J Bacteriol Virol.
2020 Sep;50(3):141-149. 10.4167/jbv.2020.50.3.141.
Overview of anti-Hepatitis B virus agents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Viral Disease Research, Center for Infectious Disease Research, Korea National Institute of Health, Chungbuk 28159, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2512132
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2020.50.3.141
Abstract
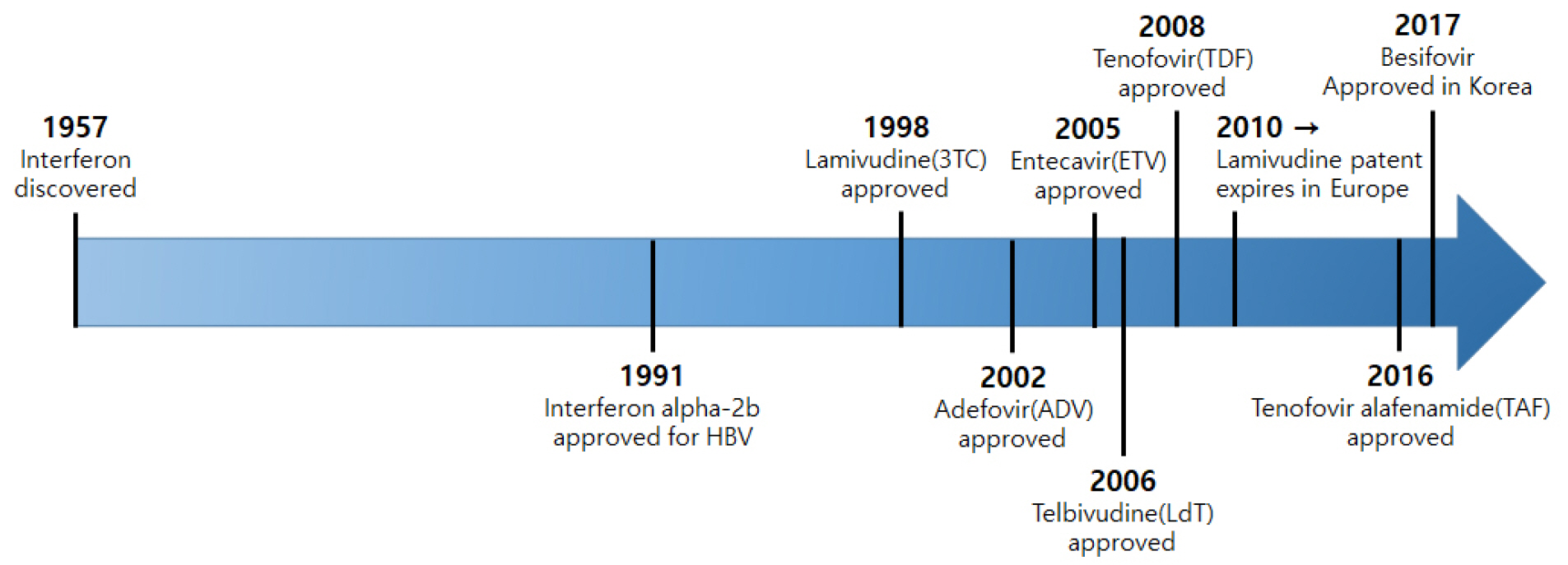
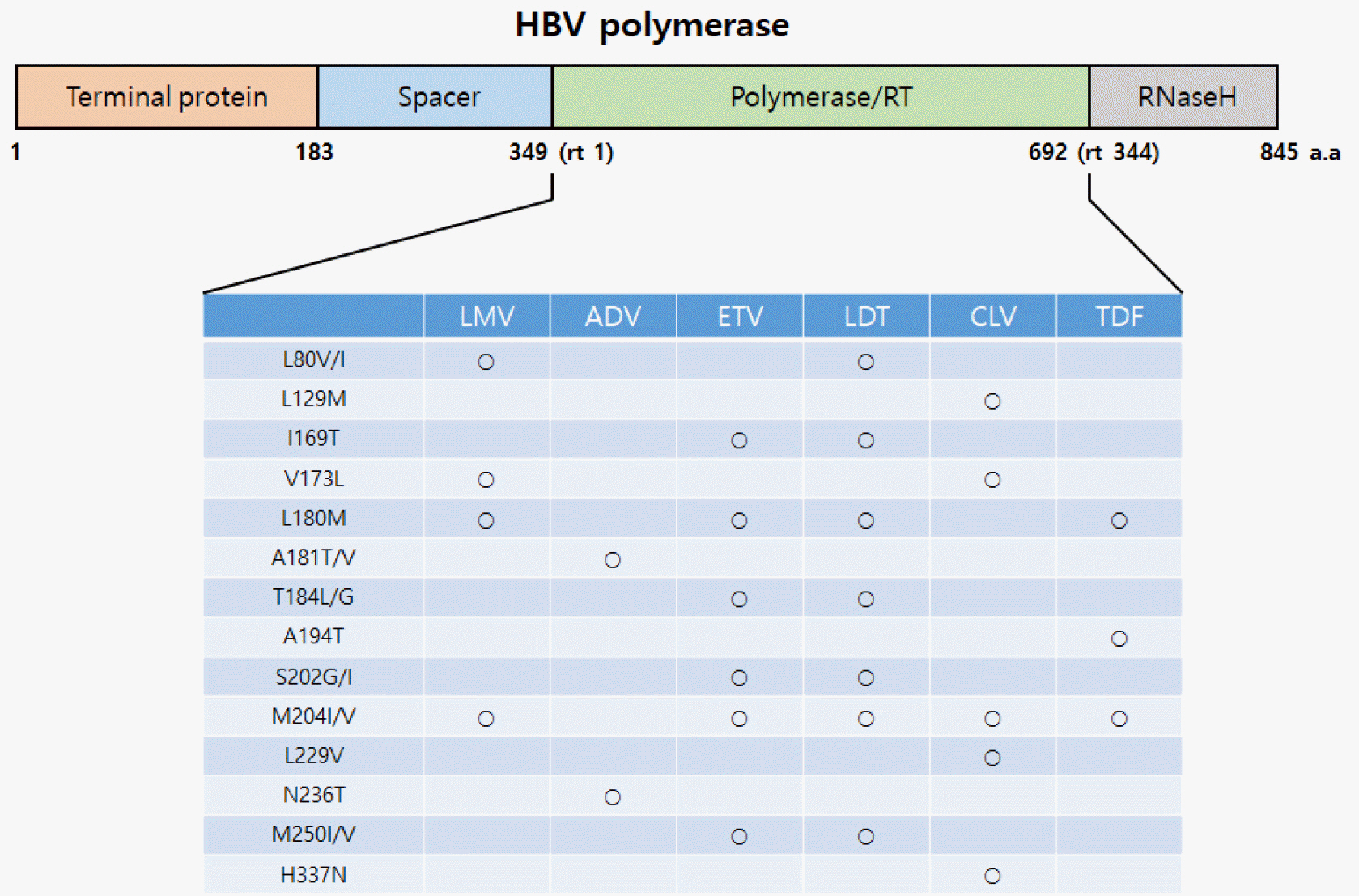
- Since the first FDA approval of Lamivudine in 1998, many nucleo(t)side analogs such as Lamivudine, Adefovir, and Entecavir have been used. However, they only inhibit DNA synthesis, and if their administration is stopped a viral breakthrough can develop, making long-term administration necessary, ultimately followed by the development of resistance. Tenofovir has been developed and drug-resistant mutations have decreased significantly, but the problem of resistance due to long-term drug use still remains, along with the drug safety problem. In this review, we introduce the recent trend in the development of hepatitis B treatment agents and the Korea National Research Institute of Health (KNIH) research for the development of a novel treatment for hepatitis B (drug repositioning) without resistance and which targets the various life cycles of HBV.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kee MK, Shin YH, Kim K, Ahn SH. Hepatitis B virus cohort studies worldwide. Public Health Weekly Report 2018;11:5708-20.2. Lin SYC, Magalis BR, Salemi M, Liu HF. Origin and dissemination of hepatitis B virus genotype C in East Asia revealed by phylodynamic analysis and historical correlates. J Viral Hepat 2019;26:145-54.DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13006. PMID: 30199591. PMCID: PMC7166934.3. Kim JH, Park YK, Park ES, Kim KH. Molecular diagnosis and treatment of drug-resistant hepatitis B virus. World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:5708-20.DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i19.5708. PMID: 24914332. PMCID: PMC4024781.4. Fanning GC, Zoulim F, Hou J, Bertoletti A. Therapeutic strategies for hepatitis B virus infection: towards a cure. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019;18:827-44.DOI: 10.1038/s41573-019-0037-0. PMID: 31455905.5. Lopatin U. Drugs in the Pipeline for HBV. Clin Liver Dis 2019;23:535-55.DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2019.04.006. PMID: 31266626.6. Tang LSY, Covert E, Wilson E, Kottilil S. Chronic Hepatitis B Infection: A Review. JAMA 2018;319:1802-13.DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.3795. PMID: 29715359.7. Quercia R, Perno CF, Koteff J, Moore K, McCoig C, St Clair M, et al. Twenty-Five Years of Lamivudine: Current and Future Use for the Treatment of HIV-1 Infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2018;78:125-35.DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001660. PMID: 29474268. PMCID: PMC5959256.8. Yuen MF, Seto WK, Fung J, Wong DKH, Yuen JCH, Lai CL. Three years of continuous entecavir therapy in treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B patients: viral suppression, viral resistance, and clinical safety. Am J Gastroenterol 2011;106:1264-71.DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2011.45. PMID: 21364549.9. European Association For The Study Of The Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J hepatol 2012;57:167-85.DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.02.010. PMID: 22436845.10. Yoo BC, Kim JH, Chung YH, Lee KS, Paik SW, Ryu SH, et al. Twenty-four-week clevudine therapy showed potent and sustained antiviral activity in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2007;45:1172-8.DOI: 10.1002/hep.21629. PMID: 17464992.11. Perry CM, Simpson D. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: in chronic hepatitis B. Drugs 2009;69:2245-56.DOI: 10.2165/10482940-000000000-00000. PMID: 19852527.12. De Clercq E, Holý A. Acyclic nucleoside phosphonates: a key class of antiviral drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2005;4:928-40.DOI: 10.1038/nrd1877. PMID: 16264436.13. Gish R, Jia JD, Locarnini S, Zoulim F. Selection of chronic hepatitis B therapy with high barrier to resistance. Lancet Infect Dis 2012;12:341-53.DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70314-0.14. van Hemert FJ, Berkhout B, Zaaijer HL. Differential binding of tenofovir and adefovir to reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B virus. PLoS One 2014;9:e106324.DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106324. PMID: 25180507. PMCID: PMC4152281.15. Park ES, Lee AR, Kim DH, Lee JH, Yoo JJ, Ahn SH, et al. Identification of a quadruple mutation that confers tenofovir resistance in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Hepatol 2019;70:1093-102.DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.006. PMID: 30794889.16. Mak LY, Seto WK, Lai CL, Yuen MF. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Besifovir for the Treatment of HBV Infection. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2018; 14:101-6.DOI: 10.1080/17425255.2018.1417983. PMID: 29237296.17. Zoulim F, Locarnini S. Heaptitis B Resistance to Nucleos(t)ide Analogues. Gastroenterology 2009;137:1593-1608.DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.08.063. PMID: 19737565.18. Villet S, Pichoud C, Billioud G, Barraud L, Durantel S, Trépo C, et al. Impact of hepatitis B virus rtA181V/T mutants on hepatitis B treatment failure. J Hepatol 2008;48:747-55.DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.01.027. PMID: 18331765.19. Colonno RJ, Rose R, Baldick CJ, Levine S, Pokornowski K, Yu CF, et al. Entecavir resistance is rare in nucleoside naïve patients with hepatitis B. Hepatology 2006;44:1656-65.DOI: 10.1002/hep.21422. PMID: 17133475.20. Levine S, Hernandez D, Yamanaka G, Zhang S, Rose R, Weinheimer S et al. Efficacies of entecavir against lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus replication and recombinant polymerases in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2002;46:2525-32.DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.8.2525-2532.2002. PMID: 12121928. PMCID: PMC127388.21. Locarnini S, Mason WS. Cellular and virological mechanisms of HBV drug resistance. J Hepatol 2006;44:422-31.DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.11.036. PMID: 16364492.22. Seifer M, Patty A, Serra I, Li B, Standring DN. Telbivudine, a nucleoside analog inhibitor of HBV polymerase, has a different in vitro cross-resistance profile than the nucleotide analog inhibitors adefovir and tenofovir. Antiviral Res 2009;81:147-55.DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.10.008. PMID: 19028525.23. Kwon SY, Park YK, Ahn SH, Cho ES, Choe WH, Lee CH, et al. Identification and characterization of clevudine-resistant mutants of hepatitis B virus isolated from chronic hepatitis B patients. J Virol 2010;84:4494-503.DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02066-09. PMID: 20164224. PMCID: PMC2863790.24. Amini-Bavil-Olyaee S, Herbers U, Sheldon J, Luedde T, Trautwein C, Tacke F. The rtA194T polymerase mutation impacts viral replication and susceptibility to tenofovir in hepatitis B e antigen-positive and hepatitis B e antigen-negative hepatitis B virus strains. Hepatology 2009;49:1158-65.DOI: 10.1002/hep.22790. PMID: 19263474.25. Kreutz C. Hepatitis B virus mutants resistant to Tenofovir. Med Life Clin 2019;1:1009.26. Lai CL, Ahn SH, Lee KS, Um SH, Cho M, Yoon SK, et al. Phase IIb multicentred randomised trial of besifovir (LB80380) versus entecavir in Asian patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2014;63:996-1004.DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305138. PMID: 23979965.27. Terrault NA, Bzowej NH, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, Murad MH. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2016;63:261-83.DOI: 10.1002/hep.28156. PMID: 26566064. PMCID: PMC5987259.28. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2017;67:370-98.29. Cornberg M, Lok ASF, Terrault NA, Zoulim F, 2019 EASL-AASLD HBV Treatment Endpoints Conference Faculty. Guidance for design and endpoints of clinical trials in chronic hepatitis B-report from the 2019 EASL-AASLD HBV treatment endpoints conference. J Hepatol 2020;72:539-57.DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.11.003. PMID: 31730789.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination
- Transplacental transmission of hepatitis B virus from carrier nothers to neonates
- Anti-infective potential of catechins and their derivatives against viral hepatitis
- Mutations in the pre-core region of hepatitis B virus DNA in a patient with severe anti-HBe positive chronic hepatitis B
- Pre-S Defective Hepatitis B Virus in Patients with Acute and chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection