J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Jan;37(1):e4. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e4.
Kidney Transplantation From Deceased Donors With Bloodstream Infection: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul Metropolitan Government-Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Surgery, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 7Transplantation Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2524182
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e4
Abstract
- Background
The use of organs from donors with infection is limited because of the possibility of transmission. We aimed to investigate the transmission after deceased donor transplantation with bloodstream infection (BSI).
Methods
A retrospective study of patients undergoing kidney or pancreas transplantation at five tertiary centers in Korea from January 2009 and November 2019 was performed. We analyzed the outcomes after transplantation from deceased donors with BSI.
Results
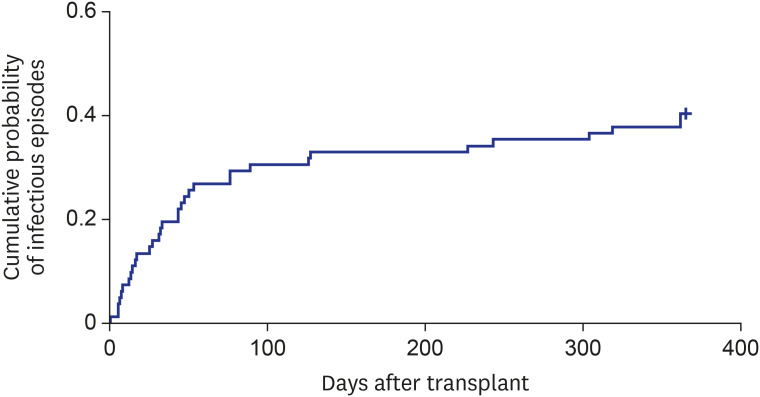
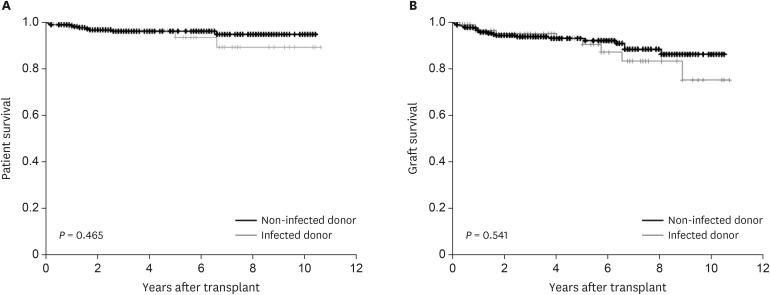
Eighty-six recipients received transplantation from 69 donors with BSI. The most common isolated pathogens from donors were Gram-positive bacteria (72.0%), followed by Gram-negative bacteria (22.7%), and fungi (5.3%). Appropriate antimicrobial agents were used in 47.8% of donors before transplantation. Transmission occurred only in 1 of 83 recipients (1.2%) from bacteremic donors and 1 of 6 recipients (16.7%) from fungemic donors. One-year patient and graft survival was 97.5%and 96.3%, respectively. There was no significant difference in graft and patient survival between patients who received organs from infected donors and noninfected donors.
Conclusion
Using organs from donors with bacteremia seems to be a safe option with low transmission risk. The overall prognosis of using organs from donors with BSI is favorable.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bowring MG, Holscher CM, Zhou S, Massie AB, Garonzik-Wang J, Kucirka LM, et al. Turn down for what? Patient outcomes associated with declining increased infectious risk kidneys. Am J Transplant. 2018; 18(3):617–624. PMID: 29116674.
Article2. Ison MG, Hager J, Blumberg E, Burdick J, Carney K, Cutler J, et al. Donor-derived disease transmission events in the United States: data reviewed by the OPTN/UNOS Disease Transmission Advisory Committee. Am J Transplant. 2009; 9(8):1929–1935. PMID: 19538493.
Article3. Caballero F, Lopez-Navidad A, Perea M, Cabrer C, Guirado L, Solà R. Successful liver and kidney transplantation from cadaveric donors with left-sided bacterial endocarditis. Am J Transplant. 2005; 5(4 Pt 1):781–787. PMID: 15760402.
Article4. Cohen J, Michowiz R, Ashkenazi T, Pitlik S, Singer P. Successful organ transplantation from donors with Acinetobacter baumannii septic shock. Transplantation. 2006; 81(6):853–855. PMID: 16570007.5. Goldberg E, Bishara J, Lev S, Singer P, Cohen J. Organ transplantation from a donor colonized with a multidrug-resistant organism: a case report. Transpl Infect Dis. 2012; 14(3):296–299. PMID: 22176504.
Article6. Ariza-Heredia EJ, Patel R, Blumberg EA, Walker RC, Lewis R, Evans J, et al. Outcomes of transplantation using organs from a donor infected with Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC)-producing K. pneumoniae . Transpl Infect Dis. 2012; 14(3):229–236. PMID: 22624726.7. Wan Q, Liu H, Ye S, Ye Q. Confirmed transmission of bacterial or fungal infection to kidney transplant recipients from donated after cardiac death (DCD) donors in China: a single-center analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2017; 23:3770–3779. PMID: 28771455.
Article8. Ison MG, Nalesnik MA. An update on donor-derived disease transmission in organ transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2011; 11(6):1123–1130. PMID: 21443676.
Article9. Len O, Gavaldà J, Blanes M, Montejo M, San Juan R, Moreno A, et al. Donor infection and transmission to the recipient of a solid allograft. Am J Transplant. 2008; 8(11):2420–2425. PMID: 18925908.
Article10. Lumbreras C, Sanz F, González A, Pérez G, Ramos MJ, Aguado JM, et al. Clinical significance of donor-unrecognized bacteremia in the outcome of solid-organ transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2001; 33(5):722–726. PMID: 11477528.
Article11. Garzoni C, Ison MG. Uniform definitions for donor-derived infectious disease transmissions in solid organ transplantation. Transplantation. 2011; 92(12):1297–1300. PMID: 21996654.
Article12. Mallon DH, Summers DM, Bradley JA, Pettigrew GJ. Defining delayed graft function after renal transplantation: simplest is best. Transplantation. 2013; 96(10):885–889. PMID: 24056620.13. Corman Dincer P, Tore Altun G, Birtan D, Arslantas R, Sarici Mert N, Özdemir I, et al. Incidence and risk factors for systemic infection in deceased donors. Transplant Proc. 2019; 51(7):2195–2197. PMID: 31378467.
Article14. Albano L, Bretagne S, Mamzer-Bruneel MF, Kacso I, Desnos-Ollivier M, Guerrini P, et al. Evidence that graft-site candidiasis after kidney transplantation is acquired during organ recovery: a multicenter study in France. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 48(2):194–202. PMID: 19090753.
Article15. Wolfe CR, Ison MG. AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Donor-derived infections: guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin Transplant. 2019; 33(9):e13547. PMID: 30903670.
Article16. Huaman MA, Vilchez V, Mei X, Davenport D, Gedaly R. Donor positive blood culture is associated with delayed graft function in kidney transplant recipients: a propensity score analysis of the UNOS database. Clin Transplant. 2016; 30(4):415–420. PMID: 26840885.
Article17. Freeman RB, Giatras I, Falagas ME, Supran S, O'Connor K, Bradley J, et al. Outcome of transplantation of organs procured from bacteremic donors. Transplantation. 1999; 68(8):1107–1111. PMID: 10551637.18. González-Segura C, Pascual M, García Huete L, Cañizares R, Torras J, Corral L, et al. Donors with positive blood culture: could they transmit infections to the recipients? Transplant Proc. 2005; 37(9):3664–3666. PMID: 16386498.
Article19. Yuan X, Chen C, Zhou J, Han M, Wang X, Wang C, et al. Organ donation and transplantation from donors with systemic infection: a single-center experience. Transplant Proc. 2016; 48(7):2454–2457. PMID: 27742320.
Article20. Outerelo C, Gouveia R, Mateus A, Cruz P, Oliveira C, Ramos A. Infected donors in renal transplantation: expanding the donor pool. Transplant Proc. 2013; 45(3):1054–1056. PMID: 23622623.
Article21. Wendt JM, Kaul D, Limbago BM, Ramesh M, Cohle S, Denison AM, et al. Transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection through solid organ transplantation: confirmation via whole genome sequencing. Am J Transplant. 2014; 14(11):2633–2639. PMID: 25250717.22. Kieslichova E, Protus M, Nemcova D, Uchytilova E. Single mutidrug resistant enterobacteriacae donor-derived infection in four solid organ transplant recipients: a case report. BMC Surg. 2019; 19(1):111. PMID: 31412850.
Article23. Kumar D, Cattral MS, Robicsek A, Gaudreau C, Humar A. Outbreak of pseudomonas aeruginosa by multiple organ transplantation from a common donor. Transplantation. 2003; 75(7):1053–1055. PMID: 12698099.24. Kim SH, Ha YE, Youn JC, Park JS, Sung H, Kim MN, et al. Fatal scedosporiosis in multiple solid organ allografts transmitted from a nearly-drowned donor. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15(3):833–840. PMID: 25639881.
Article25. Mularoni A, Bertani A, Vizzini G, Gona F, Campanella M, Spada M, et al. Outcome of transplantation using organs from donors infected or colonized with carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacteria. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15(10):2674–2682. PMID: 25981339.
Article26. Singh N, Huprikar S, Burdette SD, Morris MI, Blair JE, Wheat LJ, et al. Donor-derived fungal infections in organ transplant recipients: guidelines of the American Society of Transplantation, Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Am J Transplant. 2012; 12(9):2414–2428. PMID: 22694672.
Article27. Farnon EC, Kokko KE, Budge PJ, Mbaeyi C, Lutterloh EC, Qvarnstrom Y, et al. Transmission of Balamuthia mandrillaris by organ transplantation. Clin Infect Dis. 2016; 63(7):878–888. PMID: 27358357.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Kidney transplantation from deceased donors with bloodstream infection: a multicenter retrospective study
- A Preliminary Study to Revise the Marginal Donor Criteria of KONOS in Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation
- Outcome of living donor kidney transplant and deceased donor kidney transplant: a retrospective cohort study at national kidney and transplant institute
- Erratum: Pediatric kidney transplantation is different from adult kidney transplantation
- Current Status of Deceased Donor Organ Recovery and Sharing in Korea