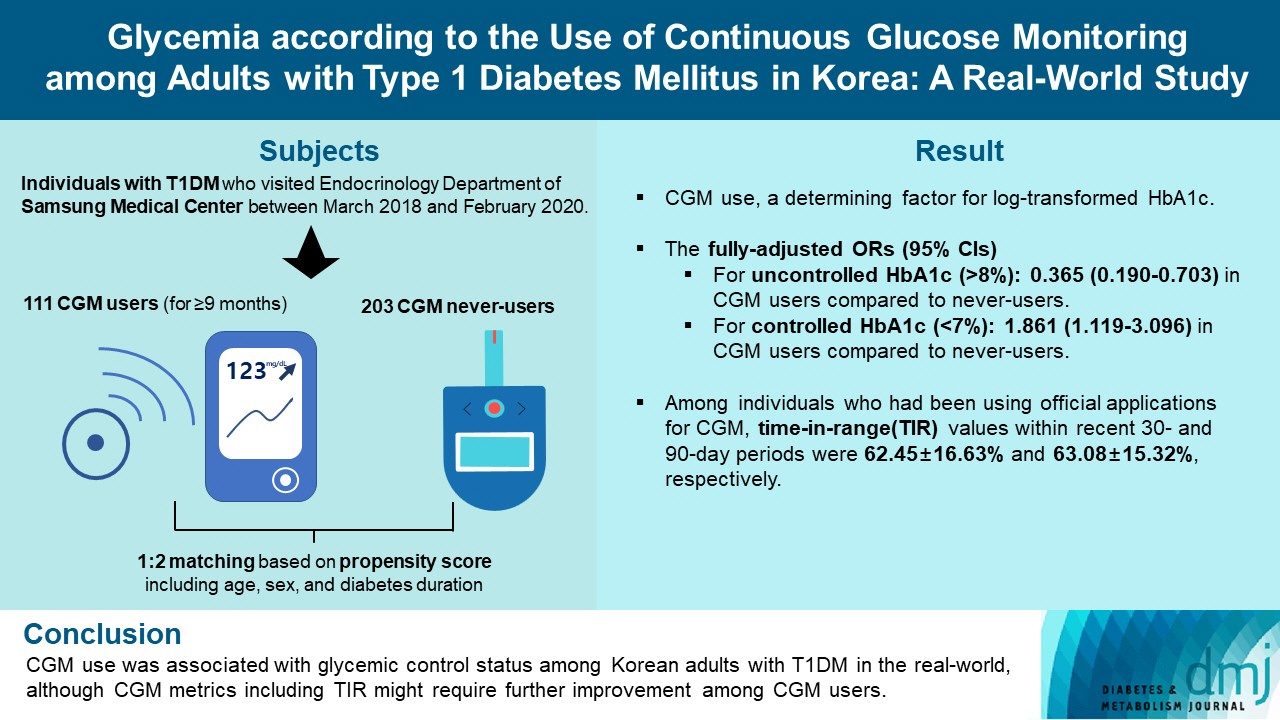
We explored the association between continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use and glycemia among adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and determined the status of CGM metrics among adults with T1DM using CGM in the real-world.
Methods
For this propensity-matched cross-sectional study, individuals with T1DM who visited the outpatient clinic of the Endocrinology Department of Samsung Medical Center between March 2018 and February 2020 were screened. Among them, 111 CGM users (for ≥9 months) were matched based on propensity score considering age, sex, and diabetes duration in a 1:2 ratio with 203 CGM never-users. The association between CGM use and glycemic measures was explored. In a subpopulation of CGM users who had been using official applications (not “do-it-yourself” software) such that Ambulatory Glucose Profile data for ≥1 month were available (n=87), standardized CGM metrics were summarized.
Results
Linear regression analyses identified CGM use as a determining factor for log-transformed glycosylated hemoglobin. The fully-adjusted odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for uncontrolled glycosylated hemoglobin (>8%) were 0.365 (95% CI, 0.190 to 0.703) in CGM users compared to never-users. The fully-adjusted OR for controlled glycosylated hemoglobin (<7%) was 1.861 (95% CI, 1.119 to 3.096) in CGM users compared to never-users. Among individuals who had been using official applications for CGM, time in range (TIR) values within recent 30- and 90-day periods were 62.45%±16.63% and 63.08%±15.32%, respectively.
Conclusion
CGM use was associated with glycemic control status among Korean adults with T1DM in the real-world, although CGM metrics including TIR might require further improvement among CGM users.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Navigating the Seas of Glycemic Control: The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):345-346. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0125.
Reference
-
1. Battelino T, Danne T, Bergenstal RM, Amiel SA, Beck R, Biester T, et al. Clinical targets for continuous glucose monitoring data interpretation: recommendations from the international consensus on time in range. Diabetes Care. 2019; 42:1593–603.2. Choe J, Won SH, Choe Y, Park SH, Lee YJ, Lee J, et al. Temporal trends for diabetes management and glycemic control between 2010 and 2019 in Korean children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022; 24:201–11.
Article3. Danne T, Nimri R, Battelino T, Bergenstal RM, Close KL, DeVries JH, et al. International consensus on use of continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care. 2017; 40:1631–40.4. Beck RW, Riddlesworth T, Ruedy K, Ahmann A, Bergenstal R, Haller S, et al. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes using insulin injections: the DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2017; 317:371–8.
