Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2022 Nov;26(4):308-312. 10.14701/ahbps.22-030.
Preoperative estimation of hemi-liver volume using standard liver volume and portal vein diameter ratio in living donor liver transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Surgery, King Abdulaziz Medical City, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
- KMID: 2536379
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.22-030
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
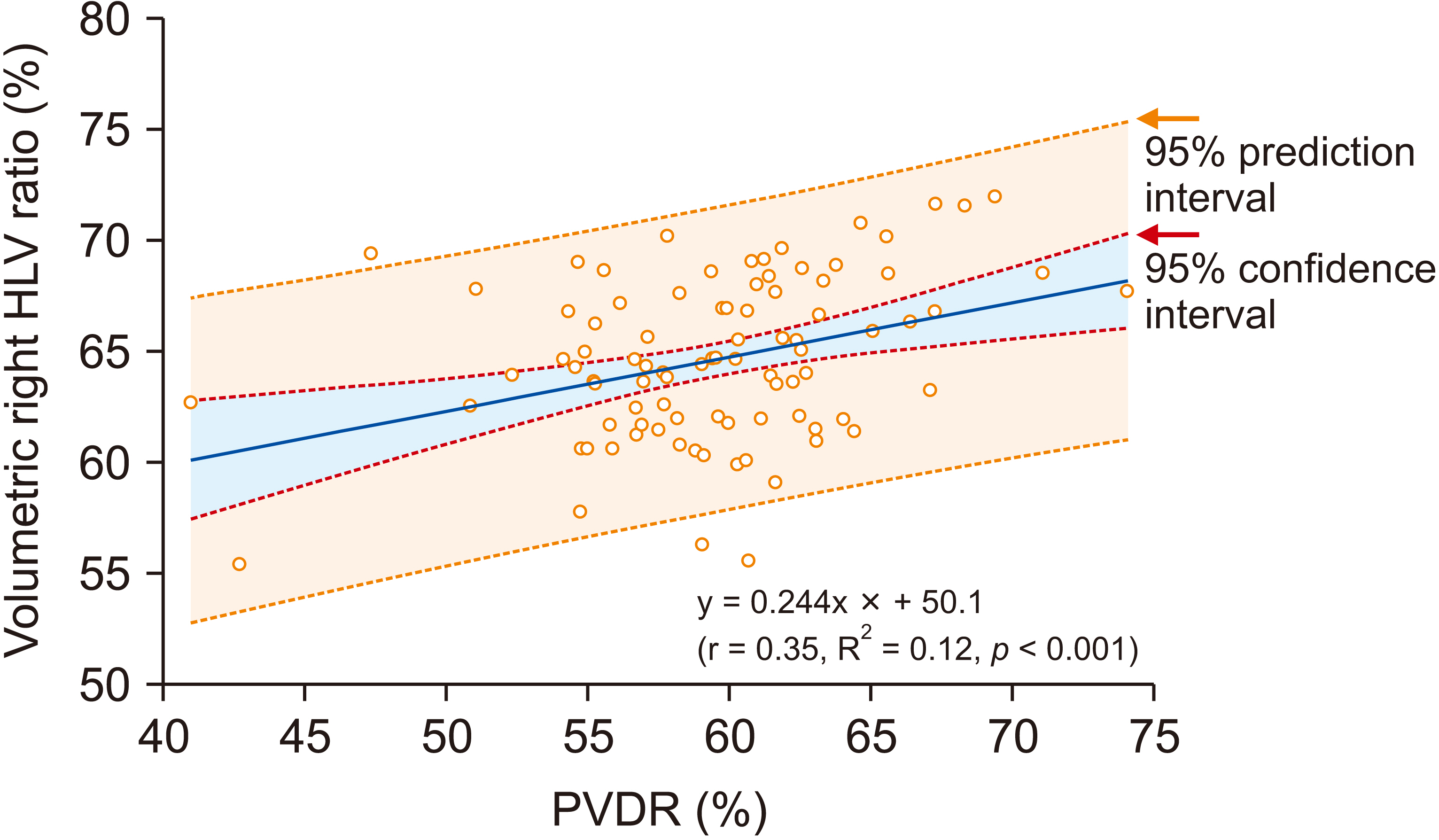
Although body surface area (BSA)-based standard liver volume (SLV) formulae have been used for living donor liver transplantation and hepatic resection, hemi-liver volume (HLV) is needed more frequently. HLV can be assessed using right or left portal vein diameter (RPVD or LPVD). The aim of this study was to validate the reliability of using portal vein diameter ratio (PVDR) for assessing HLV in living liver donors.
Methods
This study included 92 living liver donors (59 males and 33 females) who underwent surgery between January 2020 and December 2020. Computed tomography (CT) images were used for measurements.
Results
Mean age of donors was 35.5 ± 7.2 years. CT volumetry-measured total liver volume (TLV), right HLV, left HLV, and percentage of right HLV in TLV were 1,442.9 ± 314.2 mL, 931.5 ± 206.4 mL, 551.4 ± 126.5 mL, and 64.6% ± 3.6%, respectively. RPVD, LPVD, and main portal vein diameter were 12.2 ± 1.5 mm, 10.0 ± 1.3 mm, and 15.3 ± 1.7 mm, respectively (corresponding square values: 149.9 ± 36.9 mm2 , 101.5 ± 25.2 mm2 , and 237.2 ± 52.2 mm2 , respectively). The sum of RPVD2 and LPVD2 was 251.1 ± 56.9 mm2 . BSA-based SLV was 1,279.5 ± 188.7 mL (error rate: 9.1% ± 14.4%). SLV formula- and PVDR-based right HLV was 760.0 ± 130.7 mL (error rate: 16.2% ± 13.3%).
Conclusions
Combining BSA-based SLV and PVDR appears to be a simple method to predict right or left HLV in living donors or split liver transplantation.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hwang S, Lee SG, Lee YJ, Sung KB, Park KM, Kim KH, et al. 2006; Lessons learned from 1,000 living donor liver transplantations in a single center: how to make living donations safe. Liver Transpl. 12:920–927. DOI: 10.1002/lt.20734. PMID: 16721780.2. Vernuccio F, Whitney SA, Ravindra K, Marin D. 2021; CT and MR imaging evaluation of living liver donors. Abdom Radiol (NY). 46:17–28. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-019-02385-6. PMID: 31901101.3. Kwon HJ, Kim KW, Jang JK, Lee J, Song GW, Lee SG. 2020; Reproducibility and reliability of computed tomography volumetry in estimation of the right-lobe graft weight in adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation: Cantlie's line vs portal vein territorialization. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 27:541–547. DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.749. PMID: 32353894.4. Lim MC, Tan CH, Cai J, Zheng J, Kow AW. 2014; CT volumetry of the liver: where does it stand in clinical practice? Clin Radiol. 69:887–895. DOI: 10.1016/j.crad.2013.12.021. PMID: 24824973.5. Yang X, Yang JD, Yu HC, Choi Y, Yang K, Lee TB, et al. 2018; Dr. Liver: a preoperative planning system of liver graft volumetry for living donor liver transplantation. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 158:11–19. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.01.024. PMID: 29544776.6. Mochizuki K, Takatsuki M, Soyama A, Hidaka M, Obatake M, Eguchi S. 2012; The usefulness of a high-speed 3D-image analysis system in pediatric living donor liver transplantation. Ann Transplant. 17:31–34. DOI: 10.12659/AOT.882633. PMID: 22466906.7. Wang F, Pan KT, Chu SY, Chan KM, Chou HS, Wu TJ, et al. 2011; Preoperative estimation of the liver graft weight in adult right lobe living donor liver transplantation using maximal portal vein diameters. Liver Transpl. 17:373–380. DOI: 10.1002/lt.22274. PMID: 21445920.8. Takeshige K, Kuroda H, Fukaya Y, Suzuki H, Hasegawa M, Yamamoto S. 1982; The role of portal blood factors in regeneration of the liver. World J Surg. 6:603–609. DOI: 10.1007/BF01657876. PMID: 7135989.9. Tongyoo A, Pomfret EA, Pomposelli JJ. 2012; Accurate estimation of living donor right hemi-liver volume from portal vein diameter measurement and standard liver volume calculation. Am J Transplant. 12:1229–1239. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03909.x. PMID: 22221803.10. Mosteller RD. 1987; Simplified calculation of body-surface area. N Engl J Med. 317:1098. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM198710223171717. PMID: 3657876.11. Hwang S, Ha TY, Song GW, Jung DH, Ahn CS, Moon DB, et al. 2015; Quantified risk assessment for major hepatectomy via the indocyanine green clearance rate and liver volumetry combined with standard liver volume. J Gastrointest Surg. 19:1305–1314. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-015-2846-8. PMID: 25947549.12. Gondolesi GE, Yoshizumi T, Bodian C, Kim-Schluger L, Schiano T, Fishbein T, et al. 2004; Accurate method for clinical assessment of right lobe liver weight in adult living-related liver transplant. Transplant Proc. 36:1429–1433. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2004.04.094. PMID: 15251351.13. Lee WC, Lee CS, Soong RS, Lee CF, Wu TJ, Chou HS, et al. 2011; Split liver transplantation in adults: preoperative estimation of the weight of right and left hemiliver grafts. Liver Transpl. 17:93–94. DOI: 10.1002/lt.22213. PMID: 21254350.14. Sgro JC, Charters C, Chandler JG, Grambort DE, Orloff MJ. 1973; Site of origin of the hepatotrophic portal blood factor involved in liver regeneration. Surg Forum. 24:377–379.15. Pomposelli JJ, Tongyoo A, Wald C, Pomfret EA. 2012; Variability of standard liver volume estimation versus software-assisted total liver volume measurement. Liver Transpl. 18:1083–1092. DOI: 10.1002/lt.23461. PMID: 22532341.16. Hashimoto T, Sugawara Y, Tamura S, Hasegawa K, Kishi Y, Kokudo N, et al. 2006; Estimation of standard liver volume in Japanese living liver donors. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:1710–1713. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04433.x. PMID: 16984594.17. Yuan D, Lu T, Wei YG, Li B, Yan LN, Zeng Y, et al. 2008; Estimation of standard liver volume for liver transplantation in the Chinese population. Transplant Proc. 40:3536–3540. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2008.07.135. PMID: 19100432.18. Poovathumkadavil A, Leung KF, Al Ghamdi HM, Othman Iel H, Meshikhes AW. 2010; Standard formula for liver volume in Middle Eastern Arabic adults. Transplant Proc. 42:3600–3605. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2010.07.098. PMID: 21094823.19. Urata K, Kawasaki S, Matsunami H, Hashikura Y, Ikegami T, Ishizone S, et al. 1995; Calculation of child and adult standard liver volume for liver transplantation. Hepatology. 21:1317–1321. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840210515. PMID: 7737637.20. Hwang S, Lee SG, Lee YJ, Park KM, Jeon HB, Kim PN, et al. 1997; Calculation of standard liver volume of Korean adults. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1:59–65.21. Lee SG, Park KM, Hwang S, Lee YJ, Kim KH, Ahn CS, et al. 2002; Adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation at the Asan Medical Center, Korea. Asian J Surg. 25:277–284. DOI: 10.1016/S1015-9584(09)60192-5. PMID: 12470999.22. Feng LM, Wang PQ, Yu H, Chen RT, Wang J, Sheng X, et al. 2017; New formula for predicting standard liver volume in Chinese adults. World J Gastroenterol. 23:4968–4977. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4968. PMID: 28785151. PMCID: PMC5526767.23. Yang G, Hwang S, Song GW, Jung DH. 2021; Comparison of skeletal muscle index-based formula and body surface area-based formula for calculating standard liver volume. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 25:192–197. DOI: 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.2.192. PMID: 34053921. PMCID: PMC8180406.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Portal vein fenestration: a case report of an unusual portal vein developmental anomaly
- Portal flow augmentation using meso-reno-portal anastomosis during liver transplantation with severe portal vein thrombosis
- Prevention and Management of Small-for-Size Syndrome of Liver Transplantation
- Living Donor Liver Transplantation in Adults Using the Right Lobe
- Liver Regeneration and Factors Influencing Liver Regeneration in Donors and Recipients of Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation Using Right Lobe Graft