Anesth Pain Med.
2022 Oct;17(4):420-428. 10.17085/apm.22176.
C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio is a predictor of 1-year mortality following liver transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Laboratory for Cardiovascular Dynamics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2535341
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.22176
Abstract
- Background
Considering the importance of the inflammatory status of recipients on outcomes following liver transplantation (LT), we investigated the association between C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio (CAR) and one-year mortality following LT and compared it with other parameters reflecting patients’ underlying inflammatory status.
Methods
A total of 3,614 consecutive adult LT recipients were retrospectively evaluated. Prognostic parameters were analyzed using area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) analysis, and subsequent cutoffs were derived. For survival analysis, Cox proportional hazards and Kaplan-Meier analyses were performed.
Results
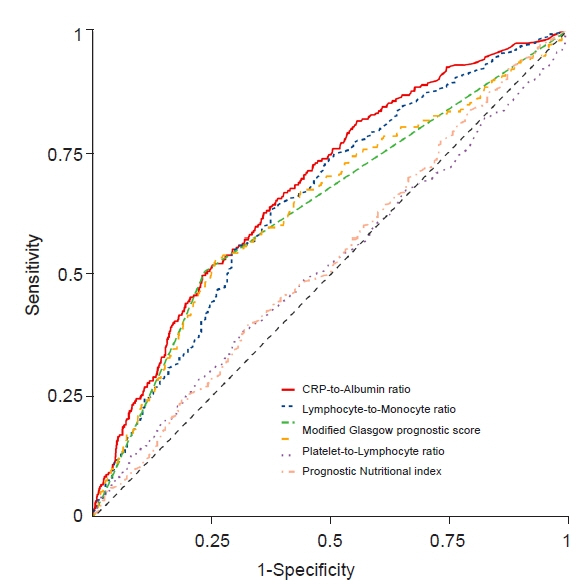
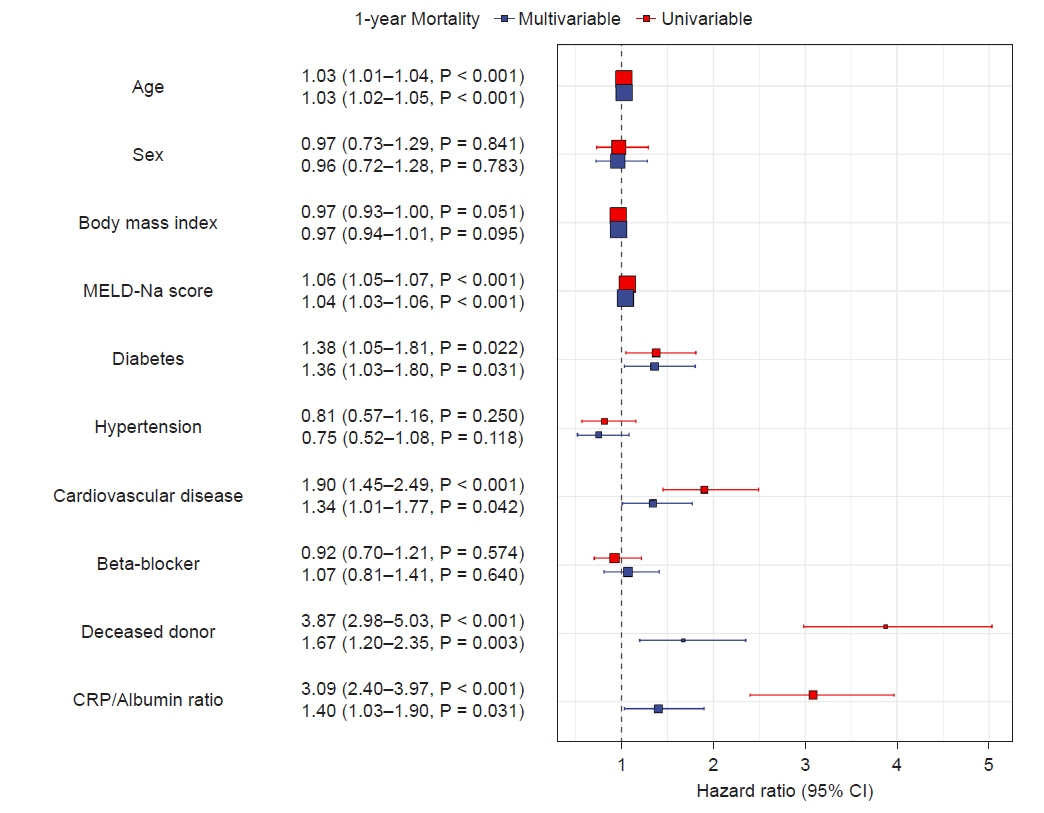
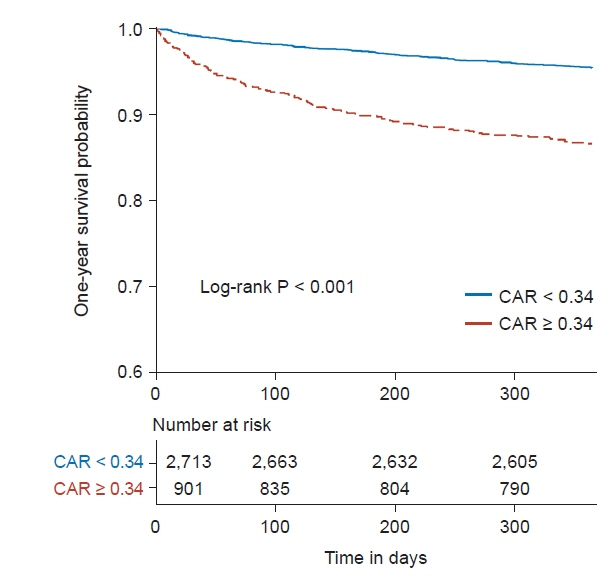
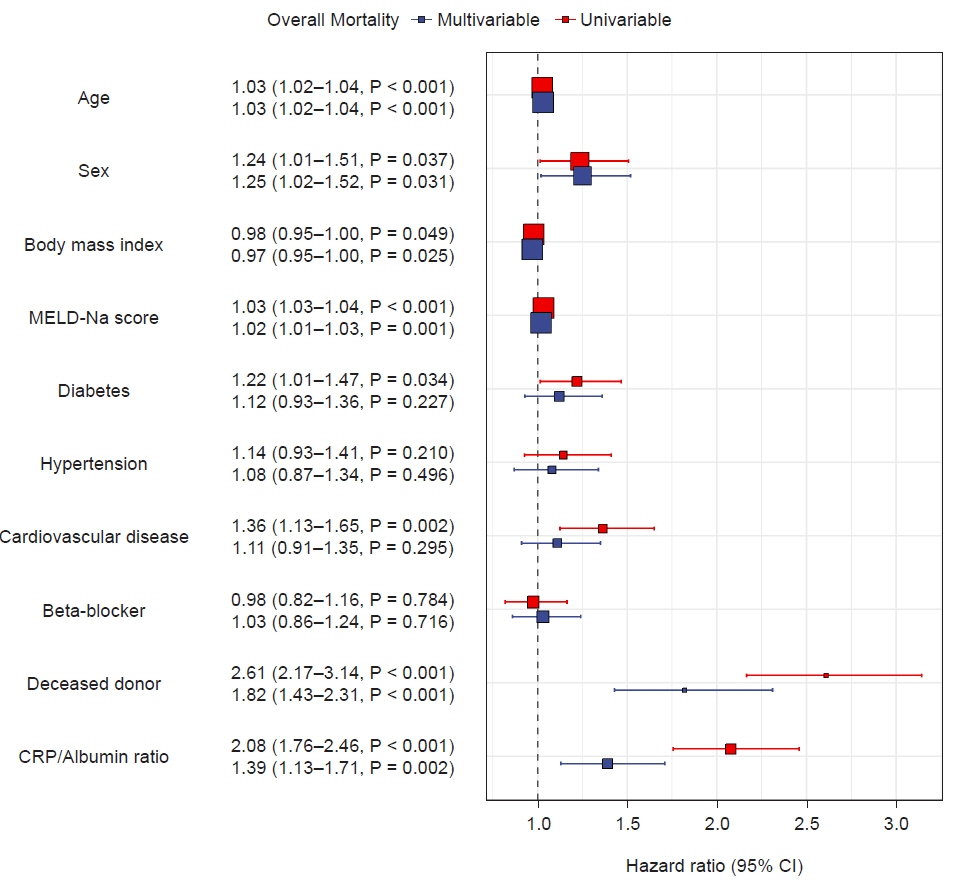
The AUROC for CAR to predict one-year mortality after LT was 0.68 (0.65–0.72), which was the highest compared with other inflammatory parameters, with the best cutoff of 0.34. A CAR ≥ 0.34 was associated with a significantly higher one-year mortality rate (13.3% vs. 5.8 %, log-rank P < 0.001) and overall mortality rate (24.5% vs. 12.9%, log-rank P = 0.039). A CAR ≥ 0.34 was an independent predictor of one-year mortality (hazard ratio, 1.40 [1.03–1.90], P = 0.031) and overall mortality (hazard ratio 1.39 [1.13–1.71], P = 0.002) after multivariable adjustment.
