Korean J Gastroenterol.
2022 Jul;80(1):28-33. 10.4166/kjg.2022.036.
Eosinophil and Mast Cell Counts in the Stomach and Duodenum of Patients with Functional Dyspepsia without a Helicobacter pylori infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Departments of Pathology and Translational Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Ilsan Medical Center, CHA University, School of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2532164
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2022.036
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Symptom-based subtyping of functional dyspepsia (FD) is used to segregate patients into groups with homogenous pathophysiological mechanisms. This study examined whether subtyping could reflect the duodenal and gastric microinflammation in FD patients.
Methods
Twenty-one FD patients without Helicobacter pylori infection were recruited. An endoscopic biopsy was performed in the duodenum 2nd portion, stomach antrum, and body. The eosinophil and mast cell counts per high-power field (×40) were investigated by H&E and c-kit staining, respectively. The degree of inflammatory cell infiltration, atrophy, and intestinal metaplasia was also determined by H&E staining in the stomach. The baseline characteristics and eosinophil and mast cell infiltrations were compared among the three groups (epigastric pain syndrome, postprandial distress syndrome, and overlap).
Results
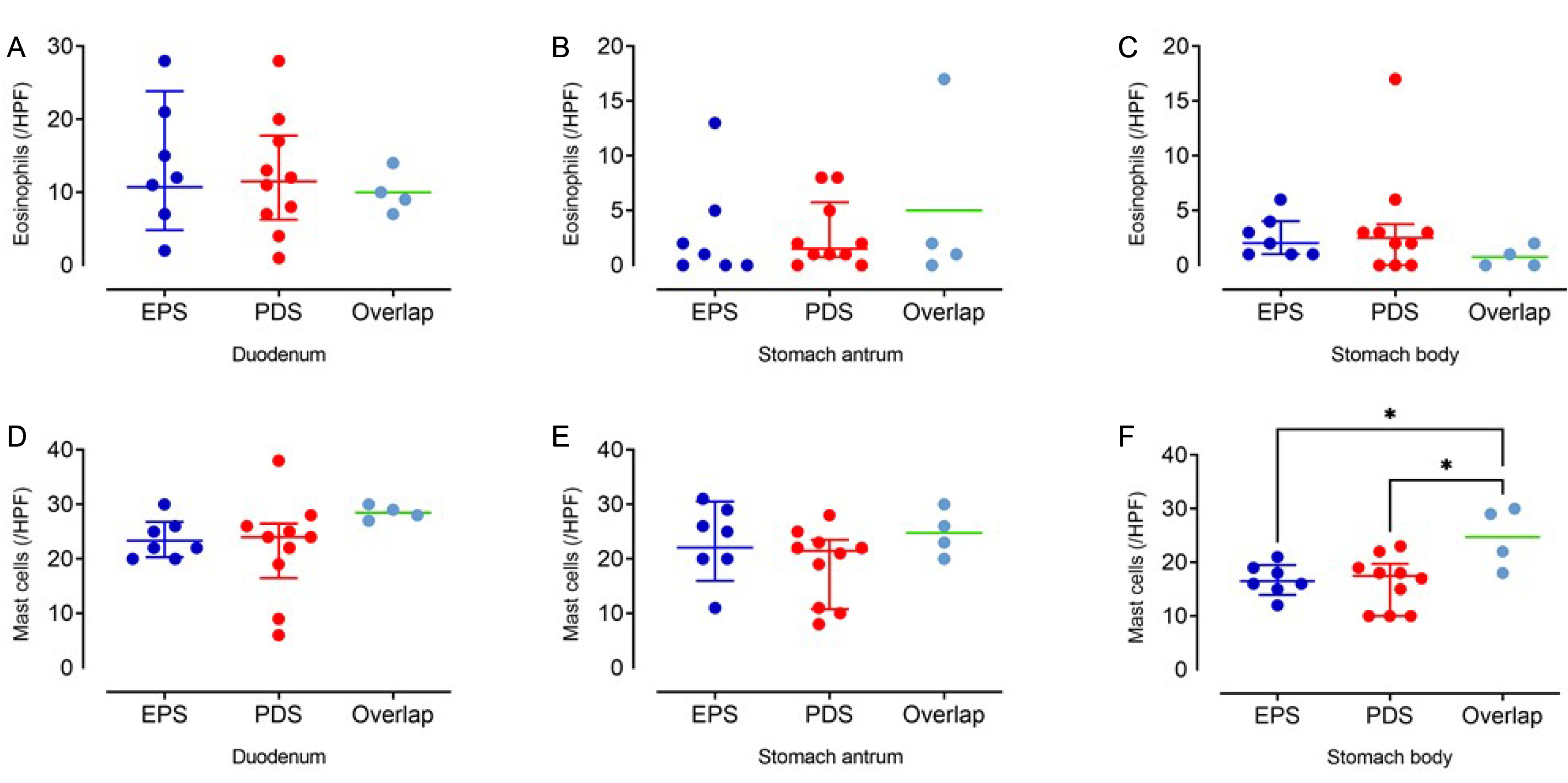
According to the symptom assessment, seven subjects were classified into the epigastric pain syndrome group, 10 into the postprandial syndrome group, and four into the overlap group. The baseline variables were similar in the three groups. Eosinophil infiltration was more prominent in the duodenum than in the stomach. In contrast, mast cell infiltration was similar in the duodenum and stomach. The eosinophil counts in the duodenum were similar in the three groups. The eosinophil counts in the stomach and mast cell counts in the duodenum and stomach were also similar in the three groups.
