Chonnam Med J.
2014 Dec;50(3):115-118. 10.4068/cmj.2014.50.3.115.
Recurrent Pneumothorax after Etanercept Therapy in a Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Rheumatology, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Asan, Korea. spring0107@naver.com
- KMID: 2172156
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2014.50.3.115
Abstract
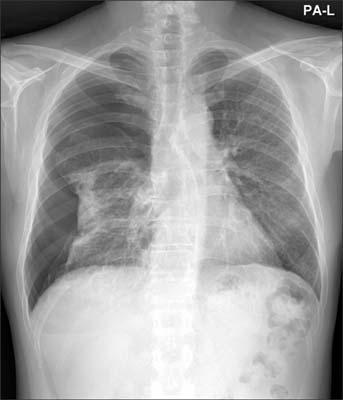
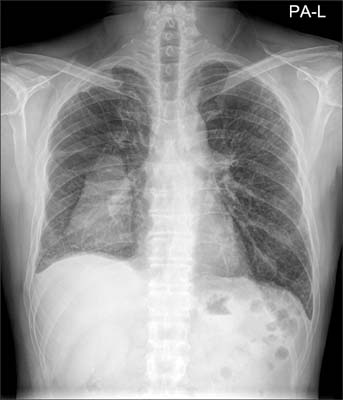
- The use of anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) agents for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients who are refractory to disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs is gradually increasing. Etanercept is the first anti-TNF agent to be approved for RA treatment and is also the most widely used. However, aggravation of interstitial lung disease after etanercept treatment in RA patients has been reported recently. We report the first case of recurrent spontaneous pneumothorax with progression of interstitial lung disease after initiating etanercept therapy. The withdrawal of etanercept and a change to adalimumab, a different class of TNF inhibitor, achieved clinical stabilization.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jarvis B, Faulds D. Etanercept: a review of its use in rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs. 1999; 57:945–966.2. Piguet PF, Vesin C. Treatment by human recombinant soluble TNF receptor of pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin or silica in mice. Eur Respir J. 1994; 7:515–518.
Article3. Peno-Green L, Lluberas G, Kingsley T, Brantley S. Lung injury linked to etanercept therapy. Chest. 2002; 122:1858–1860.
Article4. Hagiwara K, Sato T, Takagi-Kobayashi S, Hasegawa S, Shigihara N, Akiyama O. Acute exacerbation of preexisting interstitial lung disease after administration of etanercept for rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2007; 34:1151–1154.5. Fries JF, Williams CA, Morfeld D, Singh G, Sibley J. Reduction in long-term disability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis by disease-modifying antirheumatic drug-based treatment strategies. Arthritis Rheum. 1996; 39:616–622.
Article6. Hadjinicolaou AV, Nisar MK, Bhagat S, Parfrey H, Chilvers ER, Ostör AJ. Non-infectious pulmonary complications of newer biological agents for rheumatic diseases--a systematic literature review. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011; 50:2297–2305.
Article7. Khasnis AA, Calabrese LH. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and lung disease: a paradox of efficacy and risk. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 40:147–163.
Article8. Thavarajah K, Wu P, Rhew EJ, Yeldandi AK, Kamp DW. Pulmonary complications of tumor necrosis factor-targeted therapy. Respir Med. 2009; 103:661–669.
Article9. Morjaria JB, Chauhan AJ, Babu KS, Polosa R, Davies DE, Holgate ST. The role of a soluble TNFalpha receptor fusion protein (etanercept) in corticosteroid refractory asthma: a double blind, randomised, placebo controlled trial. Thorax. 2008; 63:584–591.
Article10. Allen JT, Spiteri MA. Growth factors in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: relative roles. Respir Res. 2002; 3:13.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Etanercept-related Cutaneous Nodulosis in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis with Secondary Amyloidosis and Chronic Kidney Disease with a Good Response to Etanercept
- Etanercept-Induced Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- A case of encephalitis in a juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patient treated with etanercept
- A Case of Tuberculous Arthritis Following the Use of Etanercept