Kosin Med J.
2022 Jun;37(2):146-153. 10.7180/kmj.22.110.
A prospective study of the correlation between hepatic fibrosis and noninvasively measured fibrosis markers including serum M2BPGi and acoustic radiation force impulse elastography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Chang Kee-Ryo Memorial Liver Institute, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 4Department of Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 5Division of Hepatobiliary and Pancreas Surgery, Department of Surgery, Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2532045
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.22.110
Abstract
- Background
Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi) was introduced as a noninvasively measurable serologic marker for liver fibrosis. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI) elastography is another noninvasive method of measuring hepatic fibrosis. There are limited data about the correlations between histologic fibrosis grade and noninvasively measured markers, including M2BPGi and ARFI.
Methods
This prospective study was conducted among patients admitted consecutively for liver resection, cholecystectomy, or liver biopsy. ARFI elastography, serum M2BPGi levels, and the AST to Platelet Ratio Index (APRI) score were evaluated before histologic evaluation. Histologic interpretation was performed by a single pathologist using the METAVIR scoring system.
Results
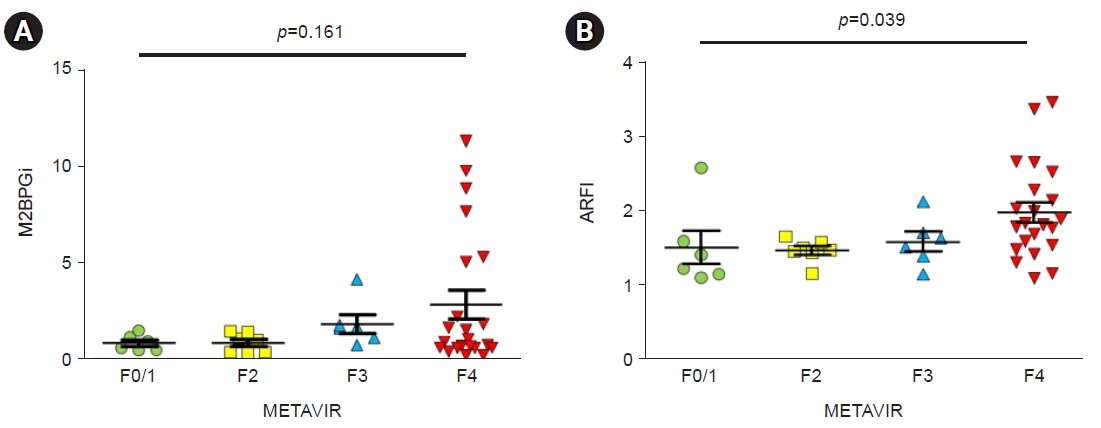
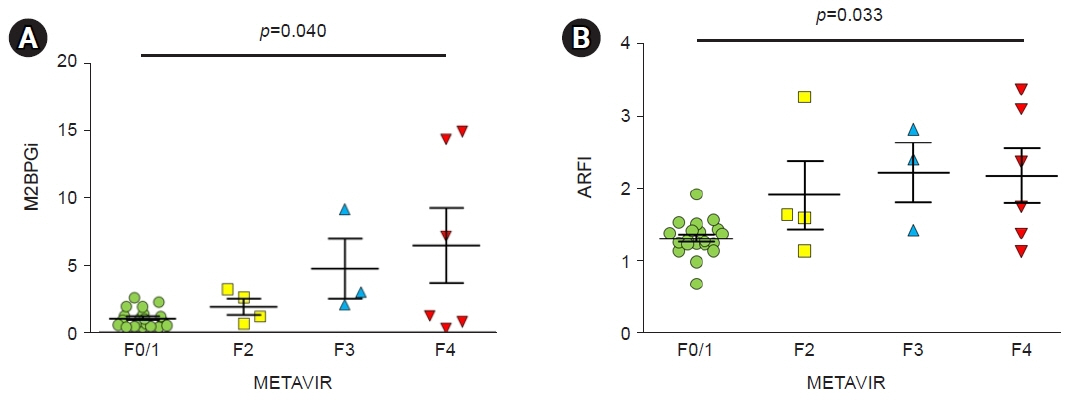
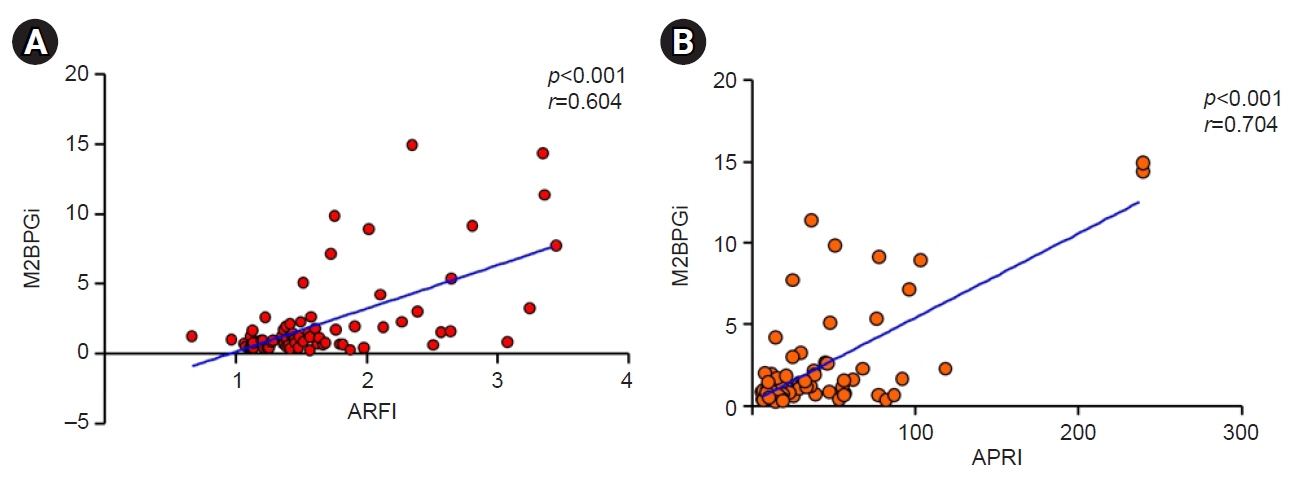
In patients with high METAVIR scores, M2BPGi levels and ARFI values showed statistically significant differences between patients with fibrosis and those without fibrosis. In 41 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, as METAVIR scores increased, M2BPGi levels also tended to increase (p=0.161). ARFI values changed significantly as METAVIR scores increased (p=0.039). In 33 patients without hepatocellular carcinoma, as METAVIR scores increased, M2BPGi levels significantly increased (p=0.040). ARFI values also changed significantly as METAVIR scores increased (p=0.033). M2BPGi levels were significantly correlated with ARFI values (r=0.604, p<0.001), and APRI values (r=0.704, p<0.001), respectively.
Conclusions
Serum M2BPGi levels increased with liver fibrosis severity and could be a good marker for diagnosing advanced hepatic fibrosis regardless of the cause of liver disease.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ahmad W, Ijaz B, Gull S, Asad S, Khaliq S, Jahan S, et al. A brief review on molecular, genetic and imaging techniques for HCV fibrosis evaluation. Virol J. 2011; 8:53.
Article2. Parkes J, Guha IN, Harris S, Rosenberg WM, Roderick PJ. Systematic review of the diagnostic performance of serum markers of liver fibrosis in alcoholic liver disease. Comp Hepatol. 2012; 11:5.
Article3. Poynard T, Halfon P, Castera L, Munteanu M, Imbert-Bismut F, Ratziu V, et al. Standardization of ROC curve areas for diagnostic evaluation of liver fibrosis markers based on prevalences of fibrosis stages. Clin Chem. 2007; 53:1615–22.
Article4. Schuppan D, Afdhal NH. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet. 2008; 371:838–51.
Article5. Castera L, Pinzani M. Biopsy and non-invasive methods for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis: does it take two to tango? Gut. 2010; 59:861–6.
Article6. Theise ND. Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach. Mod Pathol. 2007; 20 Suppl 1:S3–14.
Article7. Brunt EM. Grading and staging the histopathological lesions of chronic hepatitis: the Knodell histology activity index and beyond. Hepatology. 2000; 31:241–6.
Article8. Nightingale K. Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) imaging: a review. Curr Med Imaging Rev. 2011; 7:328–39.
Article9. Haque M, Robinson C, Owen D, Yoshida EM, Harris A. Comparison of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI) to liver biopsy histologic scores in the evaluation of chronic liver disease: a pilot study. Ann Hepatol. 2010; 9:289–93.
Article10. Narimatsu H. Development of M2BPGi: a novel fibrosis serum glyco-biomarker for chronic hepatitis/cirrhosis diagnostics. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2015; 12:683–93.
Article11. Toshima T, Shirabe K, Ikegami T, Yoshizumi T, Kuno A, Togayachi A, et al. A novel serum marker, glycosylated Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein (WFA(+)-M2BP), for assessing liver fibrosis. J Gastroenterol. 2015; 50:76–84.
Article12. Tamaki N, Kurosaki M, Loomba R, Izumi N. Clinical utility of Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer in chronic liver diseases. Ann Lab Med. 2021; 41:16–24.
Article13. Bedossa P, Poynard T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology. 1996; 24:289–93.
Article14. Li Q, Song J, Huang Y, Li X, Zhuo Q, Li W, et al. The gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase to platelet ratio does not show advantages than APRI and Fib-4 in diagnosing significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a retrospective cohort study in China. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e3372.15. Rosenberg I, Cherayil BJ, Isselbacher KJ, Pillai S. Mac-2-binding glycoproteins: putative ligands for a cytosolic beta-galactoside lectin. J Biol Chem. 1991; 266:18731–6.
Article16. Kuno A, Ikehara Y, Tanaka Y, Ito K, Matsuda A, Sekiya S, et al. A serum “sweet-doughnut” protein facilitates fibrosis evaluation and therapy assessment in patients with viral hepatitis. Sci Rep. 2013; 3:1065.
Article17. Yamasaki K, Tateyama M, Abiru S, Komori A, Nagaoka S, Saeki A, et al. Elevated serum levels of Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive human Mac-2 binding protein predict the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C patients. Hepatology. 2014; 60:1563–70.
Article18. Nishikawa H, Enomoto H, Iwata Y, Kishino K, Shimono Y, Hasegawa K, et al. Serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2-binding protein for patients with chronic hepatitis B and C: a comparative study. J Viral Hepat. 2016; 23:977–84.
Article19. Shigefuku R, Takahashi H, Nakano H, Watanabe T, Matsunaga K, Matsumoto N, et al. Correlations of hepatic hemodynamics, liver function, and fibrosis markers in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: comparison with chronic hepatitis related to hepatitis C virus. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17:1545.
Article20. Burak Ozkan M, Bilgici MC, Eren E, Caltepe G. Diagnostic accuracy of point shear wave elastography in the detection of portal hypertension in pediatric patients. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2018; 99:151–6.
Article21. Attia D, Schoenemeier B, Rodt T, Negm AA, Lenzen H, Lankisch TO, et al. Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness with acoustic radiation force impulse quantification elastography for diagnosing clinically significant portal hypertension. Ultraschall Med. 2015; 36:603–10.
Article22. Takuma Y, Nouso K, Morimoto Y, Tomokuni J, Sahara A, Takabatake H, et al. Portal hypertension in patients with liver cirrhosis: diagnostic accuracy of spleen stiffness. Radiology. 2016; 279:609–19.
Article23. Salzl P, Reiberger T, Ferlitsch M, Payer BA, Schwengerer B, Trauner M, et al. Evaluation of portal hypertension and varices by acoustic radiation force impulse imaging of the liver compared to transient elastography and AST to platelet ratio index. Ultraschall Med. 2014; 35:528–33.
Article24. Hai Y, Chong W, Eisenbrey JR, Forsberg F. Network meta-analysis: noninvasive imaging modalities for identifying clinically significant portal hypertension. Dig Dis Sci. 2021; Jul. 17. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-07168-y.
Article25. Lin ZH, Xin YN, Dong QJ, Wang Q, Jiang XJ, Zhan SH, et al. Performance of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the staging of hepatitis C-related fibrosis: an updated meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2011; 53:726–36.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Application of Non-invasive Diagnostic Tests for Liver Fibrosis
- Diagnostic Efficacy of Serum Mac-2 Binding Protein Glycosylation Isomer and Other Markers for Liver Fibrosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases
- Ultrasound-based Liver Elastography: Recent Advances
- Applications of acoustic radiation force impulse quantification in chronic kidney disease: a review
- Clinical Application of Non-invasive Diagnosis for Hepatic Fibrosis