Lab Med Online.
2020 Oct;10(4):326-329. 10.47429/lmo.2020.10.4.326.
A Case of Partial D Type VI-3 Confirmed by RHD Genotyping
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Health Sciences and Technology, SAIHST, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2512273
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2020.10.4.326
Abstract
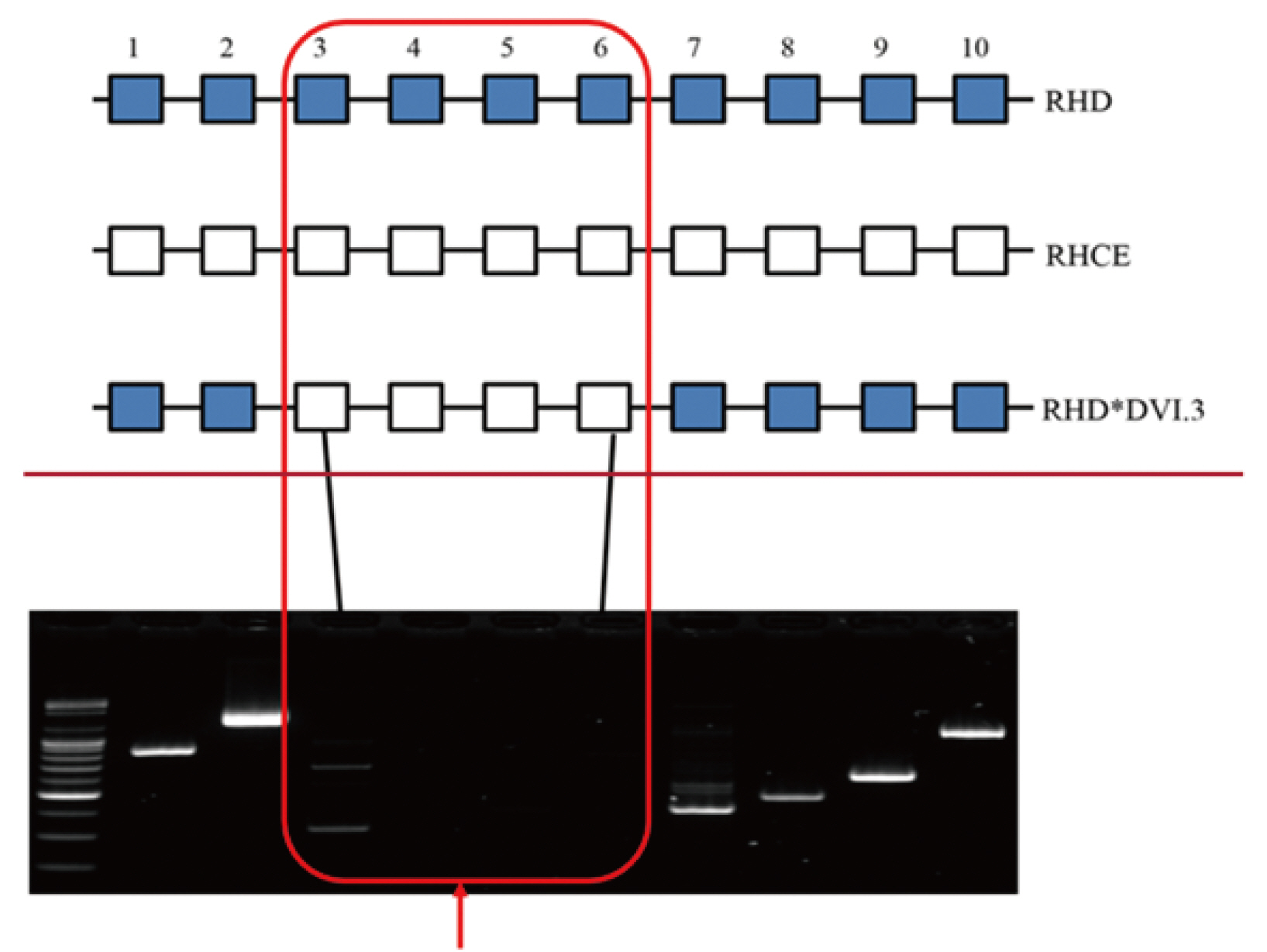
- Weak D and partial D result in quantitative and qualitative changes in RhD protein expression respectively. It is difficult to discriminate weak D from partial D by serological tests alone. RHD genotyping is a useful method that complements serological results. A 64-year-old woman visited our hospital for microvascular decompression surgery. Her blood type was O, D negative by manual tube test and as per auto analyzer results (QWALYS-3 system; DIAGAST, France). Weak D and partial D tests were performed by using two different monoclonal anti-D reagents (Bioscot; Merck Millipore, UK; Bioclone; Ortho Clinical Diagnostics, USA) and a panel of nine monoclonal antibodies, including anti-D IgM and IgG (D-Screen; DIAGAST, France). However, these serological tests could not confirm the subtype of partial D. Therefore, sequencing of RHD exon 1 to 10 was additionally performed for the patient and the case was revealed to be partial DVI type 3.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Seo MH, Won EJ, Hong YJ, Chun S, Kwon JR, Choi YS, et al. 2016; An effective diagnostic strategy for accurate detection of RhD variants including Asian DEL type in apparently RhD-negative blood donors in Korea. Vox Sang. 111:425–30. DOI: 10.1111/vox.12450. PMID: 27864976.
