Clin Endosc.
2021 May;54(3):301-308. 10.5946/ce.2021.103.
What You Need to Know Before Performing Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Hepaticogastrostomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Rajavithi Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand
- 2Department of Surgery, Rajavithi Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand
- 3Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
- KMID: 2516308
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2021.103
Abstract
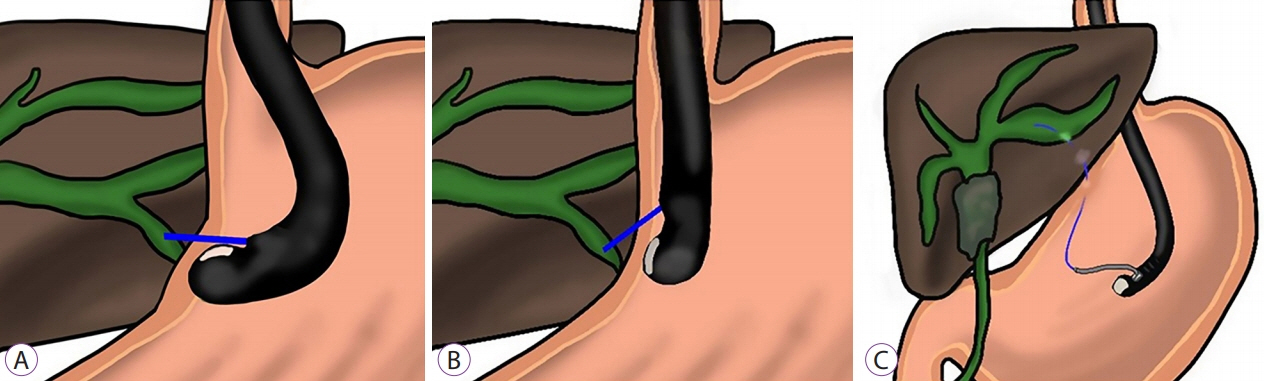
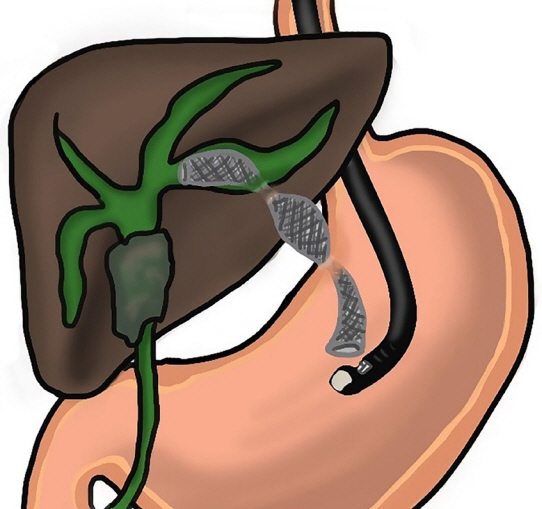
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is the primary treatment modality for bile duct obstruction. When ERCP is unsuccessful, percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage can be an alternative method. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage (EUS-BD) has emerged as a treatment option for biliary obstruction, especially after ERCP failure. EUS-BD offers transluminal intrahepatic and extrahepatic drainage through a transgastric and transduodenal approach. EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy (EUS-HGS) is an excellent choice for patients with hilar strictures or those with a surgically altered anatomy. The optimal steps in EUS-HGS are case selection, bile duct visualization, puncture-site selection, wire insertion and manipulation, tract dilation, and stent placement. Caution should be taken at each step to prevent complications. Dedicated devices for EUS-HGS have been developed to improve the technical success rate and reduce complications. This technical review focuses on the essential practical points at each step of EUS-HGS.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Teoh AYB, Dhir V, Kida M, et al. Consensus guidelines on the optimal management in interventional EUS procedures: results from the Asian EUS group RAND/UCLA expert panel. Gut. 2018; 67:1209–1228.
Article2. Han SY, Kim S-O, So H, Shin E, Kim DU, Park DH. EUS-guided biliary drainage versus ERCP for first-line palliation of malignant distal biliary obstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:16551.
Article3. Nakai Y, Isayama H, Yamamoto N, et al. Indications for endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS)-guided biliary intervention: does EUS always come after failed endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography? Dig Endosc. 2017; 29:218–225.4. Nakai Y, Kogure H, Isayama H, Koike K. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage for unresectable hilar malignant biliary obstruction. Clin Endosc. 2019; 52:220–225.
Article5. Nakai Y, Kogure H, Isayama H, Koike K. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage for benign biliary diseases. Clin Endosc. 2019; 52:212–219.
Article6. Burmester E, Niehaus J, Leineweber T, Huetteroth T. EUS-cholangio-drainage of the bile duct: report of 4 cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:246–251.
Article7. Patel V, McLaughlin SW, Shlansky-Goldberg R, et al. Complication rates of percutaneous biliary drainage in the presence of ascites. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2019; 44:1901–1906.
Article8. Kedia P, Gaidhane M, Kahaleh M. Endoscopic guided biliary drainage: how can we achieve efficient biliary drainage? Clin Endosc. 2013; 46:543–551.
Article9. Kamata K, Takenaka M, Minaga K, et al. Stent migration during EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy in a patient with massive ascites: Troubleshooting using additional EUS-guided antegrade stenting. Arab J Gastroenterol. 2017; 18:120–121.
Article10. Ogura T, Higuchi K. Technical tips for endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:3945–3951.
Article11. Isayama H, Nakai Y, Itoi T, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for safe performance of endoscopic ultrasound/ultrasonography-guided biliary drainage: 2018. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2019; 26:249–269.
Article12. Okuno N, Hara K, Mizuno N, et al. Infectious peritonitis after endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage in a patient with ascites. Gastrointestinal Intervention. 2018; 7:40–43.
Article13. Park SJ, Choi J-H, Park DH, et al. Expanding indication: EUS-guided hepaticoduodenostomy for isolated right intrahepatic duct obstruction (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:374–380.
Article14. Minaga K, Kitano M. Recent advances in endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage. Dig Endosc. 2018; 30:38–47.
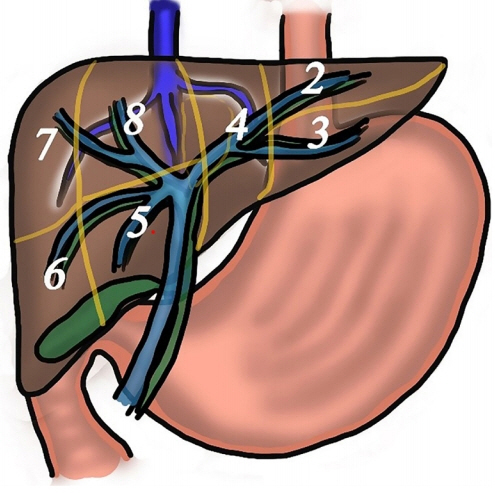
Article15. Tsujino T, Samarasena JB, Chang KJ. EUS anatomy of the liver segments. Endosc Ultrasound. 2018; 7:246–251.
Article16. Okuno N, Hara K, Mizuno N, et al. Risks of transesophageal endoscopic ultrasonography-guided biliary drainage. Gastrointestinal Intervention. 2017; 6:82–84.
Article17. Oh D, Park DH, Song TJ, et al. Optimal biliary access point and learning curve for endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy with transmural stenting. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2017; 10:42–53.
Article18. Yamamoto Y, Ogura T, Nishioka N, et al. Risk factors for adverse events associated with bile leak during EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy. Endosc Ultrasound. 2020; 9:110–115.
Article19. Ogura T, Nishioka N, Ueno S, et al. Effect of echoendoscope angle on success of guidewire manipulation during endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy. Endoscopy. 2021; 53:369–375.
Article20. Shiomi H, Masuda A, Kodama Y. Novel approach for successful endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy using a double-guidewire technique. Dig Endosc. 2019; 31:e50–e51.
Article21. ASGE Technology Committee, Hwang JH, Aslanian HR, et al. Devices for use with EUS. VideoGIE. 2017; 2:35–45.
Article22. Martínez B, Martínez J, Casellas JA, Aparicio JR. Endoscopic ultrasound- guided rendezvous in benign biliary or pancreatic disorders with a 22-gauge needle and a 0.018-inch guidewire. Endosc Int Open. 2019; 7:E1038–E1043.23. Kanno Y, Ito K, Sakai T, Okano H. Novel combination of a 0.018-inch guidewire, dedicated thin dilator, and 22-gauge needle for EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy. VideoGIE. 2020; 5:355–358.
Article24. Honjo M, Itoi T, Tsuchiya T, et al. Safety and efficacy of ultra-tapered mechanical dilator for EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy and pancreatic duct drainage compared with electrocautery dilator (with video). Endosc Ultrasound. 2018; 7:376–382.
Article25. Tyberg A, Desai AP, Kumta NA, et al. EUS-guided biliary drainage after failed ERCP: a novel algorithm individualized based on patient anatomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 84:941–946.
Article26. Park DH, Jang JW, Lee SS, Seo D-W, Lee SK, Kim M-H. EUS-guided biliary drainage with transluminal stenting after failed ERCP: predictors of adverse events and long-term results. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:1276–1284.
Article27. Ogura T, Nakai Y, Iwashita T, Higuchi K, Itoi T. Novel fine gauge electrocautery dilator for endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage: experimental and clinical evaluation study (with video). Endosc Int Open. 2019; 7:E1652–E1657.
Article28. Prachayakul V, Aswakul P. A novel technique for endoscopic ultrasound- guided biliary drainage. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:4758–4763.29. Amano M, Ogura T, Onda S, et al. Prospective clinical study of endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage using novel balloon catheter (with video). J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 32:716–720.
Article30. Kanno Y, Ito K, Koshita S, et al. Efficacy of a newly developed dilator for endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 9:304–309.
Article31. Paik WH, Park DH, Choi J-H, et al. Simplified fistula dilation technique and modified stent deployment maneuver for EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:5051–5059.
Article32. Maehara K, Hijioka S, Nagashio Y, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy or hepaticojejunostomy without dilation using a stent with a thinner delivery system. Endosc Int Open. 2020; 8:E1034–E1038.
Article33. Park DH, Lee TH, Paik WH, et al. Feasibility and safety of a novel dedicated device for one-step EUS-guided biliary drainage: a randomized trial. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 30:1461–1466.
Article34. Prachayakul V, Aswakul P. Feasibility and safety of using soehendra stent retriever as a new technique for biliary access in endoscopic ultrasound- guided biliary drainage. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:2725–2730.35. Umeda J, Itoi T, Tsuchiya T, et al. A newly designed plastic stent for EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy: a prospective preliminary feasibility study (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:390–396.e2.
Article36. De Cassan C, Bories E, Pesenti C, et al. Use of partially covered and uncovered metallic prosthesis for endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy: results of a retrospective monocentric study. Endosc Ultrasound. 2017; 6:329–335.
Article37. Cho DH, Lee SS, Oh D, et al. Long-term outcomes of a newly developed hybrid metal stent for EUS-guided biliary drainage (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:1067–1075.
Article38. Okuno N, Hara K, Mizuno N, et al. Efficacy of the 6-mm fully covered self-expandable metal stent during endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy as a primary biliary drainage for the cases estimated difficult endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a prospective clinical study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018; 33:1413–1421.39. Lee NJ, Shin JH, Lee SS, Park DH, Lee SK, Yoon H-K. Transcatheter arterial embolization for iatrogenic bleeding after endoscopic ultrasound- guided pancreaticobiliary drainage. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2018; 99:717–724.40. Prachayakul V, Thamtorawat S, Siripipattanamongkol C, Thanathanee P. Bleeding left hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: a complication of endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy. Endoscopy. 2013; 45 Suppl 2 UCTN:E223–E224.
Article41. Ogura T, Higuchi K. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy: technical review and tips to prevent adverse events. Gut Liver. 2021; 15:196–205.
Article42. Chantarojanasiri T, Aswakul P, Prachayakul V. Uncommon complications of therapeutic endoscopic ultrasonography: what, why, and how to prevent. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 7:960–968.
Article43. Khashab MA, Dewitt J. Treatment and prevention of wire shearing during EUS-guided biliary drainage. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:921–923.
Article44. Ogura T, Masuda D, Takeuchi T, Fukunishi S, Higuchi K. Liver impaction technique to prevent shearing of the guidewire during endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy. Endoscopy. 2015; 47:E583–E584.
Article45. Ryou M, Benias PC, Kumbhari V. Initial clinical experience of a steerable access device for EUS-guided biliary drainage. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020; 91:178–184.
Article46. Lakhtakia S, Chavan R, Ramchandani M, Basha J, Reddy DN. EUS-guided rendezvous with a steerable access needle in choledocholithiasis. VideoGIE. 2020; 5:359–361.
Article47. Paik WH, Park DH. Outcomes and limitations: EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy. Endosc Ultrasound. 2019; 8:S44–S49.
Article48. Martins FP, Rossini LG, Ferrari AP. Migration of a covered metallic stent following endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy: fatal complication. Endoscopy. 2010; 42 Suppl 2:E126–E127.
Article49. Fujisawa T, Saito H, Isayama H. Endoscopic removal of a metal stent that migrated into the peritoneal cavity after endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy. Dig Endosc. 2019; 31:e74–e75.
Article50. van Geenen EJM, Siersema PD. Stent migration into the abdominal cavity after EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 87:617–618.
Article51. Shima Y, Isayama H, Ito Y, et al. Crisscross anchor-stents to prevent metal stent migration during endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy. Endoscopy. 2014; 46 Suppl 1 UCTN:E563.
Article52. Hamada T, Nakai Y, Isayama H, Koike K. Tandem stent placement as a rescue for stent misplacement in endoscopic ultrasonography-guided hepaticogastrostomy. Dig Endosc. 2013; 25:340–341.
Article53. Miyano A, Ogura T, Yamamoto K, Okuda A, Nishioka N, Higuchi K. Clinical impact of the intra-scope channel stent release technique in preventing stent migration during EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy. J Gastrointest Surg. 2018; 22:1312–1318.
Article54. Ogura T, Yamamoto K, Sano T, et al. Stent length is impact factor associated with stent patency in endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 30:1748–1752.
Article55. Wang S, Guo J, Sun S, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided repositioning of a migrated metal hepatogastrostomy stent using foreign body forceps. Endoscopy. 2016; 48 Suppl 1 UCTN:E28–E29.
Article56. Nakai Y, Isayama H, Yamamoto N, et al. Safety and effectiveness of a long, partially covered metal stent for endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy in patients with malignant biliary obstruction. Endoscopy. 2016; 48:1125–1128.
Article57. Ogura T, Kurisu Y, Masuda D, et al. Novel method of endoscopic ultrasound- guided hepaticogastrostomy to prevent stent dysfunction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 29:1815–1821.58. Nakai Y, Sato T, Hakuta R, et al. Long-term outcomes of a long, partially covered metal stent for EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy in patients with malignant biliary obstruction (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2020; 92:623–631.e1.
Article59. Ogura T, Takenaka M, Shiomi H, et al. Long-term outcomes of EUS-guided transluminal stent deployment for benign biliary disease: multicenter clinical experience (with videos). Endosc Ultrasound. 2019; 8:398–403.
Article60. Kawakami H, Itoi T, Ban T. Intrahepatic biliary stones extraction via an EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy route confirmed by peroral transluminal video cholangioscopy (with video). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2020; 27:E11–E12.
Article61. Sato T, Nakai Y, Kogure H, Isayama H, Koike K. Electrohydraulic lithotripsy through a fistula of EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy: a new approach for right intrahepatic stones. VideoGIE. 2019; 4:420–422.
Article62. Ogura T, Nishioka N, Higuchi K. Transluminal intrahepatic bile duct stone removal using coaxial basket catheter via the previously created EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy tract (with videos). Endosc Ultrasound. 2019; 8:133–135.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent development of endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage
- Technical Review of Developments in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Hepaticogastrostomy
- Follow-up computed tomography can prevent stent migration after endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy by puncturing both B2 and B3: a single center experience
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Hepaticogastrostomy: Technical Review and Tips to Prevent Adverse Events