Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2022 Feb;15(1):91-99. 10.21053/ceo.2021.01459.
Effectiveness of Intratympanic Dexamethasone Injection for Tinnitus Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Kroea
- 3Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chonbuk National University-Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- KMID: 2527117
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2021.01459
Abstract
Objectives
. Intratympanic dexamethasone injection (ITDI) has been introduced as a treatment option for subjective tinnitus. However, the effects of ITDI on patients with tinnitus remain unclear. In the present systematic review and metaanalysis, we evaluated the effectiveness of ITDI for tinnitus treatment.
Methods
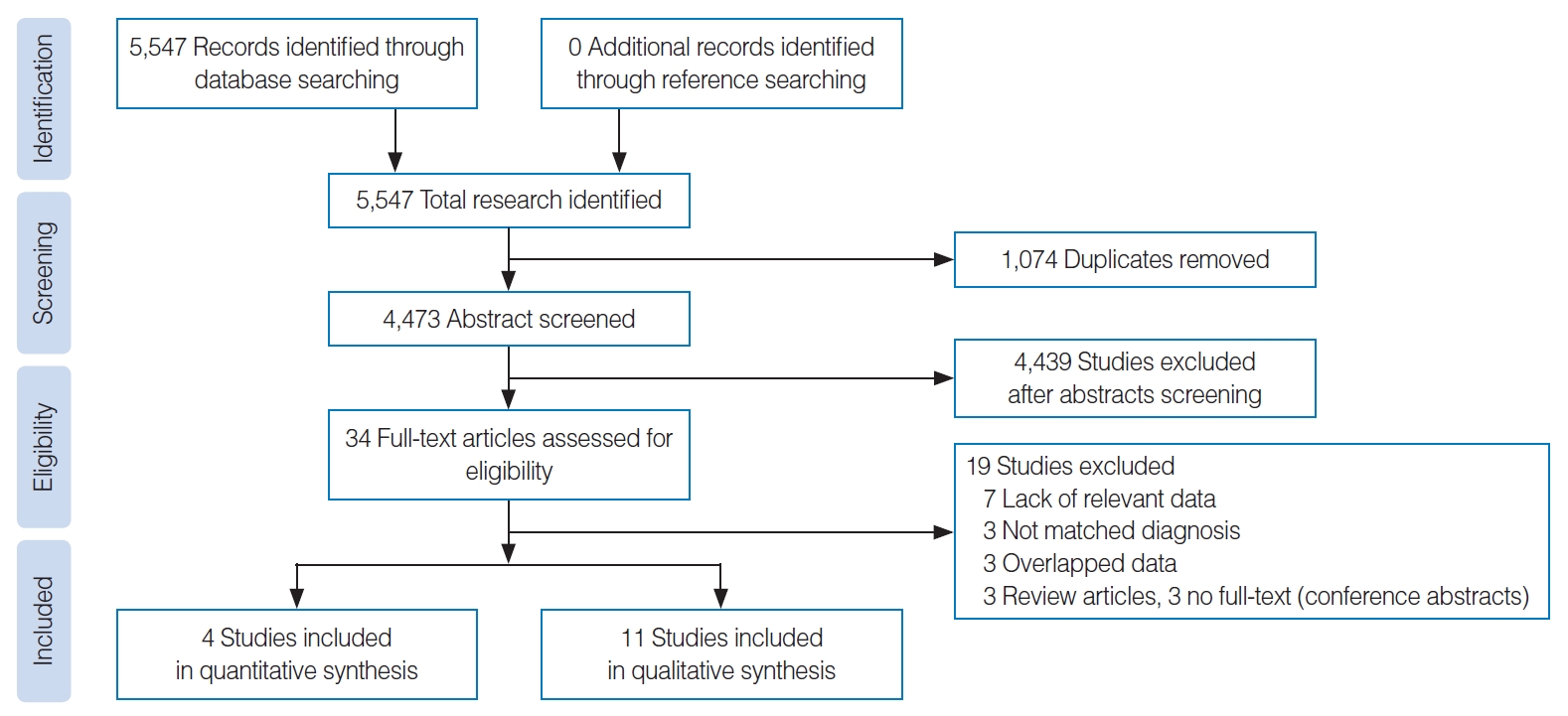
. We searched Medline, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and Embase. Four double-blind randomized controlled trials that tested the efficacy of ITDI compared with a placebo were deemed eligible for a quantitative meta-analysis, while four prospective studies and seven retrospective studies reporting the effectiveness of ITDI on tinnitus treatment were included in a qualitative synthesis.
Results
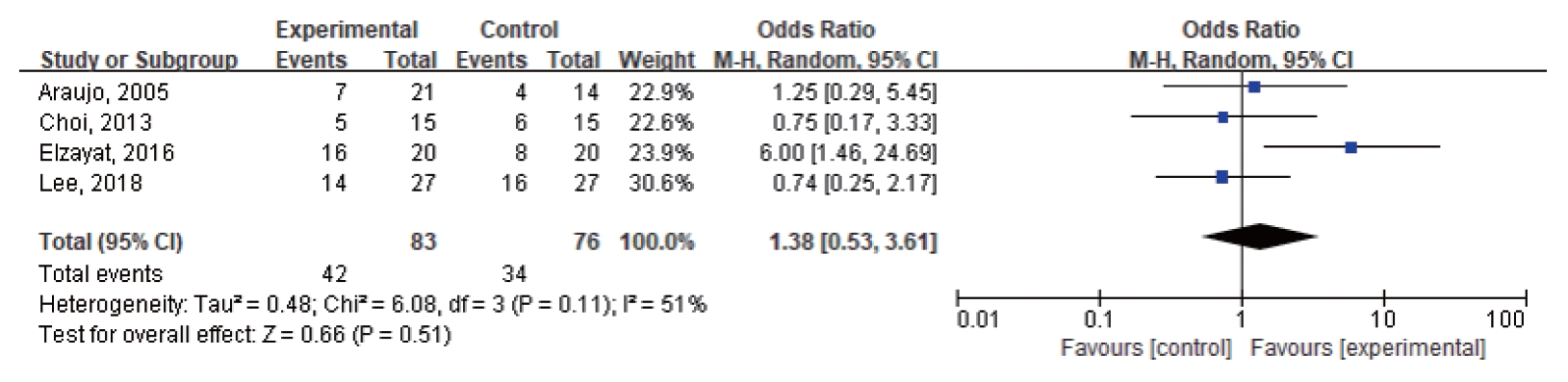
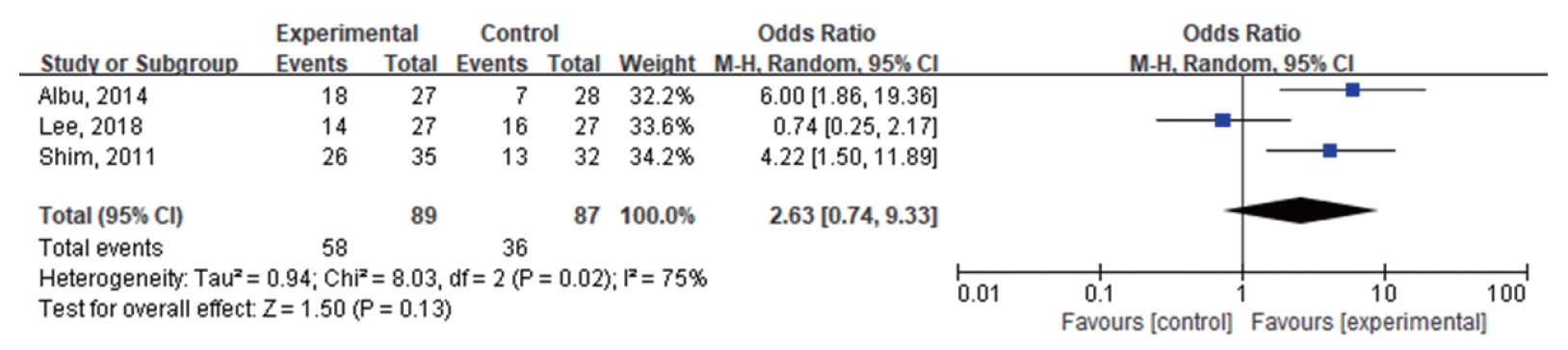
. In the four studies included in the quantitative meta-analysis, ITDI did not show evidence of tinnitus improvement compared with placebo (odds ratio [OR], 1.38; 95% confidence interval, 0.53–3.61). In the 11 studies included in the qualitative synthesis, seven retrospective studies without controls reported rates of tinnitus improvement after ITDI ranging from 35.9% to 91.3%. In the four prospective studies with controls, ITDI seemed to be effective when combined with other drugs for tinnitus treatment.
Conclusion
. ITDI alone did not show a significant effect for treating tinnitus compared with placebo. However, the potential of combination treatment of ITDI with other drugs for tinnitus therapy should be further studied in more systematic research.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cima RF, Mazurek B, Haider H, Kikidis D, Lapira A, Norena A, et al. A multidisciplinary European guideline for tinnitus: diagnostics, assessment, and treatment. HNO. 2019; Mar. 67(Suppl 1):10–42.
Article2. Haider HF, Bojic T, Ribeiro SF, Paco J, Hall DA, Szczepek AJ. Pathophysiology of subjective tinnitus: triggers and maintenance. Front Neurosci. 2018; Nov. 12:866.
Article3. Tunkel DE, Bauer CA, Sun GH, Rosenfeld RM, Chandrasekhar SS, Cunningham ER Jr, et al. Clinical practice guideline: tinnitus. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014; Oct. 151(2 Suppl):S1–S40.4. Levine RA. Somatic (craniocervical) tinnitus and the dorsal cochlear nucleus hypothesis. Am J Otolaryngol. 1999; Nov-Dec. 20(6):351–62.
Article5. Sakata E, Itoh A, Ohtsu K, Nakazawa H, Noguchi T. Treatment of cochlear tinnitus: effect of transtympanic infusion with dexamesasone fluid. Audiol Japan. 1983; 26(2):148–51.6. Shulman A, Goldstein B. Intratympanic drug therapy with steroids for tinnitus control: a preliminary report. Int Tinnitus J. 2000; 6(1):10–20.7. Araujo MF, Oliveira CA, Bahmad FM Jr. Intratympanic dexamethasone injections as a treatment for severe, disabling tinnitus: does it work. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005; Feb. 131(2):113–7.
Article8. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; Jul. 6(7):e1000097.
Article9. Choi SJ, Lee JB, Lim HJ, In SM, Kim JY, Bae KH, et al. Intratympanic dexamethasone injection for refractory tinnitus: prospective placebo-controlled study. Laryngoscope. 2013; Nov. 123(11):2817–22.
Article10. Elzayat S, El-Sherif H, Hegazy H, Gabr T, El-Tahan AR. Tinnitus: evaluation of intratympanic injection of combined lidocaine and corticosteroids. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2016; Jun. 78(3):159–66.
Article11. Lee HJ, Kim MB, Yoo SY, Park SN, Nam EC, Moon IS, et al. Clinical effect of intratympanic dexamethasone injection in acute unilateral tinnitus: a prospective, placebo-controlled, multicenter study. Laryngoscope. 2018; Jan. 128(1):184–8.
Article12. Shim HJ, Lee ES, An YH, Kim DH. Comparison of long-term outcome of intratympanic dexamethasone therapy between acute noise-induced tinnitus and acute idiopathic tinnitus. J Int Adv Otol. 2017; Apr. 13(1):53–60.
Article13. Kokubu M. Transtympanic injection of steroid for tinnitus. Oto-Rhino-Laryngology Tokyo. 1985; 28(1):25–30.14. Sakata E, Ito Y, Itoh A. Clinical experiences of steroid targeting therapy to inner ear for control of tinnitus. int tinnitus J. 1997; 3(2):117–21.15. Cesarani A, Capobianco S, Soi D, Giuliano DA, Alpini D. Intratympanic dexamethasone treatment for control of subjective idiopathic tinnitus: our clinical experience. Int Tinnitus J. 2002; 8(2):111–4.16. Karabulut H, Acar B, Babademez MA, Tuncay S, Karasen RM. Intratympanically dexamethasone injection application effects as a treatment of tinnitus. Anatol J Clin Investig. 2009; 3(3):154–8.17. An YH, Yu KK, Kwak MY, Yoon SW, Shim HJ. Prognostic factors for the outcomes of intratympanic dexamethasone in the treatment of acute subjective tinnitus. Otol Neurotol. 2014; Sep. 35(8):1330–7.
Article18. Yoshida T, Teranishi M, Iwata T, Otake H, Nakashima T. Intratympanic injection of dexamethasone for treatment of tinnitus in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Audiol Res. 2012; Jan. 2(1):e2.
Article19. Shim HJ, Song SJ, Choi AY, Hyung Lee R, Yoon SW. Comparison of various treatment modalities for acute tinnitus. Laryngoscope. 2011; Dec. 121(12):2619–25.
Article20. Albu S, Chirtes F. Intratympanic dexamethasone plus melatonin versus melatonin only in the treatment of unilateral acute idiopathic tinnitus. Am J Otolaryngol. 2014; Sep-Oct. 35(5):617–22.
Article21. She W, Dai Y, Du X, Chen F, Ding X, Cui X. Treatment of subjective tinnitus: a comparative clinical study of intratympanic steroid injection vs. oral carbamazepine. Med Sci Monit. 2009; Jun. 15(6):PI35–9.22. Kim YH, Lee DY, Lee DH, Oh S. Tympanic membrane perforation after intratympanic steroid injection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022; Feb. 166(2):249–59.
Article23. Gunter BW, Platt DM, Rowlett JK. Differential interactions engendered by benzodiazepine and neuroactive steroid combinations on schedule-controlled responding in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015; Oct. 137:53–9.
Article24. Sakata E, Itoh A, Itoh Y. Treatment of cochlear-tinnitus with dexamethasone infusion into the tympanic cavity. Int Tinnitus J. 1996; 2:129–35.25. Pitovski DZ, Drescher MJ, Drescher DG. Glucocorticoid receptors in the mammalian inner ear: RU 28362 binding sites. Hear Res. 1994; Jun. 77(1-2):216–20.
Article26. Yilmaz I, Yilmazer C, Erkan AN, Aslan SG, Ozluoglu LN. Intratympanic dexamethasone injection effects on transient-evoked otoacoustic emission. Am J Otolaryngol. 2005; Mar-Apr. 26(2):113–7.
Article27. Newman CW, Jacobson GP, Spitzer JB. Development of the tinnitus handicap inventory. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996; Feb. 122(2):143–8.
Article28. Newman CW, Sandridge SA, Jacobson GP. Psychometric adequacy of the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory (THI) for evaluating treatment outcome. J Am Acad Audiol. 1998; Apr. 9(2):153–60.29. Shea JJ Jr, Ge X. Dexamethasone perfusion of the labyrinth plus intravenous dexamethasone for Meniere’s disease. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1996; Apr. 29(2):353–8.
Article30. Moller AR. The role of neural plasticity in tinnitus. Prog Brain Res. 2007; 166:37–45.31. Sanchez TG, da Silva Lima A, Brandao AL, Lorenzi MC, Bento RF. Somatic modulation of tinnitus: test reliability and results after repetitive muscle contraction training. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2007; Jan. 116(1):30–5.
Article32. Kwak MY, Yang CJ, Shim HJ, Song CI, Kim JY, Lee IW, et al. Intratympanic steroid injection for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: impact of injection interval on therapeutic efficacy. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2020; Dec. 47(6):982–9.
Article33. Silverstein H, Rowan PT, Olds MJ, Rosenberg SI. Inner ear perfusion and the role of round window patency. Am J Otol. 1997; Sep. 18(5):586–9.34. Nordang L, Linder B, Anniko M. Morphologic changes in round window membrane after topical hydrocortisone and dexamethasone treatment. Otol Neurotol. 2003; Mar. 24(2):339–43.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intratympanic Steroid Injection in Tinnitus Management
- The Effect of Intratympanic Dexamethasone on Tinnitus in Inner Ear Diseases
- Intratympanic Drug Injection for Inner Ear Disease
- An Introduction of the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Comparison of the Efficacy of Systemic and Combined Highly Frequent Intratympanic Steroid Treatment on Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss