Ann Rehabil Med.
2021 Apr;45(2):141-149. 10.5535/arm.20235.
Cephalic Index of Korean Children With Normal Brain Development During the First 7 Years of Life Based on Computed Tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2515395
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.20235
Abstract
Objective
To identify the normal range, distribution, and age-dependent differences in the cephalic index (CI) of Korean children with normal brain development and develop a classification of the current CI for Korean children up to 7 years of age.
Methods
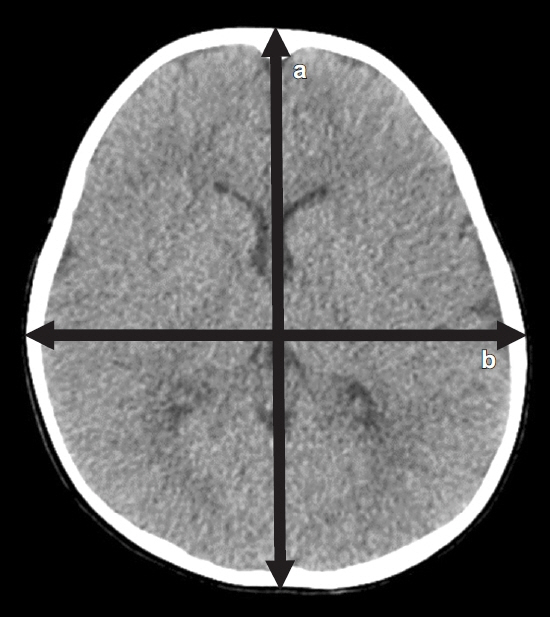
We retrospectively analyzed 1,389 children who visited our hospital in the emergency room between October 2015 and September 2020 because of suspected head injuries. Finally, 1,248 children (741 male and 507 female) were enrolled after excluding abnormal medical or familial history and divided into 10 groups by age. The CI was measured using brain computed tomography and calculated according to the following equation: cephalic width/cephalic length×100.
Results
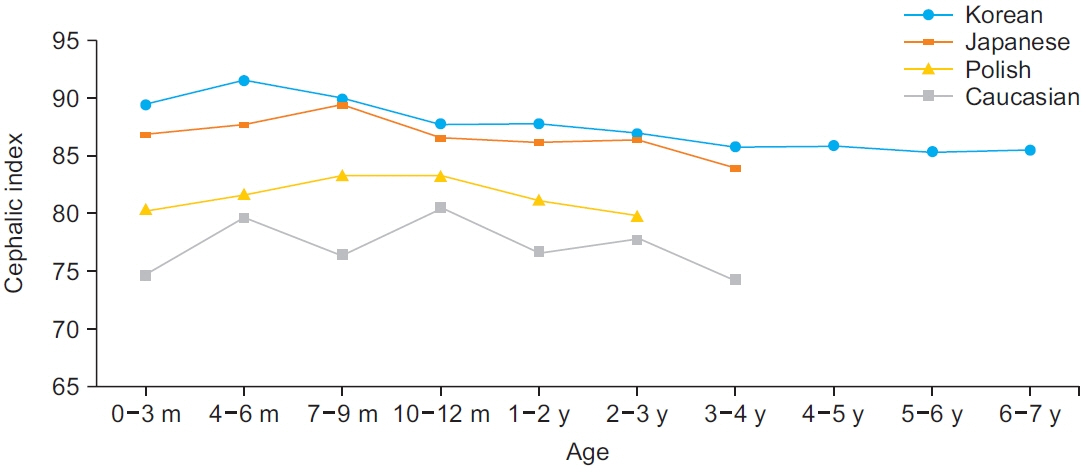
The averages of CI by age groups were as follows: 89.29 (0–3 months group, n=44); 91.41 (4–6 months group, n=63); 89.68 (7–9 months group, n=62); 87.52 (10–12 months group, n=41); 87.64 (≥2 years group, n=243); 86.63 (≥3 years group, n=178); 85.62 (≥4 years group, n=232); 85.77 (≥5 years group, n=201); 85.15 (≥6 years group, n=75); and 85.34 (≥7 years group, n=109). The CI of Korean children in normal brain development was confirmed to be large, showing a notable difference compared to that of Caucasians.
Conclusion
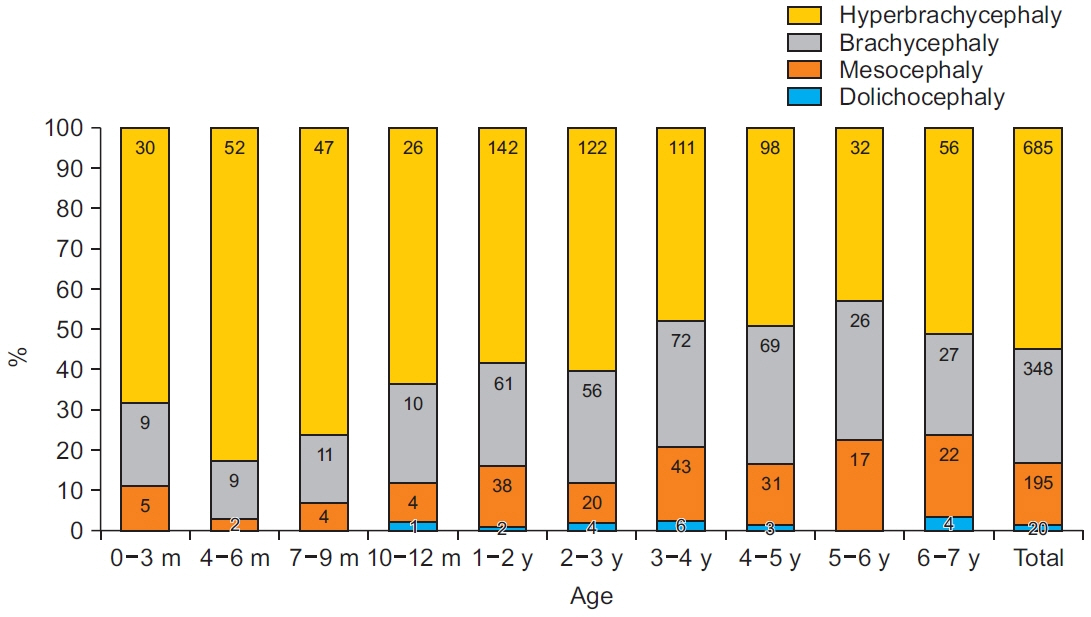
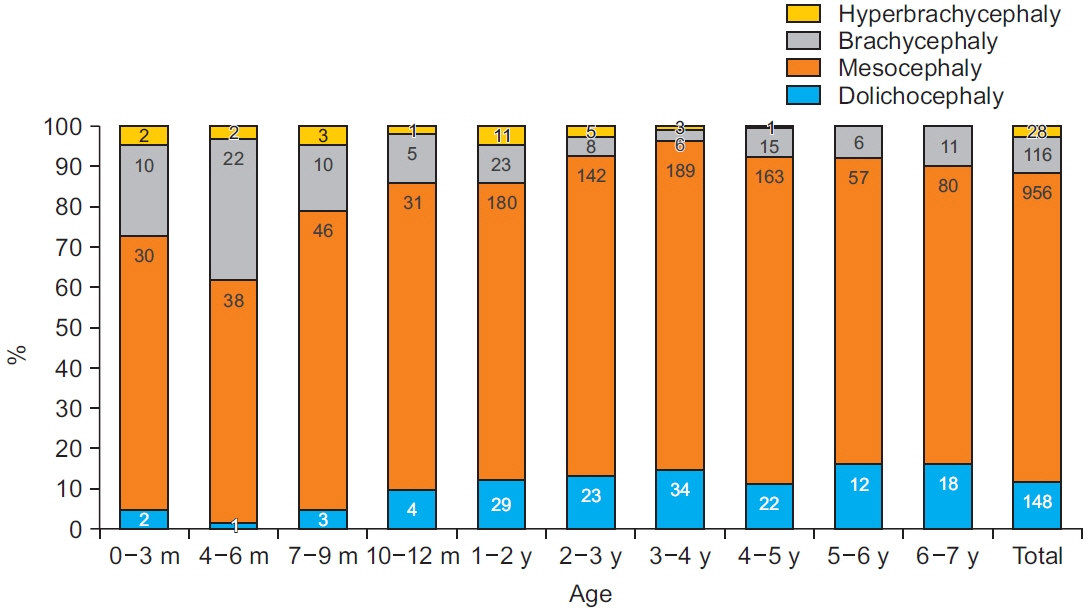
The current CI of Korean children will provide a valuable reference for diagnosing and treating cranial deformities, especially dolichocephaly and brachycephaly as well as to monitor the morphology of the cranium in clinics.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gonzalez-Santos J, Gonzalez-Bernal JJ, De-la-Fuente Anuncibay R, Soto-Camara R, Cubo E, Aguilar-Parra JM, et al. Infant cranial deformity: cranial helmet therapy or physiotherapy? Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020; 17:2612.2. Rogers GF. Deformational plagiocephaly, brachycephaly, and scaphocephaly. Part I: terminology, diagnosis, and etiopathogenesis. J Craniofac Surg. 2011; 22:9–16.3. van Lindert EJ, Siepel FJ, Delye H, Ettema AM, Berge SJ, Maal TJ, et al. Validation of cephalic index measurements in scaphocephaly. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013; 29:1007–14.
Article4. Panchal J, Marsh JL, Park TS, Kaufman B, Pilgram T, Huang SH. Sagittal craniosynostosis outcome assessment for two methods and timings of intervention. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999; 103:1574–84.
Article5. Rogers GF. Deformational plagiocephaly, brachycephaly, and scaphocephaly. Part II: prevention and treatment. J Craniofac Surg. 2011; 22:17–23.6. Cohen MM. History, terminology, and classfication of craniosynostosis. Craniosynostosis: diagnosis, evaluation, and management. New York, NY: Oxford University Press;2000. p. 103–11.7. Haas LL. Roentgenological skull measurements and their diagnostic applications. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1952; 67:197–209.8. Triarhou LC. Anders Retzius (1796-1860). J Neurol. 2013; 260:1445–6.
Article9. Fruhwald J, Schicho KA, Figl M, Benesch T, Watzinger F, Kainberger F. Accuracy of craniofacial measurements: computed tomography and three-dimensional computed tomography compared with stereolithographic models. J Craniofac Surg. 2008; 19:22–6.10. Waitzman AA, Posnick JC, Armstrong DC, Pron GE. Craniofacial skeletal measurements based on computed tomography: part I. Accuracy and reproducibility. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1992; 29:112–7.
Article11. Graham JM Jr, Kreutzman J, Earl D, Halberg A, Samayoa C, Guo X. Deformational brachycephaly in supine-sleeping infants. J Pediatr. 2005; 146:253–7.
Article12. Likus W, Bajor G, Gruszczynska K, Baron J, Markowski J, Machnikowska-Sokolowska M, et al. Cephalic index in the first three years of life: study of children with normal brain development based on computed tomography. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014; 2014:502836.
Article13. Waitzman AA, Posnick JC, Armstrong DC, Pron GE. Craniofacial skeletal measurements based on computed tomography: part II. Normal values and growth trends. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1992; 29:118–28.
Article14. Koizumi T, Komuro Y, Hashizume K, Yanai A. Cephalic index of Japanese children with normal brain development. J Craniofac Surg. 2010; 21:1434–7.
Article15. Yang W, Chen J, Shen W, Wang C, Wu Z, Chang Q, et al. Prevalence of positional skull deformities in 530 premature infants with a corrected age of up to 6 months: a multicenter study. BMC Pediatr. 2019; 19:520.
Article16. Jung HY, Kim CH, Chang SY. A study on the correlations among cephalofacial measurements in Korean students. Chung-Ang J Med. 1986; 11:99–110.17. Yun S, Han K, Yeo H, Lee M, Kim J, Son D. Chronologic change of Korean cephalic index (0 to 20 years) obtained from a cephalograph. J Korean Cleft PalateCraniofac Assoc. 2011; 12:6–11.18. Wilbrand JF, Schmidtberg K, Bierther U, Streckbein P, Pons-Kuehnemann J, Christophis P, et al. Clinical classification of infant nonsynostotic cranial deformity. J Pediatr. 2012; 161:1120–5.
Article19. Gripp KW, Slavotinek AM, Hall JG, Allanson JE. Handbook of physical measurements. New York, NY: Oxford University Press;2013. p. 96–7.20. Hadlock FP, Deter RL, Carpenter RJ, Park SK. Estimating fetal age: effect of head shape on BPD. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981; 137:83–5.
Article21. MacKenzie AP, Stephenson CD, Funai EF. Prenatal assessment of gestational age, date of delivery, and fetal weight [Internet]. Waltham, MA: UpToDate;c2021 [cited 2021 Mar 1]. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/prenatal-assessment-of-gestational-age-date-of-delivery-and-fetal-weight.22. Ifflaender S, Rudiger M, Konstantelos D, Lange U, Burkhardt W. Individual course of cranial symmetry and proportion in preterm infants up to 6 months of corrected age. Early Hum Dev. 2014; 90:511–5.23. Wu GT, Audlin JR, Grewal JS, Tatum SA. Comparing caliper versus computed tomography measurements of cranial dimensions in children. Laryngoscope. 2020; Sep. 12. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.29086.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Study in Frontal Ventricular Measurement and Correlation between Cerebroventricular Index and Cephalic Index on Normal Computed Tomography
- A Case of Cephalic Brain-like Heterotopia
- Comparison of Speech-Language, Mental-Motor Development and Brain Radiologic Findings in Children with Cerebral Palsy and Other Delayed Development
- Normal development of the paranasal sinuses in children: a CT study
- In search of subcortical and cortical morphologic alterations of a normal brain through aging: an investigation by computed tomography scan