J Neurocrit Care.
2022 Jun;15(1):46-51. 10.18700/jnc.210032.
Takotsubo syndrome and myasthenic crisis after radiocontrast media-induced anaphylaxis: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 3Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2531999
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18700/jnc.210032
Abstract
- Background
Takotsubo syndrome and myasthenic crisis can be triggered by physical stress. We present the case of a woman who developed Takotsubo syndrome and myasthenic crisis following radiocontrast media-induced anaphylaxis.
Case Report
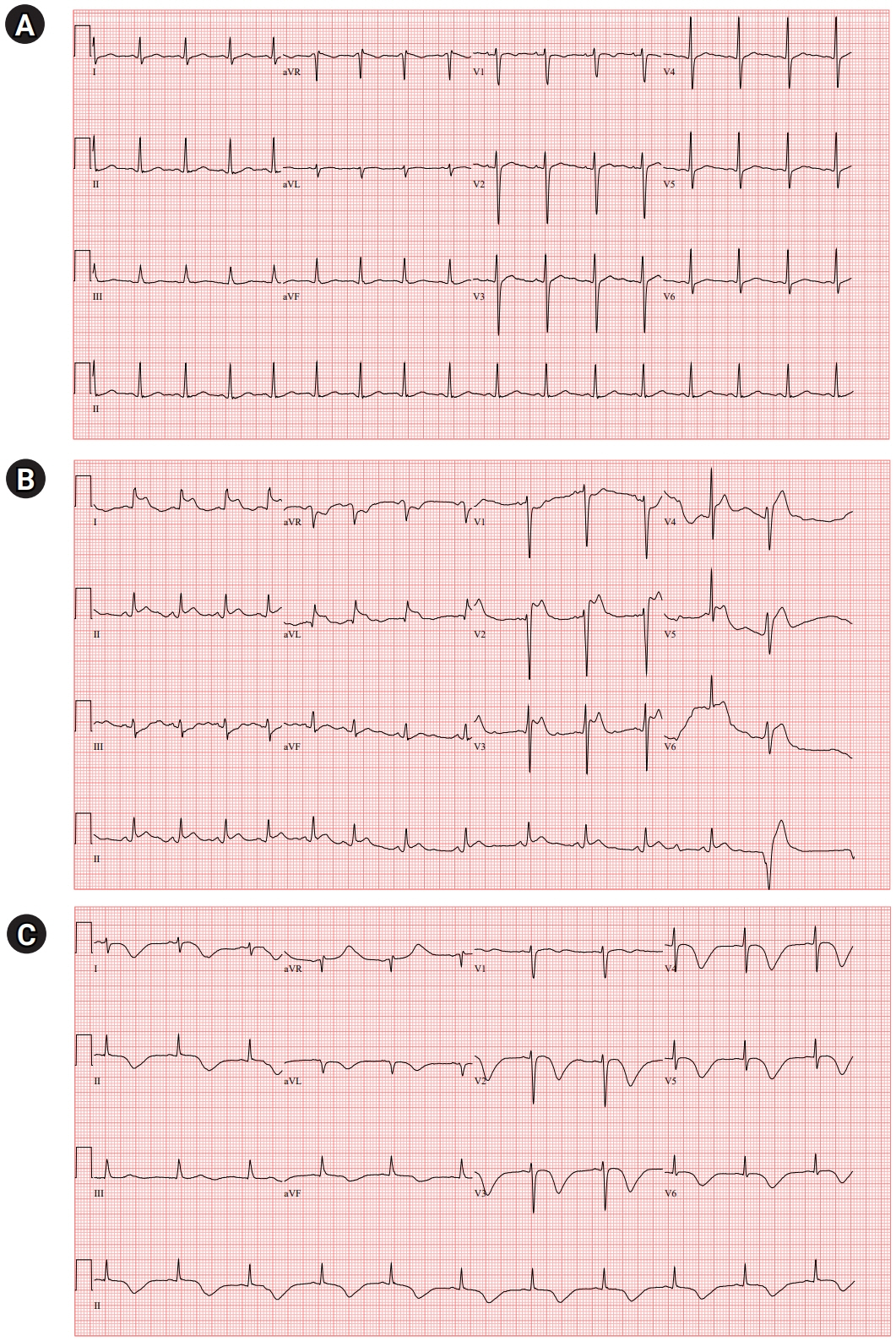
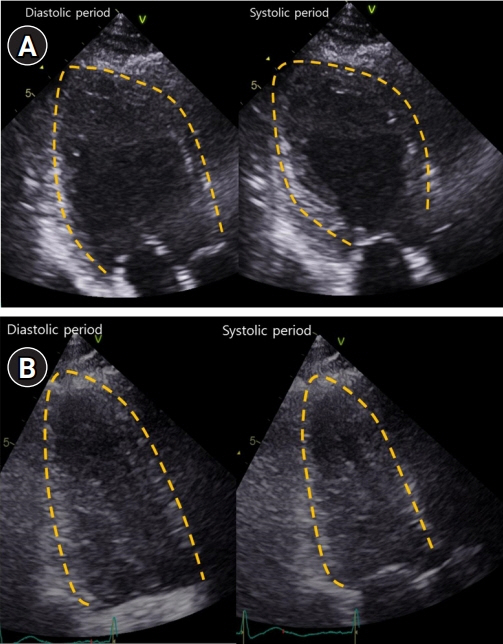
A 39-year-old woman presented with diplopia and ptosis. After chest computed tomography scan, her consciousness was stupor and her oxygen saturation decreased. Electrocardiography showed ST elevation, and cardiac enzyme levels increased. Echocardiography revealed severe left ventricular dysfunction. Myasthenia gravis was diagnosed based on anti-acetylcholine receptor antibody and repetitive nerve stimulation test. Extubation failed, and her weakness worsened. Her neurological condition gradually improved after steroid therapy. Repeat echocardiography demonstrated complete recovery of left ventricular dysfunction.
Conclusion
Takotsubo syndrome can be triggered by anaphylaxis and can occur in patients with neurological disorders; therefore, neurologists need to know about this disorder. The combination of Takotsubo syndrome and myasthenic crisis is rare, but may be associated with a poor prognosis.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ghadri JR, Wittstein IS, Prasad A, Sharkey S, Dote K, Akashi YJ, et al. International expert consensus document on Takotsubo syndrome (part I): clinical characteristics, diagnostic criteria, and pathophysiology. Eur Heart J. 2018; 39:2032–46.
Article2. Wendell LC, Levine JM. Myasthenic crisis. Neurohospitalist. 2011; 1:16–22.
Article3. Rawish E, Stiermaier T, Santoro F, Brunetti ND, Eitel I. Current knowledge and future challenges in Takotsubo syndrome: part 1-pathophysiology and diagnosis. J Clin Med. 2021; 10:479.
Article4. Kounis NG, Koniari I. Anaphylaxis affects primarily the heart and coronary arteries: implications of Kounis syndrome. Asia Pac Allergy. 2019; 9:e13.
Article5. Vultaggio A, Matucci A, Del Pace S, Simonetti I, Parronchi P, Rossi O, et al. Tako-Tsubo-like syndrome during anaphylactic reaction. Eur J Heart Fail. 2007; 9:209–11.
Article6. Kumar A, Qureshi A. Possible link between apical ballooning syndrome during anaphylaxis and inappropriate administration of epinephrine-1. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010; 85:397–8.
Article7. Soufras GD, Kounis NG. Adrenaline administration for anaphylaxis and the risk of Takotsubo and Kounis syndrome. Int J Cardiol. 2013; 166:281–2.
Article8. Cardona V, Ansotegui IJ, Ebisawa M, El-Gamal Y, Fernandez Rivas M, Fineman S, et al. World allergy organization anaphylaxis guidance 2020. World Allergy Organ J. 2020; 13:100472.
Article9. Rathish D, Karalliyadda M. Takotsubo syndrome in patients with myasthenia gravis: a systematic review of previously reported cases. BMC Neurol. 2019; 19:281.
Article10. Desai R, Abbas SA, Fong HK, Lodhi MU, Doshi R, Savani S, et al. Burden and impact of Takotsubo syndrome in myasthenic crisis: a national inpatient perspective on the under-recognized but potentially fatal association. Int J Cardiol. 2020; 299:63–6.
Article11. Narayanaswami P, Sanders DB, Wolfe G, Benatar M, Cea G, Evoli A, et al. International consensus guidance for management of myasthenia gravis: 2020 update. Neurology. 2021; 96:114–22.
Article12. Mehrizi M, Pascuzzi RM. Complications of radiologic contrast in patients with myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve. 2014; 50:443–4.
Article13. Somashekar DK, Davenport MS, Cohan RH, Dillman JR, Ellis JH. Effect of intravenous low-osmolality iodinated contrast media on patients with myasthenia gravis. Radiology. 2013; 267:727–34.
Article14. Kounis NG. Kounis syndrome: an update on epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapeutic management. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2016; 54:1545–59.
Article15. Yanagawa Y, Nishi K, Tomiharu N, Kawaguchi T. A case of takotsubo cardiomyopathy associated with Kounis syndrome. Int J Cardiol. 2009; 132:e65–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acute Respiratory Failure Caused by Non-ionic Radiocontrast Media in a Bronchial Asthma Patient
- Clinical Features and Treatment Patterns of Radiocontrast Mediainduced Anaphylaxis in the Emergency Department
- A Case of Reversal of Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy in Patient with Pheochromocytoma
- Anaphylaxis and Acute Coronary Syndrome Secondary to Intravenous Gadolinium-based Contrast Agent: Kounis Syndrome
- A case of stress-induced cardiomyopathy with an "inverted Takotsubo" contractile pattern