Korean J healthc assoc Infect Control Prev.
2022 Jun;27(1):18-27. 10.14192/kjicp.2022.27.1.18.
Current Status and Infection Control of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju, Korea
- 2Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju, Korea
- KMID: 2530822
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14192/kjicp.2022.27.1.18
Abstract
- Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is an emerging tick-borne infectious disease caused by a novel Dabie bandavirus belonging to the genus Bandavirus. The incidence of SFTS has been increasing in East Asia, posing a great concern to public health in endemic areas. Although SFTS has a high case-fatality rate, there is currently no effective treatment for SFTS. Therefore, early diagnosis and prevention of SFTS are essential. Primarily, SFTS is a tick-borne zoonosis, but human-to-human transmission can also occur in healthcare workers or family members by exposure to patients’ blood or body fluids. We review the current epidemiological characteristics of SFTS in Korea and the key infection control measures in hospitals and household settings.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Liu Q, He B, Huang SY, Wei F, Zhu XQ. 2014; Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, an emerging tick-borne zoonosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 14:763–72. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70718-2. PMID: 24837566.
Article2. Yu XJ, Liang MF, Zhang SY, Liu Y, Li JD, Sun YL, et al. 2011; Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N Engl J Med. 364:1523–32. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1010095. PMID: 21410387. PMCID: PMC3113718.
Article3. Kim KH, Yi J, Kim G, Choi SJ, Jun KI, Kim NH, et al. 2013; Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 19:1892–4. DOI: 10.3201/eid1911.130792. PMID: 24206586. PMCID: PMC3837670.
Article4. Takahashi T, Maeda K, Suzuki T, Ishido A, Shigeoka T, Tominaga T, et al. 2014; The first identification and retrospective study of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Japan. J Infect Dis. 209:816–27. DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jit603. PMID: 24231186. PMCID: PMC7107388.
Article5. Peng SH, Yang SL, Tang SE, Wang TC, Hsu TC, Su CL, et al. 2020; Human case of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection, Taiwan, 2019. Emerg Infect Dis. 26:1612–4. DOI: 10.3201/eid2607.200104. PMID: 32568054. PMCID: PMC7323535.
Article6. Tran XC, Yun Y, Van An L, Kim SH, Thao NTP, Man PKC, et al. 2019; Endemic severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, Vietnam. Emerg Infect Dis. 25:1029–31. DOI: 10.3201/eid2505.181463. PMID: 31002059. PMCID: PMC6478219.
Article7. Silvas JA, Aguilar PV. 2017; The emergence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 97:992–6. DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0967. PMID: 28820686. PMCID: PMC5637595.
Article8. Liu Y, Li Q, Hu W, Wu J, Wang Y, Mei L, et al. 2012; Person-to-person transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 12:156–60. DOI: 10.1089/vbz.2011.0758. PMID: 21955213.
Article9. Bao CJ, Guo XL, Qi X, Hu JL, Zhou MH, Varma JK, et al. 2011; A family cluster of infections by a newly recognized bunyavirus in eastern China, 2007: further evidence of person-to-person transmission. Clin Infect Dis. 53:1208–14. DOI: 10.1093/cid/cir732. PMID: 22028437.
Article10. Yoo JR, Heo ST, Park D, Kim H, Fukuma A, Fukushi S, et al. 2016; Family cluster analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection in Korea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 95:1351–7. DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0527. PMID: 27928083. PMCID: PMC5154449.
Article11. Jiang XL, Zhang S, Jiang M, Bi ZQ, Liang MF, Ding SJ, et al. 2015; A cluster of person-to-person transmission cases caused by SFTS virus in Penglai, China. Clin Microbiol Infect. 21:274–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2014.10.006. PMID: 25687766.
Article12. Jia B, Wu W, Huang R, Wang G, Song P, Li Y, et al. 2018; Characterization of clinical features and outcome for human-to-human transmitted severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Infect Dis (Lond). 50:601–8. DOI: 10.1080/23744235.2018.1449962. PMID: 29542384.