Article5. Lind M, Polonsky W, Hirsch IB, Heise T, Bolinder J, Dahlqvist S, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring vs conventional therapy for glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes treated with multiple daily insulin injections: the GOLD Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2017; 317:379–87.
Article6. Tumminia A, Crimi S, Sciacca L, Buscema M, Frittitta L, Squatrito S, et al. Efficacy of real-time continuous glucose monitoring on glycaemic control and glucose variability in type 1 diabetic patients treated with either insulin pumps or multiple insulin injection therapy: a randomized controlled crossover trial. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015; 31:61–8.
Article7. Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group. Tamborlane WV, Beck RW, Bode BW, Buckingham B, Chase HP, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring and intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1464–76.
Article8. Battelino T, Conget I, Olsen B, Schutz-Fuhrmann I, Hommel E, Hoogma R, et al. The use and efficacy of continuous glucose monitoring in type 1 diabetes treated with insulin pump therapy: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia. 2012; 55:3155–62.
Article9. Deiss D, Bolinder J, Riveline JP, Battelino T, Bosi E, Tubiana-Rufi N, et al. Improved glycemic control in poorly controlled patients with type 1 diabetes using real-time continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:2730–2.
Article10. O’Connell MA, Donath S, O’Neal DN, Colman PG, Ambler GR, Jones TW, et al. Glycaemic impact of patient-led use of sensor-guided pump therapy in type 1 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia. 2009; 52:1250–7.11. American Diabetes Association. 7. Diabetes technology: standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 2021; 44(Suppl 1):S85–99.12. Hur KY, Moon MK, Park JS, Kim SK, Lee SH, Yun JS, et al. 2021 Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J. 2021; 45:461–81.13. Yoo JH, Kim G, Lee HJ, Sim KH, Jin SM, Kim JH. Effect of structured individualized education on continuous glucose monitoring use in poorly controlled patients with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022; 184:109209.
Article14. Sequeira PA, Montoya L, Ruelas V, Xing D, Chen V, Beck R, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring pilot in low-income type 1 diabetes patients. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013; 15:855–8.15. Foster NC, Beck RW, Miller KM, Clements MA, Rickels MR, DiMeglio LA, et al. State of type 1 diabetes management and outcomes from the T1D exchange in 2016–2018. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2019; 21:66–72.
Article16. Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 150:604–12.
Article17. Bolinder J, Antuna R, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn P, Kroger J, Weitgasser R. Novel glucose-sensing technology and hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre, non-masked, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016; 388:2254–63.
Article18. Seyed Ahmadi S, Westman K, Pivodic A, Olafsdottir AF, Dahlqvist S, Hirsch IB, et al. The association between HbA1c and time in hypoglycemia during CGM and self-monitoring of blood glucose in people with type 1 diabetes and multiple daily insulin injections: a randomized clinical trial (GOLD-4). Diabetes Care. 2020; 43:2017–24.
Article19. Heinemann L, Freckmann G, Ehrmann D, Faber-Heinemann G, Guerra S, Waldenmaier D, et al. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 1 diabetes and impaired hypoglycaemia awareness or severe hypoglycaemia treated with multiple daily insulin injections (HypoDE): a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018; 391:1367–77.
Article20. van Beers CA, DeVries JH, Kleijer SJ, Smits MM, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn PH, Kramer MH, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring for patients with type 1 diabetes and impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia (IN CONTROL): a randomised, open-label, crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016; 4:893–902.
Article21. Lu J, Ma X, Zhou J, Zhang L, Mo Y, Ying L, et al. Association of time in range, as assessed by continuous glucose monitoring, with diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:2370–6.
Article22. Beck RW, Bergenstal RM, Riddlesworth TD, Kollman C, Li Z, Brown AS, et al. Validation of time in range as an outcome measure for diabetes clinical trials. Diabetes Care. 2019; 42:400–5.
Article23. Yoo JH, Choi MS, Ahn J, Park SW, Kim Y, Hur KY, et al. Association between continuous glucose monitoring-derived time in range, other core metrics, and albuminuria in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020; 22:768–76.
Article24. Beck RW, Bergenstal RM, Cheng P, Kollman C, Carlson AL, Johnson ML, et al. The relationships between time in range, hyperglycemia metrics, and HbA1c. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2019; 13:614–26.25. Vigersky RA, McMahon C. The relationship of hemoglobin A1C to time-in-range in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2019; 21:81–5.
Article26. Jin SM, Kim TH, Bae JC, Hur KY, Lee MS, Lee MK, et al. Clinical factors associated with absolute and relative measures of glycemic variability determined by continuous glucose monitoring: an analysis of 480 subjects. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014; 104:266–72.
Article27. Monnier L, Colette C, Wojtusciszyn A, Dejager S, Renard E, Molinari N, et al. Toward defining the threshold between low and high glucose variability in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2017; 40:832–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Glucose Management Using Continuous Glucose Monitors
- Patient Education in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus through Continuous Glucose Monitoring Reports
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
- The Present and Future of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
- Management of Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Current Status and Suggestions