J Korean Acad Oral Health.
2021 Dec;45(4):233-238. 10.11149/jkaoh.2021.45.4.233.
Effect of commercial pomegranate drink on the tooth enamel surface
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Public Health, Chonnam National University Graduate School, Gwangju, Korea
- 2Department of Preventive and Public Health Dentistry, Gwangju, Korea
- 3Dental Science Research Institute, Chonnam National University School of Dentistry, Gwangju, Korea
- KMID: 2524201
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11149/jkaoh.2021.45.4.233
Abstract
Objectives
This study examines the pH and titratable acidity of pomegranate drinks sold in Korea to identify the risk of dental erosion, and to provide basic data for oral health when consuming such drinks.
Methods
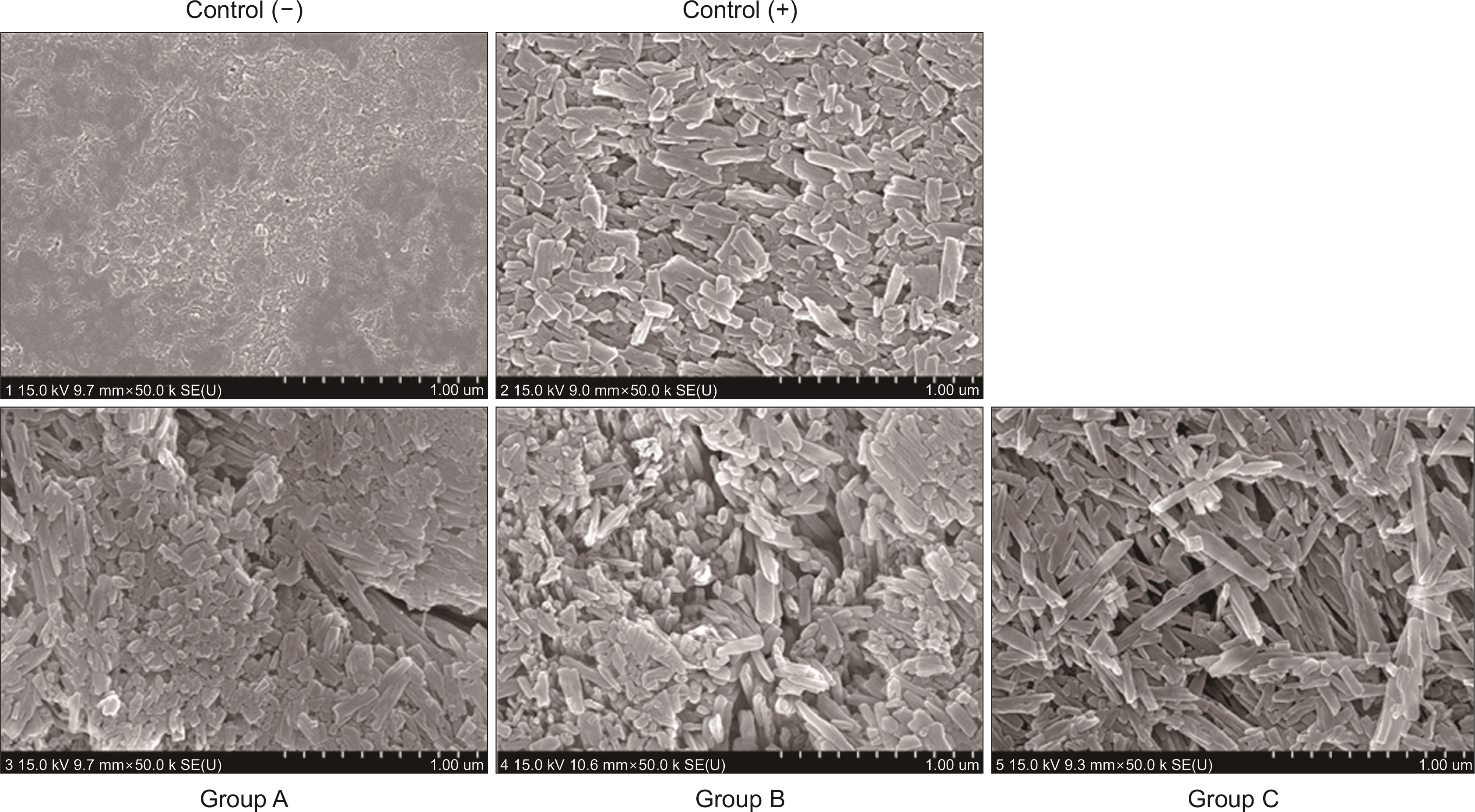
The experiment included 5 groups: As experimental drinks, Sunkist pomegranate (Group A), Beauty liked pomegranate (Group B), Pomegranate juice 100 (Group C) were selected, and Jeju Samdasoo and Coca-Cola were selected for negative and positive controls. The components of the experimental beverage were analyzed, and the degree of erosion was measured using the Vickers hardness number (VHN) and by scanning electron microscope images.
Results
When comparing the surface microhardness before and 30 minutes after beverage immersion, there was a significant difference in the positive control group, Group A, Group B, and Group C (P<0.05), while there was no significant difference in the negative control group (P>0.05). The difference in surface microhardness (ΔVHN) was found in Group C (-117.33±17.41), Group A (-112.90±15.19), the positive control group (-103.80±13.23), Group B (-90.82±24.60), and the negative control group (-13.44±14.60), in that order. The positive control group, Group A, Group B, and Group C showed a significant difference from the negative control group (P<0.05), and Group B showed a significant difference from Group A, and Group C (P<0.05), whereas Group A, Group B, and Group C did not differ significantly from the positive control group (P>0.05).
Conclusions
This study found that the low pH and high titratable acidity of commercially available pomegranate drinks can potentially cause dental erosion. Therefore, it is imperative to provide dietary guidance so that consumers can recognize the possibility of dental erosion when consuming pomegranate drinks and manage their oral health.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Shin Y, Kim SD, Kjm BS, Yun ES, Chang MS, Jung SO, et al. 2011; The content of minerals and vitamins in commercial beverages and liquid teas. J Fd Hyg Safety. 26:322–329.2. Lee EJ, Lee KR, Kim JY. 2017; Analysis of beverages usage motives according to selection attributes of beverage shop. J Korean Soc Food Cult. 32:118–127. DOI: 10.7318/KJFC/2017.32.1.027.3. Jun MK, Lee DH, Lee SM. 2016; Assessment of nutrient and sugar content and pH of some commercial beverages. J Dent Hyg Sci. 16:464–471. DOI: 10.17135/jdhs.2016.16.6.464.
Article4. Food Information Statistics System. 2020. Food market newsletter read with aTFIS fruits and vegetables. Food Information Statistics System;Naju, Jeollanam-do: p. 1–12.5. Choi HC, Ma JA. 2021. What are the most imported and consumed foods. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;Cheongju, Chungcheongbuk-do: p. 1–4.6. Kim HS, Oh KY, Lee SM, Kim JY, Lee SH, Jang JS, et al. 2021; Effect of extraction methods on the quality of pomegranate juice and physiological activity. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 50:136–148. DOI: 10.3746/jkfn.2021.50.2.136.
Article7. Kim MS, Yun SH, Na HS, Park HJ, Choi GC, Yang SI, et al. 2013; Chemical compositions and functional characteristics of korean and imported pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). J Korean Food Preserv. 20:342–347. DOI: 10.11002/kjfp.2013.20.3.342.
Article8. Shin WS. 2020. Our food story pomegranate No.94 geographical indication agricultural products - goheung pomegranate. Gunpo Citizen's Newspaper;Gunpo-si, Gyeonggi-do: p. 1.9. Devipriya N, Srinivasan M, Sudheer AR, Menon VP. 2007; Effect of ellagic acid, a natural polyphenol, on alcohol-induced prooxidant and antioxidant imbalance: a drug dose dependent study. Singapore Med J. 48:311–318. PMID: 17384878.10. Shukla M, Gupta K, Rasheed Z, Khan KA, Haqqi TM. 2008; Bioavailable constituents/metabolites of pomegranate (Punicagranatum L) preferentially inhibit COX2 activity ex vivo and IL-1beta-induced PGE2 production in human chondrocytes in vitro. J Inflamm (Lond). 5:9. DOI: 10.1186/1476-9255-5-9. PMID: 18554383. PMCID: PMC2438359.
Article11. Aggarwal BB, Shishodia S. 2006; Molecular targets of dietary agents for prevention and therapy of cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 71:1397–1421. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.02.009. PMID: 16563357.
Article12. Kim JH. 2019. Inhibitory effect of pomegranate extract powder on periodontitis in rats [doctoral dissertation]. Chosun University;Gwangju: [Korean].13. Sowmya K, Sunder K, Lakshminarayan N. 2011; Effect of pomegranate juice on dental plaque microorganisms (Streptococci and Lactobacilli). Anc Sci Life. 31:49–51. PMID: 23284205. PMCID: PMC3530267.14. Wee JH, Jung HJ, Jung KO, Sung HM, Shin YR, Park JH, et al. 2015; Pomegranate extract improves menopausal syndrome in ovariectomized rats. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 44:506–515. DOI: 10.3746/jkfn.2015.44.4.506.
Article15. Kim MK, Jeon JH, Park HJ, Bae CH, Park JS, Bae SK, et al. 2014; Effect of energy drinks on the dental enamel erosion and mouse teeth growth. Korean Society for Biotechnology and Bioengineering Journal. 29:112–117. DOI: 10.7841/ksbbj.2014.29.2.112.
Article16. Jun MK, Lee DH, Lee SM. 2016; Assessment of Nutrient and Sugar Content and pH of Some Commercial Beverages. J Dent Hyg Sci. 16:464–471. DOI: 10.17135/jdhs.2016.16.6.464.
Article17. Choi CH, Youn HJ, Noh HJ, Hong SJ. 2008; Surface microhardness changes caused by Coca-cola on sound enamel of bovine teeth. J Korean Acad Oral Health. 32:152–159.18. Lee GJ, Jin SY, Kim HJ, Min JB. 2017; Treatment of dental erosion caused by intrinsic and extrinsic etiology:a case report. J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci. 33:42–46. DOI: 10.14368/jdras.2017.33.1.42.19. Lee HJ, Hong SJ, Choi CH. 2013; Erosive effect of hangover-curing beverages on enamel surface. J Korean Acad Oral Health. 37:119–125. DOI: 10.11149/jkaoh.2013.37.3.119.
Article20. Kim HS, Oh KY, Lee SM, Kim JY, Lee SH, Jang JS, et al. 2021; Effect of extraction methods on the quality of pomegranate juice and physiological activity. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 50:136–148. DOI: 10.3746/jkfn.2021.50.2.136.
Article21. Kim EJ, Lee HJ, Lee EJ, Bae KH, Jin BH, Paik DI. 2012; Effects of pH and titratable acidity on the erosive potential of acidic drinks. J Korean Acad Oral Health. 36:13–19.22. Reddy A, Norris DF, Momeni SS, Waldo B, Ruby JD. 2016; The pH of beverages in the United States. J Am Dent Assoc. 147:255–263. DOI: 10.1016/j.adaj.2015.10.019. PMID: 26653863. PMCID: PMC4808596.23. Willershausen B, Callaway A, Azrak B, Duschner H. 2008; Influence of apple juice on human enamel surfaces of the first and second dentition - an in vitro study. Eur J Med Res. 13:349–354. PMID: 18700193.24. Kim DE, Kim KH, Kim AO, Jeong SS, Choi CH, Hong SJ. 2016; The erosive effect of commercial red ginseng beverages on bovine enamel surfaces. J Korean Acad Oral Health. 40:198–205. DOI: 10.11149/jkaoh.2016.40.3.198.
Article25. Amaechi BT, Higham SM, Edgar WM, Milosevic A. 1999; Thickness of acquired salivary pellicle as a determinant of the sites of dental erosion. J Dent Res. 78:1821–1828. DOI: 10.1177/00220345990780120901. PMID: 10598912.
Article26. Shim JH, Jeong TS, Kim S. 2004; A study on the enamel erosion by fermented milks. J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent. 31:555–563.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of red vinegar drink on the surface of sound enamel
- Effect of commercial alcoholic drinks on sound enamel surface of bovine teeth
- The experimental study of the effect of zinc phosphate cement on the solubility of enamel
- A comparative study of roughness of enamel surface to various interdental enamel stripping methods in vitro
- Effect of Commercial Effervescent Vitamin Tablets on Bovine Enamel