J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Feb;37(8):e64. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e64.
Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Propensity Score Matched Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2526798
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e64
Abstract
- Background
In patients with early-stage breast cancer, the treatment results of hypofractionated radiation therapy (RT) and conventional RT are evaluated in efficacy and cost.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated 280 patients with early-stage (Tis-2N0M0) breast cancer (including 100 hypofractionated RT patients) with regards to treatment outcomes according to the RT schedule. The median whole-breast RT dose was 42.56 Gy/16 fractions for hypofractionated RT and 50.4 Gy/28 fractions for conventional RT. Most patients (n = 260, 92.9%) additionally received a tumor bed boost RT. We used propensity score matching (PSM) analysis to balance the baseline risk factors for recurrence. The co-primary endpoints of this study were disease-free survival (DFS) and ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence (IBTR). DFS or IBTR was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier survival curve and log-rank test.
Results
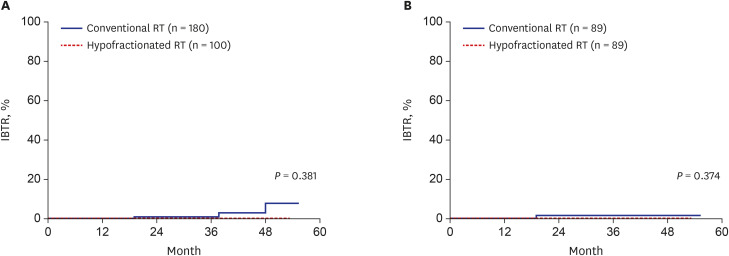
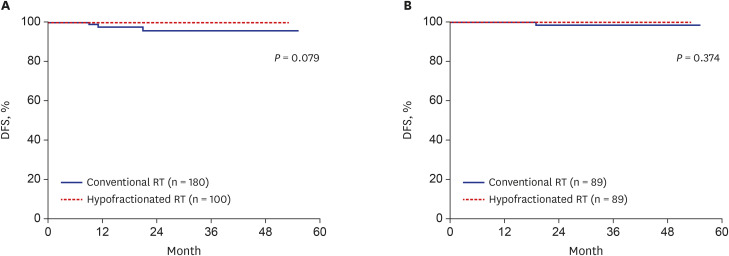
Total 89 pairs of matched patients (1:1 matching, n = 178) were finally evaluated. The median follow-up was 23.6 months. After matching, the 3-year DFS was 100% in the hypofractionated RT group and 98.4% in the conventional RT group; there was no significant difference in DFS between the groups (P = 0.374). Furthermore, the IBTR did not differ between the hypofractionated RT and conventional RT groups (P = 0.374) after matching. The 3-year overall survival was not different between two groups (both 100%). Hypofractionated RT saved 26.6% of the total cost of RT compared to conventional RT. Additionally, the acute skin toxicity rate (≥ grade 2) was also not significantly different between the groups (hypofractionated RT: 10.1% vs. conventional RT: 2.2%).
Conclusion
Hypofractionated RT showed good IBTR and DFS, which were compatible to those in conventional RT in breast cancer. Hypofractionated RT is expected to be used more widely because of its low cost and convenience.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hong S, Won YJ, Park YR, Jung KW, Kong HJ, Lee ES, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2017. Cancer Res Treat. 2020; 52(2):335–350. PMID: 32178489.
Article2. Park HJ, Oh DH, Shin KH, Kim JH, Choi DH, Park W, et al. Patterns of practice in radiotherapy for breast cancer in Korea. J Breast Cancer. 2018; 21(3):244–250. PMID: 30275852.
Article3. Andrade TR, Fonseca MC, Segreto HR, Segreto RA, Martella E, Nazário AC. Meta-analysis of long-term efficacy and safety of hypofractionated radiotherapy in the treatment of early breast cancer. Breast. 2019; 48:24–31. PMID: 31476695.
Article4. Liu L, Yang Y, Guo Q, Ren B, Peng Q, Zou L, et al. Comparing hypofractionated to conventional fractionated radiotherapy in postmastectomy breast cancer: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Radiat Oncol. 2020; 15(1):17. PMID: 31952507.
Article5. Yarnold J, Ashton A, Bliss J, Homewood J, Harper C, Hanson J, et al. Fractionation sensitivity and dose response of late adverse effects in the breast after radiotherapy for early breast cancer: long-term results of a randomised trial. Radiother Oncol. 2005; 75(1):9–17. PMID: 15878095.
Article6. Haviland JS, Owen JR, Dewar JA, Agrawal RK, Barrett J, Barrett-Lee PJ, et al. The UK Standardisation of Breast Radiotherapy (START) trials of radiotherapy hypofractionation for treatment of early breast cancer: 10-year follow-up results of two randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol. 2013; 14(11):1086–1094. PMID: 24055415.
Article7. Haviland JS, Mannino M, Griffin C, Porta N, Sydenham M, Bliss JM, et al. Late normal tissue effects in the arm and shoulder following lymphatic radiotherapy: Results from the UK START (Standardisation of Breast Radiotherapy) trials. Radiother Oncol. 2018; 126(1):155–162. PMID: 29153463.
Article8. Brunt AM, Haviland JS, Sydenham M, Agrawal RK, Algurafi H, Alhasso A, et al. Ten-year results of FAST: a randomized controlled trial of 5-fraction whole-breast radiotherapy for early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2020; 38(28):3261–3272. PMID: 32663119.
Article9. Offersen BV, Alsner J, Nielsen HM, Jakobsen EH, Nielsen MH, Krause M, et al. Hypofractionated versus standard fractionated radiotherapy in patients with early breast cancer or ductal carcinoma in situ in a randomized phase III trial: the DBCG HYPO trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020; 38(31):3615–3625. PMID: 32910709.
Article10. Whelan TJ, Pignol JP, Levine MN, Julian JA, MacKenzie R, Parpia S, et al. Long-term results of hypofractionated radiation therapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362(6):513–520. PMID: 20147717.
Article11. Hijal T, Al Hamad AA, Niazi T, Sultanem K, Bahoric B, Vuong T, et al. Hypofractionated radiotherapy and adjuvant chemotherapy do not increase radiation-induced dermatitis in breast cancer patients. Curr Oncol. 2010; 17(5):22–27. PMID: 20975875.
Article12. Lee BM, Chang JS, Kim SY, Keum KC, Suh CO, Kim YB. Hypofractionated radiotherapy dose scheme and application of new techniques are associated to a lower incidence of radiation pneumonitis in breast cancer patients. Front Oncol. 2020; 10:124. PMID: 32117771.
Article13. De Santis MC, Bonfantini F, Di Salvo F, Fiorentino A, Riboldi VM, Di Cosimo S, et al. Trastuzumab and hypofractionated whole breast radiotherapy: a victorious combination? Clin Breast Cancer. 2018; 18(3):e363–e371. PMID: 28958838.
Article14. Aleman BM, van Leeuwen FE. Hypofractionated adjuvant radiotherapy for breast cancer: no signs of increased risk of cardiotoxicity. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2015; 159:A8856. PMID: 25827153.15. Gradishar WJ, Anderson BO, Balassanian R, Blair SL, Burstein HJ, Cyr A, et al. NCCN guidelines insights: breast cancer, version 1.2017. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2017; 15(4):433–451. PMID: 28404755.
Article16. Moran MS, Zhao Y, Ma S, Kirova Y, Fourquet A, Chen P, et al. Association of radiotherapy boost for ductal carcinoma in situ with local control after whole-breast radiotherapy. JAMA Oncol. 2017; 3(8):1060–1068. PMID: 28358936.
Article17. Wang SL, Fang H, Song YW, Wang WH, Hu C, Liu YP, et al. Hypofractionated versus conventional fractionated postmastectomy radiotherapy for patients with high-risk breast cancer: a randomised, non-inferiority, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019; 20(3):352–360. PMID: 30711522.
Article18. Ratosa I, Chirilă ME, Steinacher M, Kozma E, Vojtíšek R, Franco P, et al. Hypofractionated radiation therapy for breast cancer: preferences amongst radiation oncologists in Europe - results from an international survey. Radiother Oncol. 2021; 155:17–26. PMID: 33065187.
Article19. Cante D, Franco P, Sciacero P, Girelli G, Pasquino M, Casanova Borca V, et al. Hypofractionated whole-breast radiotherapy and concomitant boost after breast conservation in elderly patients. Tumori. 2016; 102(2):196–202. PMID: 26350199.
Article20. De Rose F, Fogliata A, Franceschini D, Navarria P, Villa E, Iftode C, et al. Phase II trial of hypofractionated VMAT-based treatment for early stage breast cancer: 2-year toxicity and clinical results. Radiat Oncol. 2016; 11(1):120. PMID: 27639373.
Article21. Cutuli B. [Hypofractionated whole breast irradiation (WBRT): results and indications]. Cancer Radiother. 2016; 20(6-7):567–571. PMID: 27614516.22. Chesney TR, Yin JX, Rajaee N, Tricco AC, Fyles AW, Acuna SA, et al. Tamoxifen with radiotherapy compared with Tamoxifen alone in elderly women with early-stage breast cancer treated with breast conserving surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 2017; 123(1):1–9. PMID: 28391871.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-term oncological outcomes of hypofractionated versus conventional fractionated whole breast irradiation with simultaneous integrated boost in early-stage breast cancer
- Omitting Adjuvant Radiotherapy for Hormone Receptor‒Positive Early-Stage Breast Cancer in Old Age: A Propensity Score Matched SEER Analysis
- Hypofractionated Partial Breast Irradiation With Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy in Early Breast Cancer or Carcinoma In Situ: An Investigational Short-Term Analysis
- Hypofractionated whole breast irradiation: new standard in early breast cancer after breast-conserving surgery
- Radiotherapy for prostate cancer