Article2. Cho D, Choi GR, Jeon MJ, Kim KS, Seo JY, Shin MG, et al. 2003; Reactivity patterns of various anti-D reagents in 14 cases with partial D. Korean J Lab Med. 23:443–7.3. Kim DA, Kim JW. 2000; A case of partial-D category Va. Korean J Blood Transfus. 11:189–93.4. Lee HR, Chang HE, Lee K, Park KU, Song J, Han KS. 2017; Analysis of partial D subtypes by various anti-D reagents. Korean J Blood Transfus. 18:152–8.5. Fasano RM, Monaco A, Meier ER, Pary P, Lee-Stroka AH, Otridge J, et al. 2010; RH genotyping in a sickle cell disease patient contributing to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation donor selection and management. Blood. 116:2836–8. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-279372. PMID: 20644109. PMCID: PMC2974591.
Article6. Sandler SG, Chen LN, Flegel WA. 2017; Serological weak D phenotypes: a review and guidance for interpreting the RhD blood type using the RHD genotype. Br J Haematol. 179:10–9. DOI: 10.1111/bjh.14757. PMID: 28508413. PMCID: PMC5612847.7. Mark KF, editor. 2017. Technical manual. 19th ed. American Association of Blood Banks;Bethesda, Maryland: p. 304.8. Flegel WA, von Zabern I, Doescher A, Wagner FF, Vytisková J, Písacka M. 2008; DCS-1, DCS-2, and DFV share amino acid substitutions at the extracellular RhD protein vestibule. Transfusion. 48:25–33. DOI: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2007.01506.x. PMID: 17900276.
Article9. Wagner FF, Gassner C, Müller TH, Schönitzer D, Schunter F, Flegel WA. 1999; Molecular basis of weak D phenotypes. Blood. 93:385–93. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V93.1.385. PMID: 9864185.
Article10. Ma T, Yu H, Jeon S, Cho D, Chun S, Shin MG. 2019; Case of D-Variant from a Frameshift Mutation RHD 711delC. Korean J Blood Transfus. Aug(30):168–73. DOI: 10.17945/kjbt.2019.30.2.168.11. Luettringhaus TA, Cho D, Ryang DW, Flegel WA. 2006; An easy RHD genotyping strategy for D- East Asian persons applied to Korean blood donors. Transfusion. 46:2128–37. DOI: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2006.01042.x. PMID: 17176325.
Article12. Yoon J, Ko YE, Kim HN, Kim J, Jung BK, Lee SA, et al. 2016; A case of primary anti-D alloimmunization by RHD (c. 1227G>A) DEL red blood cell transfusion. Korean J Blood Transfus. 27:169–73. DOI: 10.17945/kjbt.2016.27.2.169.13. Kim KH, Kim KE, Woo KS, Han JY, Kim JM, Park KU. 2009; Primary anti-D immunization by DEL red blood cells. Korean J Lab Med. 29:361–5. DOI: 10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.4.361. PMID: 19726900. PMCID: PMC4404932.
Article14. Yang HS, Lee MY, Park TS, Cho SY, Lee HJ, Lim G, et al. 2015; Primary anti-D alloimmunization induced by "Asian type" RHD (c.1227G>A) DEL red cell transfusion. Ann Lab Med. 35:554–6. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2015.35.5.554. PMID: 26206698. PMCID: PMC4510514.15. Choi S, Chun S, Seo JY, Yang JH, Cho D. 2019; Planned transfusion of D-positive blood components in an Asia type DEL patient: Proposed modification of the Korean national guidelines for blood transfusion. Ann Lab Med. 39:102–4. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.1.102. PMID: 30215239. PMCID: PMC6143459.
Article16. Chun S, Yun JW, Park G, Cho D. 2018; The synonymous nucleotide substitution RHD 1056C>G alters mRNA splicing associated with serologically weak D phenotype. J Clin Lab Anal. 32:e22330. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22330. PMID: 28926139. PMCID: PMC6817278.17. Daniels G. 2013; Variants of RhD-current testing and clinical consequences. Br J Haematol. 161:461–70. DOI: 10.1111/bjh.12275. PMID: 23432139.18. Wagner FF, Gassner C, Muller TH, Schonitzer D, Schunter F, Flegel WA. 1998; Three molecular structures cause rhesus D category VI phenotypes with distinct immunohematologic features. Blood. 91:2157–68. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V91.6.2157.2157_2157_2168. PMID: 9490704.
Article19. Van Sandt VS, Gassner C, Emonds MP, Legler TJ, Mahieu S, Körmöczi GF. 2015; RHD variants in Flanders, Belgium. Transfusion. 55:1411–7. DOI: 10.1111/trf.12947. PMID: 25413499.20. Fichou Y, Parchure D, Gogri H, Gopalkrishnan V, Le Maréchal C, Chen JM, et al. 2018; Molecular basis of weak D expression in the Indian population and report of a novel, predominant variant RHD allele. Transfusion. 58:1540–9. DOI: 10.1111/trf.14552. PMID: 29479713.21. He J, Ying Y, Hong X, Xu X, Zhu F, Lv H. 2015; Molecular basis and zygosity determination of D variants including identification of four novel alleles in Chinese individuals. Transfusion. 55:137–43. DOI: 10.1111/trf.12797. PMID: 25070883.
Article22. Yan L, Wu J, Zhu F, Hong X, Xu X. 2007; Molecular basis of D variants in Chinese persons. Transfusion. 47:471–7. DOI: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2006.01138.x. PMID: 17319828. PMCID: PMC6905649.
Article23. Ye SH, Wu DZ, Wang MN, Wu XY, Xu HG, Xu H, et al. 2014; A comprehensive investigation of RHD polymorphisms in the Chinese Han population in Xi'an. Blood Transfus. 12:396–404. DOI: 10.2450/2013.0121-13. PMID: 24333088. PMCID: PMC4111822.24. Ye L, Wang P, Gao H, Zhang J, Wang C, Li Q, et al. 2012; Partial D phenotypes and genotypes in the Chinese population. Transfusion. 52:241–6. DOI: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2011.03266.x. PMID: 21790636. PMCID: PMC7359281.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The First Korean Case of RHD-CE(3-8)-D Hybrid Type with a D-negative Phenotype
- Clinical Indications for RHD Genotyping in Koreans
- Weak D type 33 Found in a Patient with a Weak D Phenotype: The First Case in Korea
- The Experience of RHD Genotyping in D-negative Blood Donors
- Case of D-Variant from a Frameshift Mutation RHD 711delC