Conclusions
Duodenal eosinophil infiltration was prominent in FD patients, but the eosinophil counts were similar regardless of the symptom-based subtypes of FD. Hence, the current symptom-based subtyping of FD does not reflect duodenal eosinophil and mast cell infiltration.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Talley NJ, Stanghellini V, Heading RC, Koch KL, Malagelada JR, Tytgat GN. 1999; Functional gastroduodenal disorders. Gut. 45 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):II37–II42. DOI: 10.1136/gut.45.2008.ii37. PMID: 10457043. PMCID: PMC1766695.2. Tack J, Bisschops R, Sarnelli G. 2004; Pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 127:1239–1255. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.05.030. PMID: 15481001.3. Doran S, Jones KL, Andrews JM, Horowitz M. 1998; Effects of meal volume and posture on gastric emptying of solids and appetite. Am J Physiol. 275:R1712–R1718. DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.1998.275.5.r1712. PMID: 9791094.4. Mundt MW, Hausken T, Samsom M. 2002; Effect of intragastric barostat bag on proximal and distal gastric accommodation in response to liquid meal. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 283:G681–G686. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00499.2001. PMID: 12181183.5. Karamanolis G, Caenepeel P, Arts J, Tack J. 2006; Association of the predominant symptom with clinical characteristics and pathophysiological mechanisms in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 130:296–303. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.10.019. PMID: 16472585.6. Bouras EP, Delgado-Aros S, Camilleri M, et al. 2002; SPECT imaging of the stomach: comparison with barostat, and effects of sex, age, body mass index, and fundoplication. Single photon emission computed tomography. Gut. 51:781–786. DOI: 10.1136/gut.51.6.781. PMID: 12427776. PMCID: PMC1773479.7. Stanghellini V, Chan FK, Hasler WL, et al. 2016; Gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology. 150:1380–1392. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.011. PMID: 27147122.8. Enck P, Azpiroz F, Boeckxstaens G, et al. 2017; Functional dyspepsia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:17081. DOI: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.81. PMID: 29099093.9. Miwa H, Kusano M, Arisawa T, et al. 2015; Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for functional dyspepsia. J Gastroenterol. 50:125–139. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-014-1022-3. PMID: 25586651. PMCID: PMC8831363.10. Oh JH, Kwon JG, Jung HK, et al. 2020; Clinical practice guidelines for functional dyspepsia in Korea. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 26:29–50. DOI: 10.5056/jnm19209. PMID: 31917913. PMCID: PMC6955183.11. Walker MM, Salehian SS, Murray CE, et al. 2010; Implications of eosinophilia in the normal duodenal biopsy - an association with allergy and functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 31:1229–1236. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2010.04282.x. PMID: 20222916.12. Walker MM, Aggarwal KR, Shim LS, et al. 2014; Duodenal eosinophilia and early satiety in functional dyspepsia: confirmation of a positive association in an Australian cohort. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 29:474–479. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12419. PMID: 24304041.13. Wang X, Li X, Ge W, et al. 2015; Quantitative evaluation of duodenal eosinophils and mast cells in adult patients with functional dyspepsia. Ann Diagn Pathol. 19:50–56. DOI: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2015.02.001. PMID: 25735567.14. Wauters L, Talley NJ, Walker MM, Tack J, Vanuytsel T. 2020; Novel concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gut. 69:591–600. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318536. PMID: 31784469.15. Talley NJ, Tack J, Ptak T, Gupta R, Giguère M. 2008; Itopride in functional dyspepsia: results of two phase III multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Gut. 57:740–746. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2007.132449. PMID: 17965059.16. Hallerbäck BI, Bommelaer G, Bredberg E, et al. 2002; Dose finding study of mosapride in functional dyspepsia: a placebo-controlled, randomized study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 16:959–967. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2002.01236.x. PMID: 11966505.17. Tack J, Van Den Elzen B, Tytgat G, et al. 2009; A placebo-controlled trial of the 5-HT1A agonist R-137696 on symptoms, visceral hypersensitivity and on impaired accommodation in functional dyspepsia. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 21:619–e24. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2008.01260.x. PMID: 19220756.18. Hill LD, Kozarek RA, Kraemer SJ, et al. 1996; The gastroesophageal flap valve: in vitro and in vivo observations. Gastrointest Endosc. 44:541–547. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(96)70006-8. PMID: 8934159.19. Kimura K, Satoh K, Ido K, Taniguchi Y, Takimoto T, Takemoto T. 1996; Gastritis in the Japanese stomach. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 214:17–23. DOI: 10.3109/00365529609094509. PMID: 8722400.20. Lee KJ. 2021; The usefulness of symptom-based subtypes of functional dyspepsia for predicting underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms and choosing appropriate therapeutic agents. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 27:326–336. DOI: 10.5056/jnm21042. PMID: 34210898. PMCID: PMC8266502.21. Moshiree B, Talley NJ. 2021; Functional dyspepsia: a critical appraisal of the European consensus from a global perspective. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 33:e14216. DOI: 10.1111/nmo.14216. PMID: 34337832.22. Rothenberg ME, Cohen MB. 2007; An eosinophil hypothesis for functional dyspepsia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 5:1147–1148. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2007.07.025. PMID: 17916543.23. Gargala G, Lecleire S, François A, et al. 2007; Duodenal intraepithelial T lymphocytes in patients with functional dyspepsia. World J Gastroenterol. 13:2333–2338. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i16.2333. PMID: 17511033. PMCID: PMC4147143.24. Liebregts T, Adam B, Bredack C, et al. 2011; Small bowel homing T cells are associated with symptoms and delayed gastric emptying in functional dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol. 106:1089–1098. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2010.512. PMID: 21245834.25. Lee MJ, Jung HK, Lee KE, Mun YC, Park S. 2019; Degranulated eosinophils contain more fine nerve fibers in the duodenal mucosa of patients with functional dyspepsia. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 25:212–221. DOI: 10.5056/jnm18176. PMID: 30827070. PMCID: PMC6474707.26. Järbrink-Sehgal ME, Sparkman J, Damron A, et al. 2021; Functional dyspepsia and duodenal eosinophil count and degranulation: a multiethnic US veteran cohort study. Dig Dis Sci. 66:3482–3489. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-020-06689-2. PMID: 33185786.27. Yuan HP, Li XP, Yang WR, Li FK, Li YQ. 2015; Inducible nitric oxide synthase in the duodenal mucosa is associated with mast cell degranulation in patients with functional dyspepsia. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 45:522–527. PMID: 26586703.28. Walker MM, Talley NJ, Prabhakar M, et al. 2009; Duodenal mastocytosis, eosinophilia and intraepithelial lymphocytosis as possible disease markers in the irritable bowel syndrome and functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 29:765–773. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.03937.x. PMID: 19183150. PMCID: PMC4070654.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in functional dyspepsia
- What Is the Difference Between Helicobacter pylori-Associated Dyspepsia and Functional Dyspepsia?
- Should We Still Subcategorize Helicobacter pylori-Associated Dyspepsia as Functional Disease?
- The Effect of Helicobacter pylori Infection on Gastric Emptying in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia
- Association of Helicobacter pylori Infection with Gastric Hypersensitivity in Functional Dyspepsia