Article13. Jung IY, Choi W, Kim J, Wang E, Park SW, Lee WJ, et al. 2019; Nosocomial person-to-person transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Clin Microbiol Infect. 25:633.e1–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.01.006. PMID: 30677496.
Article14. Zhu Y, Wu H, Gao J, Zhou X, Zhu R, Zhang C, et al. 2017; Two confirmed cases of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome with pneumonia: implication for a family cluster in East China. BMC Infect Dis. 17:537. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-017-2645-9. PMID: 28774267. PMCID: PMC5541732.
Article15. Chen H, Hu K, Zou J, Xiao J. 2013; A cluster of cases of human-to-human transmission caused by severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus. Int J Infect Dis. 17:e206–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2012.11.006. PMID: 23218674.
Article16. Tsuru M, Suzuki T, Murakami T, Matsui K, Maeda Y, Yoshikawa T, et al. 2021; Pathological characteristics of a patient with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) infected with SFTS virus through a sick cat's bite. Viruses. 13:204. DOI: 10.3390/v13020204. PMID: 33572914. PMCID: PMC7912689.
Article17. Yamanaka A, Kirino Y, Fujimoto S, Ueda N, Himeji D, Miura M, et al. 2020; Direct transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus from domestic cat to veterinary personnel. Emerg Infect Dis. 26:2994–8. DOI: 10.3201/eid2612.191513. PMID: 33219655. PMCID: PMC7706950.
Article18. Matsuno K, Nonoue N, Noda A, Kasajima N, Noguchi K, Takano A, et al. 2018; Fatal tickborne phlebovirus infection in captive cheetahs, Japan. Emerg Infect Dis. 24:1726–9. DOI: 10.3201/eid2409.171667. PMID: 30124411. PMCID: PMC6106400.
Article19. Miyauchi A, Sada KE, Yamamoto H, Iriyoshi H, Touyama Y, Hashimoto D, et al. 2022; Suspected transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus from a cat to a veterinarian by a single contact: a case report. Viruses. 14:223. DOI: 10.3390/v14020223. PMID: 35215817. PMCID: PMC8874511.
Article20. International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Taxonomy history. https://talk.ictvonline.org/taxonomy/p/taxonomy-history?taxnode_id=202000166. (Updated on 30 March 2022).21. Casel MA, Park SJ, Choi YK. 2021; Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: emerging novel phlebovirus and their control strategy. Exp Mol Med. 53:713–22. DOI: 10.1038/s12276-021-00610-1. PMID: 33953322. PMCID: PMC8178303.
Article22. Yun SM, Park SJ, Park SW, Choi W, Jeong HW, Choi YK, et al. 2017; Molecular genomic characterization of tick- and human-derived severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus isolates from South Korea. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 11:e0005893. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005893. PMID: 28937979. PMCID: PMC5627960.
Article23. Fu Y, Li S, Zhang Z, Man S, Li X, Zhang W, et al. 2016; Phylogeographic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus from Zhoushan Islands, China: implication for transmission across the ocean. Sci Rep. 6:19563. DOI: 10.1038/srep19563. PMID: 26806841. PMCID: PMC4726339.
Article24. Yun SM, Lee WG, Ryou J, Yang SC, Park SW, Roh JY, et al. 2014; Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in ticks collected from humans, South Korea, 2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 20:1358–61. DOI: 10.3201/eid2008.131857. PMID: 25061851. PMCID: PMC4111194.
Article25. Luo LM, Zhao L, Wen HL, Zhang ZT, Liu JW, Fang LZ, et al. 2015; Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks as reservoir and vector of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in China. Emerg Infect Dis. 21:1770–6. DOI: 10.3201/eid2110.150126. PMID: 26402039. PMCID: PMC4593435.26. Seo JW, Kim D, Yun N, Kim DM. 2021; Clinical update of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Viruses. 13:1213. DOI: 10.3390/v13071213. PMID: 34201811. PMCID: PMC8310018.
Article27. Ye C, Qi R. 2021; Risk factors for person-to-person transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 42:582–5. DOI: 10.1017/ice.2020.1258. PMID: 33161921.
Article28. Song BG, Lee WG, Ju YR. 2017; Geographical distribution of Ixodid ticks in the Republic of Korea, 2015. Public Health Wkly Rep. 10:239–45.29. Zhuang L, Sun Y, Cui XM, Tang F, Hu JG, Wang LY, et al. 2018; Transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus by Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 24:868–71. DOI: 10.3201/eid2405.151435. PMID: 29664718. PMCID: PMC5938789.30. Park SW, Song BG, Shin EH, Yun SM, Han MG, Park MY, et al. 2014; Prevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks in South Korea. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 5:975–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2014.07.020. PMID: 25164614.
Article31. Seo MG, Noh BE, Lee HS, Kim TK, Song BG, Lee HI. 2021; Nationwide temporal and geographical distribution of tick populations and phylogenetic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in ticks in Korea, 2020. Microorganisms. 9:1630. DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9081630. PMID: 34442708. PMCID: PMC8399818.
Article32. Jo YS, Kang JG, Chae JB, Cho YK, Shin JH, Jheong WH, et al. 2019; Prevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in ticks collected from national parks in Korea. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 19:284–9. DOI: 10.1089/vbz.2018.2338. PMID: 30481146.
Article33. Yoo JR, Heo ST, Song SW, Bae SG, Lee S, Choi S, et al. 2020; Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in ticks and SFTS incidence in humans, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis. 26:2292–4. DOI: 10.3201/eid2609.200065. PMID: 32818414. PMCID: PMC7454071.
Article34. Jiao Y, Zeng X, Guo X, Qi X, Zhang X, Shi Z, et al. 2012; Preparation and evaluation of recombinant severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus nucleocapsid protein for detection of total antibodies in human and animal sera by double-antigen sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 50:372–7. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01319-11. PMID: 22135253. PMCID: PMC3264160.
Article35. Lee SH, Kim HJ, Lee MJ, Byun JW, Kim DY, Kim NH, et al. 2018; Prevalence of antibodies against severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in shelter dogs in the Republic of Korea. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 9:183–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2017.09.002. PMID: 28899663.
Article36. Kimura T, Fukuma A, Shimojima M, Yamashita Y, Mizota F, Yamashita M, et al. 2018; Seroprevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) virus antibodies in humans and animals in Ehime prefecture, Japan, an endemic region of SFTS. J Infect Chemother. 24:802–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.jiac.2018.06.007. PMID: 30017796.
Article37. Li Z, Hu J, Bao C, Li P, Qi X, Qin Y, et al. 2014; Seroprevalence of antibodies against SFTS virus infection in farmers and animals, Jiangsu, China. J Clin Virol. 60:185–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2014.03.020. PMID: 24793967.
Article38. Chen C, Li P, Li KF, Wang HL, Dai YX, Cheng X, et al. 2019; Animals as amplification hosts in the spread of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 79:77–84. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2018.11.017. PMID: 30500443.
Article39. Yu KM, Yu MA, Park SJ, Kim YI, Robles NJ, Kwon HI, et al. 2018; Seroprevalence and genetic characterization of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in domestic goats in South Korea. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 9:1202–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2018.05.001. PMID: 29748119.
Article40. Kim KH, Ko MK, Kim N, Kim HH, Yi J. 2017; Seroprevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in southeastern Korea, 2015. J Korean Med Sci. 32:29–32. Erratum in: J Korean Med Sci 2018;33:e225. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.1.29. PMID: 27914128. PMCID: PMC5143294.
