J Korean Med Sci.
2021 Dec;36(50):e344. 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e344.
Adult-onset Still’s Disease after BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2523564
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e344
Abstract
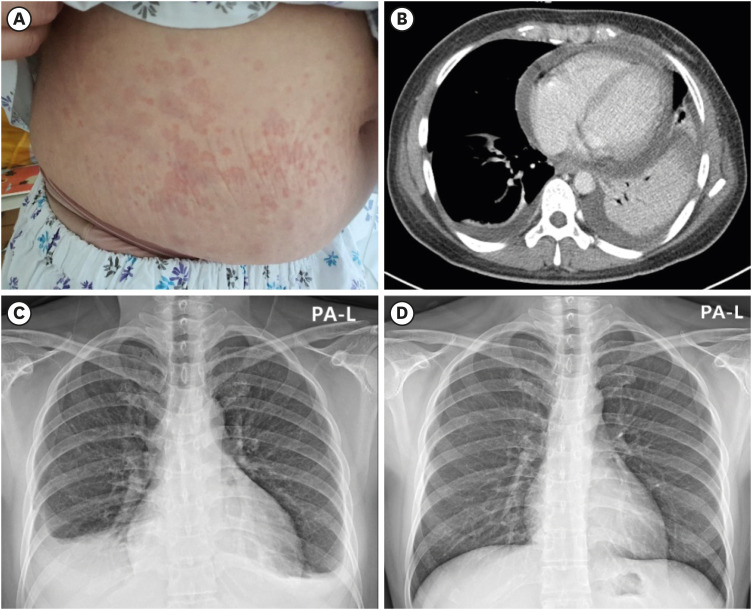
- The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is being overcome by widespread inoculation with various COVID-19 vaccines, but concerns about the safety of the vaccines are a major hurdle to widespread vaccination. We report the first case of adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) developing in a 36-year-old, previously healthy woman after the first dose of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (Pfizer). She visited our hospital due to high spiking fever and sore throat that developed 10 days after vaccination. Based on thorough investigations and changes in symptoms and signs after admission, she was diagnosed with AOSD and treated with high dose steroids and tocilizumab. This report suggests the possibility that AOSD could be triggered by COVID-19 vaccines through activation of the innate immune system.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yamaguchi M, Ohta A, Tsunematsu T, Kasukawa R, Mizushima Y, Kashiwagi H, et al. Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still’s disease. J Rheumatol. 1992; 19(3):424–430. PMID: 1578458.2. Yamamoto S, Nishimura K, Yo K, Waki D, Murabe H, Yokota T. Flare-up of adult-onset Still’s disease after receiving a second dose of BNT162b2 COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2021; 39:Suppl 132. (5):139–140.3. Bamidis AD, Koehler P, di Cristanziano V, Rasche K, Demirel B, Bacher P, et al. First manifestation of adult-onset Still’s disease after COVID-19. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021; 3(5):e319–e321. PMID: 33817663.
Article4. Leone F, Cerasuolo PG, Bosello SL, Verardi L, Fiori E, Cocciolillo F, et al. Adult-onset Still’s disease following COVID-19 vaccination. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021; 3(10):e678–e680. PMID: 34316728.
Article5. Magliulo D, Narayan S, Ue F, Boulougoura A, Badlissi F. Adult-onset Still’s disease after mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021; 3(10):e680–e682. PMID: 34316726.
Article6. Feist E, Mitrovic S, Fautrel B. Mechanisms, biomarkers and targets for adult-onset Still’s disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018; 14(10):603–618. PMID: 30218025.
Article7. Yang L, Xie X, Tu Z, Fu J, Xu D, Zhou Y. The signal pathways and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021; 6(1):255. PMID: 34234112.
Article8. Lustig Y, Sapir E, Regev-Yochay G, Cohen C, Fluss R, Olmer L, et al. BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine and correlates of humoral immune responses and dynamics: a prospective, single-centre, longitudinal cohort study in health-care workers. Lancet Respir Med. 2021; 9(9):999–1009. PMID: 34224675.
Article9. Grasland A, Le Maître F, Pouchot J, Hazera P, Bazin C, Vinceneux P. Adult-onset Still’s disease after hepatitis A and B vaccination? Rev Med Interne. 1998; 19(2):134–136. PMID: 9775130.10. Yoshioka K, Fujimoto S, Oba H, Minami M, Aoki T. Onset of adult-onset Still’s disease following influenza vaccination. Mod Rheumatol. 2011; 21(4):432–435. PMID: 21327453.
Article11. Sato T, Takeo N, Matsuda-Hirose H, Abe K, Nishida H, Hatano Y. Adult-onset Still’s disease following pneumococcal vaccination. Eur J Dermatol. Forthcoming. 2021; DOI: 10.1684/ejd.2021.4102.
Article12. Berardicurti O, Ruscitti P, Ursini F, D’Andrea S, Ciaffi J, Meliconi R, et al. Mortality in tocilizumab-treated patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020; 38(6):1247–1254. PMID: 33275094.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- New-onset Refractory Status Epilepticus after BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination
- mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine-Associated Subserosal Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis: A Case Report
- Case Reports of Acute Transverse Myelitis Associated With mRNA Vaccine for COVID-19
- A Case of Myocarditis Presenting With a Hyperechoic Nodule After the First Dose of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine
- Comparison of Adverse Events of the First Dose and the Second Dose after Vaccination of the COVID-19 Pfizer Vaccine