J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2022 May;65(3):385-396. 10.3340/jkns.2021.0289.
Complex Pathophysiology of Abusive Head Trauma with Poor Neurological Outcome in Infants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery and Children’s Medical Center, Nara Medical University, Kashihara, Japan
- KMID: 2529583
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2021.0289
Abstract
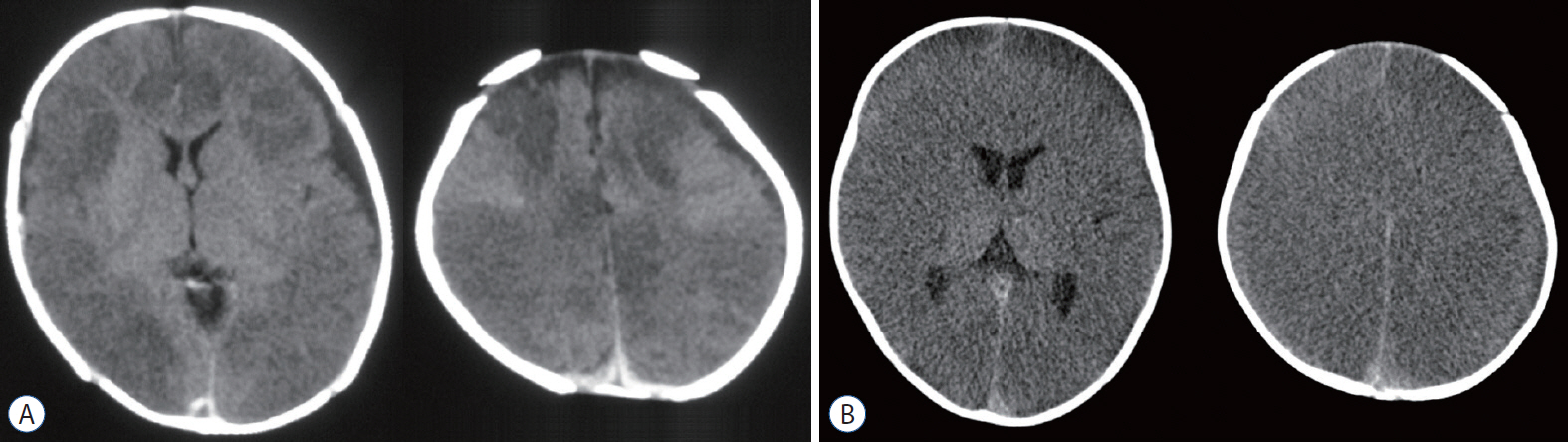
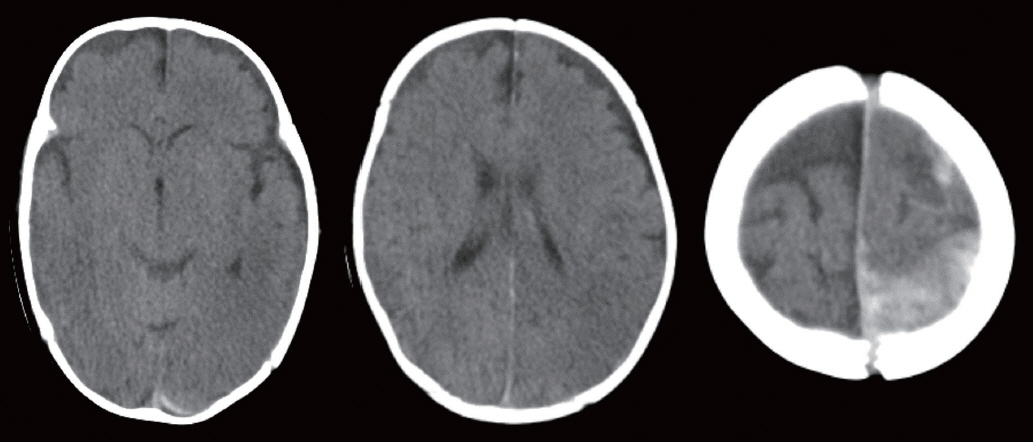
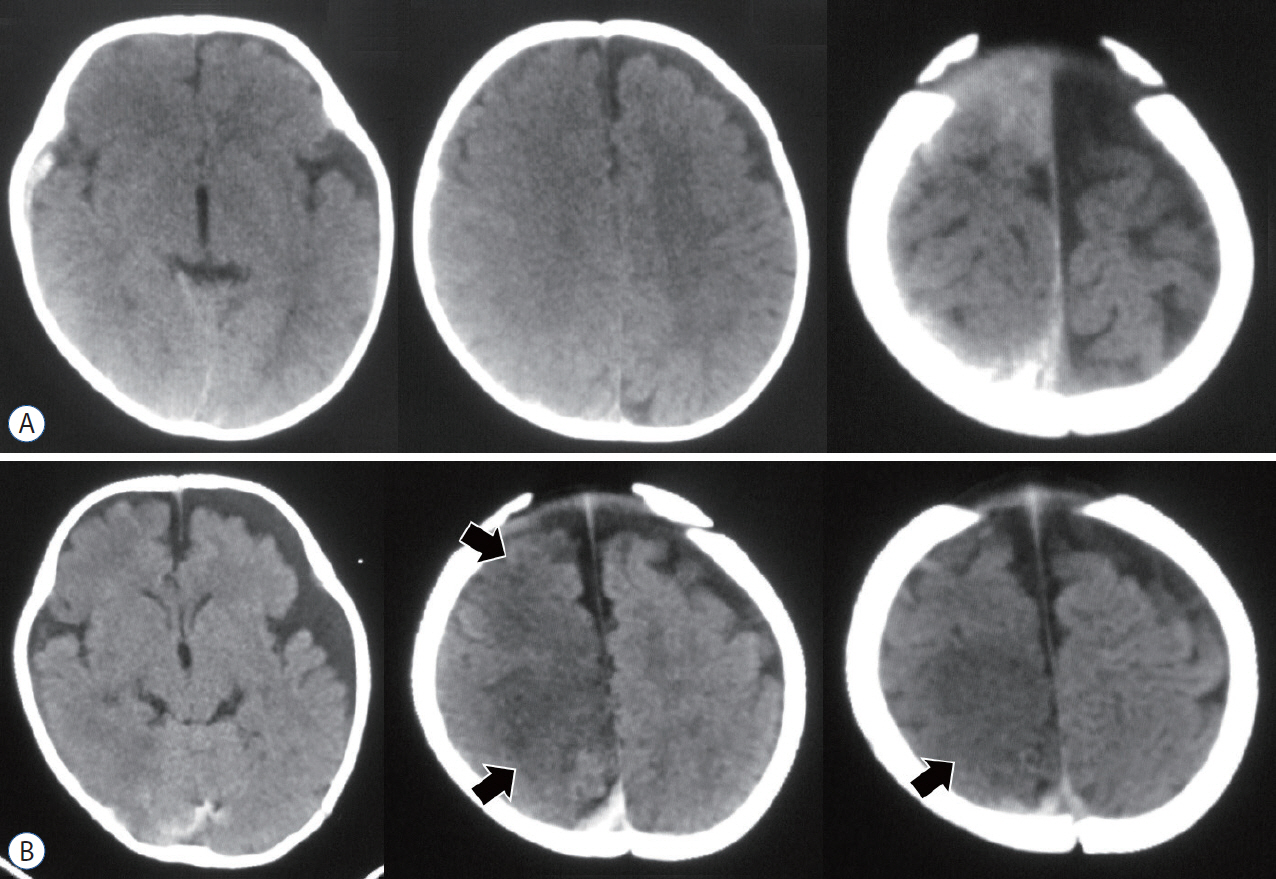
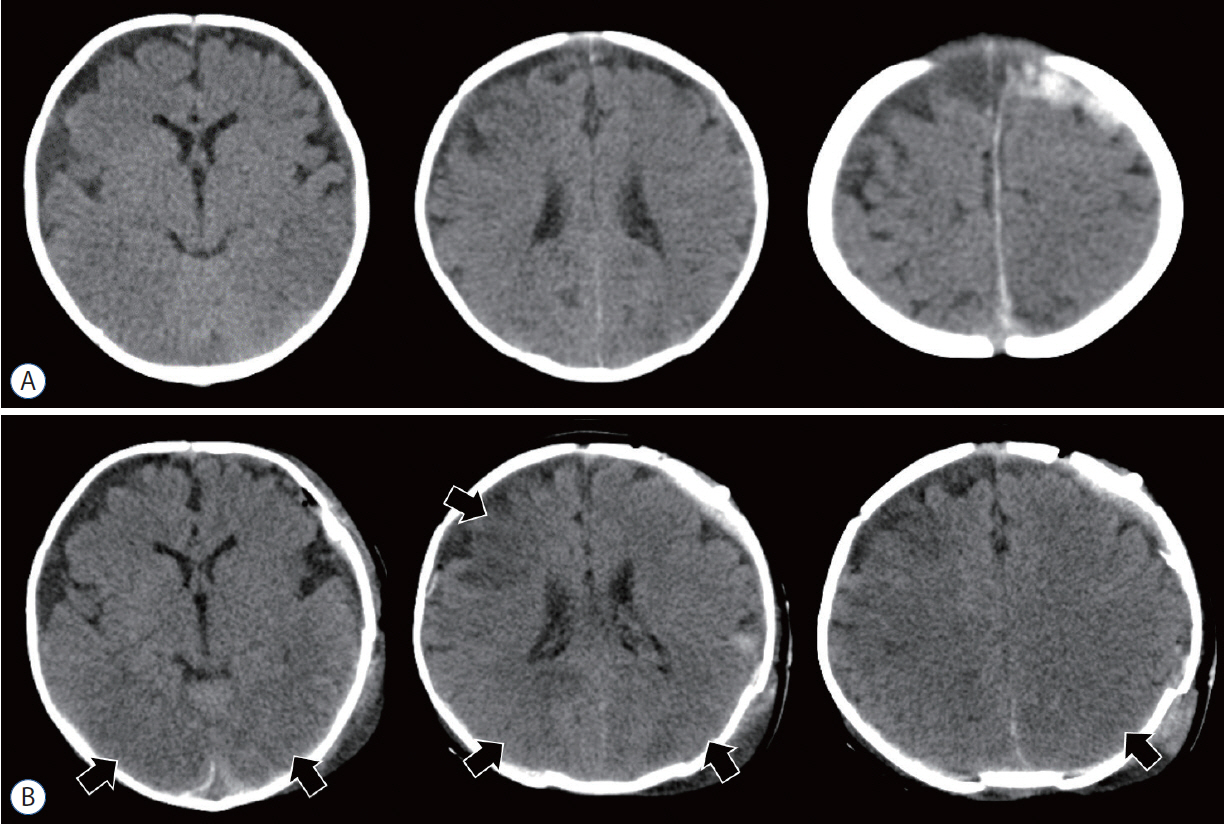
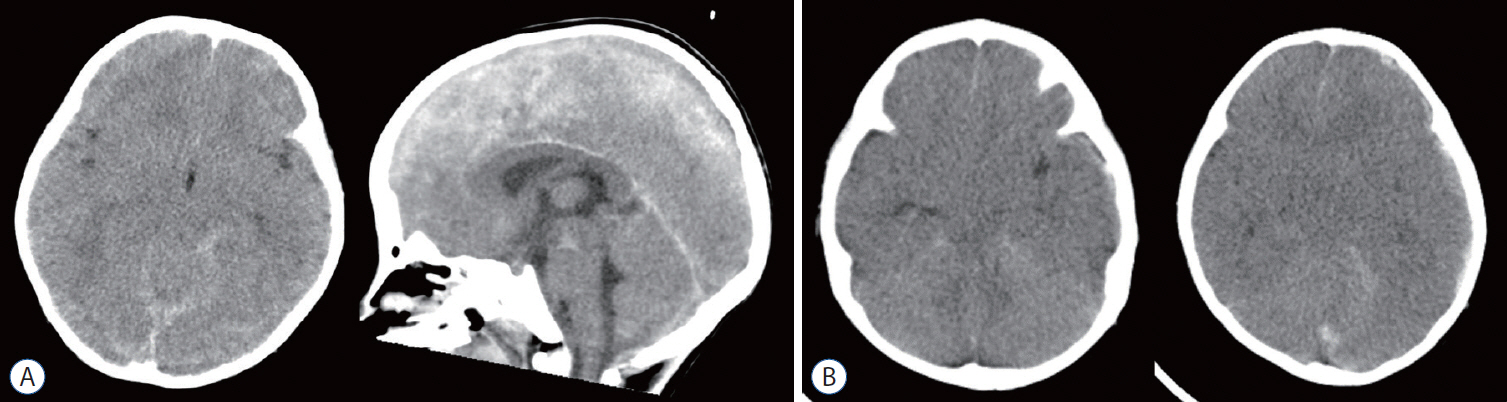
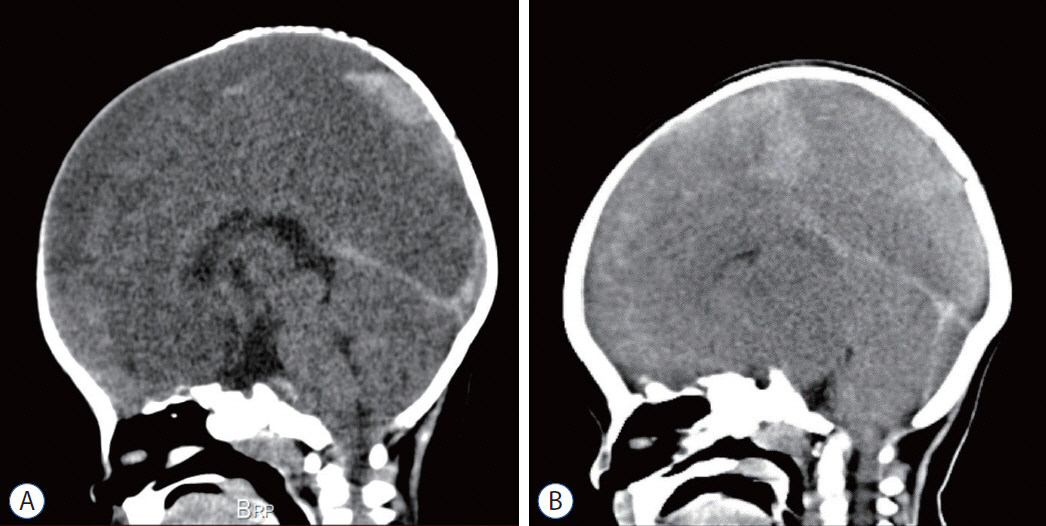
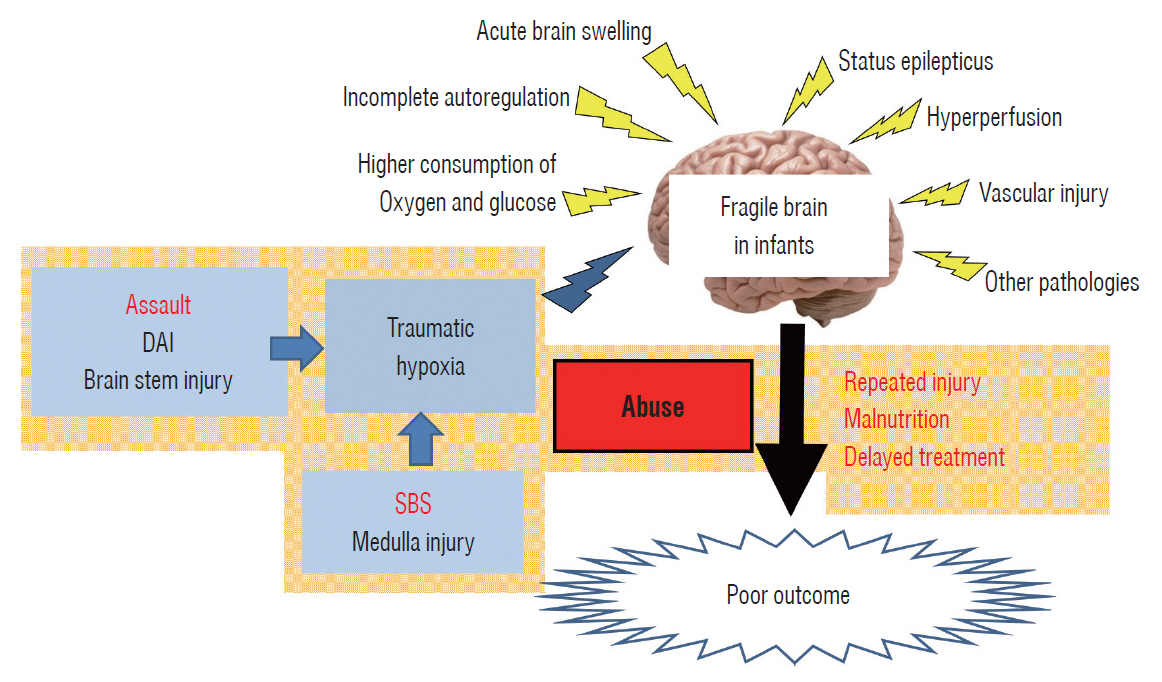
- Abusive head trauma (AHT) in infants, especially acute subdural hematoma, has an extremely poor outcome. The most decisive and important finding is the appearance of a widespread low-density area on head computed tomography. This phenomenon was traditionally thought to be caused by cerebral ischemia. However, many other pathophysiological abnormalities have been found to be intricately involved. Recent studies have found that status epilepticus and hyperperfusion injures are the major causes. Another serious problem associated with AHT is cardiopulmonary arrest (CPA). Many infants are reported to visit to the hospital with CPA, and its pathophysiology has not been fully elucidated. This paper examines the background of these pathological conditions and associated factors and elucidate the pathophysiological mechanisms resulting in poor outcomes in AHT. In addition to the intensity of assault on the head, the peculiar pathophysiological characteristics in infants, as well as the social background specific to child abuse, are found to be associated with poor outcome.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Abu Hamdeh S, Marklund N, Lewén A, Howells T, Raininko R, Wikström J, et al. Intracranial pressure elevations in diffuse axonal injury: association with nonhemorrhagic MR lesions in central mesencephalic structures. J Neurosurg. 131:604–611. 2018.
Article2. Adams JH, Doyle D, Ford I, Gennarelli TA, Graham DI, McLellan DR. Diffuse axonal injury in head injury: definition, diagnosis and grading. Histopathology. 15:49–59. 1989.
Article3. Adamsbaum C, Grabar S, Mejean N, Rey-Salmon C. Abusive head trauma: judicial admissions highlight violent and repetitive shaking. Pediatrics. 126:546–555. 2010.
Article4. Altman RL, Canter J, Patrick PA, Daley N, Butt NK, Brand DA. Parent education by maternity nurses and prevention of abusive head trauma. Pediatrics. 128:e1164–e1172. 2011.
Article5. Arndt DH, Lerner JT, Matsumoto JH, Madikians A, Yudovin S, Valino H, et al. Subclinical early posttraumatic seizures detected by continuous EEG monitoring in a consecutive pediatric cohort. Epilepsia. 54:1780–1788. 2013.
Article6. Brown RL, Brunn MA, Garcia VF. Cervical spine injuries in children: a review of 103 patients treated consecutively at a level 1 pediatric trauma center. J Pediatr Surg. 36:1107–1114. 2001.
Article7. Choudhary AK, Servaes S, Slovis TL, Palusci VJ, Hedlund GL, Narang SK, et al. Consensus statement on abusive head trauma in infants and young children. Pediatr Radiol. 48:1048–1065. 2018.
Article8. Christian CW, Block R; Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect; American Academy of Pediatrics. Abusive head trauma in infants and children. Pediatrics. 123:1409–1411. 2009.
Article9. Colombari M, Troakes C, Turrina S, Tagliaro F, De Leo D, Al-Sarraj S. Spinal cord injury as an indicator of abuse in forensic assessment of abusive head trauma (AHT). Int J Legal Med. 135:1481–1498. 2021.
Article10. Cordobes F, Lobato RD, Rivas JJ, Portillo JM, Sarabia M, Munoz MJ. Post-traumatic diffuse brain swelling: isolated or associated with cerebral axonal injury. Clinical course and intracranial pressure in 18 children. Childs Nerv Syst. 3:235–238. 1987.
Article11. Costine-Bartell BA, McGuone D, Price G, Crawford E, Keeley KL, Munoz-Pareja J, et al. Development of a model of hemispheric hypodensity ("big black brain"). J Neurotrauma. 36:815–833. 2019.
Article12. Dias MS, Rottmund CM, Cappos KM, Reed ME, Wang M, Stetter C, et al. Association of a postnatal parent education program for abusive head trauma with subsequent pediatric abusive head trauma hospitalization rates. JAMA Pediatr. 171:223–229. 2017.
Article13. Dias MS, Smith K, DeGuehery K, Mazur P, Li V, Shaffer ML. Preventing abusive head trauma among infants and young children: a hospital-based, parent education program. Pediatrics. 115:e470–e477. 2005.
Article14. Duhaime AC, Bilaniuk L, Zimmerman R. The “big black brain”: radiographic changes after severe inflicted head injury in infancy. J Neurotrauma. 10(Suppl 1):S59. 1993.15. Duhaime AC, Christian C, Moss E, Seidl T. Long-term outcome in infants with the shaking-impact syndrome. Pediatr Neurosurg. 24:292–298. 1996.
Article16. Duhaime AC, Christian CW. Abusive head trauma: evidence, obfuscation, and informed management. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 24:481–488. 2019.
Article17. Duhaime AC, Christian CW, Rorke LB, Zimmerman RA. Nonaccidental head injury in infants--the “shaken-baby syndrome”. N Engl J Med. 338:1822–1829. 1988.
Article18. Duhaime AC, Durham S. Traumatic brain injury in infants: the phenomenon of subdural hemorrhage with hemispheric hypodensity (“big black brain”). Prog Brain Res. 161:293–302. 2007.
Article19. Eder HG, Legat JA, Gruber W. Traumatic brain stem lesions in children. Childs Nerv Syst. 16:21–24. 2000.
Article20. Figueira Rodrigues Vieira G, Guedes Correa JF. Early computed tomography for acute post-traumatic diffuse axonal injury: a systematic review. Neuroradiology. 62:653–660. 2020.
Article21. Foster KA, Recker MJ, Lee PS, Bell MJ, Tyler-Kabara EC. Factors associated with hemispheric hypodensity after subdural hematoma following abusive head trauma in children. J Neurotrauma. 31:1625–1631. 2014.
Article22. Gennarelli TA, Thibault LE, Adams JH, Graham DI, Thompson CJ, Marcincin RP. Diffuse axonal injury and traumatic coma in the primate. Ann Neurol. 12:564–574. 1982.
Article23. Gerber P, Coffman K. Nonaccidental head trauma in infants. Childs Nerv Syst. 23:499–507. 2007.
Article24. Graupman P, Winston KR. Nonaccidental head trauma as a cause of childhood death. J Neurosurg. 104(4 Suppl):245–250. 2006.
Article25. Greeley CS. Abusive head trauma: a review of the evidence base. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 204:967–973. 2015.
Article26. Greiner MV, Greiner HM, Caré MM, Owens D, Shapiro R, Holland K. Adding insult to injury: nonconvulsive seizures in abusive head trauma. J Child Neurol. 30:1778–1784. 2015.27. Hasbani DM, Topjian AA, Friess SH, Kilbaugh TJ, Berg RA, Christian CW, et al. Nonconvulsive electrographic seizures are common in children with abusive head trauma*. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 14:709–715. 2013.
Article28. Karibe H, Kameyama M, Hayashi T, Narisawa A, Tominaga T. Acute subdural hematoma in infants with abusive head trauma: a literature review. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 56:264–273. 2016.
Article29. Khan NR, Fraser BD, Nguyen V, Moore K, Boop S, Vaughn BN, et al. Pediatric abusive head trauma and stroke. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 20:183–190. 2017.
Article30. Kim HJ. The prognostic factors related to traumatic brain stem injury. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 51:24–30. 2012.
Article31. Lee WJ, Lim YC, Yoon SH. Abusive head traumas in 4 infants. Korean J Neurotrauma. 16:246–253. 2020.
Article32. Mata-Mbemba D, Mugikura S, Nakagawa A, Murata T, Ishii K, Kushimoto S, et al. Traumatic midline subarachnoid hemorrhage on initial computed tomography as a marker of severe diffuse axonal injury. J Neurosurg. 129:1317–1324. 2018.
Article33. Mata-Mbemba D, Mugikura S, Nakagawa A, Murata T, Kato Y, Tatewaki Y, et al. Intraventricular hemorrhage on initial computed tomography as marker of diffuse axonal injury after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 32:359–365. 2015.
Article34. Moen KG, Brezova V, Skandsen T, Håberg AK, Folvik M, Vik A. Traumatic axonal injury: the prognostic value of lesion load in corpus callosum, brain stem, and thalamus in different magnetic resonance imaging sequences. J Neurotrauma. 31:1486–1496. 2014.
Article35. Narang SK, Estrada C, Greenberg S, Lindberg D. Acceptance of shaken baby syndrome and abusive head trauma as medical diagnoses. J Pediatr. 177:273–278. 2016.
Article36. Narang SK, Fingarson A, Lukefahr J; COUNCIL ON CHILD ABUSE AND NEGLECT. Abusive head trauma in infants and children. Pediatrics. 145:e20200203. 2020.
Article37. O'Neill BR, Handler MH, Tong S, Chapman KE. Incidence of seizures on continuous EEG monitoring following traumatic brain injury in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 16:167–176. 2015.38. Onuma T, Shimosegawa Y, Kameyama M, Arai H, Ishii K. Clinicopathological investigation of gyral high density on computerized tomography following severe head injury in children. J Neurosurg. 82:995–1001. 1995.
Article39. Paek D, Kwon DI. A review on four different paths to respiratory arrest from brain injury in children; implications for child abuse. J Forensic Leg Med. 71:101938. 2020.
Article40. Pang D. Spinal cord injury without radiographic abnormality in children, 2 decades later. Neurosurgery. 55:1325–1342. discussion 1342-1343. 2004.
Article41. Pang D, Wilberger JE Jr. Spinal cord injury without radiographic abnormalities in children. J Neurosurg. 57:114–129. 1982.
Article42. Piteau SJ, Ward MG, Barrowman NJ, Plint AC. Clinical and radiographic characteristics associated with abusive and nonabusive head trauma: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 130:315–323. 2012.
Article43. Rongchao S, Shudong Y, Zhiyi Z. Pathological and immunohistochemical study of lethal primary brain stem injuries. Diagn Pathol. 7:54. 2012.
Article44. Visocchi M, Chiaretti A, Genovese O, Di Rocco F. Haemodynamic patterns in children with posttraumatic diffuse brain swelling. A preliminary study in 6 cases with neuroradiological features consistent with diffuse axonal injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 149:347–356. 2007.
Article45. Wong AM, Yeh CH, Liu HL, Wu TW, Lin KL, Wang HS, et al. Arterial spin-labeling perfusion imaging of children with subdural hemorrhage: perfusion abnormalities in abusive head trauma. J Neuroradiol. 44:281–287. 2017.
Article46. Yokobori S, Nakae R, Yokota H, Spurlock MS, Mondello S, Gajavelli S, et al. Subdural hematoma decompression model: a model of traumatic brain injury with ischemic-reperfusional pathophysiology: a review of the literature. Behav Brain Res. 15:23–28. 2018.
Article47. Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT, Farina L. Non-accidental brain trauma in infants: diffusion imaging, contributions to understanding the injury process. J Neuroradiol. 34:109–114. 2007.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Abusive Head Trauma in Infants and Children in Japan
- Abusive Head Traumas in 4 Infants
- Imaging of Abusive Head Trauma : A Radiologists’ Perspective
- Awareness and Expectations of the Role of the Neurotrauma Society about Child Abuse: Abusive Head Traumas in 4 Infants, Case Series
- Ophthalmic Findings of Abusive Head Trauma in Korea from a Single-large Trauma Center, 2011-2022