Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2021 Aug;14(3):268-277. 10.21053/ceo.2020.01942.
Significance of Pseudo-Conductive Hearing Loss and Positional Nystagmus for Perilymphatic Fistula: Are They Related to Third-Window Effects?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2519181
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2020.01942
Abstract
Objectives
. Patients’ clinical presentation is critical for identifying suspected perilymphatic fistula (PLF). The involvement of third-window lesions in the pathomechanism of PLF has been hypothesized. This study investigated the clinical features of PLF and the relationship of the third-window effect with PLF.
Methods
. Sixty patients underwent surgical exploration for suspected PLF and the oval and round windows were reinforced. Clinical features including demographics, pure-tone audiometry (PTA), and videonystagmography were evaluated preoperatively and 1 month postoperatively. Surgical outcomes were analyzed according to the improvement of hearing and vestibular symptoms and signs. The conductive components of PTA (air-bone gap [ABG]) were measured, and the relationship between ABG closure after surgery and hearing improvement was analyzed. In addition, postoperative subjective dizziness was assessed by clinical interviews. Changes in positional nystagmus were analyzed according to ABG closure and hearing improvement.
Results
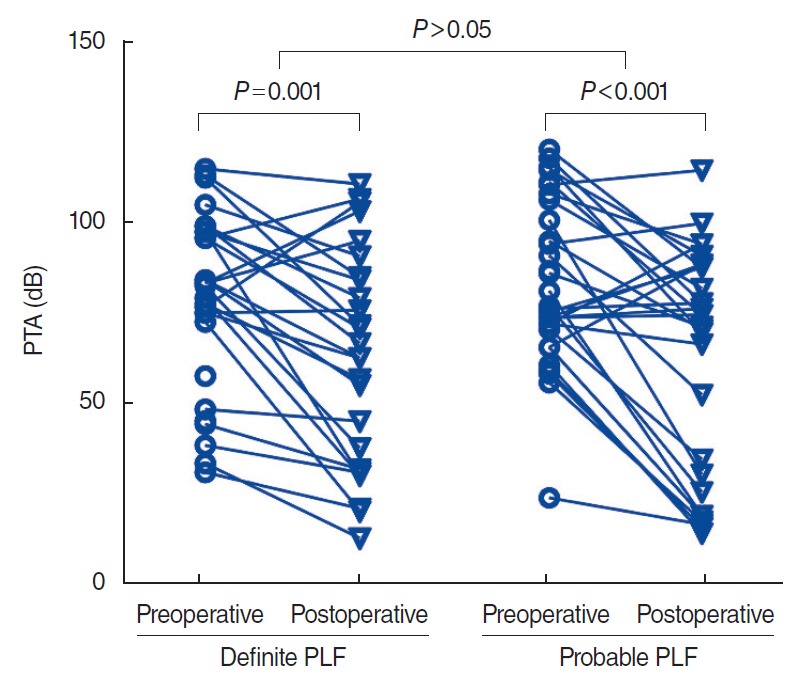
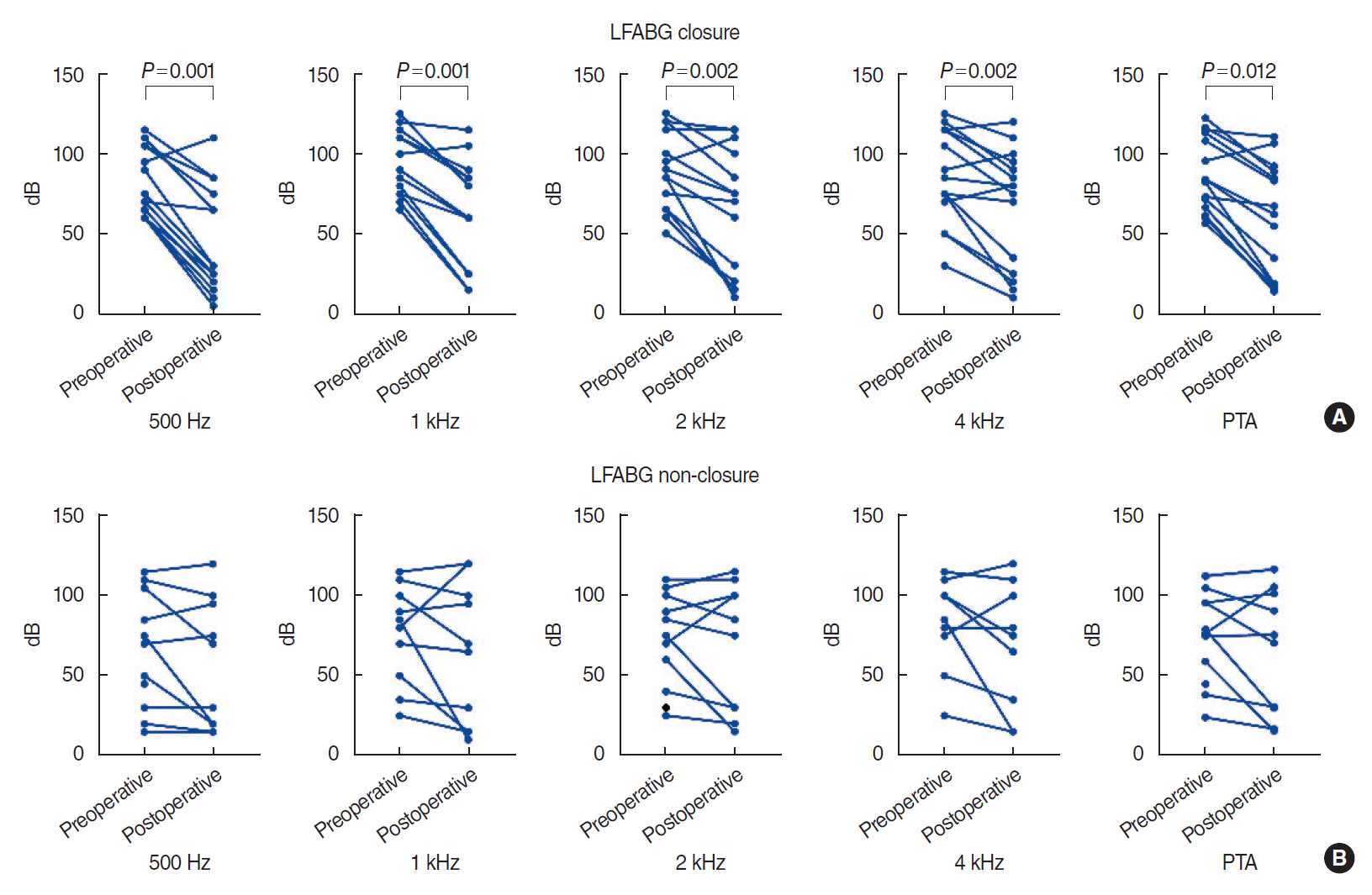
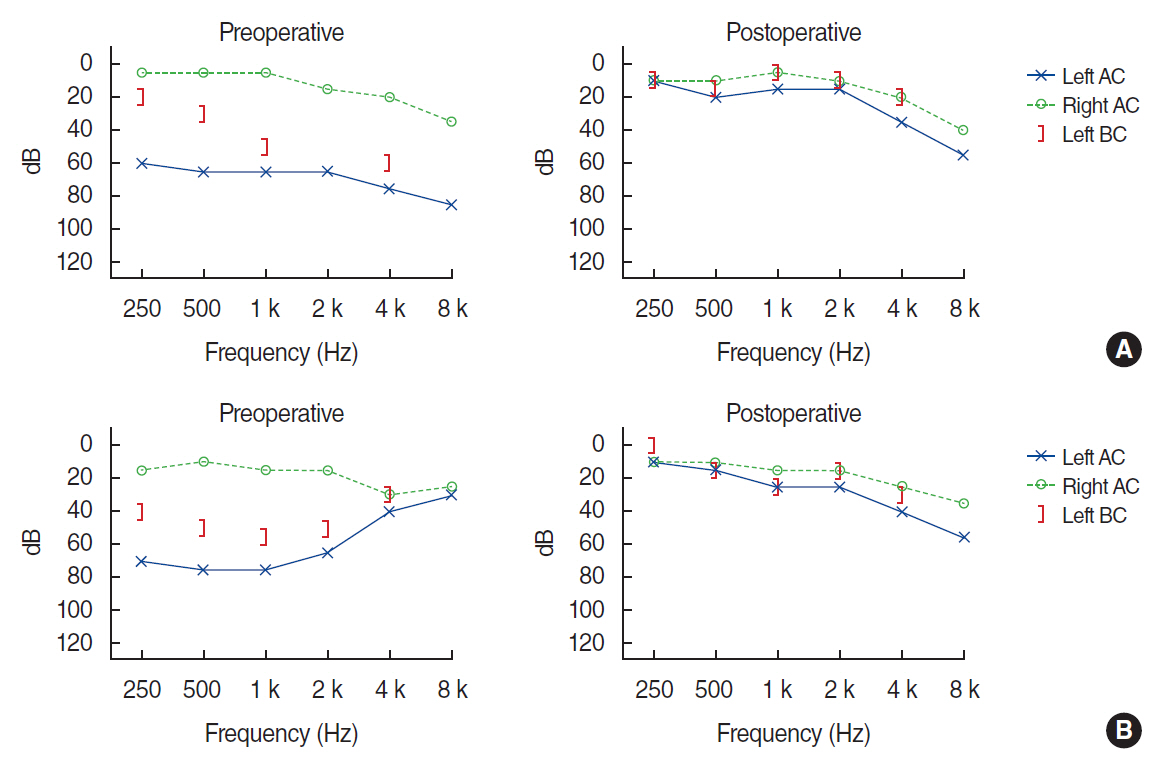
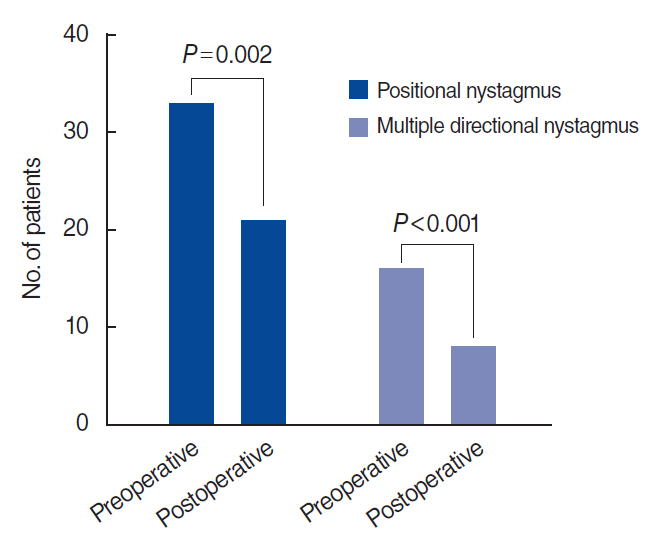
. ABG at lower frequencies (LFABG; 250 Hz, 500 Hz, 1,000 Hz) was present in 27 patients (45%). Postoperatively, PTA significantly improved after surgical repair. Among the patients with preoperative LFABG (n=27), 15 (55.5%) showed postoperative ABG closure and significant improvement in PTA at all frequencies compared with the patients without ABG closure (P=0.012). Subjective dizziness improved in 57 patients (93.3%). Positional nystagmus was found in 45 of 49 patients. Multiple canal involvement was more common than single canal involvement (67% vs. 33%). The horizontal semicircular canal was most commonly involved, followed by the posterior and anterior canals. Postoperatively, positional nystagmus disappeared, or the number of involved canals decreased in 22 of 34 patients (64.7%).
Conclusion
. Pseudo-conductive hearing loss at lower frequencies and positional nystagmus originating from multiple semicircular canals were common findings in PLF. Surgical reinforcement of the oval and round windows improved the hearing threshold accompanied by closure of ABG. A third-window lesion might explain these clinical features of PLF.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goodhill V, Brockman SJ, Harris I, Hantz O. Sudden deafness and labyrinthine window ruptures: audio-vestibular observations. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1973; Jan-Feb. 82(1):2–12.2. Hornibrook J. Perilymph fistula: fifty years of controversy. ISRN Otolaryngol. 2012; Jul. 2012:281248.