Conclusions
Preoperative CAR (≥ 0.34) was independently associated with a higher risk of one-year and overall mortality after LT. This may suggest that CAR, a simple and readily available biomarker, maybe a practical index that may assist in the risk stratification of liver transplantation outcomes.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cirera I, Bauer TM, Navasa M, Vila J, Grande L, Taurá P, et al. Bacterial translocation of enteric organisms in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2001; 34:32–7.
Article2. Thabut D, Massard J, Gangloff A, Carbonell N, Francoz C, Nguyen-Khac E, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease score and systemic inflammatory response are major prognostic factors in patients with cirrhosis and acute functional renal failure. Hepatology. 2007; 46:1872–82.
Article3. Zhang Y, Jin W, Cai X. Anti-interleukin-2 receptor antibodies for the prevention of rejection in liver transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Med. 2017; 49:365–76.
Article4. Karimi MH, Daneshmandi S, Pourfathollah AA, Geramizadeh B, Malekhosseini SA, Nikeghbalian S, et al. Association of IL-6 promoter and IFN-γ gene polymorphisms with acute rejection of liver transplantation. Mol Biol Rep. 2011; 38:4437–43.
Article5. Friedman BH, Wolf JH, Wang L, Putt ME, Shaked A, Christie JD, et al. Serum cytokine profiles associated with early allograft dysfunction in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2012; 18:166–76.
Article6. Oweira H, Lahdou I, Daniel V, Opelz G, Schmidt J, Zidan A, et al. Early post-operative acute phase response in patients with early graft dysfunction is predictive of 6-month and 12-month mortality in liver transplant recipients. Hum Immunol. 2016; 77:952–60.
Article7. Park JE, Chung KS, Song JH, Kim SY, Kim EY, Jung JY, et al. The C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as a predictor of mortality in critically Ill patients. J Clin Med. 2018; 7:333.
Article8. Oh TK, Ji E, Na HS, Min B, Jeon YT, Do SH, et al. C-reactive protein to albumin ratio predicts 30-day and 1-year mortality in postoperative patients after admission to the intensive care unit. J Clin Med. 2018; 7:39.
Article9. Køstner AH, Kersten C, Löwenmark T, Ydsten KA, Peltonen R, Isoniemi H, et al. The prognostic role of systemic inflammation in patients undergoing resection of colorectal liver metastases: C-reactive protein (CRP) is a strong negative prognostic biomarker. J Surg Oncol. 2016; 114:895–9.
Article10. Saito H, Kono Y, Murakami Y, Shishido Y, Kuroda H, Matsunaga T, et al. Prognostic significance of the preoperative ratio of C-reactive protein to albumin and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in gastric cancer patients. World J Surg. 2018; 42:1819–25.
Article11. Lin N, Li J, Ke Q, Wang L, Cao Y, Liu J. Clinical significance of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Dis Markers. 2020; 2020:4867974.
Article12. Zhang J, Zhang C, Li Q, Zhang J, Gu X, Zhao W, et al. C-reactive protein/albumin ratio is an independent prognostic predictor of survival in advanced cancer patients receiving palliative care. J Palliat Med. 2019; 22:1536–45.
Article13. Wang W, Ren D, Wang CS, Li T, Yao HC, Ma SJ. Prognostic efficacy of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Biomark Med. 2019; 13:811–20.
Article14. Kwon HM, Moon YJ, Jung KW, Park YS, Jun IG, Kim SO, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a predictor of early graft dysfunction following living donor liver transplantation. Liver Int. 2019; 39:1545–56.
Article15. Amygdalos I, Bednarsch J, Meister FA, Erren D, Mantas A, Strnad P, et al. Clinical value and limitations of the preoperative C-reactive-protein-to-albumin ratio in predicting post-operative morbidity and mortality after deceased-donor liver transplantation: a retrospective single-centre study. Transpl Int. 2021; 34:1468–80.
Article16. Park J, Lim SJ, Choi HJ, Hong SH, Park CS, Choi JH, et al. Predictive utility of the C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in early allograft dysfunction in living donor liver transplantation: a retrospective observational cohort study. PLoS One. 2019; 14:e0226369.
Article17. McMillan DC. The systemic inflammation-based Glasgow prognostic score: a decade of experience in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013; 39:534–40.
Article18. Sachs MC. plotROC: a tool for plotting ROC curves. J Stat Softw. 2017; 79:2.19. Therneau TM, Grambsch PM. Modeling survival data: extending the cox model. New York (NY): Springer;2000.20. Malik R, Mookerjee RP, Jalan R. Infection and inflammation in liver failure: two sides of the same coin. J Hepatol. 2009; 51:426–9.
Article21. Holdstock G, Ershler WB, Krawitt EL. Demonstration of non-specific B-cell stimulation in patients with cirrhosis. Gut. 1982; 23:724–8.
Article22. Piano S, Brocca A, Mareso S, Angeli P. Infections complicating cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2018; 38 Suppl 1:126–33.
Article23. Cervoni JP, Thévenot T, Weil D, Muel E, Barbot O, Sheppard F, et al. C-reactive protein predicts short-term mortality in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:1299–304.
Article24. Fairclough E, Cairns E, Hamilton J, Kelly C. Evaluation of a modified early warning system for acute medical admissions and comparison with C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as a predictor of patient outcome. Clin Med (Lond). 2009; 9:30–3.
Article25. Oh TK, Song IA, Lee JH. Clinical usefulness of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in predicting 30-day mortality in critically ill patients: a retrospective analysis. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:14977.
Article26. Ishizuka M, Nagata H, Takagi K, Iwasaki Y, Shibuya N, Kubota K. Clinical significance of the C-reactive protein to albumin ratio for survival after surgery for colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016; 23:900–7.
Article27. Haruki K, Shiba H, Shirai Y, Horiuchi T, Iwase R, Fujiwara Y, et al. The C-reactive protein to albumin ratio predicts long-term outcomes in patients with pancreatic cancer after pancreatic resection. World J Surg. 2016; 40:2254–60.
Article28. Meyer CP, Rios-Diaz AJ, Dalela D, Ravi P, Sood A, Hanske J, et al. The association of hypoalbuminemia with early perioperative outcomes - a comprehensive assessment across 16 major procedures. Am J Surg. 2017; 214:871–83.
Article29. Yang Y, Gao P, Song Y, Sun J, Chen X, Zhao J, et al. The prognostic nutritional index is a predictive indicator of prognosis and postoperative complications in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016; 42:1176–82.
Article30. Artigas A, Wernerman J, Arroyo V, Vincent JL, Levy M. Role of albumin in diseases associated with severe systemic inflammation: pathophysiologic and clinical evidence in sepsis and in decompensated cirrhosis. J Crit Care. 2016; 33:62–70.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- High-sensitivity C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as a predictor of in-hospital mortality in older adults admitted to the emergency department
- Pretransplant C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio predicts mortality in kidney transplant recipients: a retrospective cohort study
- C-Reactive Protein to Serum Albumin Ratio Is an Independent Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in Patients with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis
- Pretransplant C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio predicts mortality in kidney transplant recipients: a retrospective cohort study
- Association between C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio and 6-month mortality in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest