J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Apr;32(4):704-707. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.4.704.
A Pediatric Case of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. emyang@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 2371460
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.4.704
Abstract
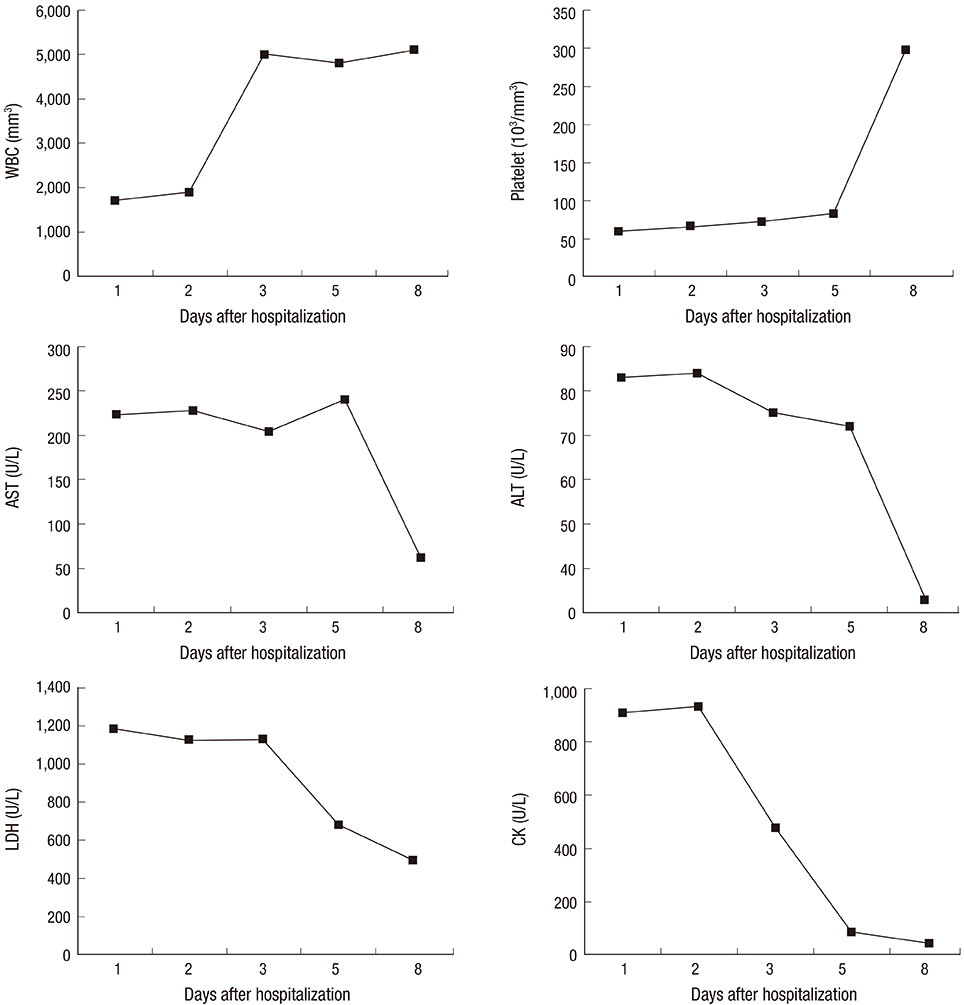
- Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is an emerging infectious disease and elderly people living in rural areas have the greatest risk of infection. We report the first pediatric case of SFTS in Korea and the clinical characteristics and disease progression in children. A 10-year-old child from Chonnam province visited the hospital with myalgia and a history of fever over the previous 8 days. Her father noticed a tick on her head and removed it before fever developed. Because the symptoms continued, her father consulted the community health center and SFTS virus was detected both from the tick (Haemaphysalis longicornis) and the patient's blood. On hospitalization, fever and severe myalgia were improved and no gastrointestinal and hemorrhagic symptoms were observed. The patient was successfully treated with a combination of steroids, IVIG, and ribavirin. In this report, a pediatric case of SFTS presents a mild clinical course but close attention must be paid to the screening of children with mild symptoms consisting of SFTS.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Xu B, Liu L, Huang X, Ma H, Zhang Y, Du Y, Wang P, Tang X, Wang H, Kang K, et al. Metagenomic analysis of fever, thrombocytopenia and leukopenia syndrome (FTLS) in Henan Province, China: discovery of a new bunyavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2011; 7:e1002369.2. Yu XJ, Liang MF, Zhang SY, Liu Y, Li JD, Sun YL, Zhang L, Zhang QF, Popov VL, Li C, et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1523–1532.3. Takahashi T, Maeda K, Suzuki T, Ishido A, Shigeoka T, Tominaga T, Kamei T, Honda M, Ninomiya D, Sakai T, et al. The first identification and retrospective study of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Japan. J Infect Dis. 2014; 209:816–827.4. Kim KH, Yi J, Kim G, Choi SJ, Jun KI, Kim NH, Choe PG, Kim NJ, Lee JK, Oh MD. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013; 19:1892–1894.5. McMullan LK, Folk SM, Kelly AJ, MacNeil A, Goldsmith CS, Metcalfe MG, Batten BC, Albariño CG, Zaki SR, Rollin PE, et al. A new phlebovirus associated with severe febrile illness in Missouri. N Engl J Med. 2012; 367:834–841.6. Park SW, Song BG, Shin EH, Yun SM, Han MG, Park MY, Park C, Ryou J. Prevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks in South Korea. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014; 5:975–977.7. Zhang YZ, He YW, Dai YA, Xiong Y, Zheng H, Zhou DJ, Li J, Sun Q, Luo XL, Cheng YL, et al. Hemorrhagic fever caused by a novel Bunyavirus in China: pathogenesis and correlates of fatal outcome. Clin Infect Dis. 2012; 54:527–533.8. Shin J, Kwon D, Youn SK, Park JH. Characteristics and factors associated with death among patients hospitalized for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015; 21:1704–1710.9. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevention of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome [Internet]. cited 22 Sep 2015. Available at http://is.cdc.go.kr/dstat/index.jsp.10. Liu Q, He B, Huang SY, Wei F, Zhu XQ. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, an emerging tick-borne zoonosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014; 14:763–772.11. Ding S, Niu G, Xu X, Li J, Zhang X, Yin H, Zhang N, Jiang X, Wang S, Liang M, et al. Age is a critical risk factor for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e111736.12. Wang LY, Cui N, Lu QB, Wo Y, Wang HY, Liu W, Cao WC. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in children: a case report. BMC Infect Dis. 2014; 14:366.13. Ma T, Sun JM, Chen LF, Shi XG, Liu K, Gong ZY, Chen J, Zhang R, Ren JP, Jiang JM. A pediatric case of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Zhejiang Province, China. J Clin Virol. 2015; 72:85–87.14. Cui N, Yang ZD, Wang BJ, Fan XJ, Yuan C. The clinical characteristics of 169 cases of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2012; 51:755–758.15. Ozsurekci Y, Arasli M, Karadag Oncel E, Caglayik DY, Kaya A, Icagasioglu FD, Engin A, Korukluoglu G, Elaldi N, Ceyhan M. Can the mild clinical course of crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever in children be explained by cytokine responses? J Med Virol. 2013; 85:1955–1959.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome
- The First Case of Non-retrospective Clinical Identification of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Patient in 2013 in South Korea
- Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Presenting with Rhabdomyolysis
- Differences of clinical manifestation of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome between Korean and Chinese patients
- Four Cases of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Occurring in Jeju