Article3. Hornibrook J. A balance test for chronic perilymph fistula. Int J Otolaryngol. 2012; 2012:163691.
Article4. Choi JE, Moon IJ, Kim H, Lee K, Cho YS, Chung WH. Diagnostic criteria of barotraumatic perilymph fistula based on clinical manifestations. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017; Jan. 137(1):16–22.
Article5. Ahn J, Son SE, Choi JE, Cho YS, Chung WH. Surgical outcomes on hearing and vestibular symptoms in barotraumatic perilymphatic fistula. Otol Neurotol. 2019; Apr. 40(4):e356–63.
Article6. Ho ML, Moonis G, Halpin CF, Curtin HD. Spectrum of third window abnormalities: semicircular canal dehiscence and beyond. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017; Jan. 38(1):2–9.
Article7. Ward BK, Carey JP, Minor LB. Superior canal dehiscence syndrome: lessons from the first 20 years. Front Neurol. 2017; Apr. 8:177.
Article8. Merchant SN, Rosowski JJ. Conductive hearing loss caused by third-window lesions of the inner ear. Otol Neurotol. 2008; Apr. 29(3):282–9.
Article9. Wackym PA, Wood SJ, Siker DA, Carter DM. Otic capsule dehiscence syndrome: superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome with no radiographically visible dehiscence. Ear Nose Throat J. 2015; Aug. 94(8):E8–24.
Article10. Park GY, Byun H, Moon IJ, Hong SH, Cho YS, Chung WH. Effects of early surgical exploration in suspected barotraumatic perilymph fistulas. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; Jun. 5(2):74–80.
Article11. Alzahrani M, Fadous R, Dufour JJ, Saliba I. Perilymphatic fistulas: can we predict the diagnosis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015; Aug. 272(8):1885–91.
Article12. Black FO, Lilly DJ, Nashner LM, Peterka RJ, Pesznecker SC. Quantitative diagnostic test for perilymph fistulas. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1987; Feb. 96(2):125–34.
Article13. Daspit CP, Churchill D, Linthicum FH Jr. Diagnosis of perilymph fistula using ENG and impedance. Laryngoscope. 1980; Feb. 90(2):217–23.
Article14. Pyykko I, Selmani Z, Zou J. Low-frequency sound pressure and transtympanic endoscopy of the middle ear in assessment of “spontaneous” perilymphatic fistula. ISRN Otolaryngol. 2012; Aug. 2012:137623.15. Black FO, Lilly DJ, Peterka RJ, Shupert C, Hemenway WG, Pesznecker SC. The dynamic posturographic pressure test for the presumptive diagnosis of perilymph fistulas. Neurol Clin. 1990; May. 8(2):361–74.
Article16. Sugimoto S, Yoshida T, Teranishi M, Okazaki Y, Naganawa S, Sone M. The relationship between endolymphatic hydrops in the vestibule and low-frequency air-bone gaps. Laryngoscope. 2018; Jul. 128(7):1658–62.
Article17. Muchnik C, Hildesheimer M, Rubinstein M, Arenberg IK. Low frequency air-bone gap in Meniere’s disease without middle ear pathology: a preliminary report. Am J Otol. 1989; Jan. 10(1):1–4.18. Bohmer A. On the pathomechanism of cochlear dysfunction in experimental perilymph fistulas. Laryngoscope. 1991; Dec. 101(12 Pt 1):1307–12.
Article19. Simmons FB. The double-membrane break syndrome in sudden hearing loss. Laryngoscope. 1979; Jan. 89(1):59–66.
Article20. Onishi ET, Fukuda Y. Perilymphatic fistula in guinea pigs: natural evolution versus surgical treatment. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; Mar-Apr. 76(2):178–84.
Article21. Kohut RI, Hinojosa R, Budetti JA. Perilymphatic fistula: a histopathologic study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1986; Sep-Oct. 95(5 Pt 1):466–71.
Article22. Black FO, Pesznecker S, Norton T, Fowler L, Lilly DJ, Shupert C, et al. Surgical management of perilymphatic fistulas: a Portland experience. Am J Otol. 1992; May. 13(3):254–62.23. Kohut RI, Hinojosa R, Thompson JN, Ryu JH. Idiopathic perilymphatic fistulas: a temporal bone histopathologic study with clinical, surgical, and histopathologic correlations. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995; Apr. 121(4):412–20.
Article24. Meyerhoff WL. Spontaneous perilymphatic fistula: myth or fact. Am J Otol. 1993; Sep. 14(5):478–81.
Article25. Nomura Y, Okuno T, Hara M, Young YH. “Floating” labyrinth: pathophysiology and treatment of perilymph fistula. Acta Otolaryngol. 1992; 112(2):186–91.26. Wackym PA, Balaban CD, Zhang P, Siker DA, Hundal JS. Third Window syndrome: surgical management of cochlea-facial nerve dehiscence. Front Neurol. 2019; Dec. 10:1281.
Article27. Park JH, Kim HJ, Kim JS, Koo JW. Costimulation of the horizontal semicircular canal during skull vibrations in superior canal Dehiscence syndrome. Audiol Neurootol. 2014; 19(3):175–83.
Article28. Deveze A, Matsuda H, Elziere M, Ikezono T. Diagnosis and treatment of perilymphatic fistula. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2018; 81:133–45.
Article29. Modugno GC, Magnani G, Brandolini C, Savastio G, Pirodda A. Could vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (VEMPs) also be useful in the diagnosis of perilymphatic fistula. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2006; Jun. 263(6):552–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Traumatic Perilymphatic Fistula Presenting with Direction-Changing Positional Nystagmus
- Two Cases of Barotraumatic Perilymph Fistula Mimicking Atypical Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo with Sudden Hearing Loss
- A Case of Perilymphatic Fistula Misdiagnosed as Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- Two Cases of Idiopathic Progressive Sensorineural Hearing Loss with Positional Nystagmus in Postpartum Period: Possible Spontaneous Perilymph Fistula?
- Delayed Positional Vertigo after Stapes Surgery