J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2022 May;65(3):397-407. 10.3340/jkns.2021.0297.
Imaging of Abusive Head Trauma : A Radiologists’ Perspective
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2529584
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2021.0297
Abstract
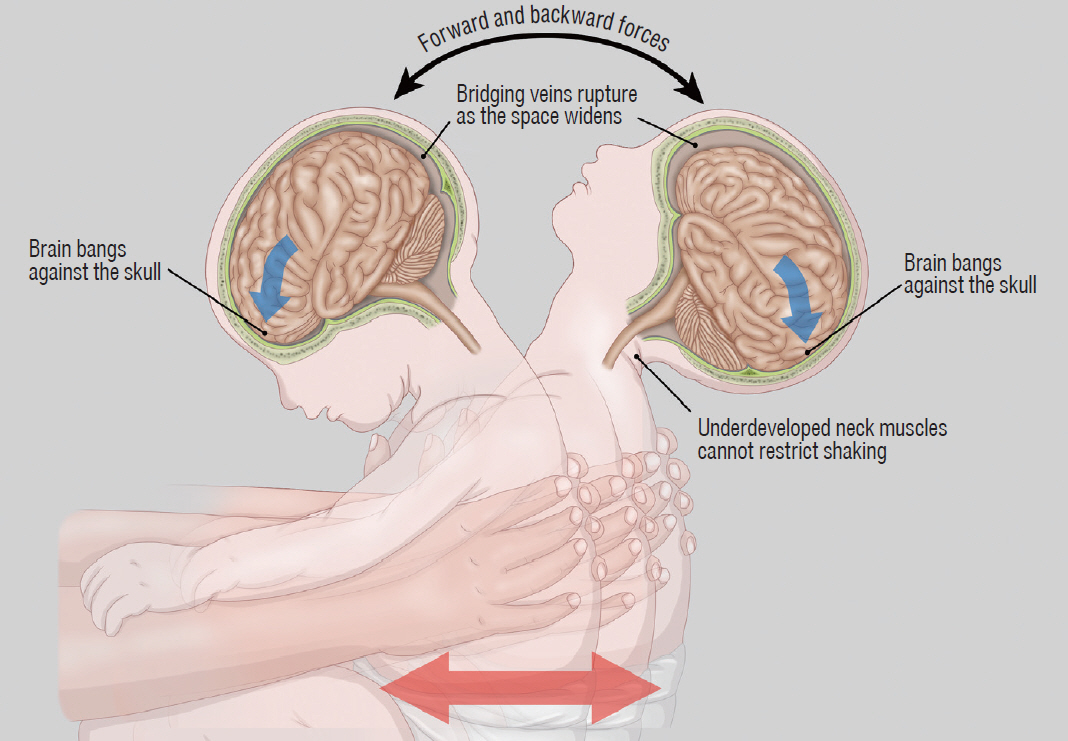
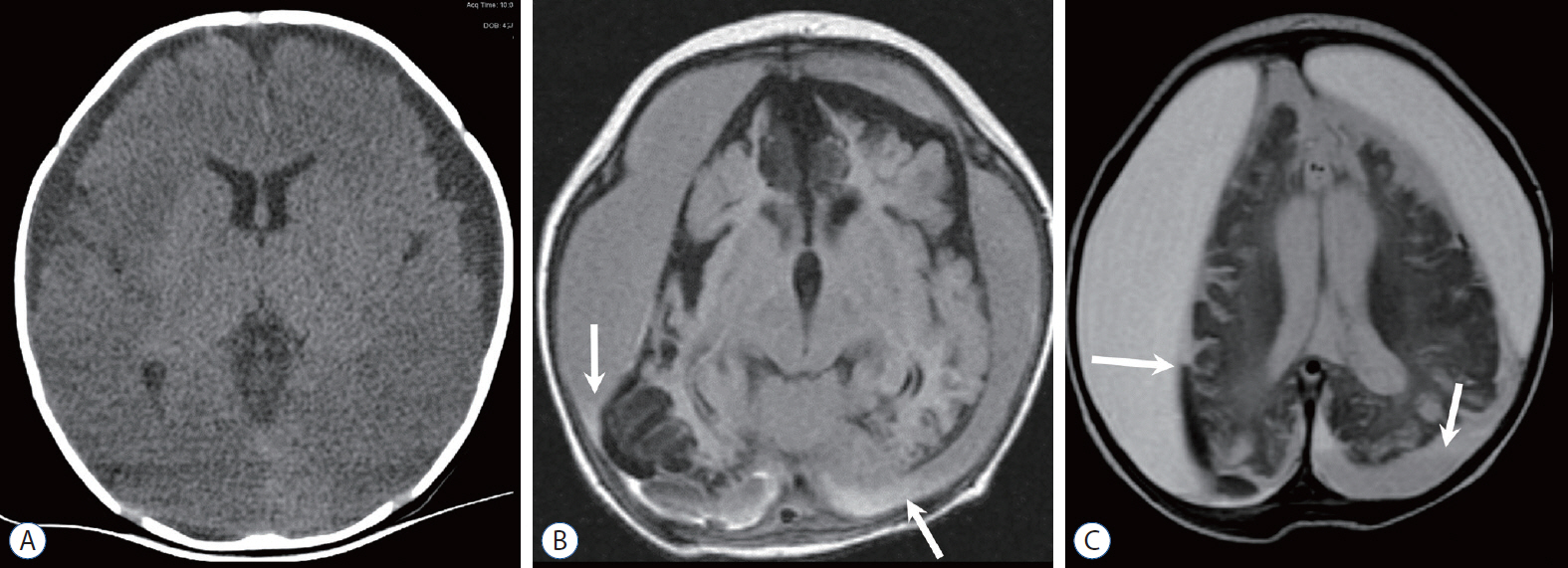
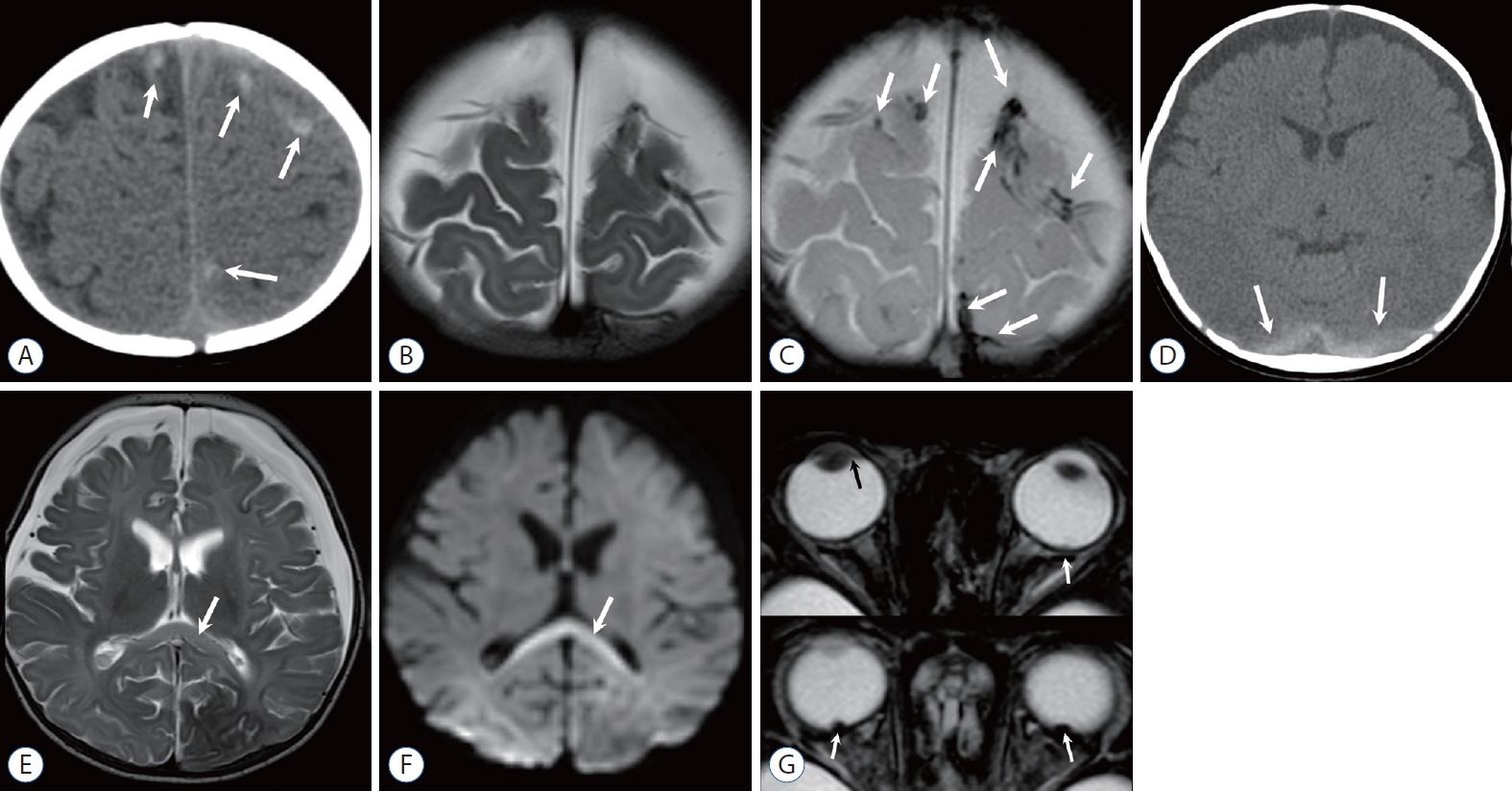
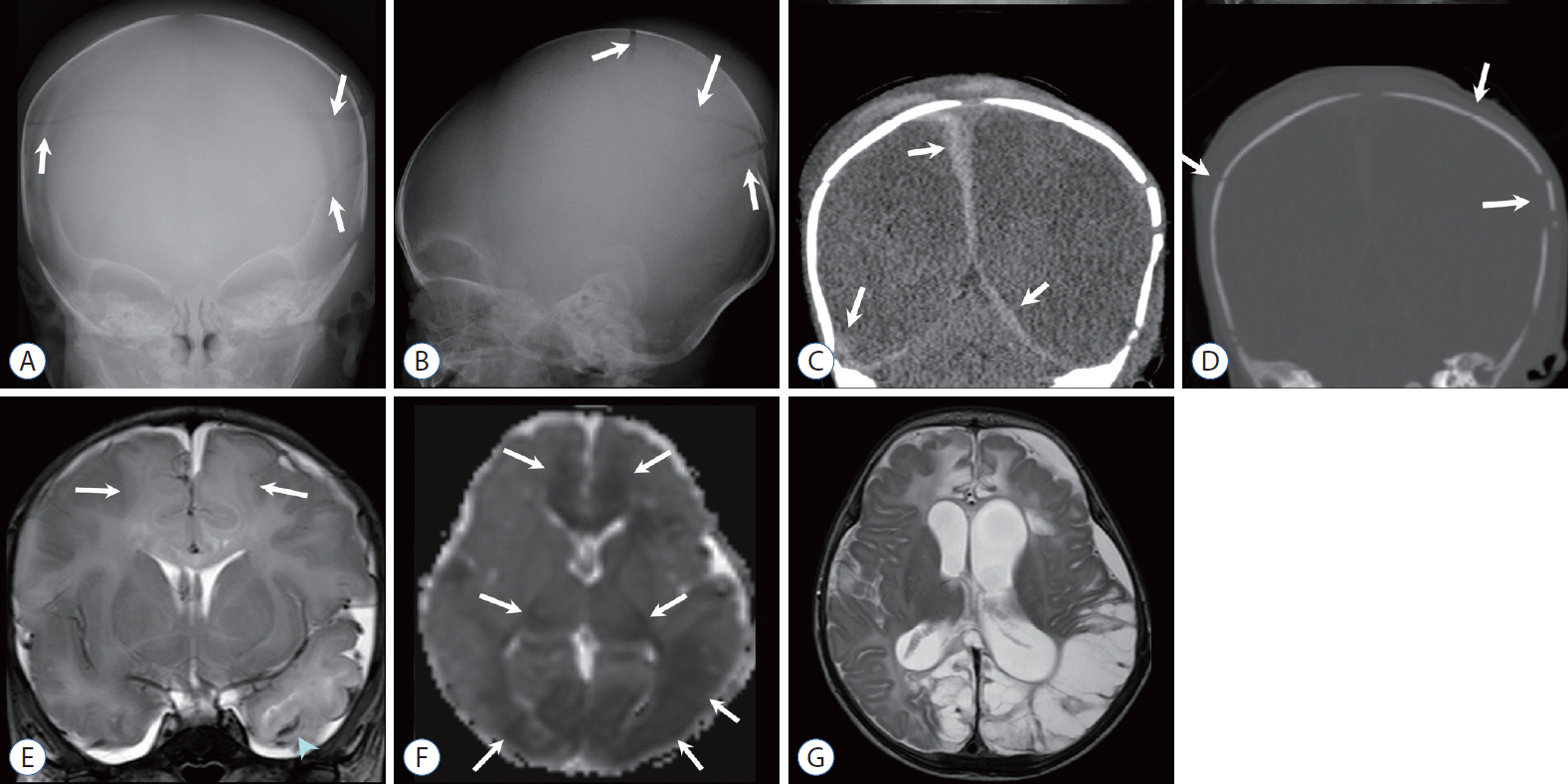
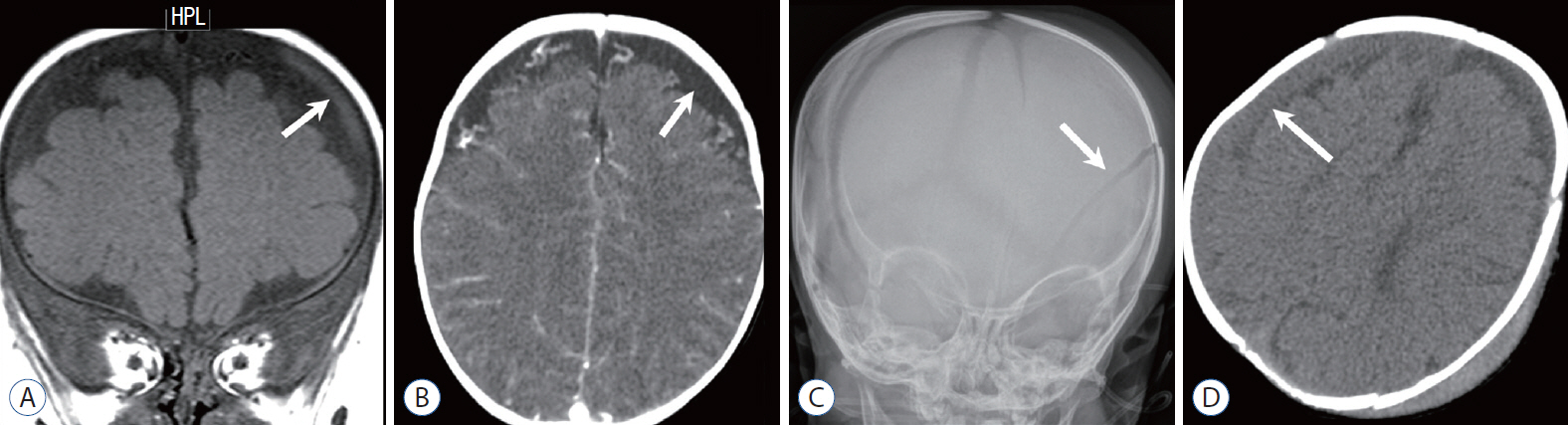
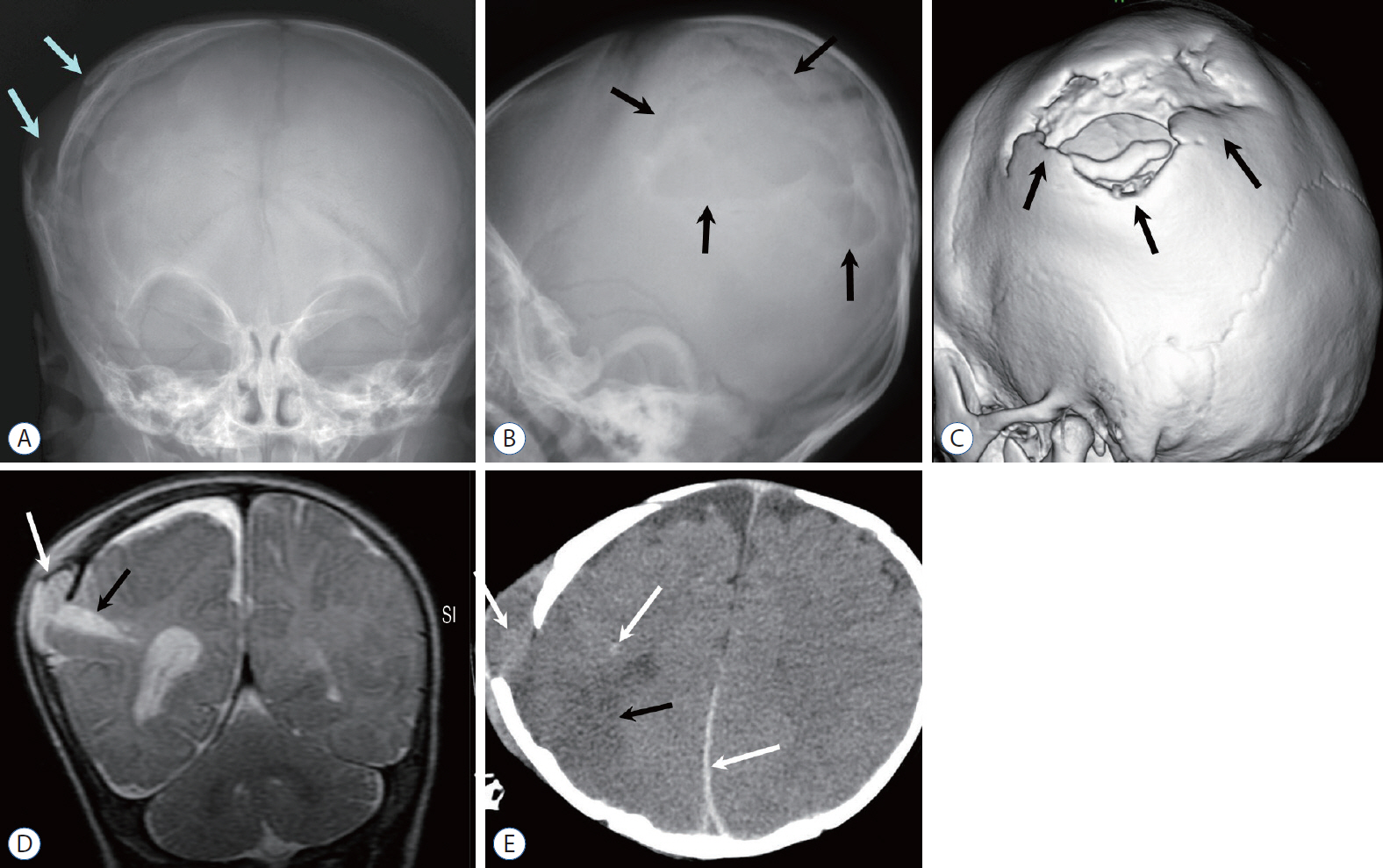
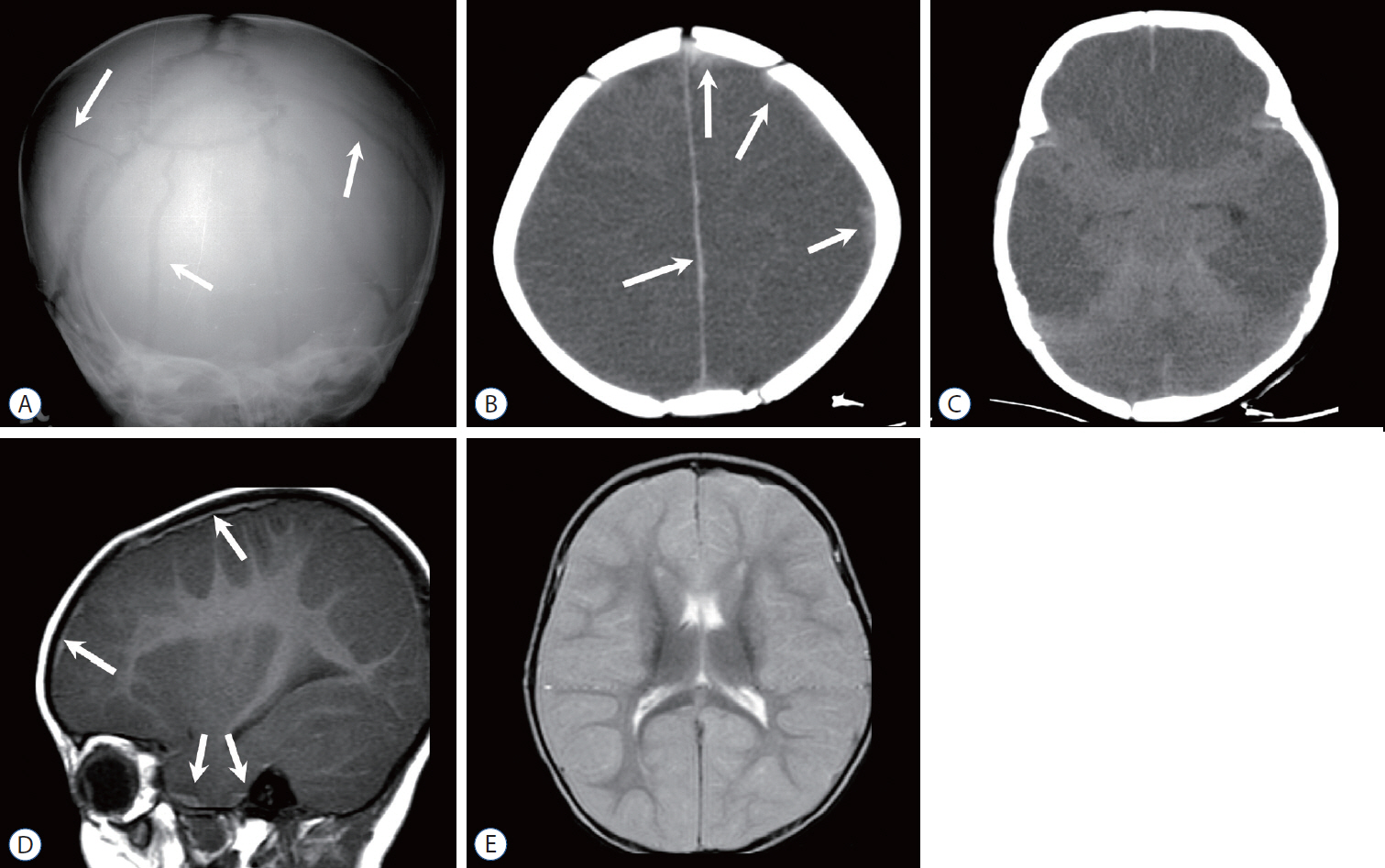
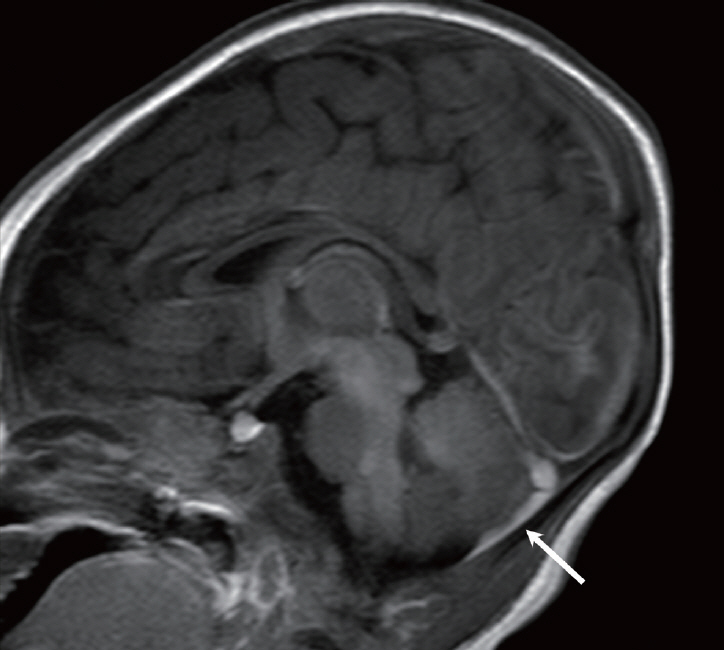
- Abusive head trauma (AHT) is the most common and serious form of child abuse and a leading cause of traumatic death in infants and young children. The biomechanics of head injuries include violent shaking, blunt impact, or a combination of both. Neuroimaging plays an important role in recognizing and distinguishing abusive injuries from lesions from accidental trauma or other causes, because clinical presentation and medical history are often nonspecific and ambiguous in this age group. Understanding common imaging features of AHT can increase recognition with high specificity for AHT. In this review, we discuss the biomechanics of AHT, imaging features of AHT, and other conditions that mimic AHT.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Altinok D, Saleem S, Zhang Z, Markman L, Smith W. MR imaging findings of retinal hemorrhage in a case of nonaccidental trauma. Pediatr Radiol. 39:290–292. 2009.
Article2. Bechtel K, Stoessel K, Leventhal JM, Ogle E, Teague B, Lavietes S, et al. Characteristics that distinguish accidental from abusive injury in hospitalized young children with head trauma. Pediatrics. 114:165–168. 2004.
Article3. Bertocci GE, Pierce MC, Deemer E, Aguel F, Janosky JE, Vogeley E. Using test dummy experiments to investigate pediatric injury risk in simulated short-distance falls. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 157:480–486. 2003.
Article4. Boehnke M, Mirsky D, Stence N, Stanley RM, Lindberg DM, ExSTRA investigators. Occult head injury is common in children with concern for physical abuse. Pediatr Radiol. 48:1123–1129. 2018.
Article5. Caffey J. Multiple fractures in the long bones of infants suffering from chronic subdural hematoma. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther. 56:163–173. 1946.6. Caffey J. On the theory and practice of shaking infants. Its potential residual effects of permanent brain damage and mental retardation. Am J Dis Child. 124:161–169. 1972.7. Caffey J. The whiplash shaken infant syndrome: manual shaking by the extremities with whiplash-induced intracranial and intraocular bleedings, linked with residual permanent brain damage and mental retardation. Pediatrics. 54:396–403. 1974.
Article8. Case ME. Distinguishing accidental from inflicted head trauma at autopsy. Pediatr Radiol 44 Suppl. 4:S632–S640. 2014.
Article9. Case ME, Graham MA, Handy TC, Jentzen JM, Monteleone JA; National Association of Medical Examiners Ad Hoc Committee on Shaken Baby Syndrome. Position paper on fatal abusive head injuries in infants and young children. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 22:112–122. 2001.
Article10. Chevignard MP, Lind K. Long-term outcome of abusive head trauma. Pediatr Radiol 44 Suppl. 4:S548–S558. 2014.
Article11. Choudhary AK, Bradford RK, Dias MS, Moore GJ, Boal DK. Spinal subdural hemorrhage in abusive head trauma: a retrospective study. Radiology. 262:216–223. 2012.
Article12. Choudhary AK, Bradford R, Dias MS, Thamburaj K, Boal DK. Venous injury in abusive head trauma. Pediatr Radiol. 45:1803–1813. 2015.
Article13. Choudhary AK, Ishak R, Zacharia TT, Dias MS. Imaging of spinal injury in abusive head trauma: a retrospective study. Pediatr Radiol. 44:1130–1140. 2014.
Article14. Choudhary AK, Servaes S, Slovis TL, Palusci VJ, Hedlund GL, Narang SK, et al. Consensus statement on abusive head trauma in infants and young children. Pediatr Radiol. 48:1048–1065. 2018.
Article15. Christian CW, Block R; Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect; American Academy of Pediatrics. Abusive head trauma in infants and children. Pediatrics. 123:1409–1411. 2009.
Article16. Danaher F, Vandeven A, Blanchard A, Newton AW. Recognizing, diagnosing, and preventing child maltreatment: an update for pediatric clinicians. Curr Opin Pediatr. 30:582–590. 2018.17. Expert Panel on Pediatric Imaging, Wootton-Gorges SL, Soares BP, Alazraki AL, Anupindi SA, Blount JP, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria® suspected physical abuse-child. J Am Coll Radiol. 14(5S):S338–S349. 2017.18. Fernando S, Obaldo RE, Walsh IR, Lowe LH. Neuroimaging of nonaccidental head trauma: pitfalls and controversies. Pediatr Radiol. 38:827–838. 2008.
Article19. Flom L, Fromkin J, Panigrahy A, Tyler-Kabara E, Berger RP. Development of a screening MRI for infants at risk for abusive head trauma. Pediatr Radiol. 46:519–526. 2016.
Article20. Foerster BR, Petrou M, Lin D, Thurnher MM, Carlson MD, Strouse PJ, et al. Neuroimaging evaluation of non-accidental head trauma with correlation to clinical outcomes: a review of 57 cases. J Pediatr. 154:573–577. 2009.
Article21. Forbes BJ, Rubin SE, Margolin E, Levin AV. Evaluation and management of retinal hemorrhages in infants with and without abusive head trauma. J AAPOS. 14:267–273. 2010.
Article22. Geddes JF, Hackshaw AK, Vowles GH, Nickols CD, Whitwell HL. Neuropathology of inflicted head injury in children. I. Patterns of brain damage. Brain. 124(Pt 7):1290–1298. 2001.
Article23. Geddes JF, Vowles GH, Hackshaw AK, Nickols CD, Scott IS, Whitwell HL. Neuropathology of inflicted head injury in children. II. Microscopic brain injury in infants. Brain. 124(Pt 7):1299–1306. 2001.
Article24. Greeley CS. Abusive head trauma: a review of the evidence base. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 204:967–973. 2015.
Article25. Greiner MV, Lawrence AP, Horn P, Newmeyer AJ, Makoroff KL. Early clinical indicators of developmental outcome in abusive head trauma. Childs Nerv Syst. 28:889–896. 2012.
Article26. Gunda D, Cornwell BO, Dahmoush HM, Jazbeh S, Alleman AM. Pediatric central nervous system imaging of nonaccidental trauma: beyond subdural hematomas. Radiographics. 39:213–228. 2019.
Article27. Huisman TA, Wagner MW, Bosemani T, Tekes A, Poretti A. Pediatric spinal trauma. J Neuroimaging. 25:337–353. 2015.
Article28. Ichord RN, Naim M, Pollock AN, Nance ML, Margulies SS, Christian CW. Hypoxic-ischemic injury complicates inflicted and accidental traumatic brain injury in young children: the role of diffusion-weighted imaging. J Neurotrauma. 24:106–118. 2007.
Article29. Jackson JE, Beres AL, Theodorou CM, Ugiliweneza B, Boakye M, Nuño M. Long-term impact of abusive head trauma in young children: outcomes at 5 and 11 years old. J Pediatr Surg. 56:2318–2325. 2021.
Article30. Kadom N, Khademian Z, Vezina G, Shalaby-Rana E, Rice A, Hinds T. Usefulness of MRI detection of cervical spine and brain injuries in the evaluation of abusive head trauma. Pediatr Radiol. 44:839–848. 2014.
Article31. Kelly P, John S, Vincent AL, Reed P. Abusive head trauma and accidental head injury: a 20-year comparative study of referrals to a hospital child protection team. Arch Dis Child. 100:1123–1130. 2015.
Article32. Kemp AM, Jaspan T, Griffiths J, Stoodley N, Mann MK, Tempest V, et al. Neuroimaging: what neuroradiological features distinguish abusive from non-abusive head trauma? A systematic review. Arch Dis Child. 96:1103–1112. 2011.
Article33. Kemp AM, Joshi AH, Mann M, Tempest V, Liu A, Holden S, et al. What are the clinical and radiological characteristics of spinal injuries from physical abuse: a systematic review. Arch Dis Child. 95:355–360. 2010.
Article34. Kemp AM, Rajaram S, Mann M, Tempest V, Farewell D, Gawne-Cain ML, et al. What neuroimaging should be performed in children in whom inflicted brain injury (iBI) is suspected? A systematic review. Clin Radiol. 64:473–483. 2009.
Article35. Kempe CH, Silverman FN, Steele BF, Droegemueller W, Silver HK. The battered-child syndrome. JAMA. 181:17–24. 1962.
Article36. Looney CB, Smith JK, Merck LH, Wolfe HM, Chescheir NC, Hamer RM, et al. Intracranial hemorrhage in asymptomatic neonates: prevalence on MR images and relationship to obstetric and neonatal risk factors. Radiology. 242:535–541. 2007.
Article37. McLean LA, Frasier LD, Hedlund GL. Does intracranial venous thrombosis cause subdural hemorrhage in the pediatric population? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 33:1281–1284. 2012.
Article38. Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism. Child abuse & neglect Korea 2020. Available at : https://www.korea.kr/archive/expDocView.do?docId=39601.39. Pfeifer CM, Hammer MR, Mangona KL, Booth TN. Non-accidental trauma: the role of radiology. Emerg Radiol. 24:207–213. 2017.
Article40. Pfeifer CM, Henry MK, Caré MM, Christian CW, Servaes S, Milla SS, et al. Debunking fringe beliefs in child abuse imaging: AJR expert panel narrative review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 217:529–540. 2021.
Article41. Porto L, Bartels MB, Zwaschka J, You SJ, Polkowski C, Luetkens J, et al. Abusive head trauma: experience improves diagnosis. Neuroradiology. 63:417–430. 2021.
Article42. Rabbitt AL, Kelly TG, Yan K, Zhang J, Bretl DA, Quijano CV. Characteristics associated with spine injury on magnetic resonance imaging in children evaluated for abusive head trauma. Pediatr Radiol. 50:83–97. 2020.
Article43. Rooks VJ, Eaton JP, Ruess L, Petermann GW, Keck-Wherley J, Pedersen RC. Prevalence and evolution of intracranial hemorrhage in asymptomatic term infants. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 29:1082–1089. 2008.
Article44. Sieswerda-Hoogendoorn T, Boos S, Spivack B, Bilo RA, van Rijn RR. Abusive head trauma part II: radiological aspects. Eur J Pediatr. 171:617–623. 2012.45. Sieswerda-Hoogendoorn T, Postema FAM, Verbaan D, Majoie CB, van Rijn RR. Age determination of subdural hematomas with CT and MRI: a systematic review. Eur J Radiol. 83:1257–1268. 2014.
Article46. Thamburaj K, Soni A, Frasier LD, Tun KN, Weber SR, Dias MS. Susceptibility-weighted imaging of retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma. Pediatr Radiol. 49:210–216. 2019.
Article47. Thompson A, Bertocci G. Pediatric bed fall computer simulation model: parametric sensitivity analysis. Med Eng Phys. 36:110–118. 2014.
Article48. Vázquez E, Delgado I, Sánchez-Montañez A, Fábrega A, Cano N. Imaging abusive head trauma: why use both computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging? Pediatr Radiol. 44 Suppl 4:S589–S603. 2014.
Article49. Wang L, Petrak M, Holz FG, Müller A, Krohne TU. Retinal hemorrhages in shaken baby syndrome. J Pediatr. 207:256. 2019.
Article50. Wilson TA, Gospodarev V, Hendrix S, Minasian T. Pediatric abusive head trauma: ThinkFirst national injury prevention foundation. Surg Neurol Int. 12:526. 2021.
Article51. Wittschieber D, Karger B, Niederstadt T, Pfeiffer H, Hahnemann ML. Subdural hygromas in abusive head trauma: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and forensic implications. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 36:432–439. 2015.
Article52. Wittschieber D, Karger B, Pfeiffer H, Hahnemann ML. Understanding subdural collections in pediatric abusive head trauma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 40:388–395. 2019.
Article53. Wright J, Painter S, Kodagali SS, Jones NR, Roalfe A, Jayawant S, et al. Disability and visual outcomes following suspected abusive head trauma in children under 2 years. Arch Dis Child. 106:590–593. 2021.
Article54. Wright JN. CNS injuries in abusive head trauma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 208:991–1001. 2017.
Article55. Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT, Farina L. Non-accidental brain trauma in infants: diffusion imaging, contributions to understanding the injury process. J Neuroradiol. 34:109–114. 2007.
Article56. Zuccoli G, Panigrahy A, Haldipur A, Willaman D, Squires J, Wolford J, et al. Susceptibility weighted imaging depicts retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma. Neuroradiology. 55:889–893. 2013.
Article