Healthc Inform Res.
2022 Jan;28(1):58-67. 10.4258/hir.2022.28.1.58.
Development and Comparison of Three Data Models for Predicting Diabetes Mellitus Using Risk Factors in a Nigerian Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Community Health and Primary Care, College of Medicine, University of Lagos, Lagos State, Nigeria
- 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Medicine, University of Lagos, Lagos State, Nigeria
- 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Lagos, Lagos State, Nigeria
- 4Endocrinology Unit, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, University of Lagos, Lagos State, Nigeria
- 5Division of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, University of Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
- 6Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, University of Lagos, Lagos State, Nigeria
- KMID: 2526494
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2022.28.1.58
Abstract
Objectives
This study developed and compared the performance of three widely used predictive models—logistic regression (LR), artificial neural network (ANN), and decision tree (DT)—to predict diabetes mellitus using the socio-demographic, lifestyle, and physical attributes of a population of Nigerians.
Methods
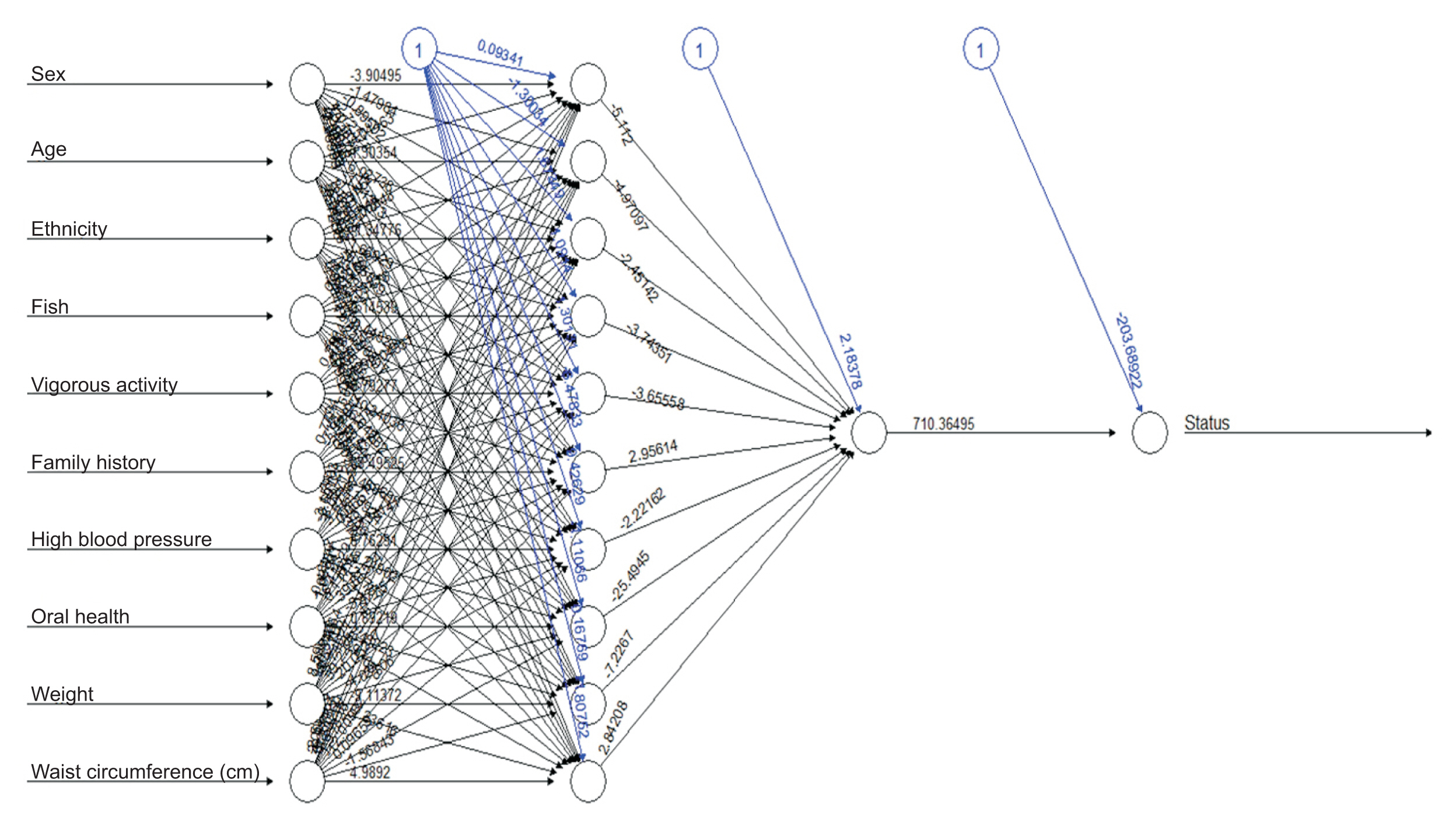
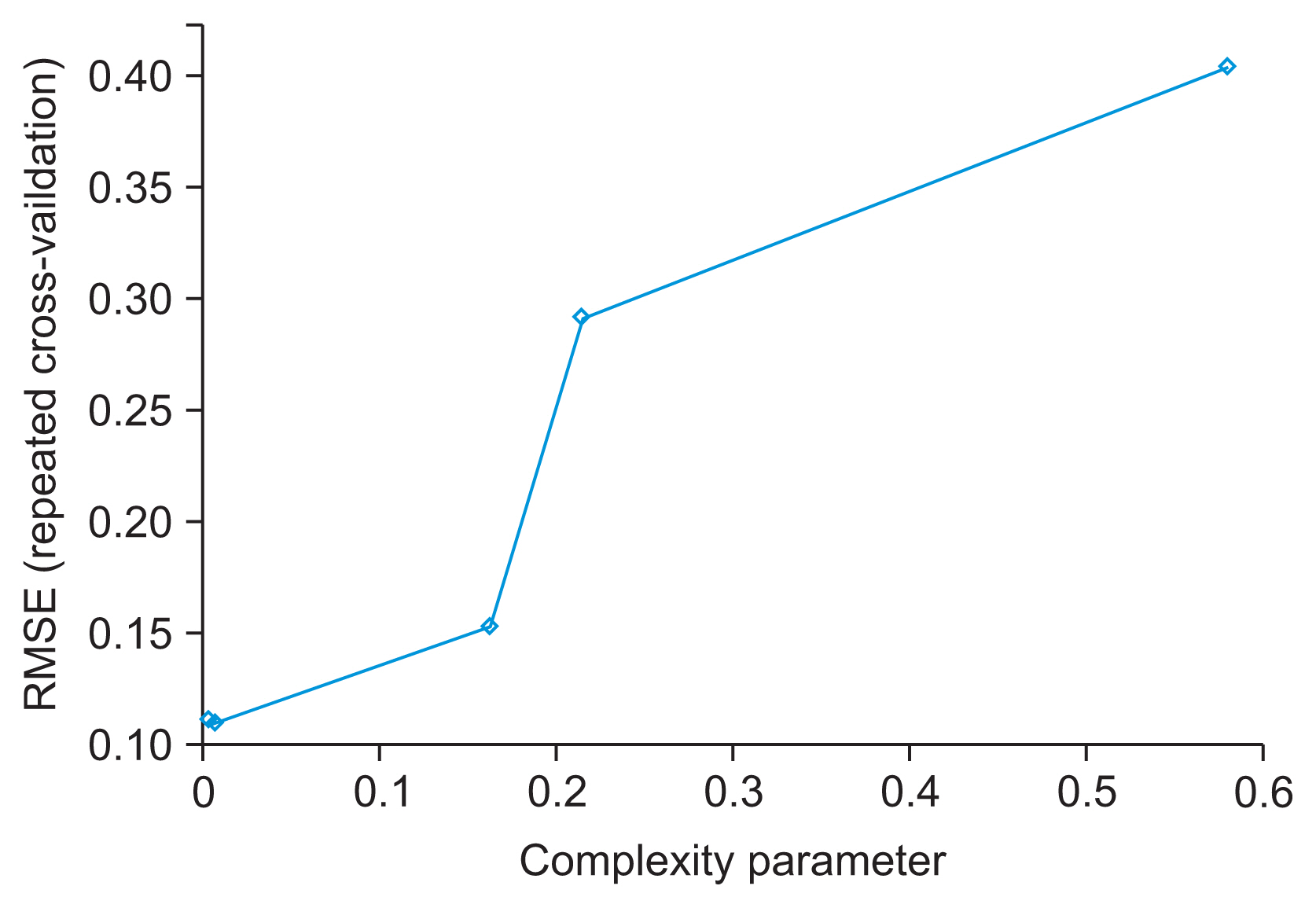
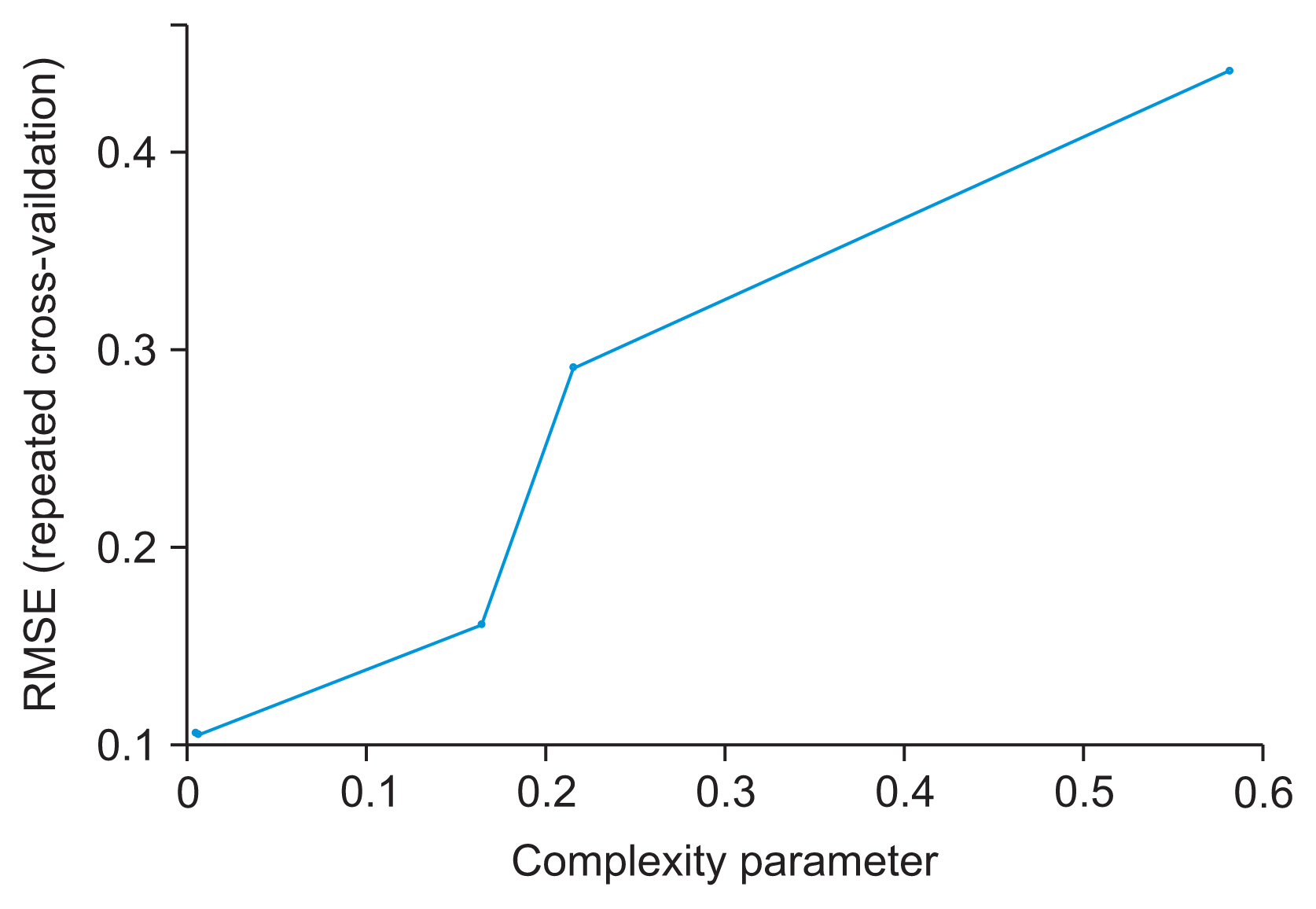
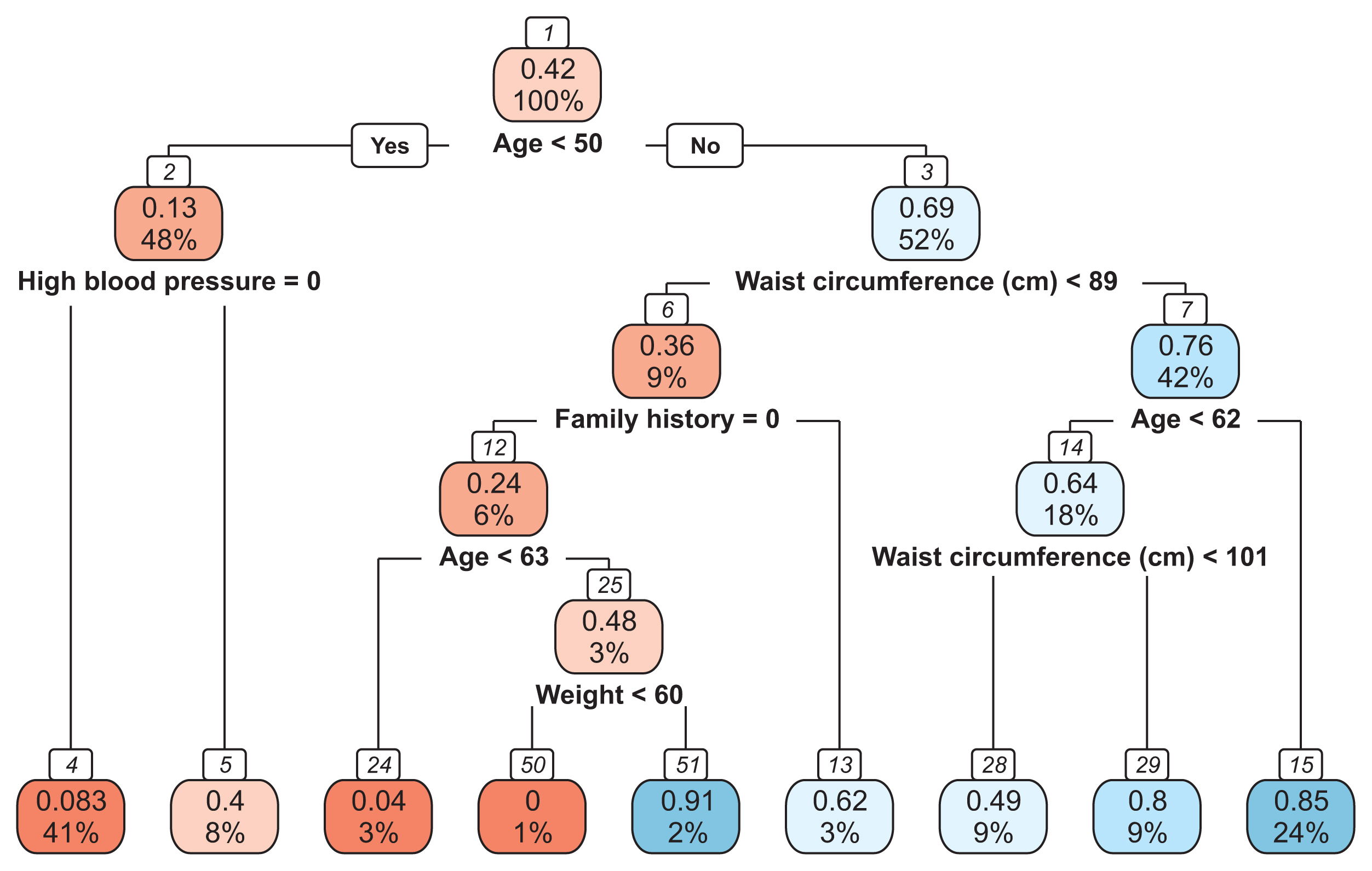
We developed three predictive models using 10 input variables. Data preprocessing steps included the removal of missing values and outliers, min-max normalization, and feature extraction using principal component analysis. Data training and validation were accomplished using 10-fold cross-validation. Accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) were used as performance evaluation metrics. Analysis and model development were performed in R version 3.6.1.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 50.52 ± 16.14 years. The classification accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV for LR were, respectively, 81.31%, 84.32%, 77.24%, 72.75%, and 82.49%. Those for ANN were 98.64%, 98.37%, 99.00%, 98.61%, and 98.83%, and those for DT were 99.05%, 99.76%, 98.08%, 98.77%, and 99.82%, respectively. The best-performing and poorest-performing classifiers were DT and LR, with 99.05% and 81.31% accuracy, respectively. Similarly, the DT algorithm achieved the best AUC value (0.992) compared to ANN (0.976) and LR (0.892).
Conclusions
Our study demonstrated that DT, LR, and ANN models can be used effectively for the prediction of diabetes mellitus in the Nigerian population based on certain risk factors. An overall comparative analysis of the models showed that the DT model performed better than LR and ANN.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet. 2016; 387(10027):1513–30.2. International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes atlas. 9th ed.Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation;2019.3. Uloko AE, Musa BM, Ramalan MA, Gezawa ID, Puepet FH, Uloko AT, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for diabetes mellitus in Nigeria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Ther. 2018; 9(3):1307–16.
Article4. Narayan KM, Chan J, Mohan V. Early identification of type 2 diabetes: policy should be aligned with health systems strengthening. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34(1):244–6.5. World Health Organization. Global report on diabetes. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2016.6. Alebiosu OC, Familoni OB, Ogunsemi OO, Raimi TH, Balogun WO, Odusan O, et al. Community based diabetes risk assessment in Ogun state, Nigeria (World Diabetes Foundation project 08–321). Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 17(4):653–8.
Article7. Abbasi A, Peelen LM, Corpeleijn E, van der Schouw YT, Stolk RP, Spijkerman AM, et al. Prediction models for risk of developing type 2 diabetes: systematic literature search and independent external validation study. BMJ. 2012; 345:e5900.
Article8. Meng XH, Huang YX, Rao DP, Zhang Q, Liu Q. Comparison of three data mining models for predicting diabetes or prediabetes by risk factors. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2013; 29(2):93–9.
Article9. Habibi S, Ahmadi M, Alizadeh S. Type 2 diabetes mellitus screening and risk factors using decision tree: results of data mining. Glob J Health Sci. 2015; 7(5):304–10.
Article10. Hajian-Tilaki K. Sample size estimation in diagnostic test studies of biomedical informatics. J Biomed Inform. 2014; 48:193–204.
Article11. World Health Organization. WHO STEPS instrument question-by-question guide (core and expanded) [Internet]. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2017. [cited at 2021 Oct 16] Available: https://www.who.int/ncds/surveillance/steps/STEPS_QbyQ_Guide.pdf .12. Novakovic J, Rankov S. Classification performance using principal component analysis and different value of the ratio R. Int J Comput Commun Control. 2011; 6(2):317–27.13. Russell S, Norvig P. Artificial intelligence: a modern approach. Englewood Cliffs (NJ): Prentice-Hall;2010.14. Nwoye EO, Nwaneri SC, Iruhe NK, Babatunde AM. Application of artificial neural network in breast cancer classification: a comparative study. J Basic Med Sci. 2014; 2(1):32–8.15. Rojas R. Neural networks: a systematic introduction. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer;1996.16. Sisodia D, Sisodia DS. Prediction of diabetes using classification algorithms. Procedia Comput Sci. 2018; 132:1578–85.
Article17. Dev VA, Eden MR. Gradient boosted decision trees for lithology classification. Comput Aided Chem Eng. 2019; 47:113–8.
Article18. Lastra G, Syed S, Kurukulasuriya LR, Manrique C, Sowers JR. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension: an update. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2014; 43(1):103–22.19. Suastika K, Dwipayana P, Semadi MS, Kuswardhani RT. Age is an important risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases. Chackrewarthy S, editor. Glucose tolerance. Rijeka, Croatia: Intech Open;2012. p. 67–76.
Article20. Ustulin M, Rhee SY, Chon S, Ahn KK, Lim JE, Oh B, et al. Importance of family history of diabetes in computing a diabetes risk score in Korean prediabetic population. Sci Rep. 2018; 8(1):15958.
Article21. Tillin T, Hughes AD, Godsland IF, Whincup P, Forouhi NG, Welsh P, et al. Insulin resistance and truncal obesity as important determinants of the greater incidence of diabetes in Indian Asians and African Caribbeans compared with Europeans: the Southall And Brent REvisited (SABRE) cohort. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36(2):383–93.22. Leite RS, Marlow NM, Fernandes JK, Hermayer K. Oral health and type 2 diabetes. Am J Med Sci. 2013; 345(4):271–3.
Article23. Lai H, Huang H, Keshavjee K, Guergachi A, Gao X. Predictive models for diabetes mellitus using machine learning techniques. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019; 19(1):101.
Article24. El_Jerjawi NS, Abu-Naser SS. Diabetes prediction using artificial neural network. Int J Adv Sci Technol. 2018; 121:54–64.25. Nai-arun N, Moungmai R. Comparison of classifiers for the risk of diabetes prediction. Procedia Comput Sci. 2015; 69:132–42.
Article26. Wang C, Li L, Wang L, Ping Z, Flory MT, Wang G, et al. Evaluating the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus using artificial neural network: an effective classification approach. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013; 100(1):111–8.
Article27. Mohamed EI, Linder R, Perriello G, Di Daniele N, Poppl SJ, De Lorenzo A. Predicting type 2 diabetes using an electronic nose-based artificial neural network analysis. Diabetes Nutr Metab. 2002; 15(4):215–21.28. Kazemnejad A, Batvandi Z, Faradmal J. Comparison of artificial neural network and binary logistic regression for determination of impaired glucose tolerance/diabetes. East Mediterr Health J. 2010; 16(6):615–20.
Article29. Li CP, Zhi XY, Ma J, Cui Z, Zhu ZL, Zhang C, et al. Performance comparison between logistic regression, decision trees, and multilayer perceptron in predicting peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012; 125(5):851–7.