Diabetes Metab J.
2022 May;46(3):476-485. 10.4093/dmj.2021.0074.
Normalized Creatinine-to-Cystatin C Ratio and Risk of Diabetes in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Diabetes, Zhongda Hospital, School of Medicine, Southeast University, Nanjing, China
- 2Department of Endocrinology, Shenzhen People’s Hospital, The Second Clinical Medical College of Jinan University and The First Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China
- 3Department of Endocrinology, Zhongda Hospital, Southeast University, Nanjing, China
- 4Adelaide Medical School and Centre of Research Excellence (CRE) in Translating Nutritional Science to Good Health, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia
- KMID: 2530186
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0074
Abstract
- Background
Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio is recently suggested to be a surrogate marker for sarcopenia. However, little is known about its association with diabetes. This study aimed to fill in this gap based on a large-scale prospective cohort.
Methods
A population-based representative sample of 5,055 participants aged ≥45 years from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study was enrolled between 2011 and 2012 and followed at least once during the subsequent surveys at 2013, 2015, or 2018. Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio was calculated and normalized by body weight. Incident diabetes was ascertained by plasma glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, self-reported history, or use of anti-diabetic drugs. Logistic regression analysis and mediation analysis were employed.
Results
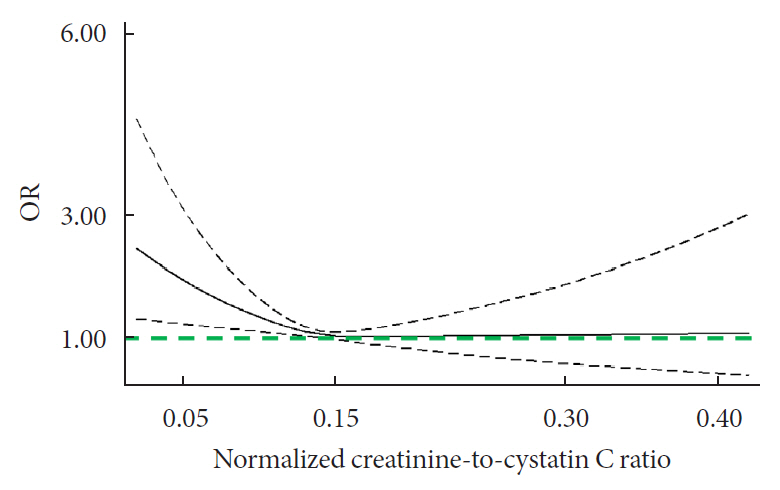
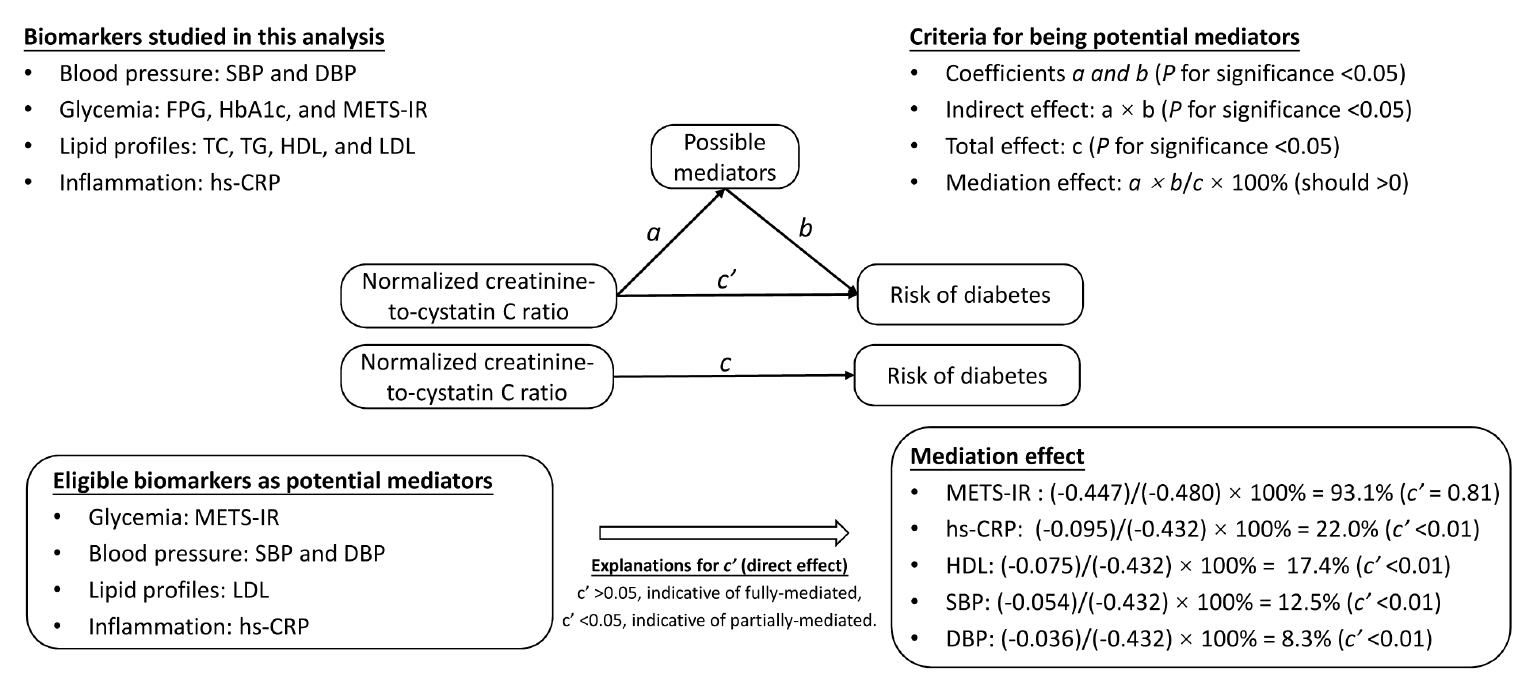
During follow-up, 634 participants developed diabetes. The risk of diabetes was gradually and significantly decreased with increased normalized creatinine–cystatin C ratio. The multivariable-adjusted odds ratio for diabetes was 0.91 (95% confidence interval, 0.83 to 0.99) per 1 standard deviation higher of normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio, and this relationship remained significant after controlling for muscle strength. The risk reduction in diabetes was significantly larger in participants with normal-weight and high normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio compared with those with overweight/obesity and high normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio (Pinteraction=0.01). Insulin resistance and inflammation appeared to be key mediators accounting for the observed relationship between normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio and risk of diabetes, with their mediating effect being 93.1% and 22.0%, respectively.
Conclusion
High normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio is associated with reduced risk of diabetes in middle-aged and older adults.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung CY, Joo YS, Kim HW, Han SH, Yoo TH, Kang SW, et al. Creatinine-cystatin C ratio and mortality in patients receiving intensive care and continuous kidney replacement therapy: a retrospective cohort study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021; 77:509–16.
Article2. Barreto EF, Poyant JO, Coville HH, Dierkhising RA, Kennedy CC, Gajic O, et al. Validation of the sarcopenia index to assess muscle mass in the critically ill: a novel application of kidney function markers. Clin Nutr. 2019; 38:1362–7.
Article3. Fu X, Tian Z, Wen S, Sun H, Thapa S, Xiong H, et al. A new index based on serum creatinine and cystatin C is useful for assessing sarcopenia in patients with advanced cancer. Nutrition. 2021; 82:111032.
Article4. Osaka T, Hamaguchi M, Hashimoto Y, Ushigome E, Tanaka M, Yamazaki M, et al. Decreased the creatinine to cystatin C ratio is a surrogate marker of sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018; 139:52–8.
Article5. Tan L, Li R, Hu X, Zhu Y, Bao T, Zuo Y, et al. Serum creatinine/cystatin C ratio as a case-finding tool for low handgrip strength in Chinese middle-aged and older adults. Sci Rep. 2020; 10:14028.
Article6. Tabara Y, Kohara K, Okada Y, Ohyagi Y, Igase M. Creatinineto-cystatin C ratio as a marker of skeletal muscle mass in older adults: J-SHIPP study. Clin Nutr. 2020; 39:1857–62.
Article7. Tang T, Zhuo Y, Xie L, Wang H, Yang M. Sarcopenia index based on serum creatinine and cystatin C is associated with 3-year mortality in hospitalized older patients. Sci Rep. 2020; 10:1260.
Article8. Lee HS, Park KW, Kang J, Ki YJ, Chang M, Han JK, et al. Sarcopenia index as a predictor of clinical outcomes in older patients with coronary artery disease. J Clin Med. 2020; 9:3121.
Article9. Komorita Y, Iwase M, Fujii H, Ide H, Ohkuma T, Jodai-Kitamura T, et al. The serum creatinine to cystatin C ratio predicts bone fracture in patients with type 2 diabetes: the Fukuoka Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018; 146:202–10.
Article10. Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019; 157:107843.
Article11. Kalyani RR, Metter EJ, Xue QL, Egan JM, Chia CW, Studenski S, et al. The relationship of lean body mass with aging to the development of diabetes. J Endocr Soc. 2020; 4:bvaa043.
Article12. Larsen BA, Wassel CL, Kritchevsky SB, Strotmeyer ES, Criqui MH, Kanaya AM, et al. Association of muscle mass, area, and strength with incident diabetes in older adults: the Health ABC Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 101:1847–55.
Article13. Li JJ, Wittert GA, Vincent A, Atlantis E, Shi Z, Appleton SL, et al. Muscle grip strength predicts incident type 2 diabetes: population-based cohort study. Metabolism. 2016; 65:883–92.
Article14. Ulmann G, Kai J, Durand JP, Neveux N, Jouinot A, De Bandt JP, et al. Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio and bioelectrical impedance analysis for the assessement of low lean body mass in cancer patients: comparison to L3-computed tomography scan. Nutrition. 2021; 81:110895.
