J Korean Med Assoc.
2008 Jul;51(7):604-611. 10.5124/jkma.2008.51.7.604.
Evolution of Radiotherapy: High-precision Radiotherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea. ybkim3@yuhs.ac, cosuh317@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2185910
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2008.51.7.604
Abstract
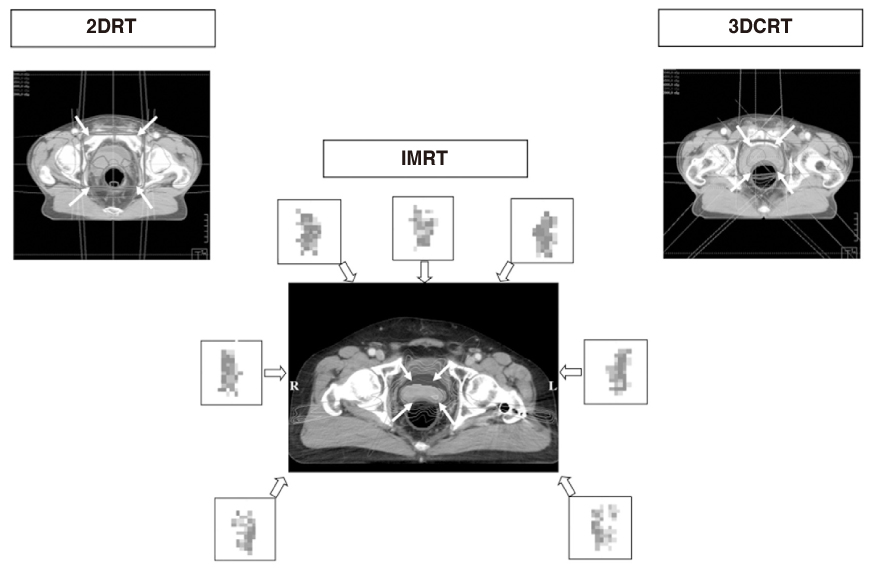
- Technological advances that have been achieved over the last two decades in the area of treatment planning and sophisticated and complicated hardware capabilities, such as computer-controlled treatments, multileaf collimators, and incorporating imaging devices into treatment machines, enable clinical implementation of high-precision radiotherapy in field of radiation oncology. High-precision radiotherapy allows the delivery of increased tumor doses with relative sparing of normal tissues compared to 3 -dimensional radiotherapy and conventional techniques. Preliminary clinical experiences of high precision radiation therapy have been encouraging by high rates of local control and decrease of toxicity. This article provides an overview of high precision radiotherapy such as intensity-modulated radiotherapy, stereotactic radiation therapy, image-guided radiotherapy, and charged particle therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Verification of Secondary Electron Generated by Head Screw in Gamma Knife Using Monte Carlo N-Particle Simulation
Heesoo Kim, Jeong-Woo Lee
Prog Med Phys. 2020;31(2):29-34. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2020.31.2.29.A Prediction Model for the Resilience and the Quality of Life in Cancer Patients with Radiotherapy
So Yeun Jun, Hyeon Jeong Ju, Je Sang Yu, Ji Hyun Lee
Asian Oncol Nurs. 2015;15(4):228-238. doi: 10.5388/aon.2015.15.4.228.
Reference
-
1. Purdy JA. Advances in three-dimensional treatment planning and conformal dose delivery. Semin Oncol. 1997. 24:655–671.2. Armstrong J, Raben A, Zelefsky M, Burt M, Leibel S, Burman C, Kutcher G, Harrison L, Hahn C, Ginsberg R, Rusch V, Kris M, Fuks Z. Promising survival with three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 1997. 44:17–22.
Article3. Lee CG. High precision radiotherapy. J Korean Med Assoc. 2004. 47:663–671.
Article4. Chung H, Kim DG. Introduction to radiosurgery. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008. 51:5–15.
Article5. Lee N, Xia P, Quivey JM, Sultanem K, Poon I, Akazawa C, Akazawa P, Weinberg V, Fu KK. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy in the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An update of the ucsf experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. 53:12–22.
Article6. Zelefsky MJ, Fuks Z, Hunt M, Yamada Y, Marion C, Ling CC, Amols H, Venkatraman ES, Leibel SA. High-dose intensity modulated radiation therapy for prostate cancer: Early toxicity and biochemical outcome in 772 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. 53:1111–1116.
Article7. Han C, Liu A, Schultheiss TE, Pezner RD, Chen YJ, Wong JY. Dosimetric comparisons of helical tomotherapy treatment plans and step-and-shoot intensity-modulated radiosurgery treatment plans in intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. 65:608–616.
Article8. Pezner RD, Liu A, Han C, Chen YJ, Schultheiss TE, Wong JY. Dosimetric comparison of helical tomotherapy treatment and step-and-shoot intensity-modulated radiotherapy of retroperitoneal sarcoma. Radiother Oncol. 2006. 81:81–87.
Article9. Schefter TE, Kavanagh BD, Timmerman RD, Cardenes HR, Baron A, Gaspar LE. A phase i trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy (sbrt) for liver metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. 62:1371–1378.
Article10. Kavanagh BD, Schefter TE, Cardenes HR, Stieber VW, Raben D, Timmerman RD, McCarter MD, Burri S, Nedzi LA, Sawyer TE, Gaspar LE. Interim analysis of a prospective phase i/ii trial of sbrt for liver metastases. Acta Oncol. 2006. 45:848–855.
Article11. Beitler JJ, Makara D, Silverman P, Lederman G. Definitive, high-dose-per-fraction, conformal, stereotactic external radiation for renal cell carcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2004. 27:646–648.
Article12. Wersall PJ, Blomgren H, Lax I, Kalkner KM, Linder C, Lundell G, Nilsson B, Nilsson S, Naslund I, Pisa P, Svedman C. Extracranial stereotactic radiotherapy for primary and metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Radiother Oncol. 2005. 77:88–95.
Article13. Madsen BL, Hsi RA, Pham HT, Presser J, Esagui L, Corman J, Myers L, Jones D. Intrafractional stability of the prostate using a stereotactic radiotherapy technique. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. 57:1285–1291.
Article14. Miralbell R, Molla M, Arnalte R, Canales S, Vargas E, Linero D, Waters S, Nouet P, Rouzaud M, Escude L. Target repositioning optimization in prostate cancer: Is intensity-modulated radiotherapy under stereotactic conditions feasible? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. 59:366–371.
Article15. Hoyer M, Roed H, Traberg Hansen A, Ohlhuis L, Petersen J, Nellemann H, Kiil Berthelsen A, Grau C, Aage Engelholm S, Von der Maase H. Phase ii study on stereotactic body radiotherapy of colorectal metastases. Acta Oncol. 2006. 45:823–830.
Article16. Koong AC, Christofferson E, Le QT, Goodman KA, Ho A, Kuo T, Ford JM, Fisher GA, Greco R, Norton J, Yang GP. Phase ii study to assess the efficacy of conventionally fractionated radiotherapy followed by a stereotactic radiosurgery boost in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. 63:320–323.
Article17. Koong AC, Le QT, Ho A, Fong B, Fisher G, Cho C, Ford J, Poen J, Gibbs IC, Mehta VK, Kee S, Trueblood W, Yang G, Bastidas JA. Phase i study of stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. 58:1017–1021.
Article18. Chang EL, Shiu AS, Lii MF, Rhines LD, Mendel E, Mahajan A, Weinberg JS, Mathews LA, Brown BW, Maor MH, Cox JD. Phase i clinical evaluation of near-simultaneous computed tomographic image-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy for spinal metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. 59:1288–1294.
Article19. Ryu S, Fang Yin F, Rock J, Zhu J, Chu A, Kagan E, Rogers L, Ajlouni M, Rosenblum M, Kim JH. Image-guided and intensity-modulated radiosurgery for patients with spinal metastasis. Cancer. 2003. 97:2013–2018.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- LINAC-based High-precision Radiotherapy: Radiosurgery, Image-guided Radiotherapy, and Respiratory-gated Radiotherapy
- High Precision Radiotherapy
- Two Cases of Extramammary Paget' s Disease Showing a Good Response to Radiotherapy
- The mixed era of stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy
- Radiation therapy for pediatric brain tumors