Article41. Han MA, Kim CM, Kim DM, Yun NR, Park SW, Han MG, et al. 2018; Seroprevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus antibodies in rural areas, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis. 24:872–4. DOI: 10.3201/eid2405.152104. PMID: 29664384. PMCID: PMC5938763.
Article42. Yoo JR, Heo ST, Kim M, Song SW, Boo JW, Lee KH. 2019; Seroprevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in the agricultural population of Jeju Island, Korea, 2015-2017. Infect Chemother. 51:337–44. DOI: 10.3947/ic.2019.51.4.337. PMID: 31668024. PMCID: PMC6940373.
Article43. Gai ZT, Zhang Y, Liang MF, Jin C, Zhang S, Zhu CB, et al. 2012; Clinical progress and risk factors for death in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients. J Infect Dis. 206:1095–102. DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jis472. PMID: 22850122.
Article44. Guo CT, Lu QB, Ding SJ, Hu CY, Hu JG, Wo Y, et al. 2016; Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) in China: an integrated data analysis. Epidemiol Infect. 144:1345–54. DOI: 10.1017/S0950268815002678. PMID: 26542444.
Article45. He Z, Wang B, Li Y, Du Y, Ma H, Li X, et al. 2020; Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiology, clinical signs, routine laboratory diagnosis, risk factors, and outcomes. BMC Infect Dis. 20:575. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-020-05303-0. PMID: 32758175. PMCID: PMC7409422.
Article46. Li JC, Zhao J, Li H, Fang LQ, Liu W. 2022; Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and treatment of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Infect Med. 1:40–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.imj.2021.10.001.
Article47. Heo ST, Yoo JR, Lee KH, Ko KS. 2015; The first case of non-retrospective clinical identification of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patient in 2013 in South Korea. J Bacteriol Virol. 45:155–8. DOI: 10.4167/jbv.2015.45.2.155.
Article48. Kim YR, Yun Y, Bae SG, Park D, Kim S, Lee JM, et al. 2018; Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection, South Korea, 2010. Emerg Infect Dis. 24:2103–5. DOI: 10.3201/eid2411.170756. PMID: 30334706. PMCID: PMC6199997.
Article49. Choi SJ, Park SW, Bae IG, Kim SH, Ryu SY, Kim HA, et al. 2016; Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in South Korea, 2013-2015. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 10:e0005264. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005264. PMID: 28033338. PMCID: PMC5226827.
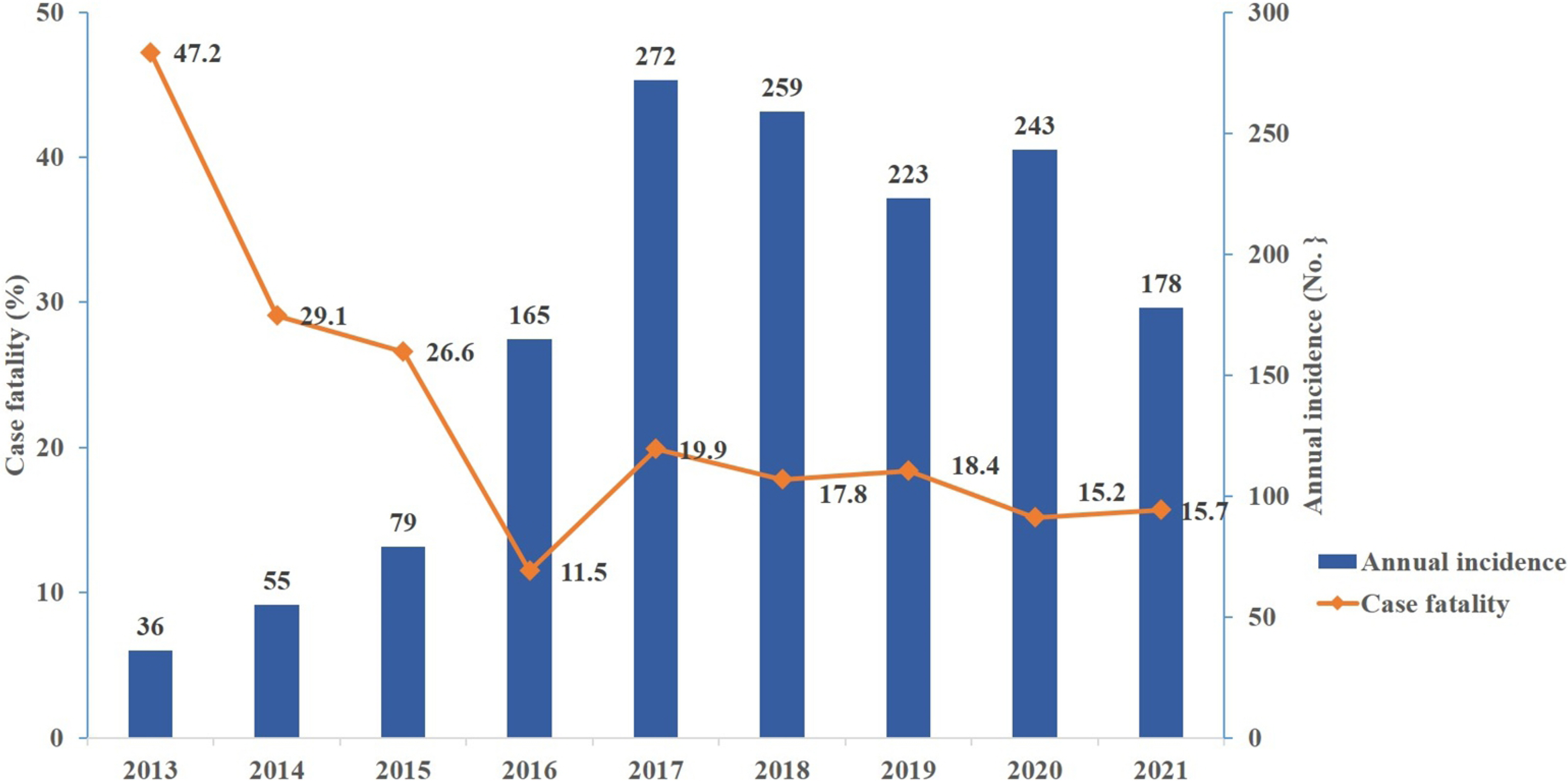
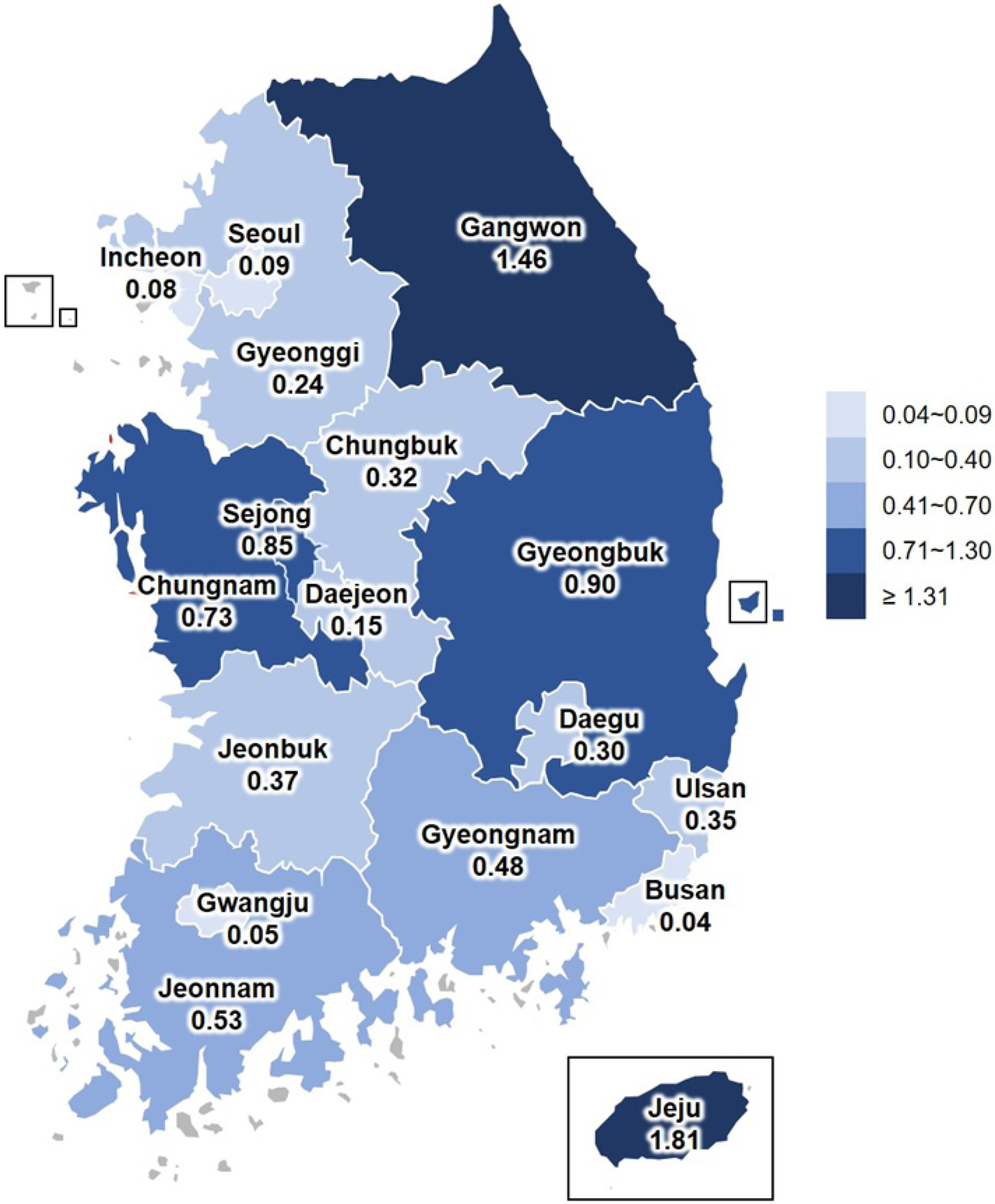
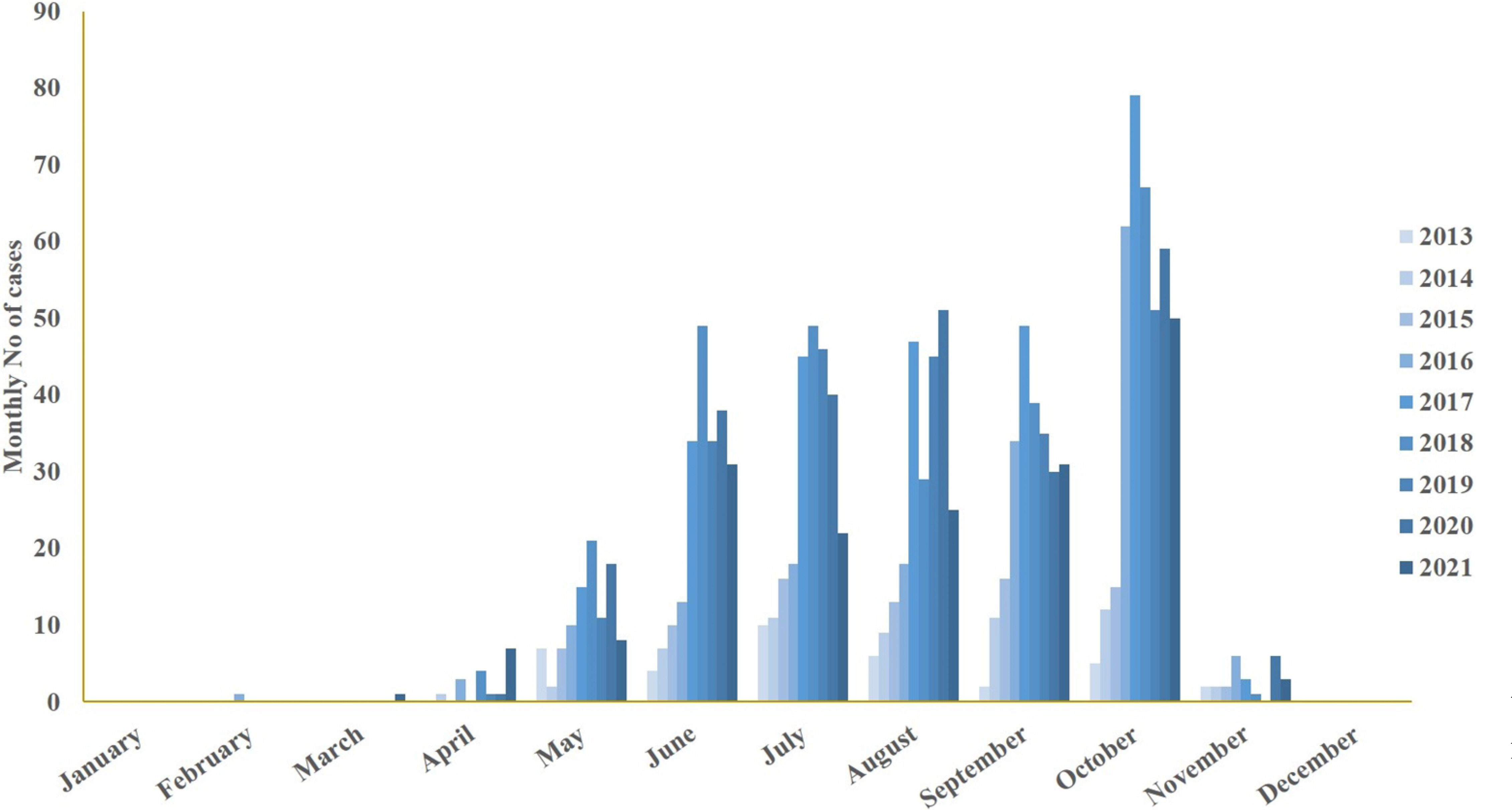
Article50. Korea Disease Control. Infectious Disease Portal. https://www.kdca.go.kr/npt/biz/npp/ist/simple/simplePdStatsMain.do#. (Updated on 30 March 2022).51. Jeong SJ, Hwang JH, Kim HS, Kwon GY. 2021; Epidemiological characteristics of patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS) from 2013 to 2020. Public Health Wkly Rep. 14:2561–72.52. Yoo JR, Heo ST. 2018; Strategies against severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome increasing in Korea. Korean J Blood Transfus. 29:117–29. DOI: 10.17945/kjbt.2018.29.2.117.
Article53. Sun J, Lu L, Yang J, Liu K, Wu H, Liu Q. 2018; Association between severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome incidence and ambient temperature. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 98:1478–83. DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.17-0991. PMID: 29557340. PMCID: PMC5953393.
Article54. Cho G, Lee S, Lee H. 2021; Estimating severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome transmission using machine learning methods in South Korea. Sci Rep. 11:21831. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-01361-9. PMID: 34750465. PMCID: PMC8575988.
Article55. He F, Zheng X, Zhang Z. 2021; Clinical features of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome and analysis of risk factors for mortality. BMC Infect Dis. 21:1253. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-021-06946-3. PMID: 34906106. PMCID: PMC8669668.
Article56. Kwon JS, Jin S, Kim JY, Ra SH, Kim T, Park SY, et al. 2021; Viral and immunologic factors associated with fatal outcome of patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Korea. Viruses. 13:2351. DOI: 10.3390/v13122351. PMID: 34960620. PMCID: PMC8703577.
Article57. Kim WY, Choi W, Park SW, Wang EB, Lee WJ, Jee Y, et al. 2015; Nosocomial transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Korea. Clin Infect Dis. 60:1681–3. DOI: 10.1093/cid/civ128. PMID: 25694652.
Article58. Moon J, Lee H, Jeon JH, Kwon Y, Kim H, Wang EB, et al. 2019; Aerosol transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus during resuscitation. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 40:238–41. Erratum in: Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2019;40:620. DOI: 10.1017/ice.2018.330. PMID: 30565531.
Article59. Yoo JR, Choi JH, Kim YR, Lee KH, Heo ST. 2019; Occupational risk of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in healthcare workers. Open Forum Infect Dis. 6:ofz210. DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofz210. PMID: 31139678. PMCID: PMC6527088.
Article60. Bae S, Chang HH, Kim SW, Kim Y, Wang E, Kim CK, et al. 2022; Nosocomial outbreak of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome among healthcare workers in a single hospital in Daegu, Korea. Int J Infect Dis. 119:95–101. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.03.048. PMID: 35358725.
Article61. Jeong EJ, Song JY, Lim CS, Lee I, Park MS, Choi MJ, et al. 2016; Viral shedding from diverse body fluids in a patient with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J Clin Virol. 80:33–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2016.04.018. PMID: 27135388.
Article62. Gong Z, Gu S, Zhang Y, Sun J, Wu X, Ling F, et al. 2015; Probable aerosol transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in southeastern China. Clin Microbiol Infect. 21:1115–20. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.07.024. PMID: 26255811.
Article63. Korea Disease Control. 2022 Guideline for infection control of tick-borne and rodent borne disease. https://kdca.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a20507020000&bid=0019. (Updated on 15 April 2022).64. Ryu BH, Kim JY, Kim T, Kim MC, Kim MJ, Chong YP, et al. 2018; Extensive severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus contamination in surrounding environment in patient rooms. Clin Microbiol Infect. 24:911.e1–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2018.01.005. PMID: 29355730.
Article65. Kaneko C, Saito A, Inagaki H, Sugiyama H, Mazimpaka E, Fujimoto S, et al. 2022; Rapid inactivation of Dabie bandavirus (SFTSV) by irradiation with deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diode. J Med Virol. 94:3438–41. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.27698. PMID: 35246855.66. Yoo JR, Lee KH, Heo ST. 2018; Surveillance results for family members of patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Zoonoses Public Health. 65:903–7. DOI: 10.1111/zph.12481. PMID: 29862661.
Article67. Reece LM, Beasley DW, Milligan GN, Sarathy VV, Barrett AD. 2018; Current status of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome vaccine development. Curr Opin Virol. 29:72–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2018.03.005. PMID: 29642053.
Article68. Robles NJC, Han HJ, Park SJ, Choi YK. 2018; Epidemiology of severe fever and thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection and the need for therapeutics for the prevention. Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 7:43–50. DOI: 10.7774/cevr.2018.7.1.43. PMID: 29399579. PMCID: PMC5795044.
Article69. Kwak JE, Kim YI, Park SJ, Yu MA, Kwon HI, Eo S, et al. 2019; Development of a SFTSV DNA vaccine that confers complete protection against lethal infection in ferrets. Nat Commun. 10:3836. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-11815-4. PMID: 31444366. PMCID: PMC6707330.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome
- Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Presenting with Rhabdomyolysis
- A Pediatric Case of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Korea
- Four Cases of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Occurring in Jeju
- Differences of clinical manifestation of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome between Korean and Chinese patients