Neonatal Med.
2022 May;29(2):57-67. 10.5385/nm.2022.29.2.57.
Neonatologist-Performed Cranial Ultrasonography in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- KMID: 2530608
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2022.29.2.57
Abstract
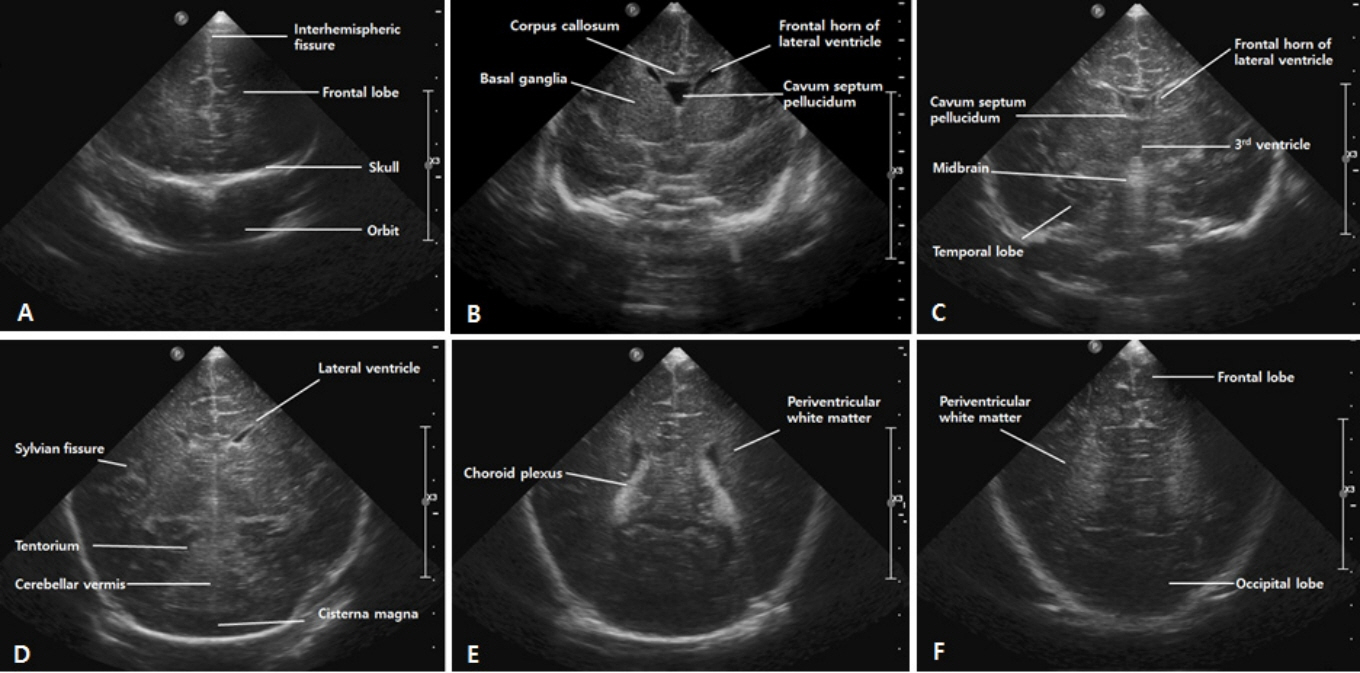
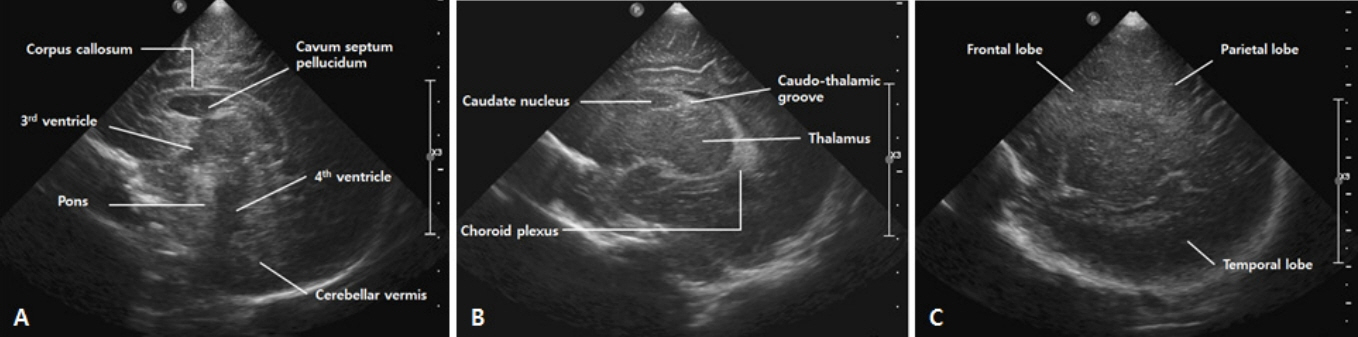
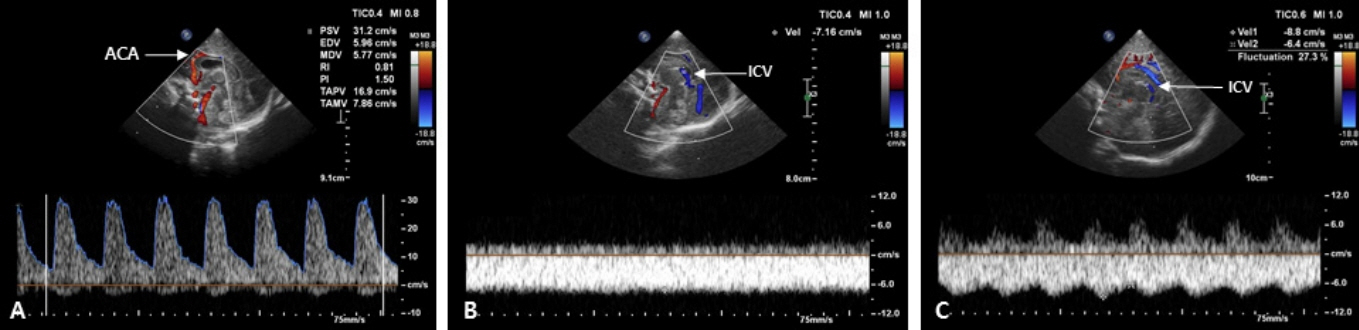
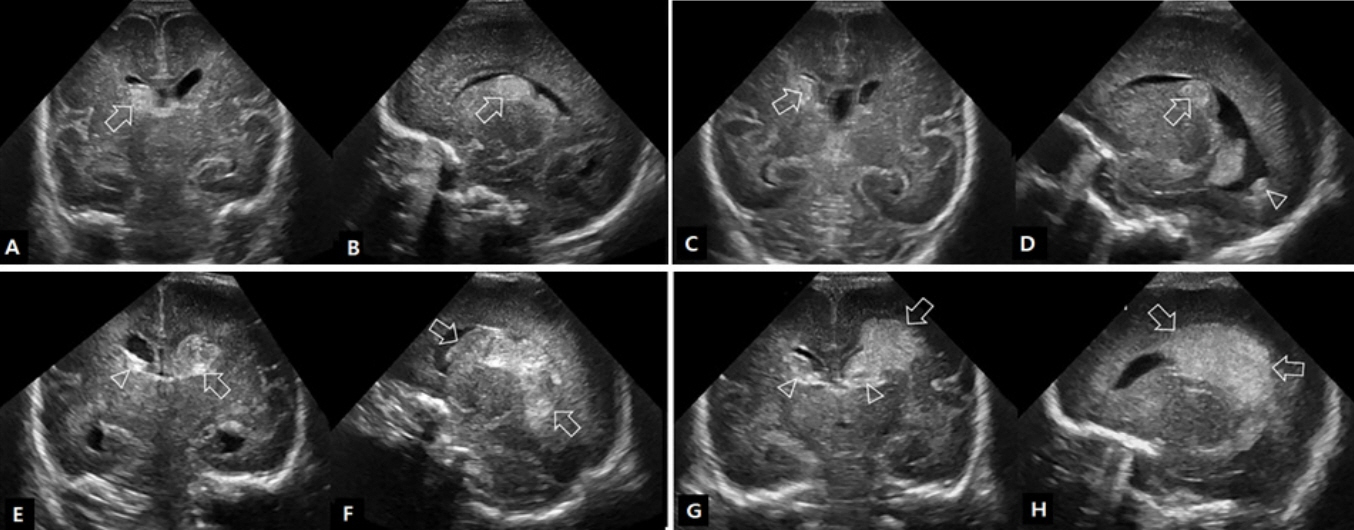
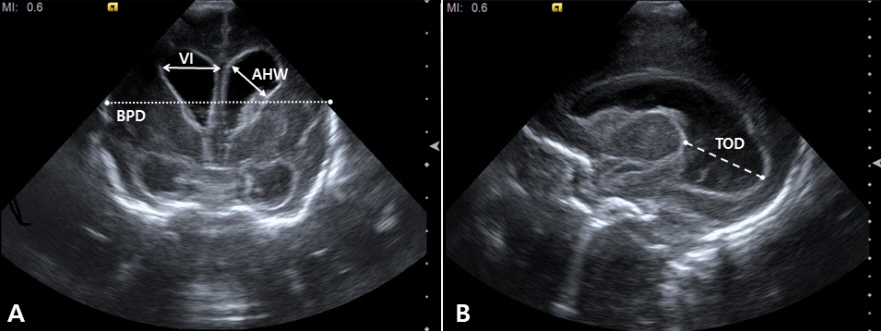
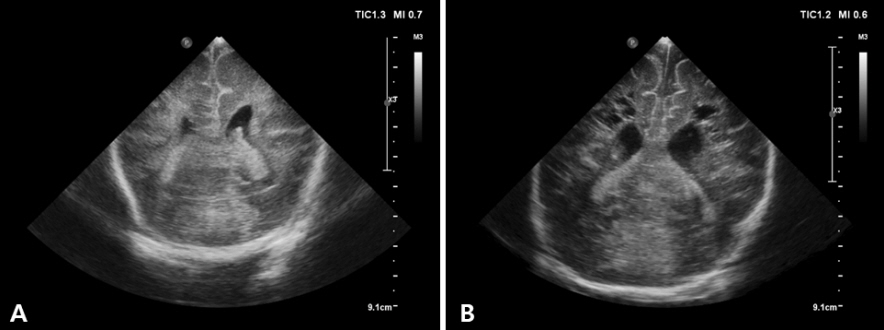
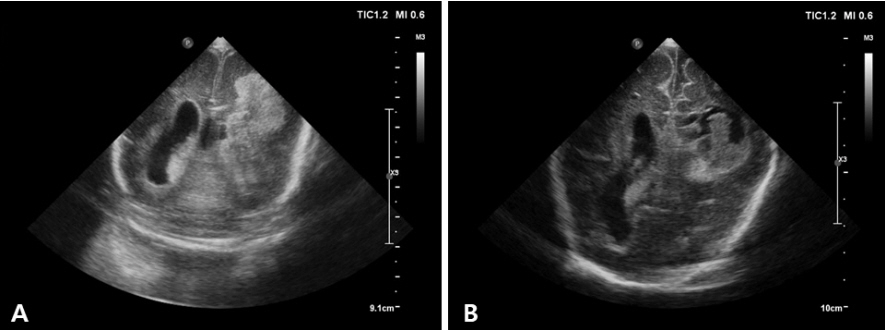
- Cranial ultrasound (CUS) is an initial screening imaging tool used to evaluate the neonatal brain. It is an accessible, inexpensive, and harmless technique that can be used at bedside as frequently as required. Timely focused CUS in the neonatal care unit can play a major role in the diagnosis, follow-up, and management of brain damage. Despite the increasing use of point-of-care ultrasonography by intensive care physicians, neonatologist-performed CUS remains unusual. This review aims to provide an overview of neonatal CUS to neonatologists, focusing on the optimal settings, standard planes of the brain, and main pathologies in preterm infants. Adding Doppler studies allows evaluation of the patency of intracranial arteries and veins, flow velocities, and indices. This may provide an opportunity for earlier targeted circulatory support to prevent brain injury and improve long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kurepa D, Boyar V, Zaghloul N, Beachy J, Zaytseva A, Teng D, et al. Sructured neonatal point-of-care ultrasound training program. Am J Perinatol. 2021; 38:e284–91.2. Ben Fadel N, Pulgar L, Khurshid F. Point of care ultrasound (POCUS) in Canadian neonatal intensive care units (NICUs): where are we? J Ultrasound. 2019; 22:201–6.3. Dudink J, Jeanne Steggerda S, Horsch S; eurUS.brain group. State-of-the-art neonatal cerebral ultrasound: technique and reporting. Pediatr Res. 2020; 87(Suppl 1):3–12.4. Riedesel EL. Neonatal cranial ultrasound: avanced techniques and image interpretation. J Pediatr Neurol. 2018; 16:106–24.5. Evans N, Gournay V, Cabanas F, Kluckow M, Leone T, Groves A, et al. Point-of-care ultrasound in the neonatal intensive care unit: international perspectives. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011; 16:61–8.6. Singh Y, Tissot C, Fraga MV, Yousef N, Cortes RG, Lopez J, et al. International evidence-based guidelines on Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS) for critically ill neonates and children issued by the POCUS Working Group of the European Society of Paediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC). Crit Care. 2020; 24:65.7. Miller LE, Stoller JZ, Fraga MV. Point-of-care ultrasound in the neonatal ICU. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020; 32:216–27.8. AIUM practice parameter for the performance of neurosonography in neonates and infants. J Ultrasound Med. 2020; 39:E57–61.9. McLean G, Malhotra A, Lombardo P, Schneider M. Cranial ultrasound screening protocols for very preterm infants. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021; 47:1645–56.10. Hand IL, Shellhaas RA, Milla SS; Committee on Fetus and Newborn, Section on Neurology, Section on Radiology. Routine neuroimaging of the preterm brain. Pediatrics. 2020; 146:e2020029082.11. Inder TE, de Vries LS, Ferriero DM, Grant PE, Ment LR, Miller SP, et al. Neuroimaging of the preterm brain: review and recommendations. J Pediatr. 2021; 237:276–87.12. Mohammad K, Scott JN, Leijser LM, Zein H, Afifi J, Piedboeuf B, et al. Consensus approach for standardizing the screening and classification of preterm brain injury diagnosed with cranial ultrasound: a Canadian perspective. Front Pediatr. 2021; 9:618236.13. The Korean Society of Neonatology. Manual of Neonatal Care. 4 ed. Seoul: The Korean Society of Neonatology;2021. p. 376–84.14. Beltempo M, Wintermark P, Lemyre B, Shalish W, Martel-Bucci A, Narvey M, et al. Predictors of severe neurologic injury on ultrasound scan of the head and risk factor-based screening for infants born preterm. J Pediatr. 2019; 214:27–33.15. Ecury-Goossen GM, Camfferman FA, Leijser LM, Govaert P, Dudink J. State of the art cranial ultrasound imaging in neonates. J Vis Exp. 2015; 96:e52238.16. O'Dell MC, Cassady C, Logsdon G, Varich L. Cinegraphic versus combined static and cinegraphic imaging for initial cranial ultrasound screening in premature infants. Pediatr Radiol. 2015; 45:1706–11.17. James AC. Practical guide to neonatal cranial ultrasound (crus): basics. Paediatr Child Health. 2018; 28:424–30.18. Caro-Dominguez P, Lecacheux C, Hernandez-Herrera C, Llorens-Salvador R. Cranial ultrasound for beginners. Transl Pediatr. 2021; 10:1117–37.19. Maller VV, Cohen HL. Neurosonography: assessing the premature infant. Pediatr Radiol. 2017; 47:1031–45.20. Couture A, Veyrac C, Baud C, Saguintaah M, Ferran JL. Advanced cranial ultrasound: transfontanellar Doppler imaging in neonates. Eur Radiol. 2001; 11:2399–410.21. Horgan JG, Rumack CM, Hay T, Manco-Johnson ML, Merenstein GB, Esola C. Absolute intracranial blood-flow velocities evaluated by duplex Doppler sonography in asymptomatic preterm and term neonates. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989; 152:1059–64.22. Romagnoli C, Giannantonio C, De Carolis MP, Gallini F, Zecca E, Papacci P. Neonatal color Doppler US study: normal values of cerebral blood flow velocities in preterm infants in the first month of life. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2006; 32:321–31.23. Ecury-Goossen GM, Raets MM, Camfferman FA, Vos RH, van Rosmalen J, Reiss IK, et al. Resistive indices of cerebral arteries in very preterm infants: values throughout stay in the neonatal intensive care unit and impact of patent ductus arteriosus. Pediatr Radiol. 2016; 46:1291–300.24. Lowe LH, Bailey Z. State-of-the-art cranial sonography: part 1, modern techniques and image interpretation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 196:1028–33.25. Taylor GA. Intracranial venous system in the newborn: evaluation of normal anatomy and flow characteristics with color Doppler US. Radiology. 1992; 183:449–52.26. Camfferman FA, de Goederen R, Govaert P, Dudink J, van Bel F, Pellicer A, et al. Diagnostic and predictive value of Doppler ultrasound for evaluation of the brain circulation in preterm infants: a systematic review. Pediatr Res. 2020; 87(Suppl 1):50–8.27. Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978; 92:529–34.28. Dorner RA, Burton VJ, Allen MC, Robinson S, Soares BP. Preterm neuroimaging and neurodevelopmental outcome: a focus on intraventricular hemorrhage, post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus, and associated brain injury. J Perinatol. 2018; 38:1431–43.29. Taylor GA, Madsen JR. Neonatal hydrocephalus: hemodynamic response to fontanelle compression: correlation with intracranial pressure and need for shunt placement. Radiology. 1996; 201:685–9.30. Nakamura Y, Okudera T, Hashimoto T. Microvasculature in germinal matrix layer: its relationship to germinal matrix hemorrhage. Mod Pathol. 1991; 4:475–80.31. Ghazi-Birry HS, Brown WR, Moody DM, Challa VR, Block SM, Reboussin DM. Human germinal matrix: venous origin of hemorrhage and vascular characteristics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997; 18:219–29.32. Van Bel F, Van de Bor M, Stijnen T, Baan J, Ruys JH. Aetiological rôle of cerebral blood-flow alterations in development and extension of peri-intraventricular haemorrhage. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1987; 29:601–14.33. Julkunen M, Parviainen T, Janas M, Tammela O. End-diastolic block in cerebral circulation may predict intraventricular hemorrhage in hypotensive extremely-low-birth-weight infants. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2008; 34:538–45.34. Ikeda T, Amizuka T, Ito Y, Mikami R, Matsuo K, Kawamura N, et al. Changes in the perfusion waveform of the internal cerebral vein and intraventricular hemorrhage in the acute management of extremely low-birth-weight infants. Eur J Pediatr. 2015; 174:331–8.35. Ikeda T, Ito Y, Mikami R, Matsuo K, Kawamura N, Yamoto A, et al. Fluctuations in internal cerebral vein and central side veins of preterm infants. Pediatr Int. 2021; 63:1319–26.36. Tanaka K, Sakamoto R, Imamura H, Naramura T, Matsumoto S, Iwai M, et al. Reversal of blood flow in deep cerebral vein in preterm intraventricular hemorrhage: two case reports. BMC Pediatr. 2020; 20:517.37. Dean LM, Taylor GA. The intracranial venous system in infants: normal and abnormal findings on duplex and color Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995; 164:151–6.38. Pooh RK, Pooh KH, Nakagawa Y, Maeda K, Fukui R, Aono T. Transvaginal Doppler assessment of fetal intracranial venous flow. Obstet Gynecol. 1999; 93(5 Pt 1):697–701.39. Ikeda T, Ito Y, Mikami R, Matsuo K, Kawamura N, Yamoto A. Hemodynamics of infants with strong fluctuations of internal cerebral vein. Pediatr Int. 2019; 61:475–81.40. Yoon SA. Is it time to add point-of-care ultrasound education to pediatric residency curriculum? Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022; 65:33–4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Neonatologist Staffing and Workload in Korean Neonatal Intensive Care Units
- Bedside ultrasound-guided percutaneous cystostomy in an infant in the neonatal intensive care unit
- Organisation of Special and Intensive Care Facilities for Babies
- Quality Improvement in Neonatal Intensive Care Units
- Evaluating Nursing Needs in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit with the Korean Patient Classification System for Neonatal Intensive Care Nurses