J Korean Med Sci.
2022 May;37(17):e138. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e138.
Predictive Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis Flare After Switching From Intravenous to Subcutaneous Formulation of Tocilizumab in RealWorld Practice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rheumatology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Information Medicine, Big Data Research Center, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2529705
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e138
Abstract
- Background
To evaluate the incidence and related factors of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) flares after switching from intravenous tocilizumab (TCZ-IV) to subcutaneous tocilizumab (TCZSC) injection in stable RA patients.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated the medical records of stable RA patients who used TCZ-IV for more than 6 months and switched to TCZ-SC between January 2013 and April 2020. RA flare was defined as an increase of more than 1.2 in the RA disease activity as assessed by the disease activity score in 28 joints. The factors associated with RA flare were evaluated by logistic regression analysis.
Results
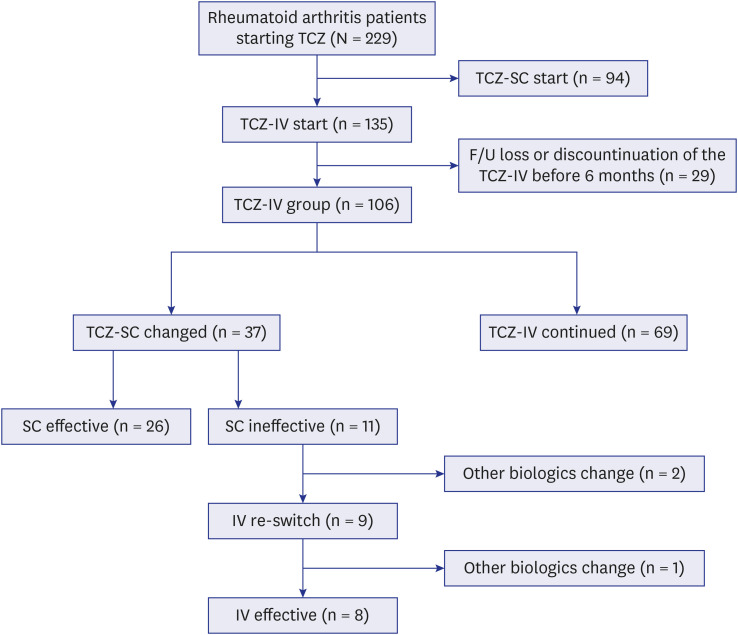
Among 106 patients treated with TCZ-IV for > 6 months, 37 patients were switched to TCZ-SC after the acquisition of remission or low disease activity. RA flares occurred in 11 (29.7%) of patients who switched TCZ-SC. Results from the multivariable logistic analysis revealed that the dose of TCZ-IV per weight at switching (odds ratio [OR], 20.70; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.22–192.84; P = 0.008) and methotrexate (MTX) non-use (OR, 8.53; 95% CI, 1.21–60.40; P = 0.032) were associated with the risk of RA flares after switching to TCZ-SC. Interestingly, most patients who switched back to TCZ-IV had their RA activity controlled again.
Conclusion
MTX non-use and high dose of TCZ-IV per weight were associated with a risk of RA flare after switching to TCZ-SC. RA patients with these factors need to be carefully observed for flare after switching from TCZ-IV to TCZ-SC.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Unver N, McAllister F. IL-6 family cytokines: key inflammatory mediators as biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018; 41:10–17. PMID: 29699936.2. Baek HJ, Lim MJ, Park W, Park SH, Shim SC, Yoo DH, et al. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in Korean patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Korean J Intern Med. 2019; 34(4):917–931. PMID: 29334721.3. Houssiau FA, Devogelaer JP, Van Damme J, de Deuxchaisnes CN, Van Snick J. Interleukin-6 in synovial fluid and serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory arthritides. Arthritis Rheum. 1988; 31(6):784–788. PMID: 3260102.4. Robak T, Gladalska A, Stepień H, Robak E. Serum levels of interleukin-6 type cytokines and soluble interleukin-6 receptor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 1998; 7(5):347–353. PMID: 9883970.5. Lee JS, Oh JS, Hong S, Lee CK, Yoo B, Kim YG. Tocilizumab-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheum Dis. 2019; 26(3):186–190.6. Burmester GR, Rubbert-Roth A, Cantagrel A, Hall S, Leszczynski P, Feldman D, et al. A randomised, double-blind, parallel-group study of the safety and efficacy of subcutaneous tocilizumab versus intravenous tocilizumab in combination with traditional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (SUMMACTA study). Ann Rheum Dis. 2014; 73(1):69–74. PMID: 23904473.7. Malaviya AP, Ostör AJ. Drug adherence to biologic DMARDS with a special emphasis on the benefits of subcutaneous abatacept. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2012; 6:589–596. PMID: 22936845.8. Barton JL. Patient preferences and satisfaction in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with biologic therapy. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2009; 3:335–344. PMID: 20016797.9. Vavricka SR, Bentele N, Scharl M, Rogler G, Zeitz J, Frei P, et al. Systematic assessment of factors influencing preferences of Crohn’s disease patients in selecting an anti-tumor necrosis factor agent (CHOOSE TNF TRIAL). Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012; 18(8):1523–1530. PMID: 21987429.10. Ogata A, Atsumi T, Fukuda T, Hirabayashi Y, Inaba M, Ishiguro N, et al. Sustainable efficacy of switching from intravenous to subcutaneous tocilizumab monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2015; 67(10):1354–1362. PMID: 25832859.11. Burmester GR, Rubbert-Roth A, Cantagrel A, Hall S, Leszczynski P, Feldman D, et al. Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous tocilizumab versus intravenous tocilizumab in combination with traditional DMARDs in patients with RA at week 97 (SUMMACTA). Ann Rheum Dis. 2016; 75(1):68–74. PMID: 26056119.12. Darloy J, Segaud N, Salmon JH, Eschard JP, Goëb V, Deprez X, et al. Tocilizumab effectiveness after switching from intravenous to subcutaneous route in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the RoSwitch study. Rheumatol Ther. 2019; 6(1):61–75. PMID: 30632015.13. Gupta R, Shipa M, Yeoh SA, Buck P, Ehrenstein MR. An unfavourable outcome following switching intravenous abatacept and tocilizumab to subcutaneous forms during the COVID-19 pandemic. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021; 60(2):977–979. PMID: 33232489.14. Iwamoto N, Fukui S, Umeda M, Nishino A, Nakashima Y, Suzuki T, et al. Evaluation of switching from intravenous to subcutaneous formulation of tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2016; 26(5):662–666. PMID: 26708444.15. van der Maas A, Lie E, Christensen R, Choy E, de Man YA, van Riel P, et al. Construct and criterion validity of several proposed DAS28-based rheumatoid arthritis flare criteria: an OMERACT cohort validation study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013; 72(11):1800–1805. PMID: 23178206.16. Rubbert-Roth A, Furst DE, Nebesky JM, Jin A, Berber E. A review of recent advances using tocilizumab in the treatment of rheumatic diseases. Rheumatol Ther. 2018; 5(1):21–42. PMID: 29502236.17. Abdallah H, Hsu JC, Lu P, Fettner S, Zhang X, Douglass W, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of subcutaneous tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis from 2 randomized, controlled trials: SUMMACTA and BREVACTA. J Clin Pharmacol. 2017; 57(4):459–468. PMID: 27599663.18. Stojanović S, Stamenković B, Nedović J, Aleksić I, Cvetković J.. Effectiveness of tocilizumab after switching from intravenous to subcutaneous formulation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a single-centre experience. Acta Fac Med Naissensis. 2021; 38(3):247–256.19. Dougados M, Kissel K, Sheeran T, Tak PP, Conaghan PG, Mola EM, et al. Adding tocilizumab or switching to tocilizumab monotherapy in methotrexate inadequate responders: 24-week symptomatic and structural results of a 2-year randomised controlled strategy trial in rheumatoid arthritis (ACT-RAY). Ann Rheum Dis. 2013; 72(1):43–50. PMID: 22562983.20. Bijlsma JW, Welsing PM, Woodworth TG, Middelink LM, Pethö-Schramm A, Bernasconi C, et al. Early rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab, methotrexate, or their combination (U-Act-Early): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, strategy trial. Lancet. 2016; 388(10042):343–355. PMID: 27287832.21. Burmester GR, Rigby WF, van Vollenhoven RF, Kay J, Rubbert-Roth A, Blanco R, et al. Tocilizumab combination therapy or monotherapy or methotrexate monotherapy in methotrexate-naive patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: 2-year clinical and radiographic results from the randomised, placebo-controlled FUNCTION trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017; 76(7):1279–1284. PMID: 28389552.22. Kojima T, Yabe Y, Kaneko A, Takahashi N, Funahashi K, Kato D, et al. Importance of methotrexate therapy concomitant with tocilizumab treatment in achieving better clinical outcomes for rheumatoid arthritis patients with high disease activity: an observational cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015; 54(1):113–120. PMID: 25102861.23. Kaneko Y, Atsumi T, Tanaka Y, Inoo M, Kobayashi-Haraoka H, Amano K, et al. Comparison of adding tocilizumab to methotrexate with switching to tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to methotrexate: 52-week results from a prospective, randomised, controlled study (SURPRISE study). Ann Rheum Dis. 2016; 75(11):1917–1923. PMID: 26733110.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Sepsis Caused by Cellulitis in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis after Tocilizumab Treatment
- Tocilizumab-induced Transaminitis in a Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient with Macrophage Activation Syndrome
- Description of the Efficacy and Safety of Three New Biologics in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis Developing in the Knee of a Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient Mistaken as a Rheumatoid Arthritis Flare-Up
- Effect of Tocilizumab on Serum Hepcidin and Anemia Response in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis