Clin Endosc.
2022 Jan;55(1):113-121. 10.5946/ce.2021.149.
Artificial Intelligence-Based Colorectal Polyp Histology Prediction by Using Narrow-Band Image-Magnifying Colonoscopy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Gastroenterology, Petz Aladar University Teaching Hospital, Gyor, Hungary
- 2Department of Physics and Chemistry, Szechenyi Istvan University, Gyor, Hungary
- 3Department of Pathology, Petz Aladar University Teaching Hospital, Gyor, Hungary
- 4Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Szechenyi Istvan University, Gyor, Hungary
- KMID: 2525057
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2021.149
Abstract
- Background/Aims
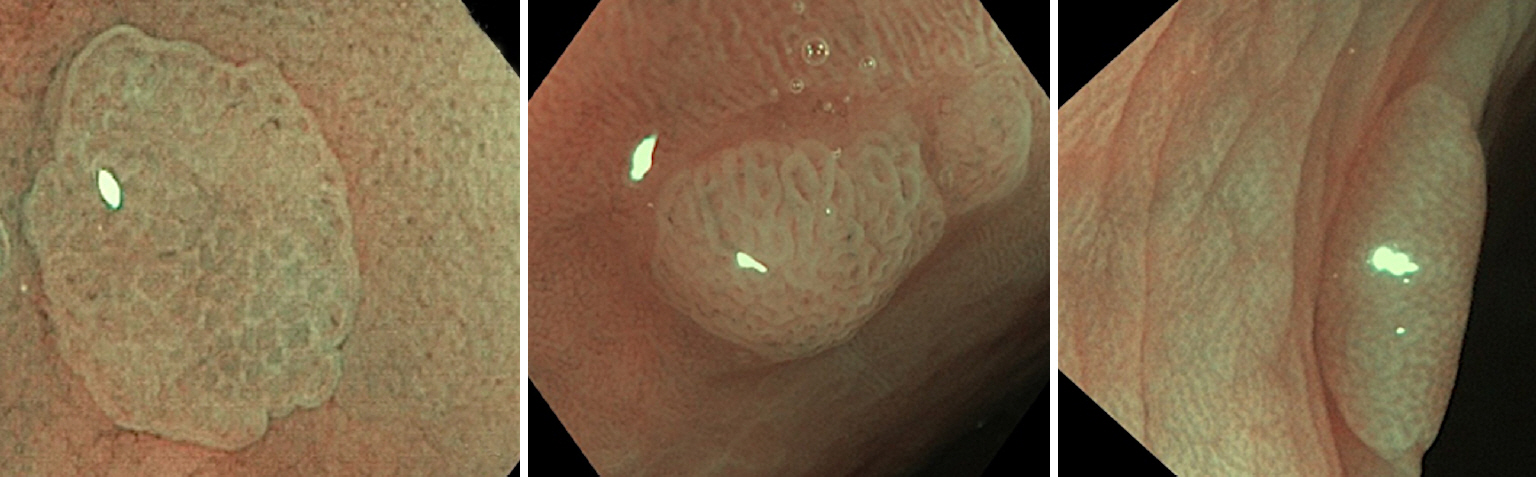
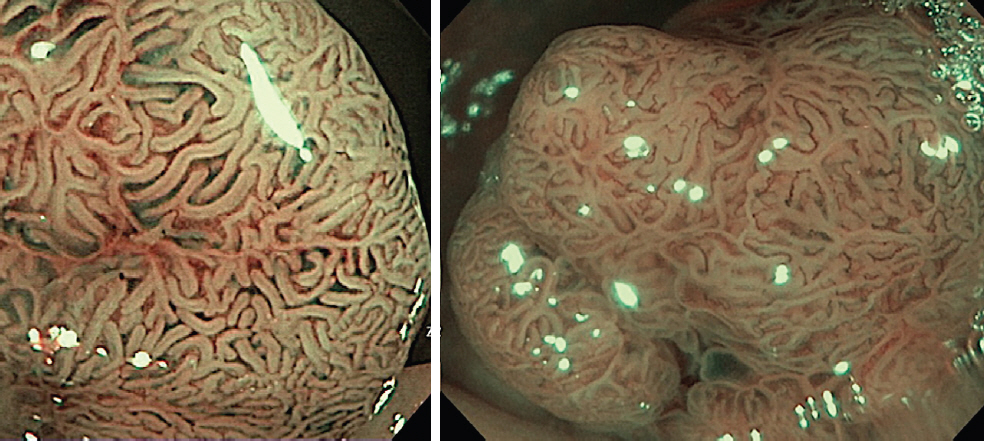
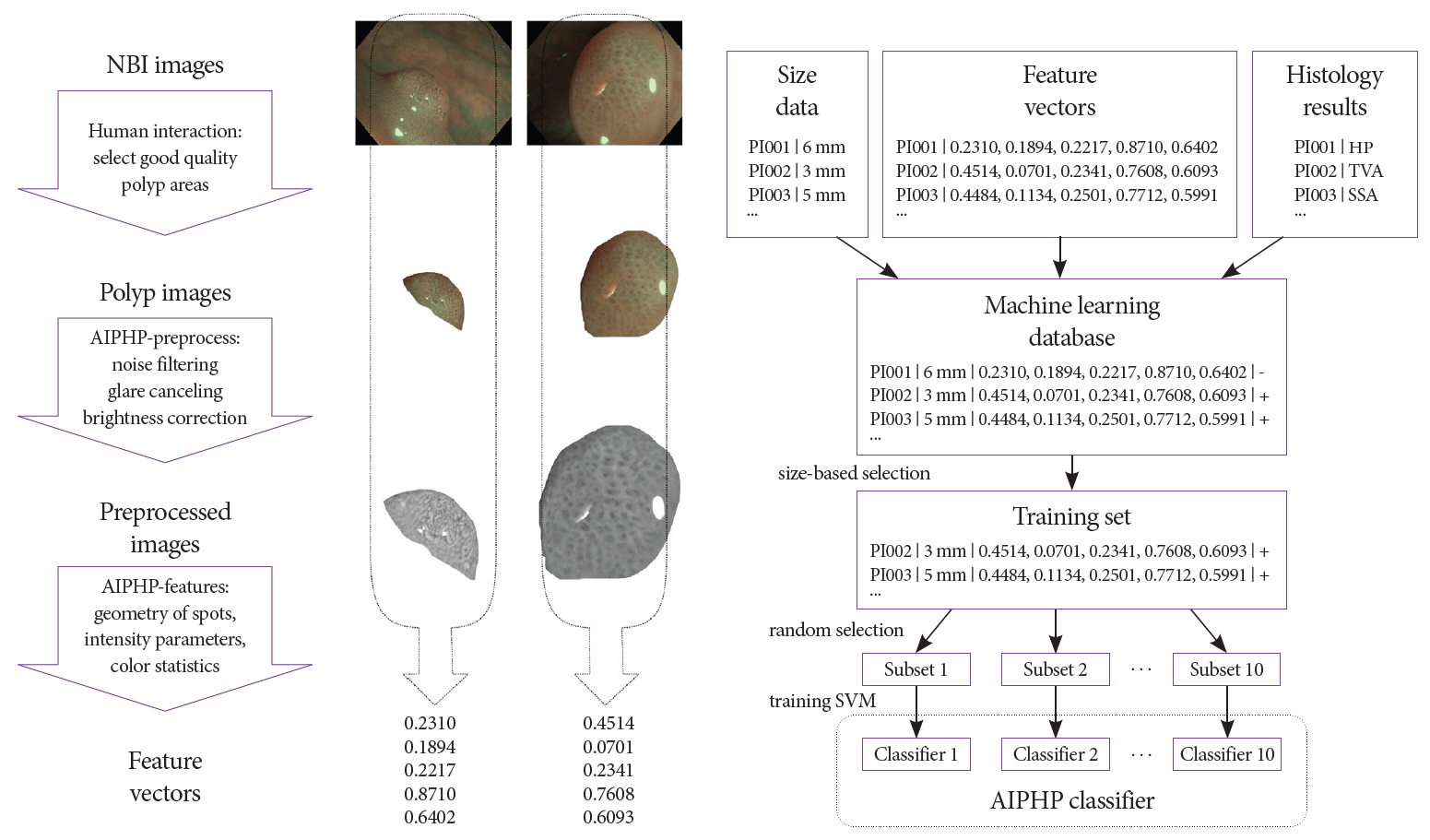
We have been developing artificial intelligence based polyp histology prediction (AIPHP) method to classify Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) magnifying colonoscopy images to predict the hyperplastic or neoplastic histology of polyps. Our aim was to analyze the accuracy of AIPHP and narrow-band imaging international colorectal endoscopic (NICE) classification based histology predictions and also to compare the results of the two methods.
Methods
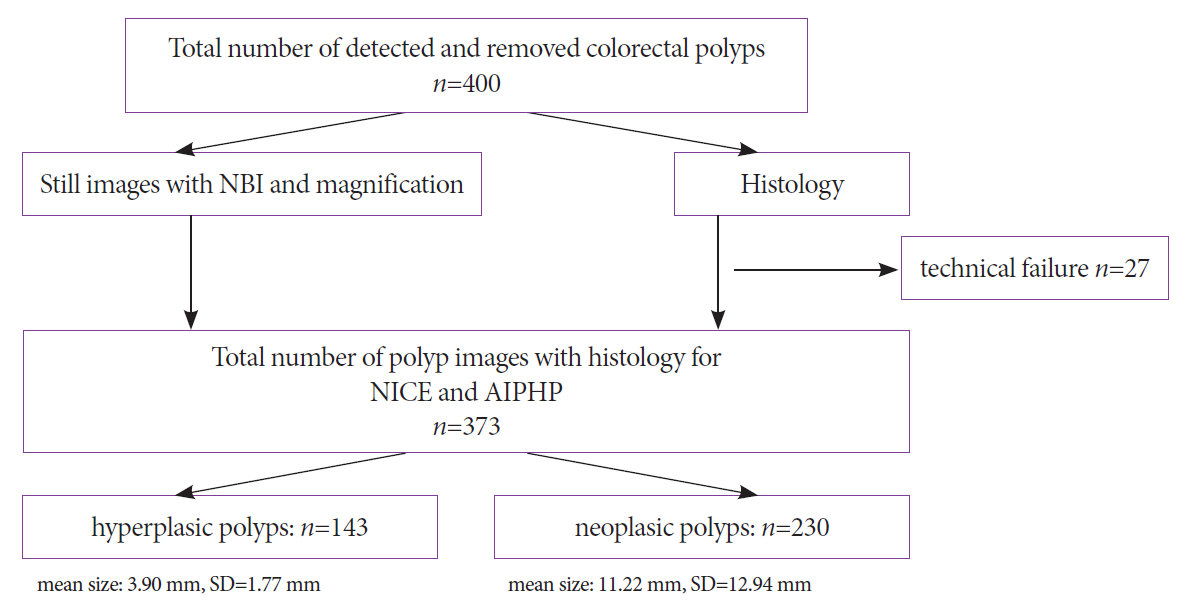
We studied 373 colorectal polyp samples taken by polypectomy from 279 patients. The documented NBI still images were analyzed by the AIPHP method and by the NICE classification parallel. The AIPHP software was created by machine learning method. The software measures five geometrical and color features on the endoscopic image.
Results
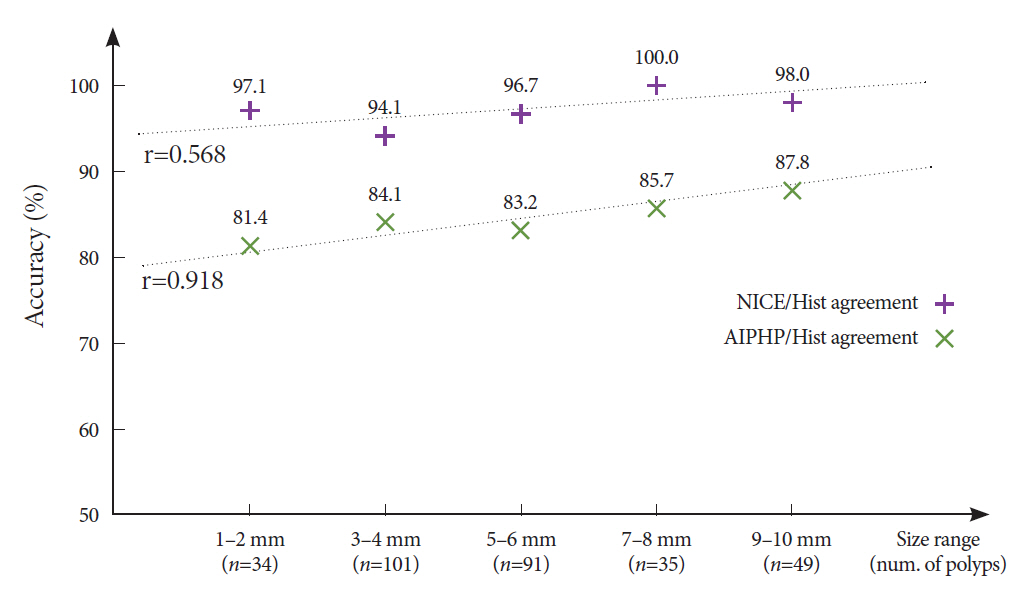
The accuracy of AIPHP was 86.6% (323/373) in total of polyps. We compared the AIPHP accuracy results for diminutive and non-diminutive polyps (82.1% vs. 92.2%; p=0.0032). The accuracy of the hyperplastic histology prediction was significantly better by NICE compared to AIPHP method both in the diminutive polyps (n=207) (95.2% vs. 82.1%) (p<0.001) and also in all evaluated polyps (n=373) (97.1% vs. 86.6%) (p<0.001)
Conclusions
Our artificial intelligence based polyp histology prediction software could predict histology with high accuracy only in the large size polyp subgroup.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. McGill SK, Evangelou E, Ioannidis JPA, Soetikno RM, Kaltenbach T. Narrow band imaging to differentiate neoplastic and non-neoplastic colorectal polyps in real time: a meta-analysis of diagnostic operating characteristics. Gut. 2013; 62:1704–1713.2. Ignjatovic A, East JE, Suzuki N, Vance M, Guenther T, Saunders BP. Optical diagnosis of small colorectal polyps at routine colonoscopy (Detect InSpect ChAracterise Resect and Discard; DISCARD trial): a prospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:1171–1178.3. Ignjatovic A, Thomas-Gibson S, East JE, et al. Development and validation of a training module on the use of narrow-band imaging in differentiation of small adenomas from hyperplastic colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:128–133.4. Hewett DG, Kaltenbach T, Sano Y, et al. Validation of a simple classification system for endoscopic diagnosis of small colorectal polyps using narrow-band imaging. Gastroenterology. 2012; 143:599–607.e1.5. Hewett DG, Huffman ME, Rex DK. Leaving distal colorectal hyperplastic polyps in place can be achieved with high accuracy by using narrow-band imaging: an observational study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:374–380.6. Rastogi A, Rao DS, Gupta N, et al. Impact of a computer-based teaching module on characterization of diminutive colon polyps by using narrow-band imaging by non-experts in academic and community practice: a video-based study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 79:390–398.7. van den Broek FJC, Reitsma JB, Curvers WL, Fockens P, Dekker E. Systematic review of narrow-band imaging for the detection and differentiation of neoplastic and nonneoplastic lesions in the colon (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:124–135.8. Ahadi M, Sokolova A, Brown I, Chou A, Gill AJ. The 2019 World health organization classification of appendiceal, colorectal and anal canal tumours: an update and critical assessment. Pathology. 2021; 53:454–461.9. Horváth A, Spindler S, Szalay M, Rácz I. Preprocessing endoscopic images of colorectal polyps. Acta Technica Jaurinensis. 2016; 9:65–82.10. Neumann H, Vieth M, Fry LC, et al. Learning curve of virtual chromoendoscopy for the prediction of hyperplastic and adenomatous colorectal lesions: a prospective 2-center study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:115–120.11. Tischendorf JJW, Gross S, Winograd R, et al. Computer-aided classification of colorectal polyps based on vascular patterns: a pilot study. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:203–207.12. Gross S, Trautwein C, Behrens A, et al. Computer-based classification of small colorectal polyps by using narrow-band imaging with optical magnification. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:1354–1359.13. Takemura Y, Yoshida S, Tanaka S, et al. Quantitative analysis and development of a computer-aided system for identification of regular pit patterns of colorectal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:1047–1051.14. Alagappan M, Brown JRG, Mori Y, Berzin TM. Artificial intelligence in gastrointestinal endoscopy: the future is almost here. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 10:239–249.15. Hassan C, Bisschops R, Bhandari P, et al. Predictive rules for optical diagnosis of <10-mm colorectal polyps based on a dedicated software. Endoscopy. 2020; 52:52–60.16. Le Berre C, Sandborn WJ, Aridhi S, et al. Application of artificial intelligence to gastroenterology and hepatology. Gastroenterology. 2020; 158:76–94.e2.17. Hassan C, Spadaccini M, Iannone A, et al. Performance of artificial intelligence in colonoscopy for adenoma and polyp detection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021; 93:77–85.e6.18. Rácz I, Horváth A, Szalai M, et al. Sa1556 digital image processing software for predicting the histology of small colorectal polyps by using narrow-band imaging magnifying colonoscopy. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2015; 81:AB259.19. Rex DK, Kahi C, O’Brien M, et al. The american society for gastrointestinal endoscopy PIVI (preservation and incorporation of valuable endoscopic innovations) on real-time endoscopic assessment of the histology of diminutive colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:419–422.20. ASGE Technology Committee, Abu Dayyeh BK, Thosani N, et al. ASGE technology committee systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting real-time endoscopic assessment of the histology of diminutive colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:502.e1–502.e16.21. Cohen J, Bosworth BP, Chak A, et al. Preservation and incorporation of valuable endoscopic innovations (PIVI) on the use of endoscopy simulators for training and assessing skill. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:471–475.22. Tanaka S, Kaltenbach T, Chayama K, Soetikno R. High-magnification colonoscopy (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 64:604–613.23. Kanao H, Tanaka S, Oka S, Hirata M, Yoshida S, Chayama K. Narrow-band imaging magnification predicts the histology and invasion depth of colorectal tumors. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:631–636.24. Tanaka S, Sano Y. Aim to unify the narrow band imaging (NBI) magnifying classification for colorectal tumors: current status in Japan from a summary of the consensus symposium in the 79th annual meeting of the Japan gastroenterological endoscopy society. Dig Endosc. 2011; 23(Suppl 1):131–139.25. Oba S, Tanaka S, Sano Y, Oka S, Chayama K. Current status of narrow-band imaging magnifying colonoscopy for colorectal neoplasia in Japan. Digestion. 2011; 83:167–172.26. Takemura Y, Yoshida S, Tanaka S, et al. Computer-aided system for predicting the histology of colorectal tumors by using narrow-band imaging magnifying colonoscopy (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:179–185.27. Kominami Y, Yoshida S, Tanaka S, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of colorectal polyp histology by using a real-time image recognition system and narrow-band imaging magnifying colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:643–649.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Artificial intelligence-based colorectal polyp histology prediction using narrow-band image-magnifying colonoscopy: a stepping stone for clinical practice
- Response to Artificial intelligence-based colorectal polyp histology prediction using narrow-band image-magnifying colonoscopy: a stepping stone for clinical practice
- Application of artificial intelligence for diagnosis of early gastric cancer based on magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging
- Polyp Detection, Characterization, and Management Using Narrow-Band Imaging with/without Magnification
- Estimation of Invasion Depth: The First Key to Successful Colorectal ESD