J Rheum Dis.
2022 Apr;29(2):61-70. 10.4078/jrd.2022.29.2.61.
Recent Advances in Basic and Clinical Aspects of Rheumatoid Arthritis-associated Interstitial Lung Diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea
- KMID: 2527544
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2022.29.2.61
Abstract
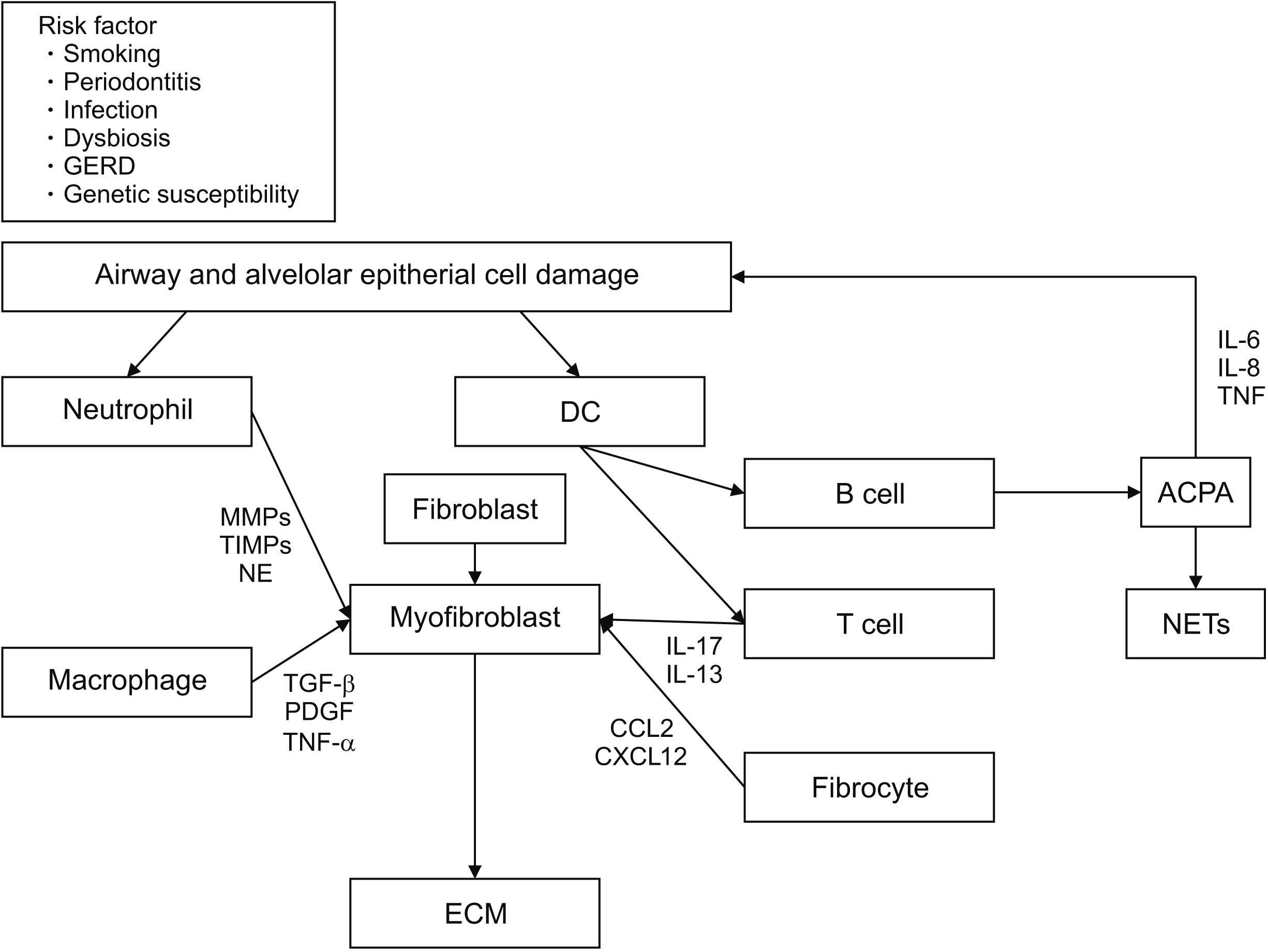
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common autoimmune disease that mainly affects the joints and systemic organs, such as the skin, eyes, heart, gastrointestinal tract, and lungs. In particular, among various pulmonary involvements, interstitial lung disease (ILD) is closely related to the selection of anti-rheumatic drugs and the long-term prognosis of patients with RA. Although the exact pathogenesis of RA-ILD is not well defined, several mechanistic pathways, similar to those of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, have been elucidated recently. Conversely, RA-related autoantibodies, including anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody, are detectable in circulation and in the lungs, even in the absence of articular symptoms. RA-ILD can also predate years before the occurrence of joint symptoms. This evidence supports the fact that local dysregulated mucosal immunity in the lung causes systemic autoimmunity, resulting in clinically evident polyarthritis of RA. Because the early diagnosis of RA-ILD is important, imaging tests, such as computed tomography and pulmonary function tests, are being used for early diagnosis, but there is no clear guideline for the early diagnosis of RA-ILD and selection of optimal disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs for the treatment of patients with RA with ILD. In addition, the efficacy of nintedanib, a new anti-fibrotic agent, for RA-ILD treatment, has been investigated recently. This review collectively discusses the basic and clinical aspects, such as pathogenesis, animal models, diagnosis, and treatment, of RA-ILD.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cassone G, Manfredi A, Vacchi C, Luppi F, Coppi F, Salvarani C, et al. 2020; Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: lights and shadows. J Clin Med. 9:1082. DOI: 10.3390/jcm9041082. PMID: 32290218. PMCID: PMC7230307.
Article2. Myasoedova E, Crowson CS, Turesson C, Gabriel SE, Matteson EL. 2011; Incidence of extraarticular rheumatoid arthritis in Olmsted County, Minnesota, in 1995-2007 versus 1985-1994: a population-based study. J Rheumatol. 38:983–9. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.101133. PMID: 21459933. PMCID: PMC3193155.
Article3. Yunt ZX, Solomon JJ. 2015; Lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 41:225–36. DOI: 10.1016/j.rdc.2014.12.004. PMID: 25836639. PMCID: PMC4415514.
Article4. Lee H, Choi HN, Kim SH, Kim JH, Park SH, Kim SK, et al. 2013; Prognostic factors of the RA patients with ILD. J Rheum Dis. 20:9–16. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2013.20.1.9.
Article5. Bendstrup E, Møller J, Kronborg-White S, Prior TS, Hyldgaard C. 2019; Interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis remains a challenge for clinicians. J Clin Med. 8:2038. DOI: 10.3390/jcm8122038. PMID: 31766446. PMCID: PMC6947091.
Article6. Wang D, Zhang J, Lau J, Wang S, Taneja V, Matteson EL, et al. 2019; Mechanisms of lung disease development in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 15:581–96. DOI: 10.1038/s41584-019-0275-x. PMID: 31455869.
Article7. Karlson EW, Chang SC, Cui J, Chibnik LB, Fraser PA, De Vivo I, et al. 2010; Gene-environment interaction between HLA-DRB1 shared epitope and heavy cigarette smoking in predicting incident rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 69:54–60. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2008.102962. PMID: 19151010. PMCID: PMC2952498.
Article8. Juge PA, Lee JS, Ebstein E, Furukawa H, Dobrinskikh E, Gazal S, et al. 2018; MUC5B promoter variant and rheumatoid arthritis with interstitial lung disease. N Engl J Med. 379:2209–19. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1801562. PMID: 30345907. PMCID: PMC6371965.9. Denneny E, Sahota J, Beatson R, Thornton D, Burchell J, Porter J. 2020; Mucins and their receptors in chronic lung disease. Clin Transl Immunology. 9:e01120. DOI: 10.1002/cti2.1120. PMID: 32194962. PMCID: PMC7077995.
Article10. Holers VM, Demoruelle MK, Kuhn KA, Buckner JH, Robinson WH, Okamoto Y, et al. 2018; Rheumatoid arthritis and the mucosal origins hypothesis: protection turns to destruction. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 14:542–57. DOI: 10.1038/s41584-018-0070-0. PMID: 30111803. PMCID: PMC6704378.
Article11. Wells AU, Denton CP. 2014; Interstitial lung disease in connective tissue disease--mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:728–39. DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.149. PMID: 25266451.
Article12. Kolahian S, Fernandez IE, Eickelberg O, Hartl D. 2016; Immune mechanisms in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 55:309–22. DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0121TR. PMID: 27149613.
Article13. Kinder BW, Brown KK, Schwarz MI, Ix JH, Kervitsky A, King TE Jr. 2008; Baseline BAL neutrophilia predicts early mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 133:226–32. DOI: 10.1378/chest.07-1948. PMID: 18071016.
Article14. Wynn TA. 2011; Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. J Exp Med. 208:1339–50. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20110551. PMID: 21727191. PMCID: PMC3136685.
Article15. Lo Re S, Dumoutier L, Couillin I, Van Vyve C, Yakoub Y, Uwambayinema F, et al. 2010; IL-17A-producing gammadelta T and Th17 lymphocytes mediate lung inflammation but not fibrosis in experimental silicosis. J Immunol. 184:6367–77. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900459. PMID: 20421647.16. Mi S, Li Z, Yang HZ, Liu H, Wang JP, Ma YG, et al. 2011; Blocking IL-17A promotes the resolution of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis via TGF-beta1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Immunol. 187:3003–14. Erratum. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1004081. PMID: 21841134.17. Simonian PL, Roark CL, Wehrmann F, Lanham AK, Born WK, et al. Diaz del Valle F. 2009; Th17-polarized immune response in a murine model of hypersensitivity pneumonitis and lung fibrosis. J Immunol. 182:657–65. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.1.657. PMID: 19109199.
Article18. Chen Y, Li C, Weng D, Song L, Tang W, Dai W, et al. 2014; Neutralization of interleukin-17A delays progression of silica-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in C57BL/6 mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 275:62–72. DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.11.012. PMID: 24291675.
Article19. Galati D, De Martino M, Trotta A, Rea G, Bruzzese D, Cicchitto G, et al. 2014; Peripheral depletion of NK cells and imbalance of the Treg/Th17 axis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. Cytokine. 66:119–26. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.12.003. PMID: 24418172.
Article20. Kotsianidis I, Nakou E, Bouchliou I, Tzouvelekis A, Spanoudakis E, Steiropoulos P, et al. 2009; Global impairment of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 179:1121–30. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200812-1936OC. PMID: 19342412.
Article21. Fernandez IE, Eickelberg O. 2012; New cellular and molecular mechanisms of lung injury and fibrosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 380:680–8. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61144-1.
Article22. Moore BB, Murray L, Das A, Wilke CA, Herrygers AB, Toews GB. 2006; The role of CCL12 in the recruitment of fibrocytes and lung fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 35:175–81. DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0239OC. PMID: 16543609. PMCID: PMC2643255.
Article23. Cavagna L, Monti S, Grosso V, Boffini N, Scorletti E, Crepaldi G, et al. 2013; The multifaceted aspects of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2013:759760. DOI: 10.1155/2013/759760. PMID: 24205507. PMCID: PMC3800606.
Article24. Kurowska W, Kuca-Warnawin EH, Radzikowska A, Maśliński W. 2017; The role of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Cent Eur J Immunol. 42:390–8. DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2017.72807. PMID: 29472818. PMCID: PMC5820977.
Article25. Catrina AI, Ytterberg AJ, Reynisdottir G, Malmström V, Klareskog L. 2014; Lungs, joints and immunity against citrullinated proteins in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:645–53. DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.115. PMID: 25072264.
Article26. Audiger C, Rahman MJ, Yun TJ, Tarbell KV, Lesage S. 2017; The importance of dendritic cells in maintaining immune tolerance. J Immunol. 198:2223–31. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601629. PMID: 28264998. PMCID: PMC5343761.
Article27. Klareskog L, Stolt P, Lundberg K, Källberg H, Bengtsson C, Grunewald J, et al. 2006; A new model for an etiology of rheumatoid arthritis: smoking may trigger HLA-DR (shared epitope)-restricted immune reactions to autoantigens modified by citrullination. Arthritis Rheum. 54:38–46. DOI: 10.1002/art.21575. PMID: 16385494.
Article28. Rangel-Moreno J, Hartson L, Navarro C, Gaxiola M, Selman M, Randall TD. 2006; Inducible bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue (iBALT) in patients with pulmonary complications of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 116:3183–94. DOI: 10.1172/JCI28756. PMID: 17143328. PMCID: PMC1678820.
Article29. Reynisdottir G, Karimi R, Joshua V, Olsen H, Hensvold AH, Harju A, et al. 2014; Structural changes and antibody enrichment in the lungs are early features of anti-citrullinated protein antibody-positive rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:31–9. DOI: 10.1002/art.38201. PMID: 24449573.
Article30. Willis VC, Demoruelle MK, Derber LA, Chartier-Logan CJ, Parish MC, Pedraza IF, et al. 2013; Sputum autoantibodies in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis and subjects at risk of future clinically apparent disease. Arthritis Rheum. 65:2545–54. DOI: 10.1002/art.38066. PMID: 23817979. PMCID: PMC4066465.31. Kim JW, Lee H, Hwang JH, Park SH, Lee HS, Kim SK, et al. 2016; Factors associated with airway disease and interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheum Dis. 23:101–8. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2016.23.2.101.
Article32. Monach P, Hattori K, Huang H, Hyatt E, Morse J, Nguyen L, et al. 2007; The K/BxN mouse model of inflammatory arthritis: theory and practice. Methods Mol Med. 136:269–82. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-59745-402-5_20. PMID: 17983155.33. Shilling RA, Williams JW, Perera J, Berry E, Wu Q, Cummings OW, et al. 2013; Autoreactive T and B cells induce the development of bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue in the lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 48:406–14. DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0065OC. PMID: 23371062. PMCID: PMC3653607.
Article34. Wiest DL, Ashe JM, Howcroft TK, Lee HM, Kemper DM, Negishi I, et al. 1997; A spontaneously arising mutation in the DLAARN motif of murine ZAP-70 abrogates kinase activity and arrests thymocyte development. Immunity. 6:663–71. DOI: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80442-2.
Article35. Yoshitomi H, Sakaguchi N, Kobayashi K, Brown GD, Tagami T, Sakihama T, et al. 2005; A role for fungal {beta}-glucans and their receptor Dectin-1 in the induction of autoimmune arthritis in genetically susceptible mice. J Exp Med. 201:949–60. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20041758. PMID: 15781585. PMCID: PMC2213107.36. Keith RC, Powers JL, Redente EF, Sergew A, Martin RJ, Gizinski A, et al. 2012; A novel model of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease in SKG mice. Exp Lung Res. 38:55–66. DOI: 10.3109/01902148.2011.636139. PMID: 22185348.
Article37. Redente EF, Aguilar MA, Black BP, Edelman BL, Bahadur AN, Humphries SM, et al. 2018; Nintedanib reduces pulmonary fibrosis in a model of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 314:L998–1009. DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00304.2017. PMID: 29543042. PMCID: PMC6335004.
Article38. Keith RC, Sokolove J, Edelman BL, Lahey L, Redente EF, Holers VM, et al. 2013; Testosterone is protective in the sexually dimorphic development of arthritis and lung disease in SKG mice. Arthritis Rheum. 65:1487–93. DOI: 10.1002/art.37943. PMID: 23529475. PMCID: PMC3672393.39. Brand DD, Latham KA, Rosloniec EF. 2007; Collagen-induced arthritis. Nat Protoc. 2:1269–75. DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2007.173. PMID: 17546023.
Article40. Schurgers E, Mertens F, Vanoirbeek JA, Put S, Mitera T, De Langhe E, et al. 2012; Pulmonary inflammation in mice with collagen-induced arthritis is conditioned by complete Freund's adjuvant and regulated by endogenous IFN-γ. Eur J Immunol. 42:3223–34. DOI: 10.1002/eji.201242573. PMID: 22930199.
Article41. Sato T, Satooka H, Ichioka S, Maruo Y, Hirata T. 2020; Citrullinated fibrinogen is a target of auto-antibodies in interstitial lung disease in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Int Immunol. 32:533–45. DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxaa021. PMID: 32239143.
Article42. Poole JA, Thiele GM, Janike K, Nelson AJ, Duryee MJ, Rentfro K, et al. 2019; Combined collagen-induced arthritis and organic dust-induced airway inflammation to model inflammatory lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Miner Res. 34:1733–43. DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.3745. PMID: 30995344. PMCID: PMC6744331.
Article43. Gao B, Lin J, Jiang Z, Yang Z, Yu H, Ding L, et al. 2018; Upregulation of chemokine CXCL10 enhances chronic pulmonary inflammation in tree shrew collagen-induced arthritis. Sci Rep. 8:9993. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28404-y. PMID: 29968810. PMCID: PMC6030082.
Article44. Correia CS, Briones MR, Guo R, Ostrowski RA. 2019; Elevated anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody titer is associated with increased risk for interstitial lung disease. Clin Rheumatol. 38:1201–6. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-018-04421-0. PMID: 30645754. PMCID: PMC8166218.
Article45. Zhu J, Zhou Y, Chen X, Li J. 2014; A metaanalysis of the increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis-related pulmonary disease as a result of serum anticitrullinated protein antibody positivity. J Rheumatol. 41:1282–9. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.131341. PMID: 24882837.
Article46. Kelly CA, Saravanan V, Nisar M, Arthanari S, Woodhead FA, Price-Forbes AN, et al. 2014; Rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: associations, prognostic factors and physiological and radiological characteristics--a large multicentre UK study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 53:1676–82. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu165. PMID: 24758887.
Article47. Kiely P, Busby AD, Nikiphorou E, Sullivan K, Walsh DA, Creamer P, et al. 2019; Is incident rheumatoid arthritis interstitial lung disease associated with methotrexate treatment? Results from a multivariate analysis in the ERAS and ERAN inception cohorts. BMJ Open. 9:e028466. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028466. PMID: 31061059. PMCID: PMC6501950.
Article48. Huang S, Kronzer VL, Dellaripa PF, Deane KD, Bolster MB, Nagaraja V, et al. 2020; Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: current update on prevalence, risk factors, and pharmacologic treatment. Curr Treatm Opt Rheumatol. 6:337–53. DOI: 10.1007/s40674-020-00160-z. PMID: 33282632. PMCID: PMC7709915.
Article49. Dai Y, Wang W, Yu Y, Hu S. 2021; Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: an overview of epidemiology, pathogenesis and management. Clin Rheumatol. 40:1211–20. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-020-05320-z. PMID: 32794076.
Article50. Hamblin MJ, Horton MR. 2011; Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: diagnostic dilemma. Pulm Med. 2011:872120. DOI: 10.1155/2011/872120. PMID: 21660199. PMCID: PMC3109679.
Article51. Morrison SC, Mody GM, Benatar SR, Meyers OL. 1996; The lungs in rheumatoid arthritis--a clinical, radiographic and pulmonary function study. S Afr Med J. 86:829–33.52. Walker WC, Wright V. 1968; Pulmonary lesions and rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 47:501–20. DOI: 10.1097/00005792-196811000-00003. PMID: 5727884.
Article53. Dawson JK, Fewins HE, Desmond J, Lynch MP, Graham DR. 2001; Fibrosing alveolitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis as assessed by high resolution computed tomography, chest radiography, and pulmonary function tests. Thorax. 56:622–7. DOI: 10.1136/thx.56.8.622. PMID: 11462065. PMCID: PMC1746113.
Article54. Kim EJ, Collard HR, King TE Jr. 2009; Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: the relevance of histopathologic and radiographic pattern. Chest. 136:1397–405. DOI: 10.1378/chest.09-0444. PMID: 19892679. PMCID: PMC2818853.
Article55. Volpicelli G, Elbarbary M, Blaivas M, Lichtenstein DA, Mathis G, Kirkpatrick AW, et al. 2012; International evidence-based recommendations for point-of-care lung ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 38:577–91. DOI: 10.1007/s00134-012-2513-4. PMID: 22392031.
Article56. Manfredi A, Cassone G, Cerri S, Venerito V, Fedele AL, Trevisani M, et al. 2019; Diagnostic accuracy of a velcro sound detector (VECTOR) for interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis patients: the InSPIRAtE validation study (INterStitial pneumonia in rheumatoid ArThritis with an electronic device). BMC Pulm Med. 19:111. DOI: 10.1186/s12890-019-0875-x. PMID: 31221137. PMCID: PMC6587236.
Article57. Moon J, Lee JS, Yoon YI, Chang SH, Lee YA, Ha YJ, et al. Study Group, Korean Rheumatoid Arthritis Interstitial Lung Disease (KORAIL). 2021; Association of serum biomarkers with pulmonary involvement of rheumatoid arthritis interstitial lung disease: from KORAIL cohort baseline data. J Rheum Dis. 28:234–41. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.4.234.
Article58. Inui N, Enomoto N, Suda T, Kageyama Y, Watanabe H, Chida K. 2008; Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in lung diseases associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Biochem. 41:1074–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2008.06.014. PMID: 18638466.
Article59. Chen J, Doyle TJ, Liu Y, Aggarwal R, Wang X, Shi Y, et al. 2015; Biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67:28–38. DOI: 10.1002/art.38904. PMID: 25302945. PMCID: PMC4624107.
Article60. Juge PA, Crestani B, Dieudé P. 2020; Recent advances in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 26:477–86. DOI: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000000710. PMID: 32701675.
Article61. Conway R, Nikiphorou E. 2020; Treating interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis - the embers of hope. Rheumatology (Oxford). 59:3589–90. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa516. PMID: 33068432.
Article62. Fragoulis GE, Nikiphorou E, Larsen J, Korsten P, Conway R. 2019; Methotrexate-associated pneumonitis and rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease: current concepts for the diagnosis and treatment. Front Med (Lausanne). 6:238. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00238. PMID: 31709258. PMCID: PMC6819370.
Article63. Gabbay E, Tarala R, Will R, Carroll G, Adler B, Cameron D, et al. 1997; Interstitial lung disease in recent onset rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 156(2 Pt 1):528–35. DOI: 10.1164/ajrccm.156.2.9609016. PMID: 9279235.
Article64. Lee HK, Kim DS, Yoo B, Seo JB, Rho JY, Colby TV, et al. 2005; Histopathologic pattern and clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Chest. 127:2019–27. DOI: 10.1378/chest.127.6.2019. PMID: 15947315.
Article65. Olson AL, Swigris JJ, Sprunger DB, Fischer A, Fernandez-Perez ER, Solomon J, et al. 2011; Rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease-associated mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 183:372–8. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201004-0622OC. PMID: 20851924. PMCID: PMC5450769.
Article66. Fragoulis GE, Conway R, Nikiphorou E. 2019; Methotrexate and interstitial lung disease: controversies and questions. A narrative review of the literature. Rheumatology (Oxford). 58:1900–6. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez337. PMID: 31504978.
Article67. Dawson JK, Quah E, Earnshaw B, Amoasii C, Mudawi T, Spencer LG. 2021; Does methotrexate cause progressive fibrotic interstitial lung disease? A systematic review. Rheumatol Int. 41:1055–64. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-020-04773-4. PMID: 33515067. PMCID: PMC8079289.
Article68. Druce KL, Iqbal K, Watson KD, Symmons DPM, Hyrich KL, Kelly C. 2017; Mortality in patients with interstitial lung disease treated with rituximab or TNFi as a first biologic. RMD Open. 3:e000473. DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000473. PMID: 28955489. PMCID: PMC5604605.
Article69. Md Yusof MY, Kabia A, Darby M, Lettieri G, Beirne P, Vital EM, et al. 2017; Effect of rituximab on the progression of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: 10 years' experience at a single centre. Rheumatology (Oxford). 56:1348–57. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex072. PMID: 28444364. PMCID: PMC5850796.
Article70. Vadillo C, Nieto MA, Romero-Bueno F, Leon L, Sanchez-Pernaute O, Rodriguez-Nieto MJ, et al. 2020; Efficacy of rituximab in slowing down progression of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: data from the NEREA Registry. Rheumatology (Oxford). 59:2099–108. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez673. PMID: 31990338.
Article71. Cassone G, Manfredi A, Atzeni F, Venerito V, Vacchi C, Picerno V, et al. 2020; Safety of abatacept in Italian patients with rheumatoid arthritis and interstitial lung disease: a multicenter retrospective study. J Clin Med. 9:277. DOI: 10.3390/jcm9010277. PMID: 31963908. PMCID: PMC7019755.
Article72. Fernández-Díaz C, Loricera J, Castañeda S, López-Mejías R, Ojeda-García C, Olivé A, et al. 2018; Abatacept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and interstitial lung disease: a national multicenter study of 63 patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 48:22–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2017.12.012. PMID: 29422324.
Article73. Mena-Vázquez N, Godoy-Navarrete FJ, Manrique-Arija S, Aguilar-Hurtado MC, Romero-Barco CM, Ureña-Garnica I, et al. 2021; Non-anti-TNF biologic agents are associated with slower worsening of interstitial lung disease secondary to rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 40:133–42. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-020-05227-9. PMID: 32557255.
Article74. Manfredi A, Cassone G, Furini F, Gremese E, Venerito V, Atzeni F, et al. 2020; Tocilizumab therapy in rheumatoid arthritis with interstitial lung disease: a multicentre retrospective study. Intern Med J. 50:1085–90. DOI: 10.1111/imj.14670. PMID: 31661185.
Article75. Wells AU, Flaherty KR, Brown KK, Inoue Y, Devaraj A, Richeldi L, et al. 2020; Nintedanib in patients with progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases-subgroup analyses by interstitial lung disease diagnosis in the INBUILD trial: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Lancet Respir Med. 8:453–60. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30036-9.76. Solomon JJ, Danoff SK, Goldberg HJ, Woodhead F, Kolb M, Chambers DC, et al. 2019; The design and rationale of the Trail1 trial: a randomized double-blind phase 2 clinical trial of pirfenidone in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Adv Ther. 36:3279–87. DOI: 10.1007/s12325-019-01086-2. PMID: 31515704.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Comparision of the Clinical, Laboratory and Radiologic Factors in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with or Without Interstitial Lung Disease
- New Diagnostic and Classification Criteria of Chronic Pain Diseases: Rheumatoid Arthritis, Fibromyalgia and Spondylarthritis
- A Case of Methotrexate: Associated Interstitial Pneumonitis in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Recurrent Pneumothorax after Etanercept Therapy in a Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient: A Case Report
- A Case of Lung Involvement Associated with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis