Int J Stem Cells.
2021 Aug;14(3):252-261. 10.15283/ijsc20182.
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes for COVID-19 Therapy, Preclinical and Clinical Evidence
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Metallurgy & Materials Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran
- 2Research Center for Advanced Technologies in Cardiovascular Medicine, Tehran Heart Center, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 3Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran
- 4Stem Cell & Regenerative Medicine Center of Excellence, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 5Tarmim Ava Baran Company, Tehran, Iran
- KMID: 2519368
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc20182
Abstract
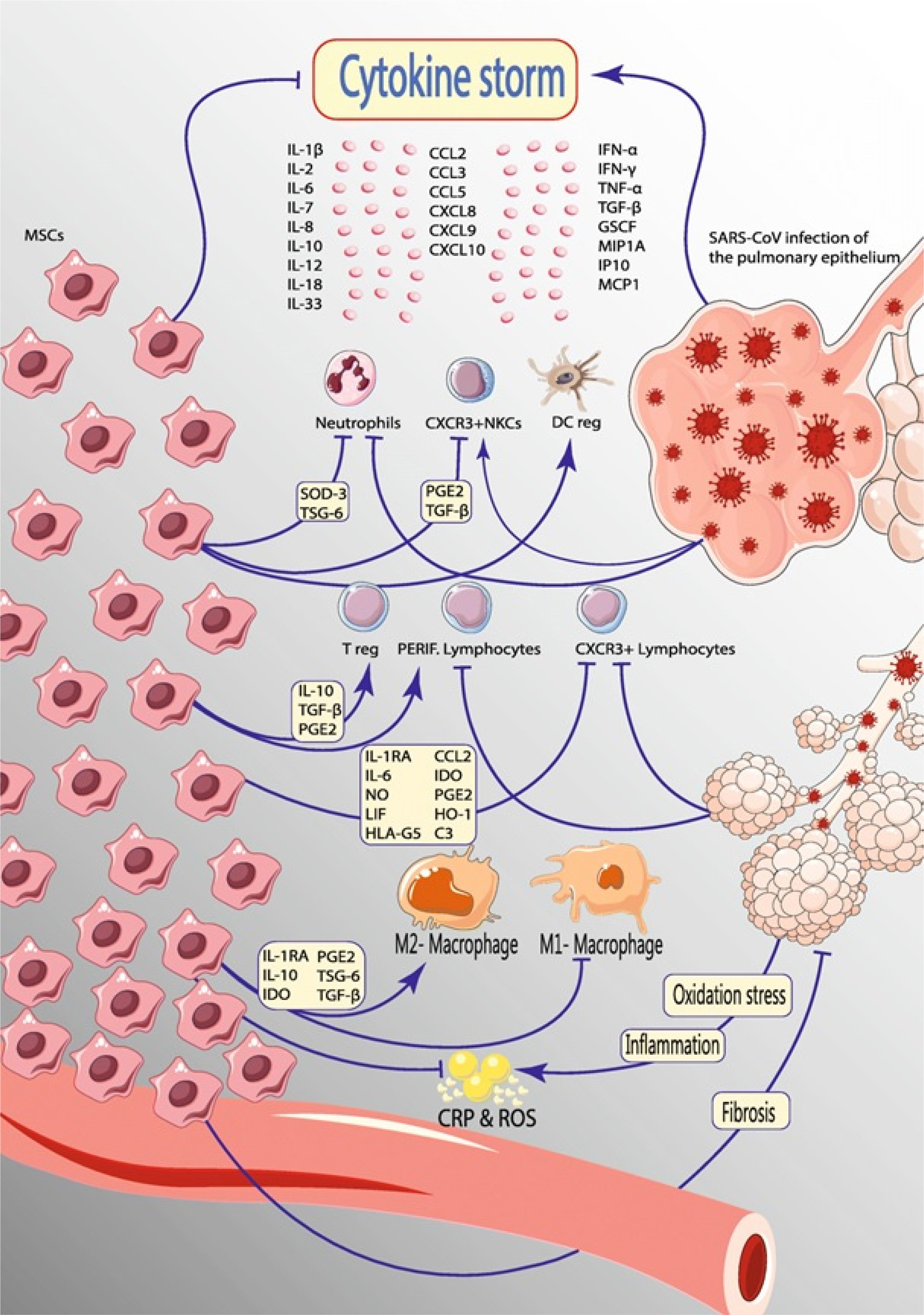
- Since the emergence of the novel coronavirus, named COVID-19, researchers are looking for a treatment to stop the devastating pandemic. During these efforts, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), the potential next generation of therapeutic methods with wide application for diseases, have successfully controlled cytokine storm following the virus infection. However, the use of MSCs has been limited due to the ethical issues, immunogenicity, and genetic modifications. Therefore, exosomes were introduced as a suitable substitute for the MSCs. In the case of COVID-19 treatment, both MSCs and exosomes exert their beneficial effect mainly through the management of the cytokine storm. This study provided the underlying mechanisms for the effect of exosomes on COVID-19 treatment and presented several preclinical and clinical studies of exosomes for COVID-19 treatment.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, Xiang J, Wang Y, Song B, Gu X, Guan L, Wei Y, Li H, Wu X, Xu J, Tu S, Zhang Y, Chen H, Cao B. 2020; Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 395:1054–1062. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. PMID: 32171076. PMCID: PMC7270627.
Article2. Zu ZY, Jiang MD, Xu PP, Chen W, Ni QQ, Lu GM, Zhang LJ. 2020; Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a perspective from China. Radiology. 296:E15–E25. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020200490. PMID: 32083985. PMCID: PMC7233368.
Article3. Pinky , Gupta S, Krishnakumar V, Sharma Y, Dinda AK, Mohanty S. 2021; Mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes: a nano platform for therapeutics and drug delivery in combating COVID-19. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 17:33–43. DOI: 10.1007/s12015-020-10002-z. PMID: 32661867. PMCID: PMC7357441.
Article4. Lee PI, Hsueh PR. 2020; Emerging threats from zoonotic coronaviruses-from SARS and MERS to 2019-nCoV. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 53:365–367. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.001. PMID: 32035811. PMCID: PMC7102579.
Article5. Kupferschmidt K, Cohen J. 2020; Race to find COVID-19 treatments accelerates. Science. 367:1412–1413. DOI: 10.1126/science.367.6485.1412. PMID: 32217705.
Article6. Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB. 2020; Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA. 323:1824–1836. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.6019. PMCID: PMC7492917. PMID: 32282022.7. Soltani S, Zakeri AM, Karimi MR, Rezayat SA, Anbaji FZ, Tabibzadeh A, Yousefi P, Zakeri A, Jafarpour A, Norouzi M, Erfani Y, Poortahmasebi V. 2020; A systematic literature review of current therapeutic approaches for COVID-19 patients. J Pharm Res Int. 32:13–25. DOI: 10.9734/jpri/2020/v32i730455.
Article8. Golchin A, Farahany TZ. 2019; Biological products: cellular therapy and FDA approved products. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 15:166–175. DOI: 10.1007/s12015-018-9866-1. PMID: 30623359.
Article9. Akkoc T. 2020; COVID-19 and mesenchymal stem cell treatment; mystery or not. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1298:167–176. DOI: 10.1007/5584_2020_557. PMID: 32648245.
Article10. Kavianpour M, Saleh M, Verdi J. 2020; The role of mesenchymal stromal cells in immune modulation of COVID-19: focus on cytokine storm. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:404. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-020-01849-7. PMID: 32948252. PMCID: PMC7499002.
Article11. Raza SS, Khan MA. 2020; Mesenchymal stem cells: a new front emerge in COVID19 treatment: mesenchymal stem cells therapy for SARS-CoV2 viral infection. Cytotherapy. [Epub ahead of print]. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2020.07.002. PMCID: PMC7362822.
Article12. Yin K, Wang S, Zhao RC. 2019; Exosomes from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: a new therapeutic paradigm. Biomark Res. 7:8. DOI: 10.1186/s40364-019-0159-x. PMID: 30992990. PMCID: PMC6450000.
Article13. Elahi FM, Farwell DG, Nolta JA, Anderson JD. 2020; Preclinical translation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Stem Cells. 38:15–21. DOI: 10.1002/stem.3061. PMID: 31381842. PMCID: PMC7004029.
Article14. Taghavi-Farahabadi M, Mahmoudi M, Soudi S, Hashemi SM. 2020; Hypothesis for the management and treatment of the COVID-19-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome and lung injury using mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Med Hypotheses. 144:109865. DOI: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109865. PMID: 32562911. PMCID: PMC7242964.
Article15. Mahmoudi M, Taghavi Farahabadi M, Hashemi SM. 2019; Exosomes: mediators of immune regulation. Immunoregu-lation. 2:3–8.
Article16. Shah TG, Predescu D, Predescu S. 2019; Mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles in acute respiratory distress syndrome: a review of current literature and potential future treatment options. Clin Transl Med. 8:25. DOI: 10.1186/s40169-019-0242-9. PMID: 31512000. PMCID: PMC6739436.
Article17. Tisoncik JR, Korth MJ, Simmons CP, Farrar J, Martin TR, Katze MG. 2012; Into the eye of the cytokine storm. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 76:16–32. DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.05015-11. PMID: 22390970. PMCID: PMC3294426.
Article18. Sengupta V, Sengupta S, Lazo A, Woods P, Nolan A, Bremer N. 2020; Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells as treatment for severe COVID-19. Stem Cells Dev. 29:747–754. DOI: 10.1089/scd.2020.0080. PMID: 32380908. PMCID: PMC7310206.
Article19. Tsuchiya A, Takeuchi S, Iwasawa T, Kumagai M, Sato T, Motegi S, Ishii Y, Koseki Y, Tomiyoshi K, Natsui K, Takeda N, Yoshida Y, Yamazaki F, Kojima Y, Watanabe Y, Kimura N, Tominaga K, Kamimura H, Takamura M, Terai S. 2020; Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes in severe novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases. Inflamm Regen. 40:14. DOI: 10.1186/s41232-020-00121-y. PMID: 32582401. PMCID: PMC7306412.
Article20. Golchin A, Seyedjafari E, Ardeshirylajimi A. 2020; Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for COVID-19: present or future. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 16:427–433. DOI: 10.1007/s12015-020-09973-w. PMID: 32281052. PMCID: PMC7152513.
Article21. Khakoo AY, Pati S, Anderson SA, Reid W, Elshal MF, Rovira II, Nguyen AT, Malide D, Combs CA, Hall G, Zhang J, Raffeld M, Rogers TB, Stetler-Stevenson W, Frank JA, Reitz M, Finkel T. 2006; Human mesenchymal stem cells exert potent antitumorigenic effects in a model of Kaposi's sarcoma. J Exp Med. 203:1235–1247. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20051921. PMID: 16636132. PMCID: PMC2121206.
Article22. Li Y, Xu J, Shi W, Chen C, Shao Y, Zhu L, Lu W, Han X. 2016; Mesenchymal stromal cell treatment prevents H9N2 avian influenza virus-induced acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 7:159. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-016-0395-z. PMID: 27793190. PMCID: PMC5084318.
Article23. Curley GF, Jerkic M, Dixon S, Hogan G, Masterson C, O'Toole D, Devaney J, Laffey JG. 2017; Cryopreserved, xeno-free human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells reduce lung injury severity and bacterial burden in rodent Escherichia coli-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 45:e202–e212. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002073. PMID: 27861182.
Article24. Nauta AJ, Fibbe WE. 2007; Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. Blood. 110:3499–3506. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-02-069716. PMID: 17664353.
Article25. Choi H, Lee RH, Bazhanov N, Oh JY, Prockop DJ. 2011; Anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6 secreted by activated MSCs attenuates zymosan-induced mouse peritonitis by decreasing TLR2/NF-κB signaling in resident macrophages. Blood. 118:330–338. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-327353. PMID: 21551236. PMCID: PMC3138686.
Article26. Gorabi AM, Kiaie N, Barreto GE, Read MI, Tafti HA, Sahebkar A. 2019; The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in treatment of neurodegene-rative diseases. Mol Neurobiol. 56:8157–8167. DOI: 10.1007/s12035-019-01663-0. PMID: 31197655.
Article27. Davis ME. 2016; Exosomes: what do we love so much about them? Circ Res. 119:1280–1282. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.309942. PMID: 27932472. PMCID: PMC5161232.28. Kourembanas S. 2015; Exosomes: vehicles of intercellular signaling, biomarkers, and vectors of cell therapy. Annu Rev Physiol. 77:13–27. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021014-071641. PMID: 25293529.
Article29. Blazquez R, Sanchez-Margallo FM, de la Rosa O, Dalemans W, Alvarez V, Tarazona R, Casado JG. 2014; Immunomodulatory potential of human adipose mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes on in vitro stimulated T cells. Front Immunol. 5:556. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00556. PMID: 25414703. PMCID: PMC4220146.
Article30. Mokarizadeh A, Delirezh N, Morshedi A, Mosayebi G, Farshid AA, Dalir-Naghadeh B. 2012; Phenotypic modulation of auto-reactive cells by insertion of tolerogenic molecules via MSC-derived exosomes. Vet Res Forum. 3:257–261. PMID: 25653768. PMCID: PMC4313045.31. Kadriyan H, Prasedya ES, Pieter NAL, Gaffar M, Punagi AQ, Bukhari A. 2020; The potential role of exosome on cytokine storm and treatment of severe COVID-19 infection. Bali Med J (Bali Med J). 9:630–636. DOI: 10.15562/bmj.v9i3.1966.
Article32. Zhu YG, Feng XM, Abbott J, Fang XH, Hao Q, Monsel A, Qu JM, Matthay MA, Lee JW. 2014; Human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles for treatment of Escherichia coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cells. 32:116–125. DOI: 10.1002/stem.1504. PMID: 23939814. PMCID: PMC3947321.
Article33. Li JW, Wei L, Han Z, Chen Z. 2019; Mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosomes alleviate ischemia/reperfusion injury in mouse lung by transporting anti-apoptotic miR-21-5p. Eur J Pharmacol. 852:68–76. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.01.022. PMID: 30682335.
Article34. Monsel A, Zhu YG, Gennai S, Hao Q, Hu S, Rouby JJ, Rosenzwajg M, Matthay MA, Lee JW. 2015; Therapeutic effects of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles in severe pneumonia in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 192:324–336. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201410-1765OC. PMID: 26067592. PMCID: PMC4584251.
Article35. DeMarino C, Pleet ML, Cowen M, Barclay RA, Akpamagbo Y, Erickson J, Ndembi N, Charurat M, Jumare J, Bwala S, Alabi P, Hogan M, Gupta A, Noren Hooten N, Evans MK, Lepene B, Zhou W, Caputi M, Romerio F, Royal W 3rd, El-Hage N, Liotta LA, Kashanchi F. 2018; Antiretroviral drugs alter the content of extracellular vesicles from HIV-1-infected cells. Sci Rep. 8:7653. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-25943-2. PMID: 29769566. PMCID: PMC5955991.
Article36. Gennai S, Monsel A, Hao Q, Park J, Matthay MA, Lee JW. 2015; Microvesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells restore alveolar fluid clearance in human lungs rejected for transplantation. Am J Transplant. 15:2404–2412. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.13271. PMID: 25847030. PMCID: PMC4792255.
Article37. Khatri M, Richardson LA, Meulia T. 2018; Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate influenza virus-induced acute lung injury in a pig model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 9:17. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-018-0774-8. PMID: 29378639. PMCID: PMC5789598.
Article38. Tang XD, Shi L, Monsel A, Li XY, Zhu HL, Zhu YG, Qu JM. 2017; Mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles attenuate acute lung injury in mice partly mediated by Ang-1 mRNA. Stem Cells. 35:1849–1859. DOI: 10.1002/stem.2619. PMID: 28376568.
Article39. Hu S, Park J, Liu A, Lee J, Zhang X, Hao Q, Lee JW. 2018; Mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles restore protein permeability across primary cultures of injured human lung microvascular endothelial cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 7:615–624. DOI: 10.1002/sctm.17-0278. PMID: 29737632. PMCID: PMC6090509.
Article40. Varkouhi AK, Jerkic M, Ormesher L, Gagnon S, Goyal S, Rabani R, Masterson C, Spring C, Chen PZ, Gu FX, Dos Santos CC, Curley GF, Laffey JG. 2019; Extracellular vesicles from interferon-γ-primed human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells reduce escherichia coli-induced acute lung injury in rats. Anesthesiology. 130:778–790. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002655. PMID: 30870158.
Article41. Park J, Kim S, Lim H, Liu A, Hu S, Lee J, Zhuo H, Hao Q, Matthay MA, Lee JW. 2019; Therapeutic effects of human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles in an ex vivo perfused human lung injured with severe E. coli pneumonia. Thorax. 74:43–50. DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2018-211576. PMID: 30076187. PMCID: PMC6295323.
Article42. Li X, Corbett AL, Taatizadeh E, Tasnim N, Little JP, Garnis C, Daugaard M, Guns E, Hoorfar M, Li ITS. 2019; Challenges and opportunities in exosome research-Pers-pectives from biology, engineering, and cancer therapy. APL Bioeng. 3:011503. DOI: 10.1063/1.5087122. PMID: 31069333. PMCID: PMC6481742.
Article43. Witwer KW, Van Balkom BWM, Bruno S, Choo A, Dominici M, Gimona M, Hill AF, De Kleijn D, Koh M, Lai RC, Mitsialis SA, Ortiz LA, Rohde E, Asada T, Toh WS, Weiss DJ, Zheng L, Giebel B, Lim SK. 2019; Defining mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC)-derived small extracellular vesicles for therapeutic applications. J Extracell Vesicles. 8:1609206. DOI: 10.1080/20013078.2019.1609206. PMID: 31069028. PMCID: PMC6493293.
Article44. Greening DW, Xu R, Ji H, Tauro BJ, Simpson RJ. 2015; A protocol for exosome isolation and characterization: evaluation of ultracentrifugation, density-gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods. Methods Mol Biol. 1295:179–209. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2550-6_15. PMID: 25820723.
Article45. Ludwig N, Whiteside TL, Reichert TE. 2019; Challenges in exosome isolation and analysis in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. 20:4684. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20194684. PMID: 31546622. PMCID: PMC6801453.
Article46. Ludwig N, Yerneni SS, Razzo BM, Whiteside TL. 2018; Exosomes from HNSCC promote angiogenesis through reprogramming of endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Res. 16:1798–1808. DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0358. PMID: 30042174.
Article47. Chettimada S, Lorenz DR, Misra V, Dillon ST, Reeves RK, Manickam C, Morgello S, Kirk GD, Mehta SH, Gabuzda D. 2018; Exosome markers associated with immune activation and oxidative stress in HIV patients on antiretroviral therapy. Sci Rep. 8:7227. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-25515-4. PMID: 29740045. PMCID: PMC5940833.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: A Promising Therapeutic Ace Card to Address Autoimmune Diseases
- The efficacy of exosomes from human chemically derived hepatic progenitors in liver damage alleviation: a preclinical experimental study
- New Approaches for Enhancement of the Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Cardiovascular Diseases
- Using Pre-Clinical Studies to Explore the Potential Clinical Uses of Exosomes Secreted from Induced Pluripotent Stem CellDerived Mesenchymal Stem cells
- Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in the Management of COVID19-Associated Lung Injury: A Review on Publications, Clinical Trials and Patent Landscape