Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2021 Aug;25(3):366-370. 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.3.366.
Microwave ablation of colorectal liver metastases: Impact of a 10-mm safety margin on local recurrence in a tertiary care hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery Unit, Department of Digestive Surgery, Vigo University Hospital, Vigo, Spain
- 2Department of Radiology, Vigo University Hospital, Vigo, Spain
- 3Liver Transplant Unit, Department of Surgery, Verona University Hospital, Verona, Italy
- KMID: 2519293
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.3.366
Abstract
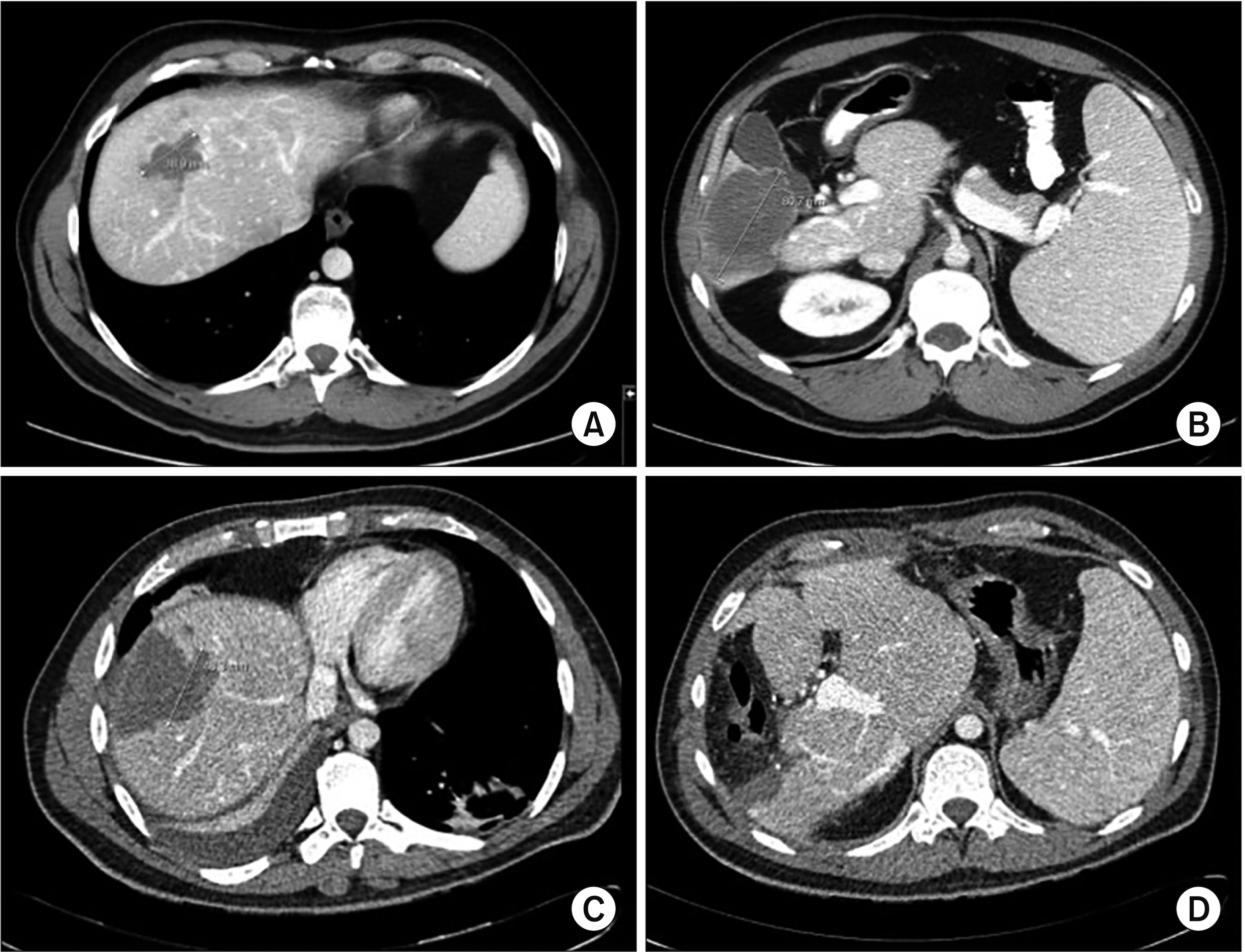
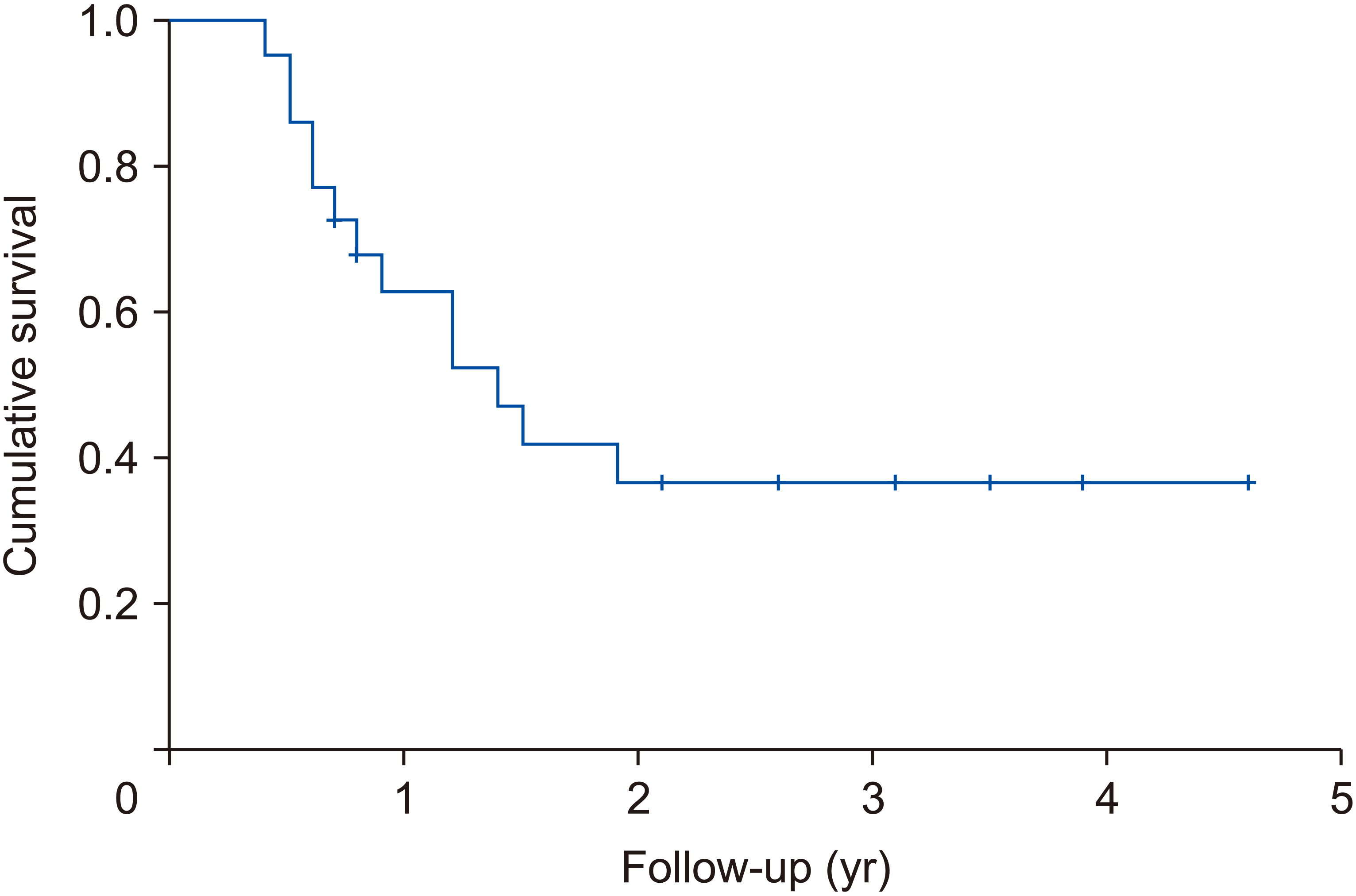
- Microwave ablation (MWA) for colorectal liver metastasis (CLM) has been traditionally considered inferior to surgery due to the higher rate of local recurrence. The study investigated whether a safety margin of 10 mm can improve local control in patients undergoing surgical MWA. Surgical MWA was used to treat 53 lesions in 22 patients with CLM at our Institution from June 2012 to June 2017. The patients’ mean age was 64.5 years, and the median size of the lesion was 16.5 mm (9–34 mm). MWA was associated with liver resection in 16 patients (72.7%). The median follow-up was 32.4 months. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify factors associated with tumor recurrence. Median ablation area was 36.6 mm2 (30–50 mm2 ). The complication rate was 22.7%. No local recurrence was observed during follow-up. Disease-free survival was 20 months (4.8–55.2 months). Univariate analysis revealed that the number of liver metastases and node-positive primary tumors were associated with tumor recurrence. Multivariate analysis revealed that node-positive primary tumor was the only factor significantly associated with tumor recurrence (p = 0.049; odds ratio, 12; 95% confidence interval, 1–143). When performed with a 10-mm safety margin, surgical MWA can lead to acceptable oncological outcomes with low morbidity. Therefore, it represents a good option in selected patients with CLM.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Diaz-Nieto R, Fenwick S, Malik H, Poston G. 2017; Defining the optimal use of ablation for metastatic colorectal cancer to the liver without high-level evidence. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 18:8. DOI: 10.1007/s11864-017-0452-6. PMID: 28214976.
Article2. Pathak S, Jones R, Tang JM, Parmar C, Fenwick S, Malik H, et al. 2011; Ablative therapies for colorectal liver metastases: a systematic review. Colorectal Dis. 13:e252–e265. DOI: 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2011.02695.x. PMID: 21689362.
Article3. Bala MM, Riemsma RP, Wolff R, Kleijnen J. 2013; Microwave coagulation for liver metastases. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (10):CD010163. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010163.pub2. PMID: 24122576.
Article4. Koda M, Tokunaga S, Miyoshi K, Kishina M, Fujise Y, Kato J, et al. 2013; Ablative margin states by magnetic resonance imaging with ferucarbotran in radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma can predict local tumor progression. J Gastroenterol. 48:1283–1292. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-012-0747-0. PMID: 23338488.
Article5. Kono M, Inoue T, Kudo M, Chishina H, Arizumi T, Takita M, et al. 2014; Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma measuring 2 cm or smaller: results and risk factors for local recurrence. Dig Dis. 32:670–677. DOI: 10.1159/000367999. PMID: 25376283.
Article6. Ke S, Ding XM, Qian XJ, Zhou YM, Cao BX, Gao K, et al. 2013; Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma sized > 3 and ≤ 5 cm: is ablative margin of more than 1 cm justified? World J Gastroenterol. 19:7389–7398. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7389.7. Liao M, Zhong X, Zhang J, Liu Y, Zhu Z, Wu H, et al. 2017; Radiofrequency ablation using a 10-mm target margin for small hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with liver cirrhosis: a prospective randomized trial. J Surg Oncol. 115:971–979. DOI: 10.1002/jso.24607. PMID: 28334430.
Article8. Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. 2004; Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 240:205–213. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae. PMID: 15273542. PMCID: PMC1360123.9. Brace CL. 2009; Radiofrequency and microwave ablation of the liver, lung, kidney, and bone: what are the differences? Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 38:135–143. DOI: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2007.10.001. PMID: 19298912. PMCID: PMC2941203.
Article10. Cirocchi R, Trastulli S, Boselli C, Montedori A, Cavaliere D, Parisi A, et al. 2012; Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (6):CD006317. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006317.pub3. PMID: 22696357.
Article11. Weng M, Zhang Y, Zhou D, Yang Y, Tang Z, Zhao M, et al. 2012; Radiofrequency ablation versus resection for colorectal cancer liver metastases: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 7:e45493. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045493. PMID: 23029051. PMCID: PMC3448670.
Article12. Beppu T, Sakamoto Y, Hasegawa K, Honda G, Tanaka K, Kotera Y, et al. 2012; A nomogram predicting disease-free survival in patients with colorectal liver metastases treated with hepatic resection: multicenter data collection as a Project Study for Hepatic Surgery of the Japanese Society of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 19:72–84. DOI: 10.1007/s00534-011-0460-z. PMID: 22020927.
Article13. Philips P, Groeschl RT, Hanna EM, Swan RZ, Turaga KK, Martinie JB, et al. 2016; Single-stage resection and microwave ablation for bilobar colorectal liver metastases. Br J Surg. 103:1048–1054. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.10159. PMID: 27191368.
Article14. Cai YL, Song PP, Tang W, Cheng NS. 2016; An updated systematic review of the evolution of ALPPS and evaluation of its advantages and disadvantages in accordance with current evidence. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e3941. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003941. PMID: 27311006. PMCID: PMC4998492.
Article15. Eisele RM, Neumann U, Neuhaus P, Schumacher G. 2009; Open surgical is superior to percutaneous access for radiofrequency ablation of hepatic metastases. World J Surg. 33:804–811. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-008-9905-1. PMID: 19184639.
Article16. Burdio F, Mulier S, Navarro A, Figueras J, Berjano E, Poves I, et al. 2008; Influence of approach on outcome in radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. Surg Oncol. 17:295–299. DOI: 10.1016/j.suronc.2008.03.002. PMID: 18472417.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Metastases from Colorectal Cancer: A Literature Review
- Ablation therapy for patients with colorectal liver metastases with and without extrahepatic metastases: evaluation of long-term outcomes and prognostic factors
- Prognostic factors associated with local recurrence in squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva
- Outcomes after a Hepatic Resection for Multiple Hepatic Metastases from Colorectal Cancer
- Treatment of Liver Metastases