Yeungnam Univ J Med.
2021 Jan;38(1):65-69. 10.12701/yujm.2020.00269.
Development of donepezil-induced hypokalemia following treatment of cognitive impairment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Incheon St. Mary’s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Eunpyeong St. Mary’s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2512069
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00269
Abstract
- Donepezil is a cholinesterase inhibitor used extensively to treat Alzheimer disease. The increased cholinergic activity is associated with adverse effects, therefore gastrointestinal symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, are common. Hypokalemia is a rare adverse event that occurs in less than 1% of donepezil-treated patients. Although hypokalemia of mild and moderate grade does not present serious signs and symptoms, severe hypokalemia often results in prolonged hospitalization and mortality. Herein, we report a case of hypokalemia developed after the initiation of donepezil therapy for cognitive impairment.
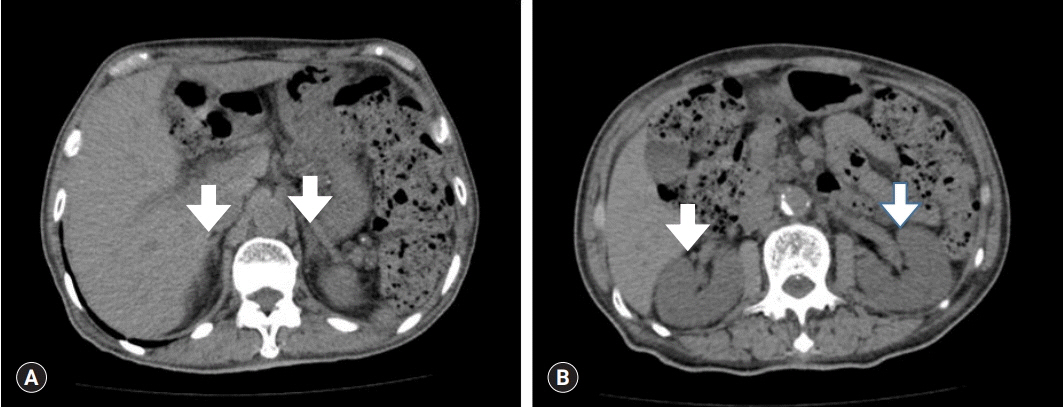
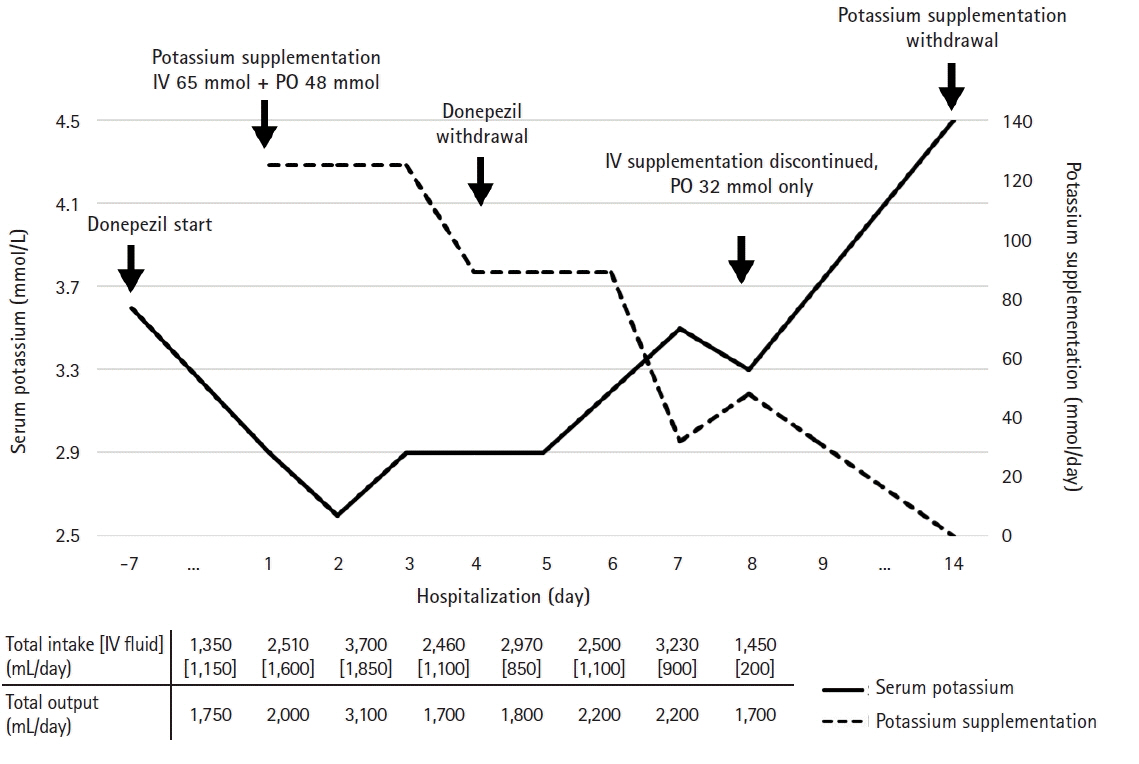
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Crop MJ, Hoorn EJ, Lindemans J, Zietse R. Hypokalaemia and subsequent hyperkalaemia in hospitalized patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007; 22:3471–7.
Article2. Widodo D, Setiawan B, Chen K, Nainggolan L, Santoso WD. The prevalence of hypokalemia in hospitalized patients with infectious diseases problem at Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital, Jakarta. Acta Med Indones. 2006; 38:202–5.3. Unwin RJ, Luft FC, Shirley DG. Pathophysiology and management of hypokalemia: a clinical perspective. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011; 7:75–84.
Article4. Paltiel O, Salakhov E, Ronen I, Berg D, Israeli A. Management of severe hypokalemia in hospitalized patients: a study of quality of care based on computerized databases. Arch Intern Med. 2001; 161:1089–95.
Article5. Li HC, Luo KX, Wang JS, Wang QX. Extrapyramidal side effect of donepezil hydrochloride in an elderly patient: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020; 99:e19443.6. Arai H, Hashimoto N, Sumitomo K, Takase T, Ishii M. Disease state changes and safety of long-term donepezil hydrochloride administration in patients with Alzheimer's disease: Japan-Great Outcome of Long-term trial with Donepezil (J-GOLD). Psychogeriatrics. 2018; 18:402–11.
Article7. Cubeddu LX. Drug-induced inhibition and trafficking disruption of ion channels: pathogenesis of QT abnormalities and drug-induced fatal arrhythmias. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2016; 12:141–54.
Article8. Manzo C, Putignano S. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus associated with donepezil: a case report. Age Ageing. 2015; 44:1062–3.
Article9. US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Highlights of prescribing information: Aricept [Internet]. Silver Spring (MD): FDA;2012. [cited 2020 Feb 20]. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/020690s035,021720s008,022568s005lbl.pdf.10. eHealthMe. Will you have hypokalemia with Donepezil? (a study of FDA data) [Internet]. eHealthMe;2020. [cited 2020 Feb 20]. https://www.ehealthme.com/ds/donepezil/hypokalemia/.11. Li XL, Hu N, Tan MS, Yu JT, Tan L. Behavioral and psychological symptoms in Alzheimer's disease. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:927804.
Article12. Seltzer B. Donepezil: a review. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2005; 1:527–36.
Article13. Dunn NR, Pearce GL, Shakir SA. Adverse effects associated with the use of donepezil in general practice in England. J Psychopharmacol. 2000; 14:406–8.
Article14. Jackson S, Ham RJ, Wilkinson D. The safety and tolerability of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004; 58(Suppl 1):1–8.
Article15. Tabish M, Mahendran M, Ray A, Vikram NK. Colistin-induced acquired Bartter-like syndrome: an unusual cause of meltdown. BMJ Case Rep. 2020; 13:e232630.
Article16. Min HK, Kim EO, Lee SJ, Chang YK, Suh KS, Yang CW, et al. Rifampin-associated tubulointersititial nephritis and Fanconi syndrome presenting as hypokalemic paralysis. BMC Nephrol. 2013; 14:13.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cognitive Enhancing Activity of Cynaroside Isolated from Lysimachia christinae on Memory Impairment Insulted by Scopolamine
- Effect of Glycyrrhizic Acid on Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Mice
- The Effects of Donepezil, an Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor, on Impaired Learning and Memory in Rodents
- Improvement of Visuo-spatial Function Assessed by Raven’s Colored Progressive Matrices in Dementia with Lewy Bodies by Donepezil Treatment
- The Change of K-MMSE Following Donepezil Medication in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease and Small Vessel Dementia, and the Characteristics of Alzheimer's Disease with Meaningful K-MMSE Change