Prog Med Phys.
2022 Dec;33(4):37-52. 10.14316/pmp.2022.33.4.37.
Image Guided Radiation Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungjoo, Korea
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea
- KMID: 2537871
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2022.33.4.37
Abstract
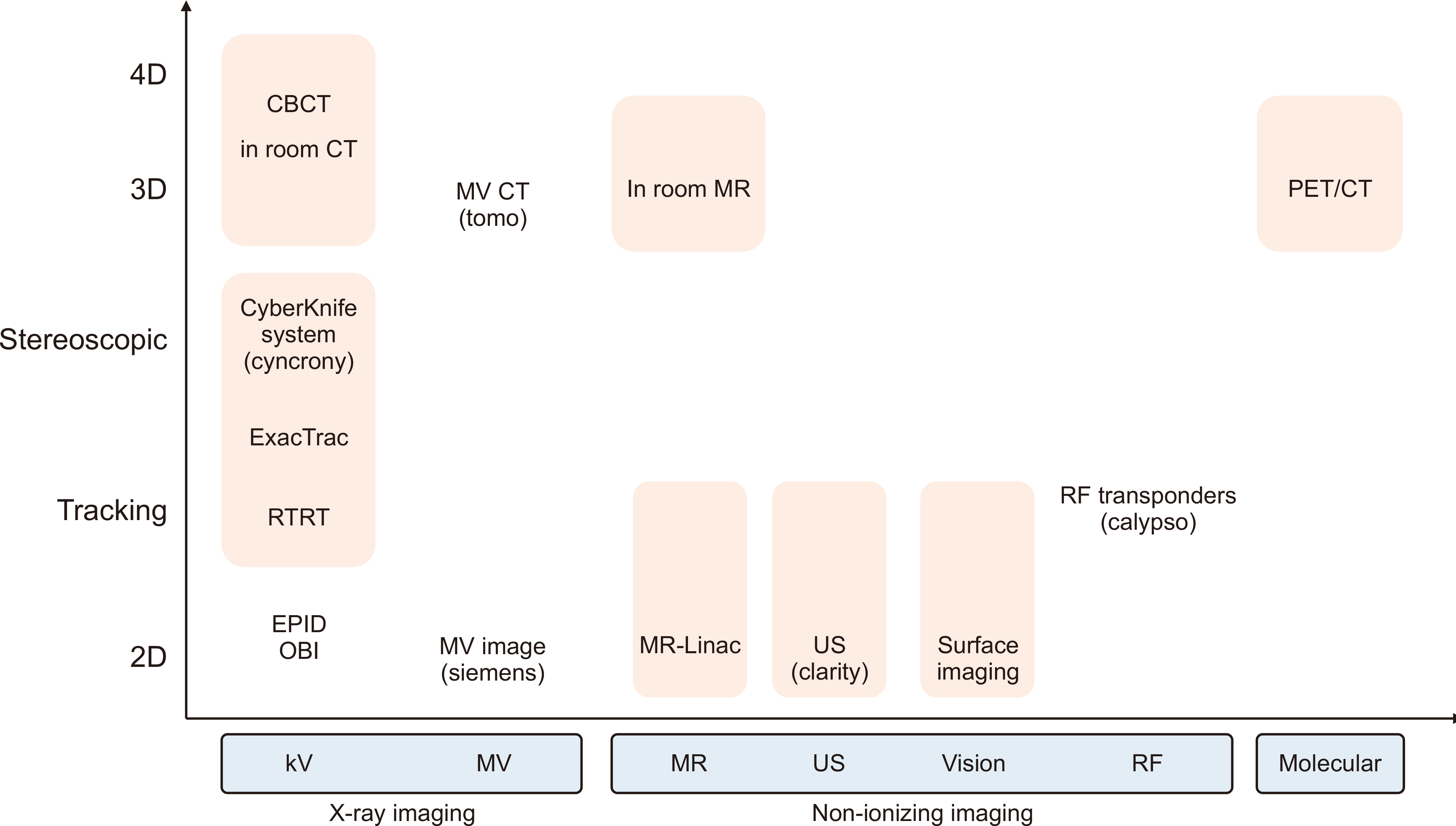
- Over the past decades, radiation therapy combined with imaging modalities that ensure optimal image guidance has revolutionized cancer treatment. The two major purposes of using imaging modalities in radiotherapy are to clearly delineate the target prior to treatment and set up the patient during radiation delivery. Image guidance secures target position prior to and during the treatment. High quality images provide an accurate definition of the treatment target and the possibility to reduce the treatment margin of the target volume, further lowering radiation toxicity and improving the quality of life of cancer patients. In this review, the various types of image guidance modalities used in radiation therapy are distinguished into ionized (kilovoltage and megavoltage image) and nonionized imaging (magnetic resonance image, ultrasound, surface imaging, and radiofrequency). The functional aspects, advantages, and limitation of imaging using these modalities are described as a subsection of each category. This review only focuses on the technological viewpoint of these modalities and any clinical aspects are omitted. Image guidance is essential, and its importance is rapidly increasing in modern radiotherapy. The most important aspect of using image guidance in clinical settings is to monitor the performance of image quality, which must be checked during the periodic quality assurance process.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Grills IS, Hugo G, Kestin LL, Galerani AP, Chao KK, Wloch J, et al. 2008; Image-guided radiotherapy via daily online cone-beam CT substantially reduces margin requirements for stereotactic lung radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 70:1045–1056. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.07.2352. PMID: 18029110.
Article2. Wortel RC, Incrocci L, Pos FJ, Lebesque JV, Witte MG, van der Heide UA, et al. 2015; Acute toxicity after image-guided intensity modulated radiation therapy compared to 3D conformal radiation therapy in prostate cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 91:737–744. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.12.017. PMID: 25752386.
Article3. Diao K, Lobos EA, Yirmibesoglu E, Basak R, Hendrix LH, Barbosa B, et al. 2017; Patient-reported quality of life during definitive and postprostatectomy image-guided radiation therapy for prostate cancer. Pract Radiat Oncol. 7:e117–e124. DOI: 10.1016/j.prro.2016.08.004. PMID: 28274402.
Article4. Huang K, Palma DA, Scott D, McGregor D, Gaede S, Yartsev S, et al. 2012; Inter- and intrafraction uncertainty in prostate bed image-guided radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 84:402–407. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.12.035. PMID: 22381905.
Article5. Jiang SB. 2006; Technical aspects of image-guided respiration-gated radiation therapy. Med Dosim. 31:141–151. DOI: 10.1016/j.meddos.2005.12.005. PMID: 16690455.
Article6. Kupelian PA, Langen KM, Willoughby TR, Zeidan OA, Meeks SL. 2008; Image-guided radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer: treating a moving target. Semin Radiat Oncol. 18:58–66. DOI: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2007.09.008. PMID: 18082589.
Article7. Foskey M, Davis B, Goyal L, Chang S, Chaney E, Strehl N, et al. 2005; Large deformation three-dimensional image registration in image-guided radiation therapy. Phys Med Biol. 50:5869–5892. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/50/24/008. PMID: 16333161.
Article8. Button MR, Staffurth JN. 2010; Clinical application of image-guided radiotherapy in bladder and prostate cancer. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 22:698–706. DOI: 10.1016/j.clon.2010.06.020. PMID: 20688494.
Article9. Biancia CD, Yorke E, Kollmeier MA. 2014; Image guided radiation therapy for bladder cancer: assessment of bladder motion using implanted fiducial markers. Pract Radiat Oncol. 4:108–115. DOI: 10.1016/j.prro.2013.07.008. PMID: 24890351.
Article10. Xing L, Thorndyke B, Schreibmann E, Yang Y, Li TF, Kim GY, et al. 2006; Overview of image-guided radiation therapy. Med Dosim. 31:91–112. DOI: 10.1016/j.meddos.2005.12.004. PMID: 16690451.
Article11. Jaffray D, Kupelian P, Djemil T, Macklis RM. 2007; Review of image-guided radiation therapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 7:89–103. DOI: 10.1586/14737140.7.1.89. PMID: 17187523.
Article12. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). 2019. Introduction of image guided radiotherapy into clinical practice. IAEA;Vienna: p. 16. DOI: 10.1586/14737140.7.1.89.13. Verellen D, De Ridder M, Storme G. 2008; A (short) history of image-guided radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 86:4–13. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2007.11.023. PMID: 18083259.
Article14. Haus AG, Pinsky SM, Marks JE. 1970; A technique for imaging patient treatment area during a therapeutic radiation exposure. Radiology. 97:653–656. DOI: 10.1148/97.3.653. PMID: 4993313.
Article15. Marks JE, Haus AG. 1976; The effect of immobilisation on localisation error in the radiotherapy of head and neck cancer. Clin Radiol. 27:175–177. DOI: 10.1016/S0009-9260(76)80140-7. PMID: 1277733.
Article16. Papiez L, Timmerman R. 2008; Hypofractionation in radiation therapy and its impact. Med Phys. 35:112–118. DOI: 10.1118/1.2816228. PMID: 18293568.
Article17. Mohamoud G, Ryan M, Moseley D. 2015; IGRT refresher series: a departmental initiative. J Med Imag Radiat Sci. 46(Suppl 1):S20–S21. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmir.2015.01.065.
Article18. Verellen D, De Ridder M, Linthout N, Tournel K, Soete G, Storme G. 2007; Innovations in image-guided radiotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:949–960. Erratum in: Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:71. DOI: 10.1038/nrc2288. PMID: 18034185.
Article19. Goyal S, Kataria T. 2014; Image guidance in radiation therapy: techniques and applications. Radiol Res Pract. 2014:705604. DOI: 10.1155/2014/705604. PMID: 25587445. PMCID: PMC4281403.
Article20. Keall PJ, Nguyen DT, O'Brien R, Zhang P, Happersett L, Bertholet J, et al. 2018; Review of real-time 3-dimensional image guided radiation therapy on standard-equipped cancer radiation therapy systems: are we at the tipping point for the era of real-time radiation therapy? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 102:922–931. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.04.016. PMID: 29784460. PMCID: PMC6800174.
Article21. Weissbluth M, Karzmark CJ, Steele RE, Selby AH. 1959; The stanford medical linear accelerator. Radiology. 72:242–253. DOI: 10.1148/72.2.242. PMID: 13634384.
Article22. Jaffray DA, Drake DG, Moreau M, Martinez AA, Wong JW. 1999; A radiographic and tomographic imaging system integrated into a medical linear accelerator for localization of bone and soft-tissue targets. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 45:773–789. DOI: 10.1016/S0360-3016(99)00118-2. PMID: 10524434.
Article23. Hong LX, Chen CC, Garg M, Yaparpalvi R, Mah D. 2009; Clinical experiences with onboard imager KV images for linear accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy setup. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 73:556–561. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.09.055. PMID: 19147020.
Article24. Wiehle R, Koth HJ, Nanko N, Grosu AL, Hodapp N. 2009; On the accuracy of isocenter verification with kV imaging in stereotactic radiosurgery. Strahlenther Onkol. 185:325–330. DOI: 10.1007/s00066-009-1871-5. PMID: 19440672.
Article25. Lee SW, Jin JY, Guan H, Martin F, Kim JH, Yin FF. 2008; Clinical assessment and characterization of a dual tube kilovoltage X-ray localization system in the radiotherapy treatment room. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 9:1–15. DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v9i1.2318. PMID: 18449161. PMCID: PMC5721528.
Article26. Ma J, Chang Z, Wang Z, Jackie Wu Q, Kirkpatrick JP, Yin FF. 2009; ExacTrac X-ray 6 degree-of-freedom image-guidance for intracranial non-invasive stereotactic radiotherapy: comparison with kilo-voltage cone-beam CT. Radiother Oncol. 93:602–608. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2009.09.009. PMID: 19846229.
Article27. Srinivasan K, Mohammadi M, Shepherd J. 2014; Applications of linac-mounted kilovoltage Cone-beam Computed Tomography in modern radiation therapy: a review. Pol J Radiol. 79:181–193. DOI: 10.12659/PJR.890745. PMID: 25006356. PMCID: PMC4085117.
Article28. Oelfke U, Tücking T, Nill S, Seeber A, Hesse B, Huber P, et al. 2006; Linac-integrated kV-cone beam CT: technical features and first applications. Med Dosim. 31:62–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.meddos.2005.12.008. PMID: 16551530.
Article29. Morin O, Gillis A, Chen J, Aubin M, Bucci MK, Roach M 3rd, et al. 2006; Megavoltage cone-beam CT: system description and clinical applications. Med Dosim. 31:51–61. DOI: 10.1016/j.meddos.2005.12.009. PMID: 16551529.
Article30. Pouliot J, Bani-Hashemi A, Chen J, Svatos M, Ghelmansarai F, Mitschke M, et al. 2005; Low-dose megavoltage cone-beam CT for radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 61:552–560. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.10.011. PMID: 15736320.
Article31. Groh BA, Siewerdsen JH, Drake DG, Wong JW, Jaffray DA. 2002; A performance comparison of flat-panel imager-based MV and kV cone-beam CT. Med Phys. 29:967–975. DOI: 10.1118/1.1477234. PMID: 12094992.
Article32. Ma CM, Paskalev K. 2006; In-room CT techniques for image-guided radiation therapy. Med Dosim. 31:30–39. DOI: 10.1016/j.meddos.2005.12.010. PMID: 16551527.
Article33. Wong JR, Grimm L, Uematsu M, Oren R, Cheng CW, Merrick S, et al. 2005; Image-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer by CT-linear accelerator combination: prostate movements and dosimetric considerations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 61:561–569. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.06.010. PMID: 15667979.
Article34. Wu M, Keil A, Constantin D, Star-Lack J, Zhu L, Fahrig R. 2014; Metal artifact correction for x-ray computed tomography using kV and selective MV imaging. Med Phys. 41:121910. DOI: 10.1118/1.4901551. PMID: 25471970. PMCID: PMC4290750.
Article35. Khan FM. 2009. The physics of radiation therapy. 4th ed. Lippincott, Willams & Wilkins;Philadelpia: p. 414–424.36. Khan FM. Treatment planning in radiation oncology. 2 nd ed. Lippincott, Willams & Wilkins;Philadelpia: p. 178–179.37. Song KH, Snyder KC, Kim J, Li H, Ning W, Rusnac R, et al. 2016; Characterization and evaluation of 2.5 MV electronic portal imaging for accurate localization of intra- and extracranial stereotactic radiosurgery. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 17:268–284. DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i4.6247. PMID: 27455505. PMCID: PMC5690040.
Article38. Forrest LJ, Mackie TR, Ruchala K, Turek M, Kapatoes J, Jaradat H, et al. 2004; The utility of megavoltage computed tomography images from a helical tomotherapy system for setup verification purposes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 60:1639–1644. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.08.016. PMID: 15590196.
Article39. Netherton T, Li Y, Gao S, Klopp A, Balter P, Court LE, et al. 2019; Experience in commissioning the halcyon linac. Med Phys. 46:4304–4313. DOI: 10.1002/mp.13723. PMID: 31310678.
Article40. Malajovich I, Teo BK, Petroccia H, Metz JM, Dong L, Li T. 2019; Characterization of the megavoltage cone-beam computed tomography (MV-CBCT) system on HalcyonTM for IGRT: image quality benchmark, clinical performance, and organ doses. Front Oncol. 9:496. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00496. PMID: 31249808. PMCID: PMC6582256.
Article41. Tang G, Moussot C, Morf D, Seppi E, Amols H. 2016; Low-dose 2.5 MV cone-beam computed tomography with thick CsI flat-panel imager. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 17:235–245. DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i4.6185. PMID: 27455493. PMCID: PMC5690043.
Article42. Yue Y, Aristophanous M, Rottmann J, Berbeco RI. 2011; 3-D fiducial motion tracking using limited MV projections in arc therapy. Med Phys. 38:3222–3231. DOI: 10.1118/1.3584197. PMID: 21815397.
Article43. Azcona JD, Li R, Mok E, Hancock S, Xing L. 2013; Automatic prostate tracking and motion assessment in volumetric modulated arc therapy with an electronic portal imaging device. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 86:762–768. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.03.007. PMID: 23608236. PMCID: PMC3686883.
Article44. Tang X, Lin T, Jiang S. 2009; A feasibility study of treatment verification using EPID cine images for hypofractionated lung radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol. 54:S1–S8. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/54/18/S01. PMID: 19687565.
Article45. Shirato H, Shimizu S, Kitamura K, Onimaru R. 2007; Organ motion in image-guided radiotherapy: lessons from real-time tumor-tracking radiotherapy. Int J Clin Oncol. 12:8–16. DOI: 10.1007/s10147-006-0633-y. PMID: 17380435.
Article46. Kashani R, Olsen JR. 2018; Magnetic resonance imaging for target delineation and daily treatment modification. Semin Radiat Oncol. 28:178–184. DOI: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2018.02.002. PMID: 29933877.
Article47. Dawson LA, Sharpe MB. 2006; Image-guided radiotherapy: rationale, benefits, and limitations. Lancet Oncol. 7:848–858. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70904-4. PMID: 17012047.
Article48. Stam MK, Crijns SP, Zonnenberg BA, Barendrecht MM, van Vulpen M, Lagendijk JJ, et al. 2012; Navigators for motion detection during real-time MRI-guided radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol. 57:6797–6805. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/57/21/6797. PMID: 23032581.
Article49. Raaijmakers AJ, Raaymakers BW, Lagendijk JJ. 2008; Magnetic-field-induced dose effects in MR-guided radiotherapy systems: dependence on the magnetic field strength. Phys Med Biol. 53:909–923. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/53/4/006. PMID: 18263948.
Article50. Raaijmakers AJ, Raaymakers BW, Lagendijk JJ. 2005; Integrating a MRI scanner with a 6 MV radiotherapy accelerator: dose increase at tissue-air interfaces in a lateral magnetic field due to returning electrons. Phys Med Biol. 50:1363–1376. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/50/7/002. PMID: 15798329.
Article51. Raaijmakers AJ, Raaymakers BW, van der Meer S, Lagendijk JJ. 2007; Integrating a MRI scanner with a 6 MV radiotherapy accelerator: impact of the surface orientation on the entrance and exit dose due to the transverse magnetic field. Phys Med Biol. 52:929–939. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/52/4/005. PMID: 17264362.
Article52. Raaymakers BW, Raaijmakers AJ, Kotte AN, Jette D, Lagendijk JJ. 2004; Integrating a MRI scanner with a 6 MV radiotherapy accelerator: dose deposition in a transverse magnetic field. Phys Med Biol. 49:4109–4118. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/49/17/019. PMID: 15470926.
Article53. Stanescu T, Schaer N, Breen S, Letourneau D, Shet K, Dickie CI, et al. 2016; Magnetic resonance guided radiation therapy: feasibility study of a linear accelerator and magnetic resonance-on-rails system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 96(Suppl 2):S61–S62. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.06.158.
Article54. Jaffray DA, Carlone MC, Milosevic MF, Breen SL, Stanescu T, Rink A, et al. 2014; A facility for magnetic resonance-guided radiation therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 24:193–195. DOI: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2014.02.012. PMID: 24931091.
Article55. Mutic S, Dempsey JF. 2014; The ViewRay system: magnetic resonance-guided and controlled radiotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 24:196–199. DOI: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2014.02.008. PMID: 24931092.
Article56. Choi CH, Park SY, Kim JI, Kim JH, Kim K, Carlson J, et al. 2017; Quality of tri-Co-60 MR-IGRT treatment plans in comparison with VMAT treatment plans for spine SABR. Br J Radiol. 90:20160652. DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20160652. PMID: 27781486. PMCID: PMC5685120.
Article57. Klüter S. 2019; Technical design and concept of a 0.35 T MR-Linac. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 18:98–101. DOI: 10.1016/j.ctro.2019.04.007. PMID: 31341983. PMCID: PMC6630153.
Article58. Raaymakers BW, Jürgenliemk-Schulz IM, Bol GH, Glitzner M, Kotte ANTJ, van Asselen B, et al. 2017; First patients treated with a 1.5 T MRI-Linac: clinical proof of concept of a high-precision, high-field MRI guided radiotherapy treatment. Phys Med Biol. 62:L41–L50. DOI: 10.1088/1361-6560/aa9517. PMID: 29135471.
Article59. Raaymakers BW, Lagendijk JJ, Overweg J, Kok JG, Raaijmakers AJ, Kerkhof EM, et al. 2009; Integrating a 1.5 T MRI scanner with a 6 MV accelerator: proof of concept. Phys Med Biol. 54:N229–N237. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/54/12/N01. PMID: 19451689.
Article60. Winkel D, Bol GH, Kroon PS, van Asselen B, Hackett SS, Werensteijn-Honingh AM, et al. 2019; Adaptive radiotherapy: The Elekta Unity MR-linac concept. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 18:54–59. DOI: 10.1016/j.ctro.2019.04.001. PMID: 31341976. PMCID: PMC6630157.
Article61. Keall PJ, Barton M, Crozier S. 2014; The Australian magnetic resonance imaging-linac program. Semin Radiat Oncol. 24:203–206. DOI: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2014.02.015. PMID: 24931094.
Article62. Fallone BG. 2014; The rotating biplanar linac-magnetic resonance imaging system. Semin Radiat Oncol. 24:200–202. DOI: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2014.02.011. PMID: 24931093.
Article63. Cusumano D, Boldrini L, Dhont J, Fiorino C, Green O, Güngör G, et al. 2021; Artificial Intelligence in magnetic Resonance guided Radiotherapy: medical and physical considerations on state of art and future perspectives. Phys Med. 85:175–191. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.05.010. PMID: 34022660.
Article64. Langen KM, Pouliot J, Anezinos C, Aubin M, Gottschalk AR, Hsu IC, et al. 2003; Evaluation of ultrasound-based prostate localization for image-guided radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 57:635–644. DOI: 10.1016/S0360-3016(03)00633-3. PMID: 14529767.
Article65. Scarbrough TJ, Golden NM, Ting JY, Fuller CD, Wong A, Kupelian PA, et al. 2006; Comparison of ultrasound and implanted seed marker prostate localization methods: implications for image-guided radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 65:378–387. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.01.008. PMID: 16563658.
Article66. Camps SM, Fontanarosa D, de With PHN, Verhaegen F, Vanneste BGL. 2018; The use of ultrasound imaging in the external beam radiotherapy workflow of prostate cancer patients. Biomed Res Int. 2018:7569590. DOI: 10.1155/2018/7569590. PMID: 29619375. PMCID: PMC5829356.
Article67. Richardson AK, Jacobs P. 2017; Intrafraction monitoring of prostate motion during radiotherapy using the Clarity® Autoscan Transperineal Ultrasound (TPUS) system. Radiography (Lond). 23:310–313. DOI: 10.1016/j.radi.2017.07.003. PMID: 28965894.
Article68. Lachaine M, Falco T. 2013; Intrafractional prostate motion management with the Clarity Autoscan System. Med Phys Int J. 1:72–80.69. Baker M, Behrens CF. 2015; Prostate displacement during transabdominal ultrasound image-guided radiotherapy assessed by real-time four-dimensional transperineal monitoring. Acta Oncol. 54:1508–1514. DOI: 10.3109/0284186X.2015.1061208. PMID: 26203927.
Article70. Brahme A, Nyman P, Skatt B. 2008; 4D laser camera for accurate patient positioning, collision avoidance, image fusion and adaptive approaches during diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Med Phys. 35:1670–1681. DOI: 10.1118/1.2889720. PMID: 18561642.
Article71. Pallotta S, Marrazzo L, Ceroti M, Silli P, Bucciolini M. 2012; A phantom evaluation of Sentinel™, a commercial laser/camera surface imaging system for patient setup verification in radiotherapy. Med Phys. 39:706–712. DOI: 10.1118/1.3675973. PMID: 22320780.
Article72. Hoisak JDP, Pawlicki T. 2018; The role of optical surface imaging Systems in Radiation Therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 28:185–193. DOI: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2018.02.003. PMID: 29933878.
Article73. Hattel SH, Andersen PA, Wahlstedt IH, Damkjaer S, Saini A, Thomsen JB. 2019; Evaluation of setup and intrafraction motion for surface guided whole-breast cancer radiotherapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 20:39–44. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12599. PMID: 31187538. PMCID: PMC6560238.
Article74. Kügele M, Edvardsson A, Berg L, Alkner S, Andersson Ljus C, Ceberg S. 2018; Dosimetric effects of intrafractional isocenter variation during deep inspiration breath-hold for breast cancer patients using surface-guided radiotherapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 19:25–38. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12214. PMID: 29139223. PMCID: PMC5768000.
Article75. Lee SK, Huang S, Zhang L, Ballangrud AM, Aristophanous M, Cervino Arriba LI, et al. 2021; Accuracy of surface-guided patient setup for conventional radiotherapy of brain and nasopharynx cancer. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 22:48–57. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13241. PMID: 33792186. PMCID: PMC8130230.
Article76. Li G, Ballangrud A, Kuo LC, Kang H, Kirov A, Lovelock M, et al. 2011; Motion monitoring for cranial frameless stereotactic radiosurgery using video-based three-dimensional optical surface imaging. Med Phys. 38:3981–3994. DOI: 10.1118/1.3596526. PMID: 21858995.
Article77. Walter F, Freislederer P, Belka C, Heinz C, Söhn M, Roeder F. 2016; Evaluation of daily patient positioning for radiotherapy with a commercial 3D surface-imaging system (Catalyst™). Radiat Oncol. 11:154. DOI: 10.1186/s13014-016-0728-1. PMID: 27881158. PMCID: PMC5122202.
Article78. Kügele M, Mannerberg A, Nørring Bekke S, Alkner S, Berg L, Mahmood F, et al. 2019; Surface guided radiotherapy (SGRT) improves breast cancer patient setup accuracy. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 20:61–68. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12700. PMID: 31478615. PMCID: PMC6753725.
Article79. Stanley DN, McConnell KA, Kirby N, Gutiérrez AN, Papanikolaou N, Rasmussen K. 2017; Comparison of initial patient setup accuracy between surface imaging and three point localization: a retrospective analysis. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 18:58–61. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12183. PMID: 28901684. PMCID: PMC5689923.
Article80. Chow VUY, Cheung MLM, Kan MWK, Chan ATC. 2022; Shift detection discrepancy between ExacTrac Dynamic system and cone-beam computed tomography. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 23:e13567. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13567. PMID: 35188333. PMCID: PMC9121052.
Article81. Das S, Liu T, Jani AB, Rossi P, Shelton J, Shi Z, et al. 2014; Comparison of image-guided radiotherapy technologies for prostate cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 37:616–623. DOI: 10.1097/COC.0b013e31827e4eb9. PMID: 23428948.
Article82. Willoughby TR, Kupelian PA, Pouliot J, Shinohara K, Aubin M, Roach M 3rd, et al. 2006; Target localization and real-time tracking using the Calypso 4D localization system in patients with localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 65:528–534. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.01.050. PMID: 16690435.
Article83. Ogunleye T, Rossi PJ, Jani AB, Fox T, Elder E. 2009; Performance evaluation of Calypso 4D localization and kilovoltage image guidance systems for interfraction motion management of prostate patients. ScientificWorldJournal. 9:449–458. DOI: 10.1100/tsw.2009.61. PMID: 19526184. PMCID: PMC5823203.
Article84. Rajendran RR, Plastaras JP, Mick R, McMichael Kohler D, Kassaee A, Vapiwala N. 2010; Daily isocenter correction with electromagnetic-based localization improves target coverage and rectal sparing during prostate radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 76:1092–1099. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.03.036. PMID: 19625136.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Practical Considerations in Preparing an Institutional Procedure of Image Guided Radiation Therapy
- Evolution of Radiotherapy: High-precision Radiotherapy
- Image-guided radiation therapy in lymphoma management
- Radiation therapy for pediatric brain tumors
- Helical Tomotherapy: Image-guided Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy