J Stroke.
2023 Jan;25(1):26-38. 10.5853/jos.2022.02306.
Diabetes and Stroke: What Are the Connections?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Diabetes Unit, Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Hadassah Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel
- 2Faculty of Medicine, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, Israel
- 3Department of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- 4Division of Neurology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA
- 5Department of Biotechnological and Applied Clinical Sciences, University of L’Aquila, L’Aquila, Italy
- KMID: 2539056
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2022.02306
Abstract
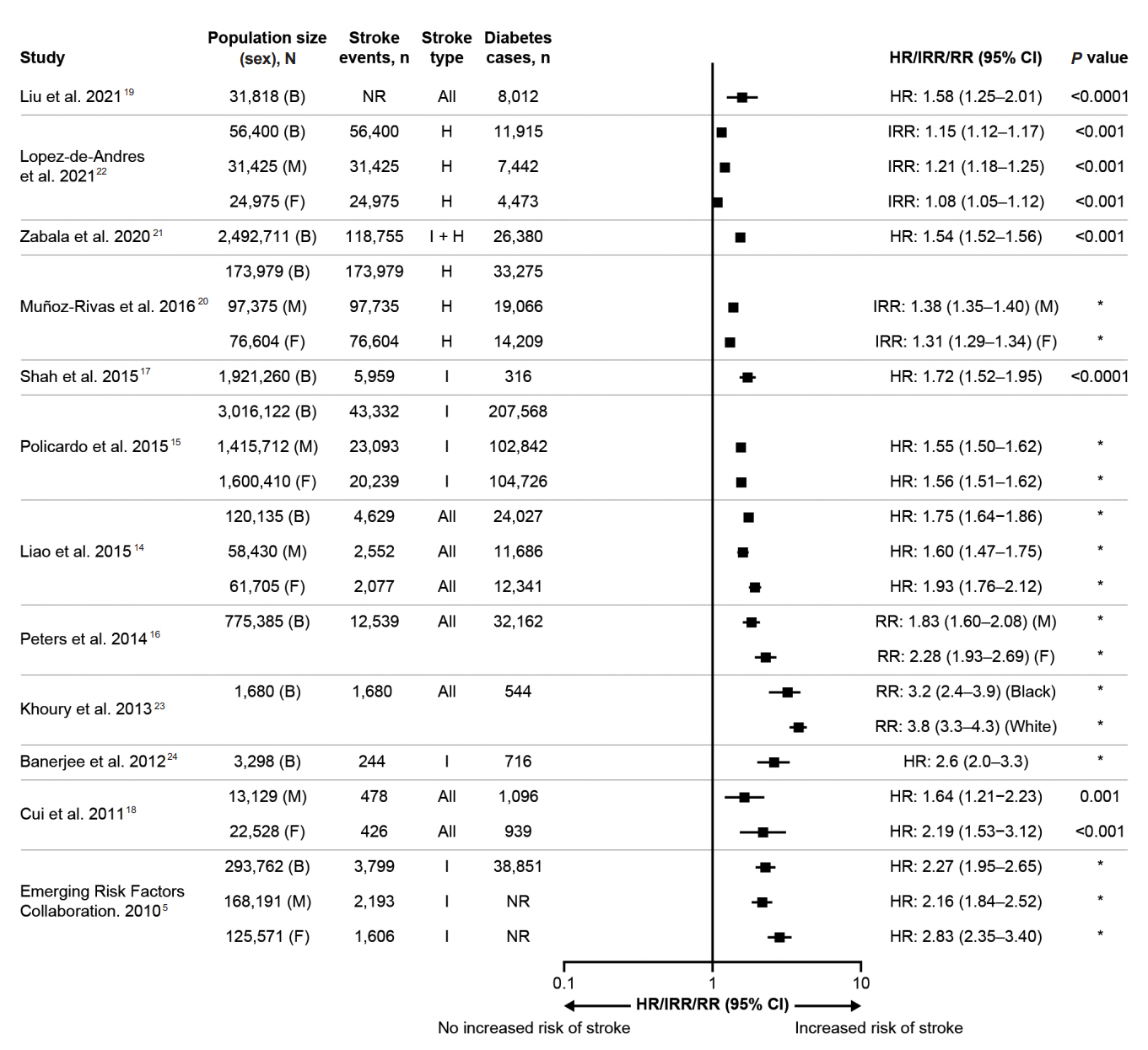
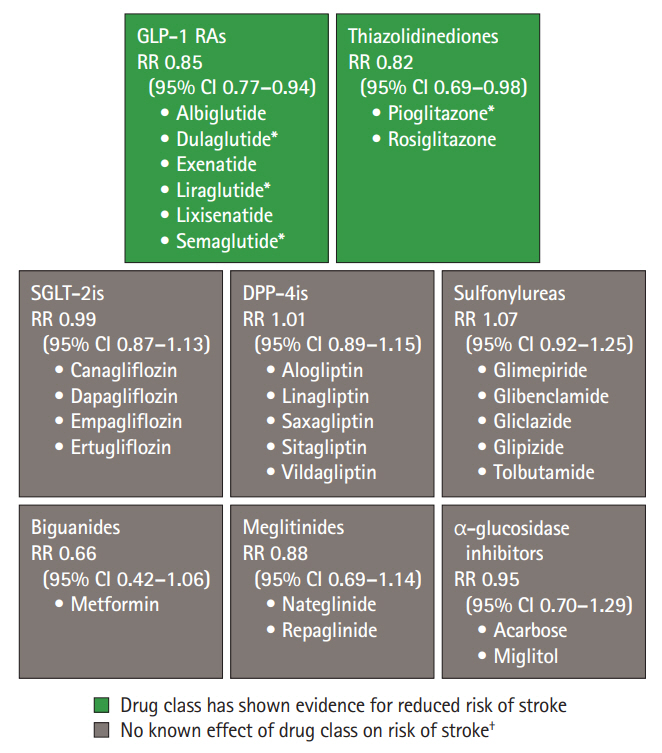
- Stroke is a major cause of death and long-term disability worldwide. Diabetes is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular complications, including stroke. People with diabetes have a 1.5–2 times higher risk of stroke compared with people without diabetes, with risk increasing with diabetes duration. These risks may also differ according to sex, with a greater risk observed among women versus men. Several mechanisms associated with diabetes lead to stroke, including large artery atherosclerosis, cerebral small vessel disease, and cardiac embolism. Hyperglycemia confers increased risk for worse outcomes in people presenting with acute ischemic stroke, compared with people with normal glycemia. Moreover, people with diabetes may have poorer post-stroke outcomes and higher risk of stroke recurrence than those without diabetes. Appropriate management of diabetes and other vascular risk factors may improve stroke outcomes and reduce the risk for recurrent stroke. Secondary stroke prevention guidelines recommend screening for diabetes following a stroke. The diabetes medications pioglitazone and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists have demonstrated protection against stroke in randomized controlled trials; this protective effect is believed to be independent of glycemic control. Neurologists are often involved in the management of modifiable risk factors for stroke (including hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and atrial fibrillation), but less often in the direct management of diabetes. This review provides an overview of the relationships between diabetes and stroke, including epidemiology, pathophysiology, post-stroke outcomes, and treatments for people with stroke and diabetes. This should aid neurologists in diabetes-related decision-making when treating people with acute or recurrent stroke.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Association of Body Composition Changes with the Development of Diabetes Mellitus: A Nation-Wide Population Study
Hyung Jun Kim, Hyung-Woo Lee, Min-Kyoung Kang, Gwang Hyun Leem, Min-Ho Kim, Tae-Jin Song
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(6):1093-1104. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0243.
Reference
-
References
1. GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021; 20:795–820.2. O’Donnell MJ, Xavier D, Liu L, Zhang H, Chin SL, Rao-Melacini P, et al. Risk factors for ischaemic and intracerebral haemorrhagic stroke in 22 countries (the INTERSTROKE study): a case-control study. Lancet. 2010; 376:112–123.3. International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes around the world in 2021 [Internet]. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation;2021. [cited 2021 Nov 12]. Available from: https://diabetesatlas.org.4. Visseren FLJ, Mach F, Smulders YM, Carballo D, Koskinas KC, Bäck M, et al. 2021 ESC guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur Heart J. 2021; 42:3227–3337.5. Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet. 2010; 375:2215–2222.6. Sun Y, Toh MP. Impact of diabetes mellitus (DM) on the health-care utilization and clinical outcomes of patients with stroke in Singapore. Value Health. 2009; 12 Suppl 3:S101–S105.7. Eriksson M, Carlberg B, Eliasson M. The disparity in long-term survival after a first stroke in patients with and without diabetes persists: the Northern Sweden MONICA study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012; 34:153–160.8. Zhang L, Li X, Wolfe CDA, O’Connell MDL, Wang Y. Diabetes as an independent risk factor for stroke recurrence in ischemic stroke patients: an updated meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology. 2021; 55:427–435.9. Lo JW, Crawford JD, Samaras K, Desmond DW, Köhler S, Staals J, et al. Association of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes with cognitive function after stroke: a STROKOG collaboration study. Stroke. 2020; 51:1640–1646.10. Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Xu H, Matsouaka RA, Xian Y, Schwamm LH, Smith EE, et al. Diabetes and long-term outcomes of ischaemic stroke: findings from get with the guidelines-stroke. Eur Heart J. 2018; 39:2376–2386.11. Li HW, Yang MC, Chung KP. Predictors for readmission of acute ischemic stroke in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. 2011; 110:627–633.12. Kleindorfer DO, Towfighi A, Chaturvedi S, Cockroft KM, Gutierrez J, Lombardi-Hill D, et al. 2021 guideline for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2021; 52:e364–e467.13. Lau LH, Lew J, Borschmann K, Thijs V, Ekinci EI. Prevalence of diabetes and its effects on stroke outcomes: a meta-analysis and literature review. J Diabetes Investig. 2019; 10:780–792.14. Liao CC, Shih CC, Yeh CC, Chang YC, Hu CJ, Lin JG, et al. Impact of diabetes on stroke risk and outcomes: two nationwide retrospective cohort studies. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e2282.15. Policardo L, Seghieri G, Francesconi P, Anichini R, Franconi F, Seghieri C, et al. Gender difference in diabetes-associated risk of first-ever and recurrent ischemic stroke. J Diabetes Complications. 2015; 29:713–717.16. Peters SA, Huxley RR, Woodward M. Diabetes as a risk factor for stroke in women compared with men: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 64 cohorts, including 775,385 individuals and 12,539 strokes. Lancet. 2014; 383:1973–1980.17. Shah AD, Langenberg C, Rapsomaniki E, Denaxas S, Pujades-Rodriguez M, Gale CP, et al. Type 2 diabetes and incidence of cardiovascular diseases: a cohort study in 1·9 million people. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015; 3:105–113.18. Cui R, Iso H, Yamagishi K, Saito I, Kokubo Y, Inoue M, et al. Diabetes mellitus and risk of stroke and its subtypes among Japanese: the Japan public health center study. Stroke. 2011; 42:2611–2614.19. Liu Y, Li J, Dou Y, Ma H. Impacts of type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension on the incidence of cardiovascular diseases and stroke in China real-world setting: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2021; 11:e053698.20. Muñoz-Rivas N, Méndez-Bailón M, Hernández-Barrera V, de Miguel-Yanes JM, Jimenez-Garcia R, Esteban-Hernández J, et al. Type 2 diabetes and hemorrhagic stroke: a population-based study in Spain from 2003 to 2012. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016; 25:1431–1443.21. Zabala A, Darsalia V, Holzmann MJ, Franzén S, Svensson AM, Eliasson B, et al. Risk of first stroke in people with type 2 diabetes and its relation to glycaemic control: a nationwide observational study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020; 22:182–190.22. Lopez-de-Andres A, Jimenez-Garcia R, Hernández-Barrera V, Jiménez-Trujillo I, de Miguel-Yanes JM, Carabantes-Alarcon D, et al. Sex-related disparities in the incidence and outcomes of hemorrhagic stroke among type 2 diabetes patients: a propensity score matching analysis using the Spanish National Hospital Discharge Database for the period 2016-18. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021; 20:138.23. Khoury JC, Kleindorfer D, Alwell K, Moomaw CJ, Woo D, Adeoye O, et al. Diabetes mellitus: a risk factor for ischemic stroke in a large biracial population. Stroke. 2013; 44:1500–1504.24. Banerjee C, Moon YP, Paik MC, Rundek T, Mora-McLaughlin C, Vieira JR, et al. Duration of diabetes and risk of ischemic stroke: the Northern Manhattan Study. Stroke. 2012; 43:1212–1217.25. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care. 2021; 45(Suppl 1):S17–S38.26. Lee M, Saver JL, Hong KS, Song S, Chang KH, Ovbiagele B. Effect of pre-diabetes on future risk of stroke: meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012; 344:e3564.27. Petrie JR, Guzik TJ, Touyz RM. Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: clinical insights and vascular mechanisms. Can J Cardiol. 2018; 34:575–584.28. Chen R, Ovbiagele B, Feng W. Diabetes and stroke: epidemiology, pathophysiology, pharmaceuticals and outcomes. Am J Med Sci. 2016; 351:380–386.29. Clarkson P, Celermajer DS, Donald AE, Sampson M, Sorensen KE, Adams M, et al. Impaired vascular reactivity in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus is related to disease duration and low density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996; 28:573–579.30. Kamel H, Healey JS. Cardioembolic stroke. Circ Res. 2017; 120:514–526.31. Kim JS, Nah HW, Park SM, Kim SK, Cho KH, Lee J, et al. Risk factors and stroke mechanisms in atherosclerotic stroke: intracranial compared with extracranial and anterior compared with posterior circulation disease. Stroke. 2012; 43:3313–3318.32. Pasi M, Cordonnier C. Clinical relevance of cerebral small vessel diseases. Stroke. 2020; 51:47–53.33. Yaghi S, Prabhakaran S, Khatri P, Liebeskind DS. Intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Stroke. 2019; 50:1286–1293.34. Poznyak A, Grechko AV, Poggio P, Myasoedova VA, Alfieri V, Orekhov AN. The diabetes mellitus–atherosclerosis connection: the role of lipid and glucose metabolism and chronic inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21:1835.35. King DE, Mainous AG 3rd, Buchanan TA, Pearson WS. C-reactive protein and glycemic control in adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:1535–1539.36. van Sloten TT, Sedaghat S, Carnethon MR, Launer LJ, Stehouwer CDA. Cerebral microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes: stroke, cognitive dysfunction, and depression. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020; 8:325–336.37. Creager MA, Lüscher TF, Cosentino F, Beckman JA. Diabetes and vascular disease: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: part I. Circulation. 2003; 108:1527–1532.38. Goette A, Lendeckel U. Atrial cardiomyopathy: pathophysiology and clinical consequences. Cells. 2021; 10:2605.39. Seyed Ahmadi S, Svensson AM, Pivodic A, Rosengren A, Lind M. Risk of atrial fibrillation in persons with type 2 diabetes and the excess risk in relation to glycaemic control and renal function: a Swedish cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020; 19:9.40. Bohne LJ, Johnson D, Rose RA, Wilton SB, Gillis AM. The association between diabetes mellitus and atrial fibrillation: clinical and mechanistic insights. Front Physiol. 2019; 10:135.41. Kruyt ND, Biessels GJ, Devries JH, Roos YB. Hyperglycemia in acute ischemic stroke: pathophysiology and clinical management. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010; 6:145–155.42. Maida CD, Daidone M, Pacinella G, Norrito RL, Pinto A, Tuttolomondo A. Diabetes and ischemic stroke: an old and new relationship an overview of the close interaction between these diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23:2397.43. Capes SE, Hunt D, Malmberg K, Pathak P, Gerstein HC. Stress hyperglycemia and prognosis of stroke in nondiabetic and diabetic patients: a systematic overview. Stroke. 2001; 32:2426–2432.44. Baird TA, Parsons MW, Phan T, Butcher KS, Desmond PM, Tress BM, et al. Persistent poststroke hyperglycemia is independently associated with infarct expansion and worse clinical outcome. Stroke. 2003; 34:2208–2214.45. Johnston KC, Bruno A, Pauls Q, Hall CE, Barrett KM, Barsan W, et al. Intensive vs standard treatment of hyperglycemia and functional outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke: the SHINE randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019; 322:326–335.46. Fuentes B, Castillo J, San José B, Leira R, Serena J, Vivancos J, et al. The prognostic value of capillary glucose levels in acute stroke: the GLycemia in Acute Stroke (GLIAS) study. Stroke. 2009; 40:562–568.47. Olaiya MT, Cadilhac DA, Kim J, Thrift AG, Courten B, Andrew NE, et al. Quality of care and one-year outcomes in patients with diabetes hospitalised for stroke or TIA: a linked registry study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021; 30:106083.48. MacDougal EL, Herman WH, Wing JJ, Morgenstern LB, Lisabeth LD. Diabetes and ischaemic stroke outcome. Diabet Med. 2018; 35:1249–1257.49. Kamalesh M, Shen J, Eckert GJ. Long term postischemic stroke mortality in diabetes: a veteran cohort analysis. Stroke. 2008; 39:2727–2731.50. Alter M, Lai SM, Friday G, Singh V, Kumar VM, Sobel E. Stroke recurrence in diabetics. Does control of blood glucose reduce risk? Stroke. 1997; 28:1153–1157.51. Kalaria RN, Akinyemi R, Ihara M. Stroke injury, cognitive impairment and vascular dementia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016; 1862:915–925.52. Shukla V, Shakya AK, Perez-Pinzon MA, Dave KR. Cerebral ischemic damage in diabetes: an inflammatory perspective. J Neuroinflammation. 2017; 14:21.53. Gæde P, Oellgaard J, Kruuse C, Rossing P, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Beneficial impact of intensified multifactorial intervention on risk of stroke: outcome of 21 years of follow-up in the randomised Steno-2 Study. Diabetologia. 2019; 62:1575–1580.54. Gyldenkerne C, Kahlert J, Olesen KKW, Thrane PG, Sørensen HT, Thomsen RW, et al. Twenty-year temporal trends in risk of ischemic stroke in incident type 2 diabetes: a Danish population-based cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45:2144–2151.55. Benn M, Emanuelsson F, Tybjærg-Hansen A, Nordestgaard BG. Impact of high glucose levels and glucose lowering on risk of ischaemic stroke: a Mendelian randomisation study and meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2021; 64:1492–1503.56. Sattar N, Lee MMY, Kristensen SL, Branch KRH, Del Prato S, Khurmi NS, et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021; 9:653–662.57. Gæde P, Oellgaard J, Carstensen B, Rossing P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH, et al. Years of life gained by multifactorial intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: 21 years follow-up on the Steno-2 randomised trial. Diabetologia. 2016; 59:2298–2307.58. Røder ME. Major adverse cardiovascular event reduction with GLP-1 and SGLT2 agents: evidence and clinical potential. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2018; 9:33–50.59. Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, Rossing P, Mingrone G, Mathieu C, et al. 2019 update to: management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. 2020; 63:221–228.60. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45(Suppl 1):S125–S143.61. Kernan WN, Viscoli CM, Furie KL, Young LH, Inzucchi SE, Gorman M, et al. Pioglitazone after ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack. N Engl J Med. 2016; 374:1321–1331.62. Patoulias DI, Boulmpou A, Teperikidis E, Katsimardou A, Siskos F, Doumas M, et al. Cardiovascular efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: a meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. World J Cardiol. 2021; 13:585–592.63. Rados DV, Falcetta MRR, Pinto LC, Leitão CB, Gross JL. All-cause mortality and cardiovascular safety of basal insulin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021; 173:108688.64. Dormandy JA, Charbonnel B, Eckland DJ, Erdmann E, MassiBenedetti M, Moules IK, et al. Secondary prevention of macrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes in the PROactive Study (PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial In macroVascular Events): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005; 366:1279–1289.65. Wilcox R, Bousser MG, Betteridge DJ, Schernthaner G, Pirags V, Kupfer S, et al. Effects of pioglitazone in patients with type 2 diabetes with or without previous stroke: results from PROactive (PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial In macroVascular Events 04). Stroke. 2007; 38:865–873.66. Verma S, Poulter NR, Bhatt DL, Bain SC, Buse JB, Leiter LA, et al. Effects of liraglutide on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with or without history of myocardial infarction or stroke. Circulation. 2018; 138:2884–2894.67. Leiter LA, Bain SC, Hramiak I, Jódar E, Madsbad S, Gondolf T, et al. Cardiovascular risk reduction with once-weekly semaglutide in subjects with type 2 diabetes: a post hoc analysis of gender, age, and baseline CV risk profile in the SUSTAIN 6 trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019; 18:73.68. Nauck MA, Meier JJ, Cavender MA, Abd El Aziz M, Drucker DJ. Cardiovascular actions and clinical outcomes with glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Circulation. 2017; 136:849–870.69. Nauck MA, Quast DR. Cardiovascular safety and benefits of semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: findings from SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021; 12:645566.70. McGuire DK, Shih WJ, Cosentino F, Charbonnel B, Cherney DZI, Dagogo-Jack S, et al. Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2021; 6:148–158.71. Goldenberg RM, Cheng AYY, Fitzpatrick T, Gilbert JD, Verma S, Hopyan JJ. Benefits of GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide 1) receptor agonists for stroke reduction in type 2 diabetes: a call to action for neurologists. Stroke. 2022; 53:1813–1822.72. Pan Y, Wang Y, Li H, Gaisano HY, Wang Y, He Y. Association of diabetes and prognosis of minor stroke and its subtypes: a prospective observational study. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0153178.73. Pfeffer MA, Claggett B, Diaz R, Dickstein K, Gerstein HC, Køber LV, et al. Lixisenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2247–2257.74. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:311–322.75. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jódar E, Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1834–1844.76. Holman RR, Bethel MA, Mentz RJ, Thompson VP, Lokhnygina Y, Buse JB, et al. Effects of once-weekly exenatide on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:1228–1239.77. Hernandez AF, Green JB, Janmohamed S, D’Agostino RB Sr, Granger CB, Jones NP, et al. Albiglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (harmony outcomes): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2018; 392:1519–1529.78. Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, Diaz R, Lakshmanan M, Pais P, et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2019; 394:121–130.79. Husain M, Birkenfeld AL, Donsmark M, Dungan K, Eliaschewitz FG, Franco DR, et al. Oral semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019; 381:841–851.80. Gerstein HC, Sattar N, Rosenstock J, Ramasundarahettige C, Pratley R, Lopes RD, et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with efpeglenatide in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021; 385:896–907.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The connection between diabetes mellitus and stroke: a brief review
- Diabetes and Stroke
- Social Welfare Approaches for Patients with Diabetes and Stroke
- Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke and diabetes: the underlying link, mechanisms and future possible therapeutic targets
- Pharmacotherapy of Diabetes Focused on Stroke