Ann Surg Treat Res.
2023 Feb;104(2):109-118. 10.4174/astr.2023.104.2.109.
Can clinicopathologic high-risk features in T3N0 colon cancer be reliable prognostic factors?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Colon and Rectal Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2539225
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2023.104.2.109
Abstract
- Purpose
The purpose of this study was to assess the reliability and prognostic significance of the high-risk feature (HRF) in patients with T3N0 colon cancer.
Methods
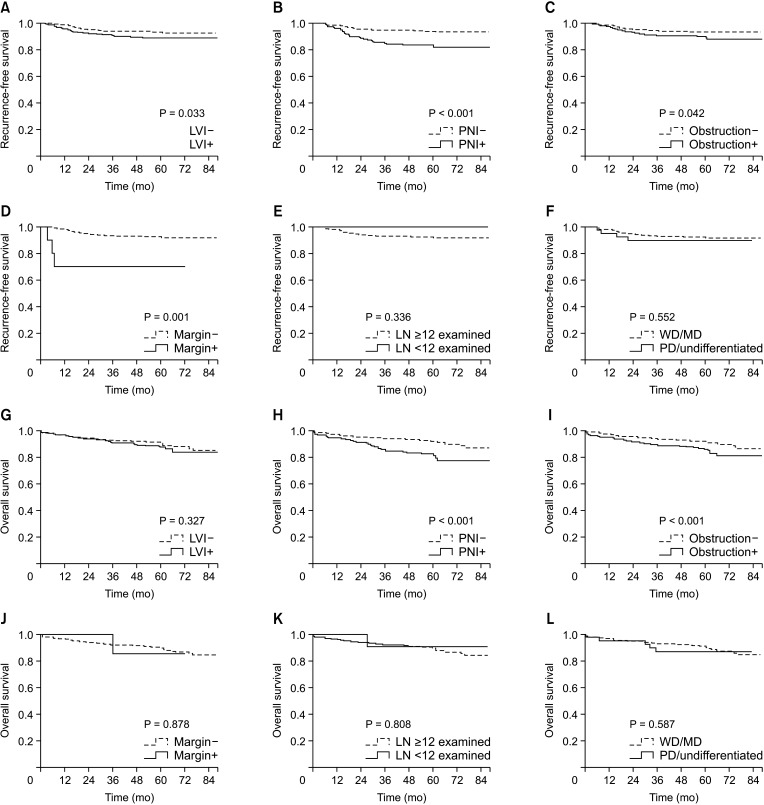
We included 1,205 patients with pT3N0 colon cancer treated with curative radical resection between 2012 and 2016. HRF was defined as lymphovascular invasion, perineural invasion, poorly/undifferentiated histology, margin involvement, and preoperative obstruction. We investigated the relationships between the number and type of HRF and recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS), as well as the effect of adjuvant treatment.
Results
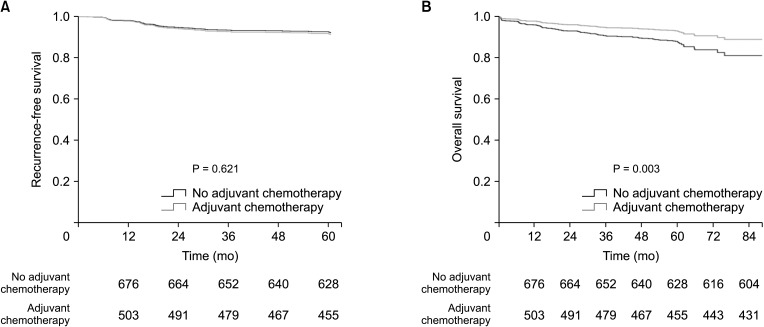
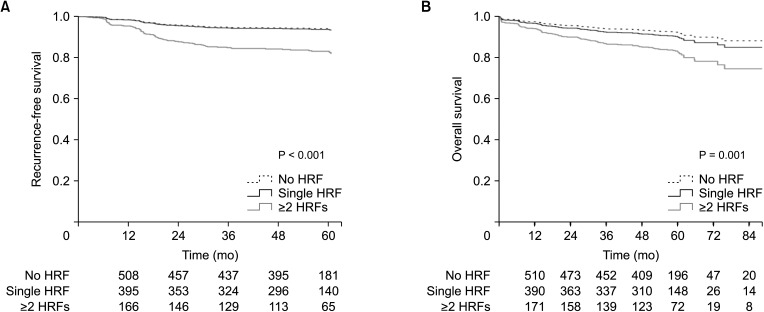
A total of 751 of the patients (62.3%) had more than 1 HRF and 515 of the patients (42.7%) underwent adjuvant treatment. Patients who had more than 2 HRFs had a significantly worse 5-year RFS and OS compared to patients who had neither HRF nor even one HRF. According to the findings of the multivariate analysis, the presence of multiple HRFs was a risk factor for a lower RFS and OS. When the quantity and type of HRF were taken into consideration in the multivariate analysis, adjuvant chemotherapy was not found to be linked with RFS or OS in patients with pT3N0 colon cancer.
Conclusion
In the present study, adjuvant treatment based on the current guideline of treatment indication was unable to enhance the prognosis of patients with pT3N0 colon cancer. The role of adjuvant treatment in T3N0 colon cancer must be examined with the HRF count in mind.
Figure
Reference
-
1. André T, Boni C, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, et al. Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:3109–3116. PMID: 19451431.2. Lykke J, Roikjaer O, Jess P, Rosenberg J. Danish Colorectal Cancer Group. Identification of risk factors associated with stage III disease in nonmetastatic colon cancer: results from a prospective national cohort study. Ann Coloproctol. 2020; 36:316–322. PMID: 32079050.3. Kannarkatt J, Joseph J, Kurniali PC, Al-Janadi A, Hrinczenko B. Adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer: a clinical dilemma. J Oncol Pract. 2017; 13:233–241. PMID: 28399381.4. Kumar A, Kennecke HF, Renouf DJ, Lim HJ, Gill S, Woods R, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy use and outcomes of patients with high-risk versus low-risk stage II colon cancer. Cancer. 2015; 121:527–534. PMID: 25332117.5. Lee MW, Kim JS, Kim JY, Lee KH. Prognostic factor and survival benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy in stage IIA colon cancer. Ann Coloproctol. 2021; 37:35–43. PMID: 32972104.6. O’Connor ES, Greenblatt DY, LoConte NK, Gangnon RE, Liou JI, Heise CP, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer with poor prognostic features. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:3381–3388. PMID: 21788561.7. Baxter NN, Kennedy EB, Bergsland E, Berlin J, George TJ, Gill S, et al. Adjuvant therapy for stage II colon cancer: ASCO guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2022; 40:892–910. PMID: 34936379.8. O’Connell JB, Maggard MA, Ko CY. Colon cancer survival rates with the new American Joint Committee on Cancer sixth edition staging. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004; 96:1420–1425. PMID: 15467030.9. Benson AB 3rd, Schrag D, Somerfield MR, Cohen AM, Figueredo AT, Flynn PJ, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology recommendations on adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:3408–3419. PMID: 15199089.10. Gill S, Loprinzi CL, Sargent DJ, Thomé SD, Alberts SR, Haller DG, et al. Pooled analysis of fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy for stage II and III colon cancer: who benefits and by how much? J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:1797–1806. PMID: 15067028.11. Pal A, Saada J, Kapur S, Tighe R, Stearns A, Hernon J, et al. Technical and clinical outcomes after colorectal stenting in malignant large bowel obstruction: a single-center experience. Ann Coloproctol. 2021; 37:85–89. PMID: 32178502.12. Tebala GD, Mingoli A, Natili A, Khan AQ, Brachini G. Surgical risk and pathological results of emergency resection in the treatment of acutely obstructing colorectal cancers: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Coloproctol. 2021; 37:21–28. PMID: 32178504.13. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®). Colon cancer [Internet]. NCCN;2022. cited 2022 Jun 9. Available from: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/colon.pdf .14. Li D, Jiang Z, Xiang L, Yang C, Long F, Liu W. A retrospective study based on SEER database: not all high-risk factors are equal for stage II colon cancer. Transl Cancer Res. 2022; 11:689–698. PMID: 35571652.15. Meyers BM, Cosby R, Quereshy F, Jonker D. Adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and III colon cancer following complete resection: a Cancer Care Ontario Systematic Review. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2017; 29:459–465. PMID: 28341242.16. Wells KO, Hawkins AT, Krishnamurthy DM, Dharmarajan S, Glasgow SC, Hunt SR, et al. Omission of adjuvant chemotherapy is associated with increased mortality in patients with T3N0 colon cancer with inadequate lymph node harvest. Dis Colon Rectum. 2017; 60:15–21. PMID: 27926553.17. Achilli P, Crippa J, Grass F, Mathis KL, D’Angelo AD, Abd El Aziz MA, et al. Survival impact of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with stage IIA colon cancer: analysis of the National Cancer Database. Int J Cancer. 2021; 148:161–169. PMID: 32638371.18. Pinto JC, Rosa I, Martins C, Marques I, da Silva JP, Fonseca R, et al. Colon adenocarcinoma stage IIA: can we predict relapse? J Gastrointest Cancer. 2020; 51:116–120. PMID: 30834501.19. Gray R, Barnwell J, McConkey C, Hills RK, Williams NS, et al. Quasar Collaborative Group. Adjuvant chemotherapy versus observation in patients with colorectal cancer: a randomised study. Lancet. 2007; 370:2020–2029. PMID: 18083404.20. Verhoeff SR, van Erning FN, Lemmens VE, de Wilt JH, Pruijt JF. Adjuvant chemotherapy is not associated with improved survival for all high-risk factors in stage II colon cancer. Int J Cancer. 2016; 139:187–193. PMID: 26914273.21. Eom T, Lee Y, Kim J, Park I, Gwak G, Cho H, et al. Prognostic factors affecting disease-free survival and overall survival in T4 colon cancer. Ann Coloproctol. 2021; 37:259–265. PMID: 34167188.22. Argilés G, Tabernero J, Labianca R, Hochhauser D, Salazar R, Iveson T, et al. Localised colon cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2020; 31:1291–1305. PMID: 32702383.23. Hajirawala LN, Yi Y, Herritt BC, Laurent ME, Klinger AL, Orangio GR, et al. Multiple high-risk features for stage II colon carcinoma portends worse survival than stage III disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 2022; 02. 28. DOI: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000002425. [Epub].24. Nakamura Y, Hokuto D, Koyama F, Matsuo Y, Nomi T, Yoshikawa T, et al. The prognosis and recurrence pattern of right- and left-sided colon cancer in stage II, stage III, and Liver metastasis after curative resection. Ann Coloproctol. 2021; 37:326–336. PMID: 32972100.25. Iveson TJ, Sobrero AF, Yoshino T, Souglakos I, Ou FS, Meyers JP, et al. Duration of adjuvant doublet chemotherapy (3 or 6 months) in patients with high-risk stage II colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2021; 39:631–641. PMID: 33439695.26. Eheman CR, O’Neil ME, Styles TS, Thompson TD, Morris CR, Babcock FA, et al. Use of adjuvant chemotherapy among stage II colon cancer patients in 10 population-based National Program of Cancer Registries. J Registry Manag. 2016; 43:179–186. PMID: 29308117.27. Schrag D, Rifas-Shiman S, Saltz L, Bach PB, Begg CB. Adjuvant chemotherapy use for Medicare beneficiaries with stage II colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:3999–4005. PMID: 12351597.28. Lee SM, Shin JS. Colorectal cancer in octogenarian and nonagenarian patients: clinicopathological features and survivals. Ann Coloproctol. 2020; 36:323–329. PMID: 33207113.29. Sabbagh C, Manceau G, Mege D, Abdalla S, Voron T, Bridoux V, et al. Is adjuvant chemotherapy necessary for obstructing stage II colon cancer?: results from a propensity score analysis of the French Surgical Association Database. Ann Surg. 2022; 275:149–156. PMID: 32068553.30. Babcock BD, Aljehani MA, Jabo B, Choi AH, Morgan JW, Selleck MJ, et al. High-risk stage II colon cancer: not all risks are created equal. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018; 25:1980–1985. PMID: 29675762.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Features of Gastric Cancer Patients with a Second Primary Cancer
- Is the Location of the Tumor Another Prognostic Factor for Patients With Colon Cancer?
- Correlation MSI Status and Other Prognostic Factors in Sporadic Colorectal Cancer
- Clinicopathologic Significance of p53 and c-erbB-2 Protein Expression in Breast Carcinoma
- Clinicopathologic Characteristics, Surgical Treatment and Outcomes for Splenic Flexure Colon Cancer