Acute Crit Care.
2021 May;36(2):143-150. 10.4266/acc.2021.00017.
Airway pressure release ventilation in mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19: a multicenter observational study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Intensive Care Department, Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital, Perth, Australia
- 2Intensive Care Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia
- 3University of Western Australia School of Medicine, Perth, Australia
- 4School of Veterinary & Life Sciences, Murdoch University, Perth, Australia
- 5Intensive Care Department, Fiona Stanley Hospital, Perth, Australia
- 6Intensive Care Department, St John of God Midland Hospital, Perth, Australia
- KMID: 2516262
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2021.00017
Abstract
- Background
Evidence prior to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic suggested that, compared with conventional ventilation strategies, airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) can improve oxygenation and reduce mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. We aimed to assess the association between APRV use and clinical outcomes among adult patients receiving mechanical ventilation for COVID-19 and hypothesized that APRV use would be associated with improved survival compared with conventional ventilation.
Methods
A total of 25 patients with COVID-19 pneumonitis was admitted to intensive care units (ICUs) for invasive ventilation in Perth, Western Australia, between February and May 2020. Eleven of these patients received APRV. The primary outcome was survival to day 90. Secondary outcomes were ventilation-free survival days to day 90, mechanical complications from ventilation, and number of days ventilated.
Results
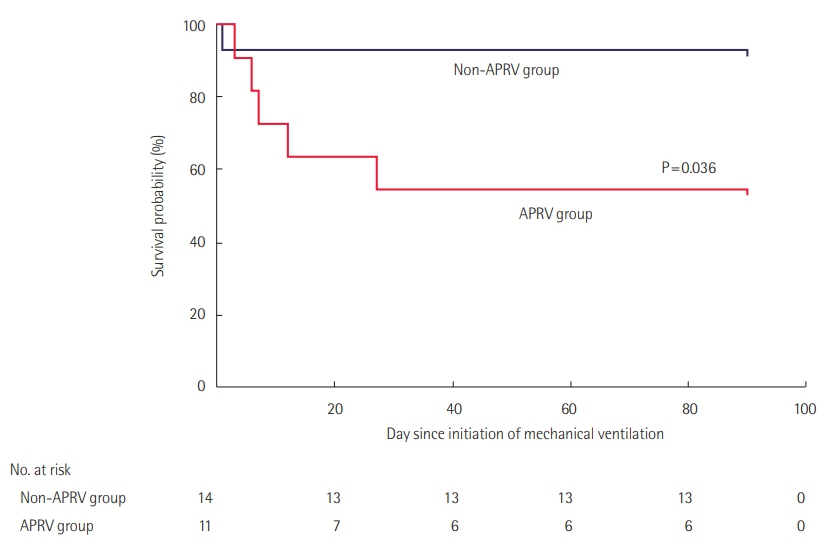
Patients who received APRV had a lower probability of survival than did those on other forms of ventilation (hazard ratio, 0.17; 95% confidence interval, 0.03–0.89; P=0.036). This finding was independent of indices of severity of illness to predict the use of APRV. Patients who received APRV also had fewer ventilator-free survival days up to 90 days after initiation of ventilation compared to patients who did not receive APRV, and survivors who received APRV had fewer ventilator-free days than survivors who received other forms of ventilation. There were no differences in mechanical complications according to mode of ventilation.
Conclusions
Based on the findings of this study, we urge caution with the use of APRV in COVID-19.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison of characteristics and ventilatory course between coronavirus disease 2019 and Middle East respiratory syndrome patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome
Imran Khalid, Romaysaa M Yamani, Maryam Imran, Muhammad Ali Akhtar, Manahil Imran, Rumaan Gul, Tabindeh Jabeen Khalid, Ghassan Y Wali
Acute Crit Care. 2021;36(3):223-231. doi: 10.4266/acc.2021.00388.
Reference
-
1. Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The species severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat Microbiol. 2020; 5:536–44.2. World Health Organization. Timeline of WHO’s response to COVID-19 [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2020. [cited 2020 Aug 29]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/29-06-2020-covidtimeline.3. World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) situation reports [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2020. [cited 2020 Aug 29]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports.4. Bouadma L, Lescure FX, Lucet JC, Yazdanpanah Y, Timsit JF. Severe SARS-CoV-2 infections: practical considerations and management strategy for intensivists. Intensive Care Med. 2020; 46:579–82.
Article5. Chen J, Qi T, Liu L, Ling Y, Qian Z, Li T, et al. Clinical progression of patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China. J Infect. 2020; 80:e1–e6.
Article6. Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in china: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA. 2020; 323:1239–42.7. Docherty AB, Harrison EM, Green CA, Hardwick HE, Pius R, Norman L, et al. Features of 20133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO clinical characterisation protocol: prospective observational cohort study. BMJ. 2020; 369:m1985.
Article8. Potere N, Valeriani E, Candeloro M, Tana M, Porreca E, Abbate A, et al. Acute complications and mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2020; 24:389.
Article9. Lim J, Litton E. Airway pressure release ventilation in adult patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2019; 47:1794–9.10. Modrykamien A, Chatburn RL, Ashton RW. Airway pressure release ventilation: an alternative mode of mechanical ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Cleve Clin J Med. 2011; 78:101–10.
Article11. Zhou Y, Jin X, Lv Y, Wang P, Yang Y, Liang G, et al. Early application of airway pressure release ventilation may reduce the duration of mechanical ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2017; 43:1648–59.
Article12. Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap): a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009; 42:377–81.13. Harris PA, Taylor R, Minor BL, Elliott V, Fernandez M, O’Neal L, et al. The REDCap consortium: Building an international community of software platform partners. J Biomed Inform. 2019; 95:103208.
Article14. Gattinoni L, Chiumello D, Rossi S. COVID-19 pneumonia: ARDS or not? Crit Care. 2020; 24:154.
Article15. Bos LD, Sinha P, Dickson RP. The perils of premature phenotyping in COVID-19: a call for caution. Eur Respir J. 2020; 56:2001768.
Article16. Bos LD, Sinha P, Dickson RP. Response to COVID-19 phenotyping correspondence. Eur Respir J. 2020; 56:2002756.
Article17. Rajendram R. Building the house of CARDS by phenotyping on the fly. Eur Respir J. 2020; 56:2002429.
Article18. Ziehr DR, Alladina J, Petri CR, Maley JH, Moskowitz A, Medoff BD, et al. Respiratory pathophysiology of mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19: a cohort study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020; 201:1560–4.
Article19. Gattinoni L, Camporota L, Marini JJ. COVID-19 phenotypes: leading or misleading? Eur Respir J. 2020; 56:2002195.
Article20. Botta M, Tsonas AM, Pillay J, Boers LS, Algera AG, Bos LD, et al. Ventilation management and clinical outcomes in invasively ventilated patients with COVID-19 (PRoVENT-COVID): a national, multicentre, observational cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2021; 9:139–48.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship between positive end-expiratory pressure levels, central venous pressure, systemic inflammation and acute renal failure in critically ill ventilated COVID-19 patients: a monocenter retrospective study in France
- Emergency exploratory laparotomy in a COVID-19 patient - A case report -
- Mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients admitted to the intensive care unit in the United States with or without respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19 pneumonia: a retrospective comparison of characteristics and outcomes
- Recurrent Desaturation Events due to Opioid-Induced Chest Wall Rigidity after Low Dose Fentanyl Administration
- Gastroesophageal Reflux in Mechanically Ventilated Preterm Infants