Korean J Orthod.
2021 Sep;51(5):329-336. 10.4041/kjod.2021.51.5.329.
External apical root resorption 6 months after initiation of orthodontic treatment: A randomized clinical trial comparing fixed appliances and orthodontic aligners
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, University of North Parana (UNOPAR), Londrina, Brazil
- KMID: 2520375
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2021.51.5.329
Abstract
Objective
To compare the magnitude of external apical root resorption (EARR) 6 months after starting orthodontic treatment using orthodontic aligners (OAs) and fixed appliances (FAs).
Methods
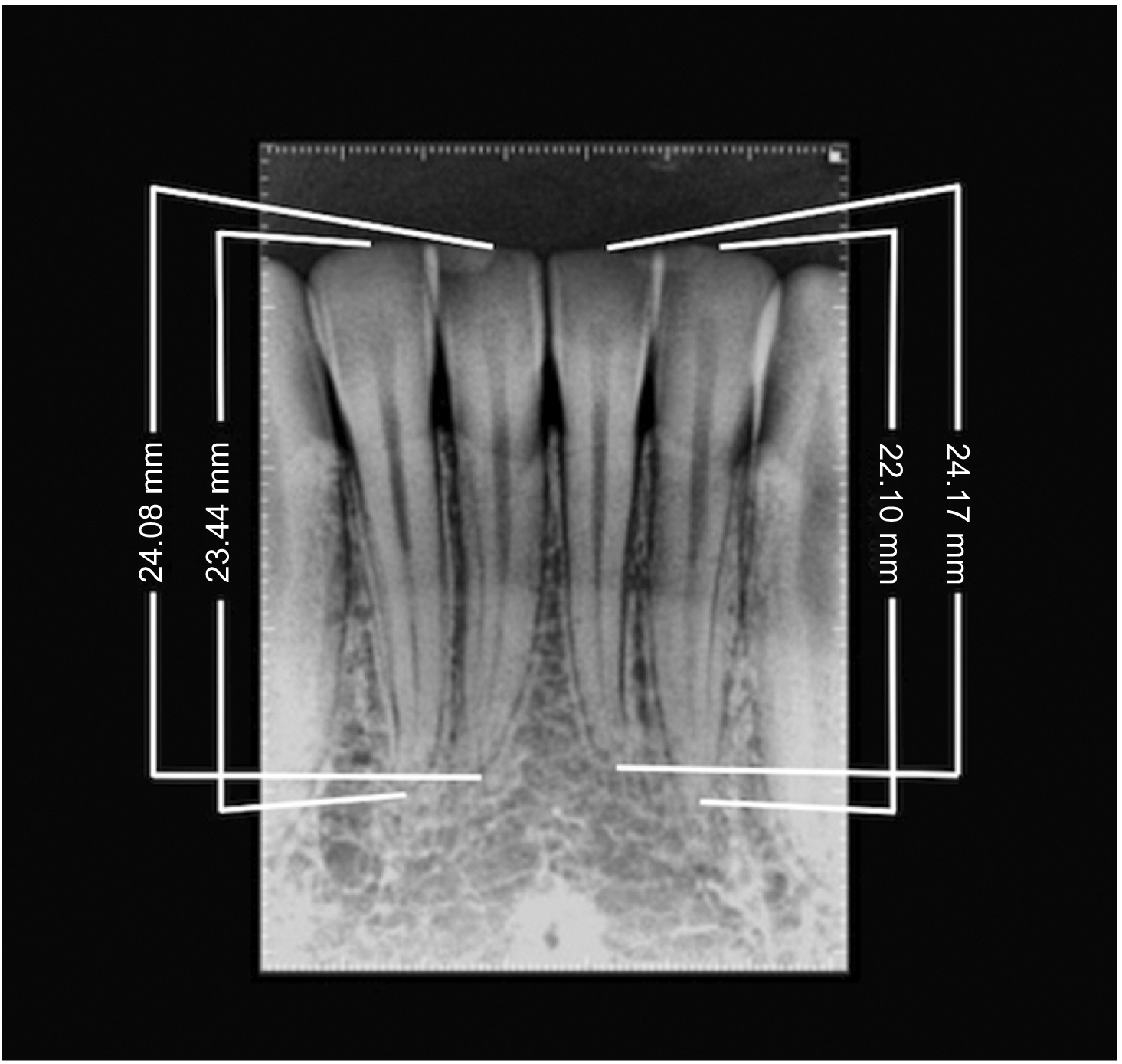
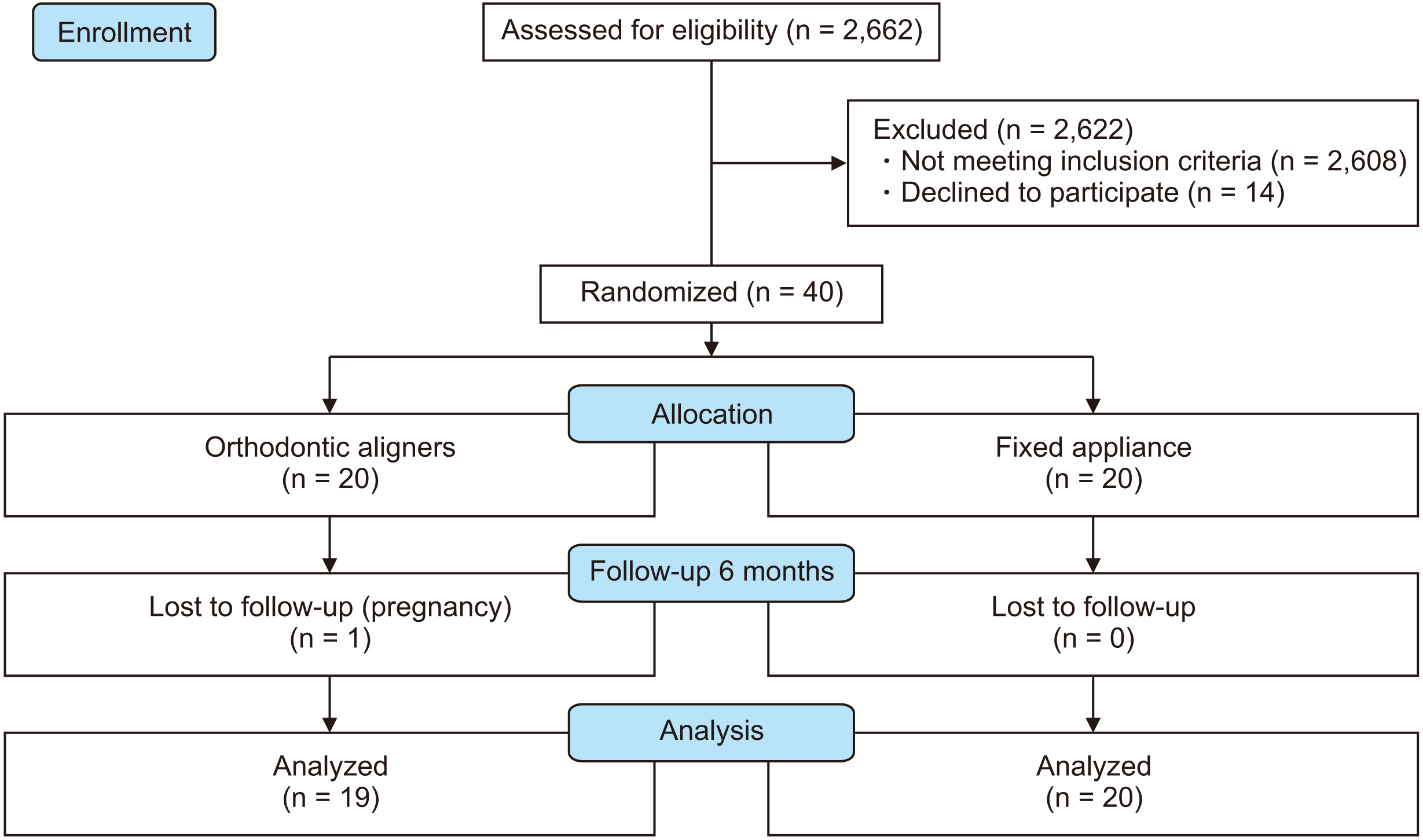
This parallel randomized clinical trial included 40 patients randomized into two groups: OA group (n = 20, 160 incisors) and FA group (n = 20, 160 incisors). For evaluation of the tooth length, periapical radiographs and standardized linear measurements of the maxillary and mandibular incisors were acquired before (T0) and 6 months after treatment initiation (T1). EARR was calculated through the difference in length between the two time points (T1-T0). Statistical comparisons were performed by means of using t-tests, chi-squared test and covariance analysis (a = 5%).
Results
Rounding of the root apex was observed in both groups; the resorption involved 2.88% of the root length, so 97.12% of the tooth length remained intact. Intragroup comparisons between the two time points revealed a significant difference, with (T1-T0) ranging from -0.52 to -0.88 mm in the FA group and from -0.52 to -0.85 mm in the OA group. In the intergroup comparisons, only tooth #21 presented a statistically significant difference (OA: -0.52 ± 0.57 mm, FA: -0.86 ± 0.60 mm); however, the overall differences between groups were not clinically relevant, ranging from 0.03 to 0.35 mm.
Conclusions
OA and FA treatment resulted in a similar degree of EARR in the maxillary and mandibular incisors at 6 months after treatment initiation. However, the amount of resorption was small and does not impair tooth longevity.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brezniak N, Wasserstein A. 2002; Orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption. Part I: the basic science aspects. Angle Orthod. 72:175–9. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(2002)072<0175:OIIRRP>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 11999941.2. Artun J, Smale I, Behbehani F, Doppel D, Van't Hof M, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM. 2005; Apical root resorption six and 12 months after initiation of fixed orthodontic appliance therapy. Angle Orthod. 75:919–26. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(2005)75[919:ARRSAM]2.0.CO;2. PMID: 16448232.3. Artun J, Van 't Hullenaar R, Doppel D, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM. 2009; Identification of orthodontic patients at risk of severe apical root resorption. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 135:448–55. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2007.06.012. PMID: 19361730.4. Sameshima GT, Sinclair PM. 2001; Predicting and preventing root resorption. Part I: diagnostic factors. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 119:505–10. DOI: 10.1067/mod.2001.113409. PMID: 11343022.
Article5. Smale I, Artun J, Behbehani F, Doppel D, van't Hof M, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM. 2005; Apical root resorption 6 months after initiation of fixed orthodontic appliance therapy. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 128:57–67. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2003.12.030. PMID: 16027626.
Article6. Iglesias-Linares A, Sonnenberg B, Solano B, Yañez-Vico RM, Solano E, Lindauer SJ, et al. 2017; Orthodontically induced external apical root resorption in patients treated with fixed appliances vs removable aligners. Angle Orthod. 87:3–10. DOI: 10.2319/02016-101.1. PMID: 27504821.
Article7. Yi J, Xiao J, Li Y, Li X, Zhao Z. 2018; External apical root resorption in non-extraction cases after clear aligner therapy or fixed orthodontic treatment. J Dent Sci. 13:48–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2017.09.007. PMID: 30895094. PMCID: PMC6388840.
Article8. Azaripour A, Weusmann J, Mahmoodi B, Peppas D, Gerhold-Ay A, Van Noorden CJ, et al. 2015; Braces versus Invisalign®: gingival parameters and patients' satisfaction during treatment: a cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health. 15:69. DOI: 10.1186/s12903-015-0060-4. PMID: 26104387. PMCID: PMC4478712.
Article9. Currell SD, Liaw A, Blackmore Grant PD, Esterman A, Nimmo A. 2019; Orthodontic mechanotherapies and their influence on external root resorption: a systematic review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 155:313–29. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2018.10.015. PMID: 30826034.
Article10. Eissa O, Carlyle T, El-Bialy T. 2018; Evaluation of root length following treatment with clear aligners and two different fixed orthodontic appliances. A pilot study J Orthod Sci. 7:11. DOI: 10.4103/jos.JOS_120_17. PMID: 29963506. PMCID: PMC6004740.11. Barbagallo LJ, Jones AS, Petocz P, Darendeliler MA. 2008; Physical properties of root cementum: part 10. Comparison of the effects of invisible removable thermoplastic appliances with light and heavy orthodontic forces on premolar cementum. A microcomputed-tomography study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 133:218–27. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.01.043. PMID: 18249288.
Article12. Nassif CE, Cotrim-Ferreira A, Conti ACCF, Valarelli DP, de Almeida Cardoso M, de Almeida-Pedrin RR. 2017; Comparative study of root resorption of maxillary incisors in patients treated with lingual and buccal orthodontics. Angle Orthod. 87:795–800. DOI: 10.2319/041117-247.1. PMID: 28737425. PMCID: PMC8317570.
Article13. Pandis N. 2011; Randomization. Part 1: sequence generation. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 140:747–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2011.06.020. PMID: 22051497.
Article14. Fleiss JL. 1986; Confidence intervals vs significance tests: quantitative interpretation. Am J Public Health. 76:587–8. DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.76.5.587. PMID: 3963291. PMCID: PMC1646597.
Article15. Lund H, Gröndahl K, Hansen K, Gröndahl HG. 2012; Apical root resorption during orthodontic treatment. A prospective study using cone beam CT. Angle Orthod. 82:480–7. DOI: 10.2319/061311-390.1. PMID: 21919826.16. Krieger E, Drechsler T, Schmidtmann I, Jacobs C, Haag S, Wehrbein H. 2013; Apical root resorption during orthodontic treatment with aligners? A retrospective radiometric study. Head Face Med. 9:21. DOI: 10.1186/1746-160X-9-21. PMID: 23941626. PMCID: PMC3751237.
Article17. Gay G, Ravera S, Castroflorio T, Garino F, Rossini G, Parrini S, et al. 2017; Root resorption during orthodontic treatment with Invisalign®: a radiometric study. Prog Orthod. 18:12. DOI: 10.1186/s40510-017-0166-0. PMID: 28503724. PMCID: PMC5430001.
Article18. Li Y, Deng S, Mei L, Li Z, Zhang X, Yang C, et al. 2020; Prevalence and severity of apical root resorption during orthodontic treatment with clear aligners and fixed appliances: a cone beam computed tomography study. Prog Orthod. 21:1. DOI: 10.1186/s40510-019-0301-1. PMID: 31903505. PMCID: PMC6943096.
Article19. Altman DG. 1991; Randomisation. BMJ. 302:1481–2. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.302.6791.1481. PMID: 1855013. PMCID: PMC1670173.
Article20. Leite V, Conti AC, Navarro R, Almeida M, Oltramari-Navarro P, Almeida R. 2012; Comparison of root resorption between self-ligating and conventional preadjusted brackets using cone beam computed tomography. Angle Orthod. 82:1078–82. DOI: 10.2319/080911-501.1. PMID: 22409394.
Article21. Levander E, Malmgren O, Eliasson S. 1994; Evaluation of root resorption in relation to two orthodontic treatment regimes. A clinical experimental study. Eur J Orthod. 16:223–8. DOI: 10.1093/ejo/16.3.223. PMID: 8062862.
Article22. Apajalahti S, Peltola JS. 2007; Apical root resorption after orthodontic treatment -- a retrospective study. Eur J Orthod. 29:408–12. DOI: 10.1093/ejo/cjm016. PMID: 17631606.23. Reitan K. 1974; Initial tissue behavior during apical root resorption. Angle Orthod. 44:68–82. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(1974)044<0068:ITBDAR>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 4520953.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of micro-osteoperforations on external apical root resorption: A randomized controlled trial
- A study on the affecting factors on root resorption
- The effet of types of orthodontic force on the root resorption and repair in rat molar
- Changes of root length and crestal bone height before and after the orthodontic treatment in nail biting patients
- Initial changes of dental plaque, gingivitis and decalcification in Korean orthodontic patients with fixed appliance