Article15. Zhao Y, Hu Y, Smith JP, Strauss J, Yang G. Cohort profile: the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS). Int J Epidemiol. 2014; 43:61–8.
Article16. Chen X, Crimmins E, Hu PP, Kim JK, Meng Q, Strauss J, et al. Venous blood-based biomarkers in the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study: rationale, design, and results from the 2015 wave. Am J Epidemiol. 2019; 188:1871–7.
Article17. Cai X, Qiu S, Liu S, Lu Y, Luo D, Li R, et al. Body-weight fluctuation and risk of diabetes in older adults: the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS). Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020; 169:108419.
Article18. Nishida K, Hashimoto Y, Kaji A, Okamura T, Sakai R, Kitagawa N, et al. Creatinine/(cystatin C × body weight) ratio is associated with skeletal muscle mass index. Endocr J. 2020; 67:733–40.
Article19. Peterson MD, Duchowny K, Meng Q, Wang Y, Chen X, Zhao Y. Low normalized grip strength is a biomarker for cardiometabolic disease and physical disabilities among U.S. and Chinese adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017; 72:1525–31.
Article20. Peterson MD, Zhang P, Choksi P, Markides KS, Al Snih S. Muscle weakness thresholds for prediction of diabetes in adults. Sports Med. 2016; 46:619–28.
Article21. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33(Suppl 1):S62–9.22. Li DY, Yin WJ, Yi YH, Zhang BK, Zhao J, Zhu CN, et al. Development and validation of a more accurate estimating equation for glomerular filtration rate in a Chinese population. Kidney Int. 2019; 95:636–46.
Article23. Bello-Chavolla OY, Almeda-Valdes P, Gomez-Velasco D, Viveros-Ruiz T, Cruz-Bautista I, Romo-Romo A, et al. METS-IR, a novel score to evaluate insulin sensitivity, is predictive of visceral adiposity and incident type 2 diabetes. Eur J Endocrinol. 2018; 178:533–44.
Article24. Weng J, Ji L, Jia W, Lu J, Zhou Z, Zou D, et al. Standards of care for type 2 diabetes in China. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016; 32:442–58.
Article25. Kim BY, Won JC, Lee JH, Kim HS, Park JH, Ha KH, et al. Diabetes fact sheets in Korea, 2018: an appraisal of current status. Diabetes Metab J. 2019; 43:487–94.
Article26. Gunzler D, Chen T, Wu P, Zhang H. Introduction to mediation analysis with structural equation modeling. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2013; 25:390–4.27. Albert JM, Geng C, Nelson S. Causal mediation analysis with a latent mediator. Biom J. 2016; 58:535–48.
Article28. Lin YL, Chen SY, Lai YH, Wang CH, Kuo CH, Liou HH, et al. Serum creatinine to cystatin C ratio predicts skeletal muscle mass and strength in patients with non-dialysis chronic kidney disease. Clin Nutr. 2020; 39:2435–41.
Article29. Hong S, Chang Y, Jung HS, Yun KE, Shin H, Ryu S. Relative muscle mass and the risk of incident type 2 diabetes: a cohort study. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0188650.
Article30. Karvonen-Gutierrez CA, Peng Q, Peterson M, Duchowny K, Nan B, Harlow S. Low grip strength predicts incident diabetes among mid-life women: the Michigan Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation. Age Ageing. 2018; 47:685–91.
Article31. Kashani KB, Frazee EN, Kukralova L, Sarvottam K, Herasevich V, Young PM, et al. Evaluating muscle mass by using markers of kidney function: development of the sarcopenia index. Crit Care Med. 2017; 45:e23–9.32. Tatsumi Y, Morimoto A, Asayama K, Sonoda N, Miyamatsu N, Ohno Y, et al. Risk of developing type 2 diabetes according to blood pressure levels and presence or absence of hypertensive treatment: the Saku study. Hypertens Res. 2019; 42:105–13.
Article33. Zhang M, Liu D, Qin P, Liu Y, Sun X, Li H, et al. Association of metabolic score for insulin resistance and its 6-year change with incident type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes. 2021; 13:725–34.
Article34. Wang X, Bao W, Liu J, Ouyang YY, Wang D, Rong S, et al. Inflammatory markers and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:166–75.35. Qiu S, Cai X, Yang B, Du Z, Cai M, Sun Z, et al. Association between cardiorespiratory fitness and risk of type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019; 27:315–24.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The association between glaucoma and all-cause mortality in middle-aged and elderly Chinese people: results from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
- The association between obesity and glaucoma in older adults: evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
- Health Conditions Sensitive to Retirement and Job Loss Among Korean Middle-aged and Older Adults
- The Value of Serum Concentration of Cystatin C as a Marker for Glomerular Filtration Rate in Children and Adolescents
- Impact of Retirement Expectation and Retirement Readiness on Retirement Anxiety among Middle-aged Nurses