Diabetes Metab J.
2021 Nov;45(6):921-932. 10.4093/dmj.2020.0187.
Ipragliflozin, an SGLT2 Inhibitor, Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Changes by Upregulating Energy Expenditure through Activation of the AMPK/ SIRT1 Pathway
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Molecular, Cellular and Cancer Biology, Graduate School of Medical Science, Brain Korea 21 Project, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Institute of Endocrine Research, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2522731
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0187
Abstract
- Background
Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are a new class of antidiabetic drugs that exhibit multiple extraglycemic effects. However, there are conflicting results regarding the effects of SGLT2 inhibition on energy expenditure and thermogenesis. Therefore, we investigated the effect of ipragliflozin (a selective SGLT2 inhibitor) on energy metabolism.
Methods
Six-week-old male 129S6/Sv mice with a high propensity for adipose tissue browning were randomly assigned to three groups: normal chow control, 60% high-fat diet (HFD)-fed control, and 60% HFD-fed ipragliflozin-treated groups. The administration of diet and medication was continued for 16 weeks.
Results
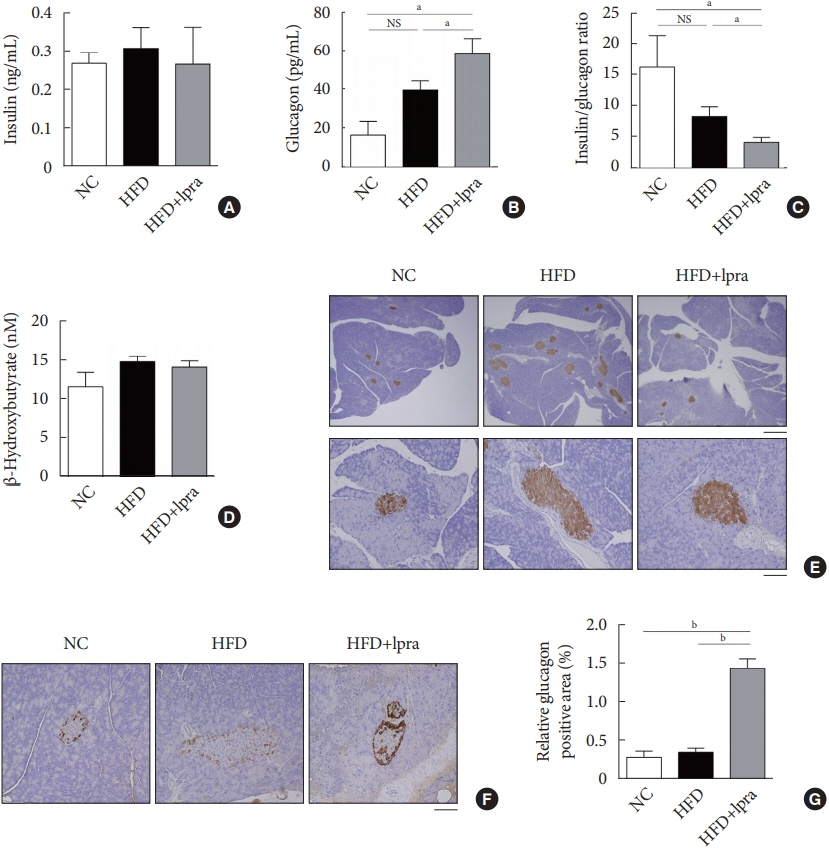
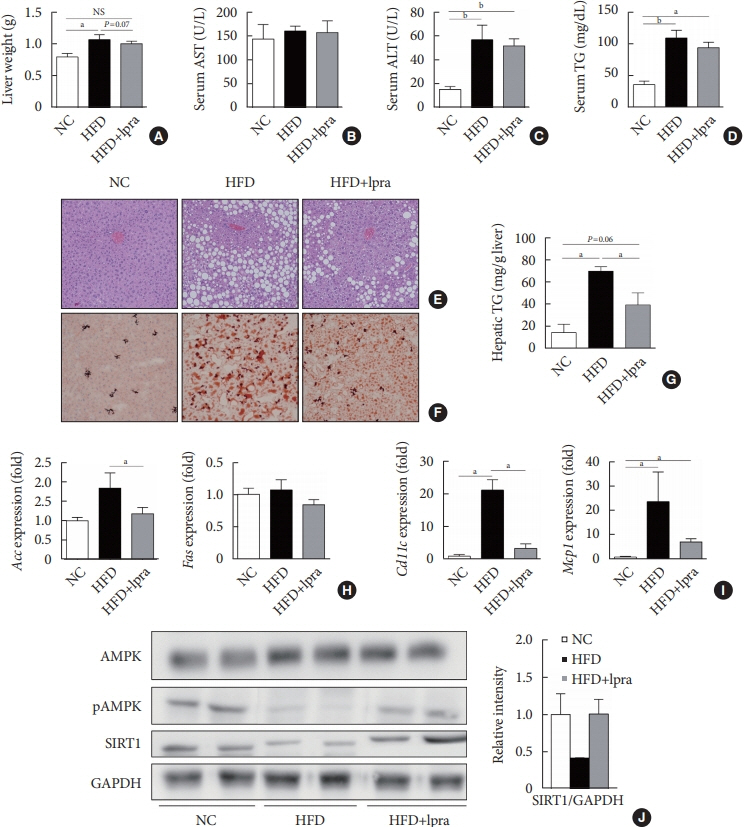
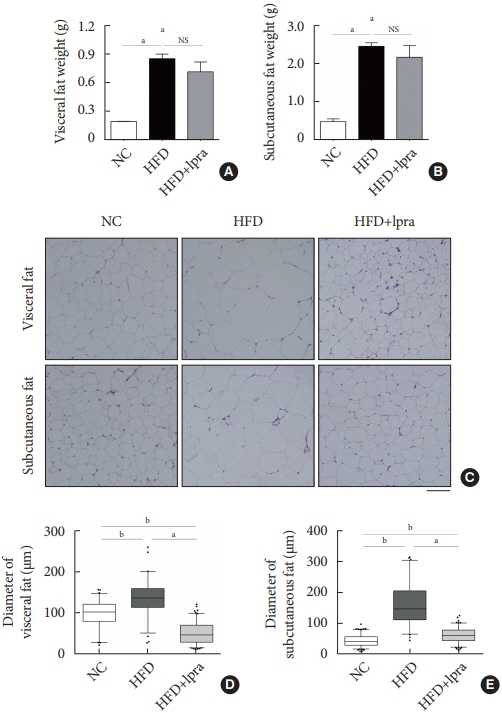
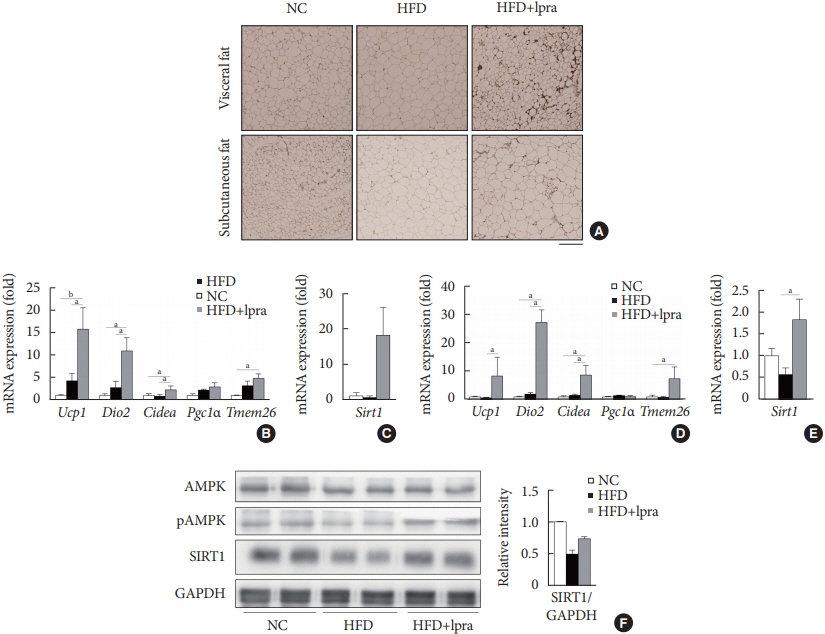
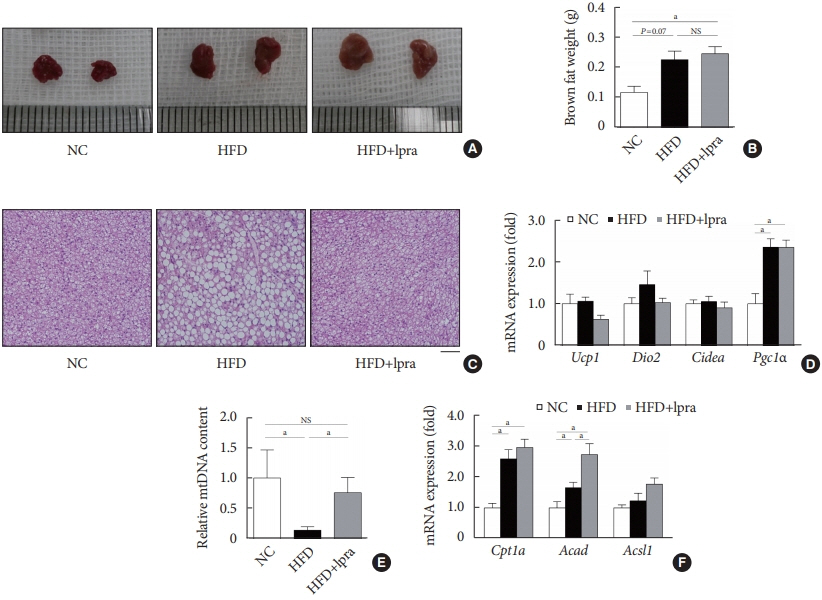
The HFD-fed mice became obese and developed hepatic steatosis and adipose tissue hypertrophy, but their random glucose levels were within the normal ranges; these features are similar to the metabolic features of a prediabetic condition. Ipragliflozin treatment markedly attenuated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis and reduced the size of hypertrophied adipocytes to that of smaller adipocytes. In the ipragliflozin treatment group, uncoupling protein 1 (Ucp1) and other thermogenesis-related genes were significantly upregulated in the visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue, and fatty acid oxidation was increased in the brown adipose tissue. These effects were associated with a significant reduction in the insulin-to-glucagon ratio and the activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) pathway in the liver and adipose tissue.
Conclusion
SGLT2 inhibition by ipragliflozin showed beneficial metabolic effects in 129S6/Sv mice with HFD-induced obesity that mimics prediabetic conditions. Our data suggest that SGLT2 inhibitors, through their upregulation of energy expenditure, may have therapeutic potential in prediabetic obesity.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hruby A, Hu FB. The epidemiology of obesity: a big picture. Pharmacoeconomics. 2015; 33:673–89.
Article2. Ye J. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity. Front Med. 2013; 7:14–24.
Article3. Guh DP, Zhang W, Bansback N, Amarsi Z, Birmingham CL, Anis AH. The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health. 2009; 9:88.
Article4. Harms M, Seale P. Brown and beige fat: development, function and therapeutic potential. Nat Med. 2013; 19:1252–63.
Article5. Kim SH, Plutzky J. Brown fat and browning for the treatment of obesity and related metabolic disorders. Diabetes Metab J. 2016; 40:12–21.
Article6. Sidossis L, Kajimura S. Brown and beige fat in humans: thermogenic adipocytes that control energy and glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 2015; 125:478–86.
Article7. Mullard A. 2013 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014; 13:85–9.
Article8. Chao EC, Henry RR. SGLT2 inhibition: a novel strategy for diabetes treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010; 9:551–9.9. Jung CH, Jang JE, Park JY. A novel therapeutic agent for type 2 diabetes mellitus: SGLT2 inhibitor. Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38:261–73.
Article10. Komiya C, Tsuchiya K, Shiba K, Miyachi Y, Furuke S, Shimazu N, et al. Ipragliflozin improves hepatic steatosis in obese mice and liver dysfunction in type 2 diabetic patients irrespective of body weight reduction. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0151511.
Article11. Chiba Y, Yamada T, Tsukita S, Takahashi K, Munakata Y, Shirai Y, et al. Dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, acutely reduces energy expenditure in BAT via neural signals in mice. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0150756.
Article12. Xu L, Nagata N, Nagashimada M, Zhuge F, Ni Y, Chen G, et al. SGLT2 Inhibition by empagliflozin promotes fat utilization and browning and attenuates inflammation and insulin resistance by polarizing M2 macrophages in diet-induced obese mice. EBioMedicine. 2017; 20:137–49.
Article13. Almind K, Kahn CR. Genetic determinants of energy expenditure and insulin resistance in diet-induced obesity in mice. Diabetes. 2004; 53:3274–85.
Article14. Mori MA, Liu M, Bezy O, Almind K, Shapiro H, Kasif S, et al. A systems biology approach identifies inflammatory abnormalities between mouse strains prior to development of metabolic disease. Diabetes. 2010; 59:2960–71.
Article15. Nair A, Morsy MA, Jacob S. Dose translation between laboratory animals and human in preclinical and clinical phases of drug development. Drug Dev Res. 2018; 79:373–82.
Article16. de Souza CJ, Eckhardt M, Gagen K, Dong M, Chen W, Laurent D, et al. Effects of pioglitazone on adipose tissue remodeling within the setting of obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2001; 50:1863–71.
Article17. Ohno H, Shinoda K, Spiegelman BM, Kajimura S. PPARγ agonists induce a white-to-brown fat conversion through stabilization of PRDM16 protein. Cell Metab. 2012; 15:395–404.
Article18. Beiroa D, Imbernon M, Gallego R, Senra A, Herranz D, Villarroya F, et al. GLP-1 agonism stimulates brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and browning through hypothalamic AMPK. Diabetes. 2014; 63:3346–58.
Article19. Xu F, Lin B, Zheng X, Chen Z, Cao H, Xu H, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonist promotes brown remodelling in mouse white adipose tissue through SIRT1. Diabetologia. 2016; 59:1059–69.
Article20. Shimasaki T, Masaki T, Mitsutomi K, Ueno D, Gotoh K, Chiba S, et al. The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor des-fluoro-sitagliptin regulates brown adipose tissue uncoupling protein levels in mice with diet-induced obesity. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e63626.
Article21. Ferrannini E, Baldi S, Frascerra S, Astiarraga B, Heise T, Bizzotto R, et al. Shift to fatty substrate utilization in response to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in subjects without diabetes and patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2016; 65:1190–5.
Article22. Ferrannini E, Muscelli E, Frascerra S, Baldi S, Mari A, Heise T, et al. Metabolic response to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Invest. 2014; 124:499–508.
Article23. Bonner C, Kerr-Conte J, Gmyr V, Queniat G, Moerman E, Thevenet J, et al. Inhibition of the glucose transporter SGLT2 with dapagliflozin in pancreatic alpha cells triggers glucagon secretion. Nat Med. 2015; 21:512–7.
Article24. Dimitriadis G, Mitrou P, Lambadiari V, Maratou E, Raptis SA. Insulin effects in muscle and adipose tissue. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011; 93 Suppl 1:S52–9.
Article25. Habegger KM, Heppner KM, Geary N, Bartness TJ, DiMarchi R, Tschop MH. The metabolic actions of glucagon revisited. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010; 6:689–97.
Article26. Billington CJ, Bartness TJ, Briggs J, Levine AS, Morley JE. Glucagon stimulation of brown adipose tissue growth and thermogenesis. Am J Physiol. 1987; 252(1 Pt 2):R160–5.
Article27. Kinoshita K, Ozaki N, Takagi Y, Murata Y, Oshida Y, Hayashi Y. Glucagon is essential for adaptive thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue. Endocrinology. 2014; 155:3484–92.
Article28. Umino H, Hasegawa K, Minakuchi H, Muraoka H, Kawaguchi T, Kanda T, et al. High basolateral glucose increases sodiumglucose cotransporter 2 and reduces sirtuin-1 in renal tubules through glucose transporter-2 detection. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:6791.
Article29. Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA. AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012; 13:251–62.
Article30. Feige JN, Lagouge M, Canto C, Strehle A, Houten SM, Milne JC, et al. Specific SIRT1 activation mimics low energy levels and protects against diet-induced metabolic disorders by enhancing fat oxidation. Cell Metab. 2008; 8:347–58.
Article31. Fulco M, Sartorelli V. Comparing and contrasting the roles of AMPK and SIRT1 in metabolic tissues. Cell Cycle. 2008; 7:3669–79.
Article32. Qiang L, Wang L, Kon N, Zhao W, Lee S, Zhang Y, et al. Brown remodeling of white adipose tissue by SirT1-dependent deacetylation of Pparγ. Cell. 2012; 150:620–32.
Article33. Hayashizaki-Someya Y, Kurosaki E, Takasu T, Mitori H, Yamazaki S, Koide K, et al. Ipragliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, exhibits a prophylactic effect on hepatic steatosis and fibrosis induced by choline-deficient l-amino acid-defined diet in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015; 754:19–24.
Article34. Sarashina A, Koiwai K, Seman LJ, Yamamura N, Taniguchi A, Negishi T, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of single doses of empagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, in healthy Japanese subjects. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2013; 28:213–9.
Article35. Tahara A, Kurosaki E, Yokono M, Yamajuku D, Kihara R, Hayashizaki Y, et al. Antidiabetic effects of SGLT2-selective inhibitor ipragliflozin in streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced mildly diabetic mice. J Pharmacol Sci. 2012; 120:36–44.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Unlocking Therapeutic Potential: Camphorquinone’s Role in Alleviating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via SIRT1/ LKB1/AMPK Pathway Activation
- Effects of high-fat diet on the testicular function of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) knockout male mice
- Cryptotanshinone promotes brown fat activity by AMPK activation to inhibit obesity
- Sour cherry ameliorates hepatic lipid synthesis in high-fat diet-induced obese mice via activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signaling
- Quercetin Upregulates Uncoupling Protein 1 in White/Brown Adipose Tissues through Sympathetic Stimulation