Korean J Gastroenterol.
2022 Nov;80(5):225-228. 10.4166/kjg.2022.079.
Collagenous Gastoduodenitis in the Form of a Gastric Ulcer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2536351
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2022.079
Abstract
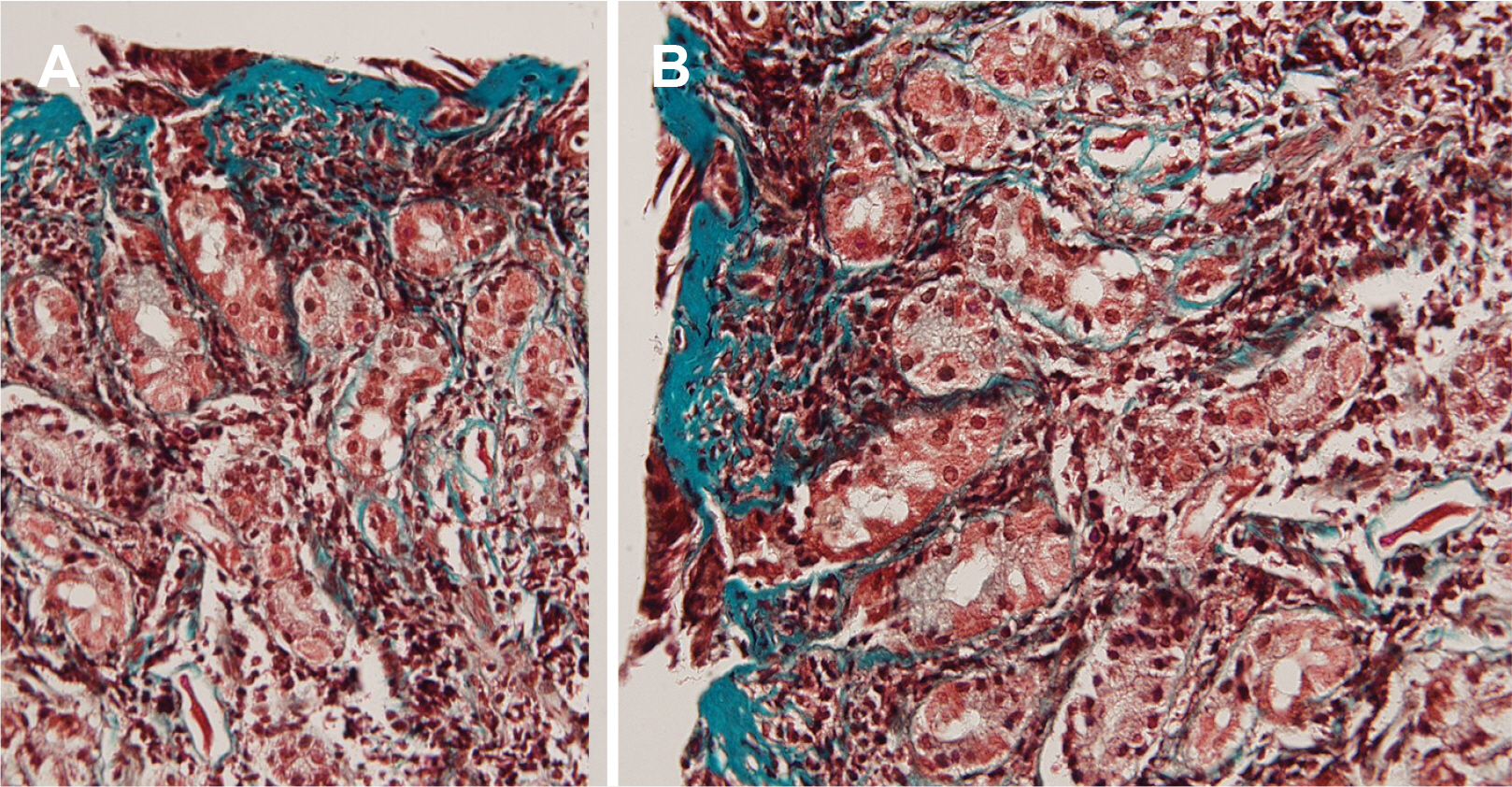
- Collagenous gastroduodenitis is a rare gastrointestinal disease diagnosed histologically by subepithelial collagen deposition in the lamina propria. Its clinical presentation is diverse. The authors encountered a 17-year-old female patient who complained of epigastric pain. Endoscopy revealed several deep ulcers in the gastric body. The gastric mucosa around the ulcer showed diffuse fine nodularity in the shape of cobblestones with open-type atrophy. The duodenal mucosa showed nodular lesions similar to those of the gastric mucosa. The gastric ulcer healed completely with proton pump inhibitor treatment. The patient was followed up, showing no remarkable mucosal change of stomach or duodenum for several years. Collagenous gastroduodenitis was diagnosed by repeated histologic examinations. This paper reports a rare case of chronic collagen gastritis with deep gastric ulcer and its long-term clinical progress.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Colletti RB, Trainer TD. 1989; Collagenous gastritis. Gastroenterology. 97:1552–1555. DOI: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90403-4. PMID: 2583419.
Article2. Lagorce-Pages C, Fabiani B, Bouvier R, Scoazec JY, Durand L, Flejou JF. 2001; Collagenous gastritis: a report of six cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 25:1174–1179. DOI: 10.1097/00000478-200109000-00008. PMID: 11688577.3. Kamimura K, Kobayashi M, Narisawa R, et al. 2007; Collagenous gastritis: endoscopic and pathologic evaluation of the nodularity of gastric mucosa. Dig Dis Sci. 52:995–1000. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-006-9278-y. PMID: 17342397.
Article4. Kamimura K, Kobayashi M, Sato Y, Aoyagi Y, Terai S. 2015; Collagenous gastritis: review. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 7:265–273. DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i3.265. PMID: 25789098. PMCID: PMC4360446.
Article5. Matta J, Alex G, Cameron DJS, Chow CW, Hardikar W, Heine RG. 2018; Pediatric collagenous gastritis and colitis: a case series and review of the literature. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 67:328–334. DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001975. PMID: 29601434.
Article6. Leung ST, Chandan VS, Murray JA, Wu TT. 2009; Collagenous gastritis: histopathologic features and association with other gastrointestinal diseases. Am J Surg Pathol. 33:788–798. DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318196a67f. PMID: 19295410.7. Tanabe J, Yasumaru M, Tsujimoto M, et al. 2013; A case of collagenous gastritis resembling nodular gastritis in endoscopic appearance. Clin J Gastroenterol. 6:442–446. DOI: 10.1007/s12328-013-0431-9. PMID: 26182135.
Article8. Kang B, Um SH, Yun J, Kim HK, Choe BH, Lee YM. 2021; Collagenous gastroduodenocolitis in a Korean adolescent: first pediatric case report in Asia. Transl Pediatr. 10:3096–3103. DOI: 10.21037/tp-21-342. PMID: 34976776. PMCID: PMC8649595.
Article9. Lee YJ, Lee M, Kim DJ, Lee S, Hong J. 2019; Three case reports of collagenous gastritis in children: lessons for an endoscopic and histologic approach to mucosal nodularity of the stomach. Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e14870. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014870. PMID: 30882690. PMCID: PMC6426568.10. Ma C, Park JY, Montgomery EA, et al. 2015; A comparative clinicopathologic study of collagenous gastritis in children and adults: the same disorder with associated immune-mediated diseases. Am J Surg Pathol. 39:802–812. DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000441. PMID: 25871617.
Article11. Mandaliya R, DiMarino AJ, Abraham S, Burkart A, Cohen S. 2013; Collagenous gastritis a rare disorder in search of a disease. Gastroenterology Res. 6:139–144. DOI: 10.4021/gr564w. PMID: 27785244. PMCID: PMC5074812.
Article12. Kawamura M, Abe S, Oikawa K, et al. 2011; Topographic differences in gastric micromucosal patterns observed by magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:477–483. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06527.x. PMID: 21155881.
Article13. Choung RS, Sharma A, Chedid VG, Absah I, Chen ZE, Murray JA. 2022; Collagenous gastritis: characteristics and response to topical budesonide. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:1977–1985.e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.11.033. PMID: 34864160.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three Cases of Coexistence of Gastric Cancer and Duodenal Ulcer
- A Case of Coexistence of Gastric Cancer and Duodenal Ulcer
- Gastric Metaplasia in Duodenum
- Study on the Gastric Cancer Initially Diagnosed as Benign Gastric Ulcer during Endoscopic Follow-up
- Bile Ductular Proliferation in the Gastric Wall after Gastric Ulcer Penetration into the Liver