Restor Dent Endod.
2020 Aug;45(3):e30. 10.5395/rde.2020.45.e30.
Micro-computed tomographic assessment of the shaping ability of the One Curve, One Shape, and ProTaper Next nickel-titanium rotary systems
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Hatay Mustafa Kemal University, Antakya, Turkey
- 2Department of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry, Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey
- 3OMFS IMPATH Research Group, Department of Imaging and Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
- 4Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University Hospitals Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
- 5Department of Endodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey
- 6Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Dentistry, Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey
- 7Department of Conservative Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey
- KMID: 2512021
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e30
Abstract
Objectives
This micro-computed tomographic (CT) study aimed to compare the shaping abilities of ProTaper Next (PTN), One Shape (OS), and One Curve (OC) files in 3-dimensionally (3D)-printed mandibular molars.
Materials and Methods
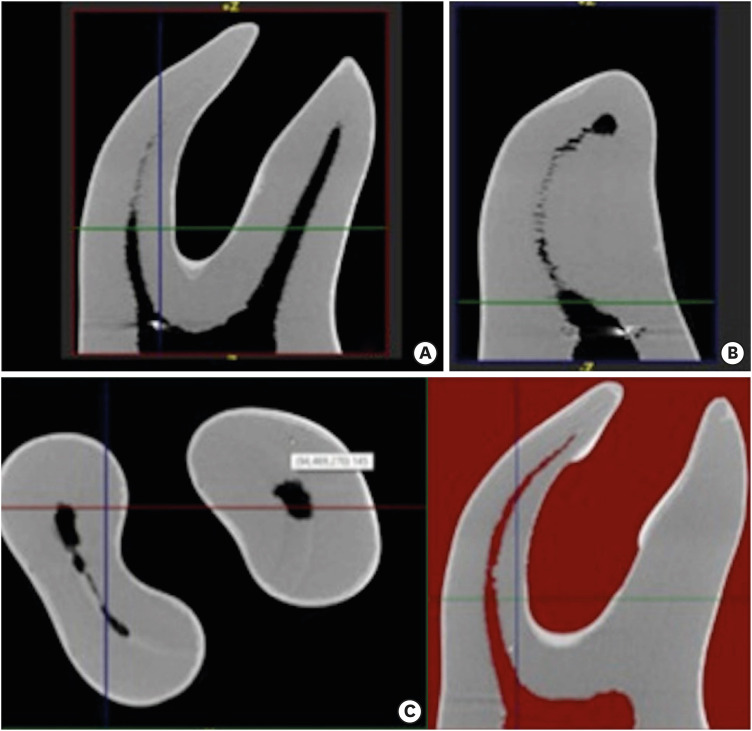
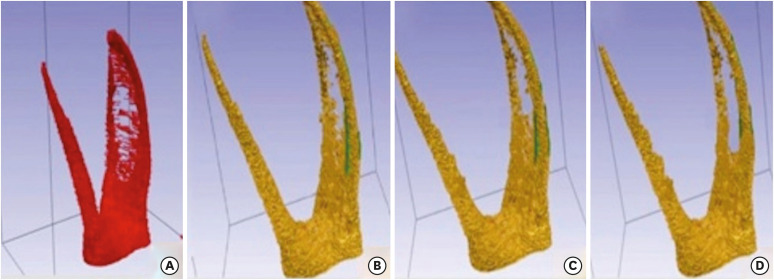
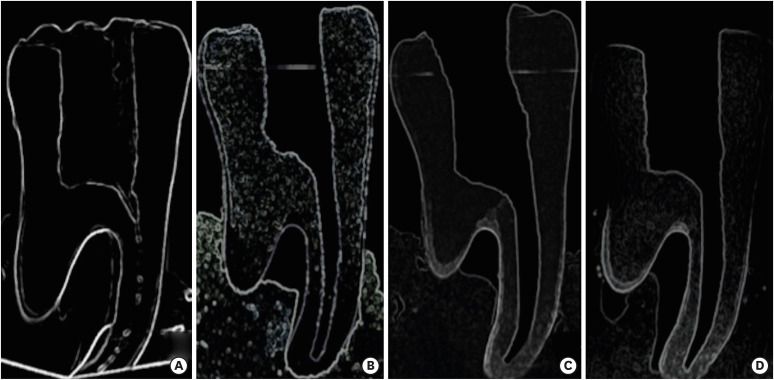
In order to ensure standardization, 3D-printed mandibular molars with a consistent mesiobuccal canal curvature (45°) were used in the present study (n = 18). Specimens were instrumented with the OC, OS, or PTN files. The teeth were scanned preand post-instrumentation using micro-CT to detect changes of the canal volume and surface area, as well as to quantify transportation of the canals after instrumentation. Two-way analysis of variance was used for statistical comparisons.
Results
No statistically significant differences were found between the OC and OS groups in the changes of the canal volume and surface area before and after instrumentation (p > 0.05). The OC files showed significantly less transportation than the OS or PTN systems for the apical section (p < 0.05). In a comparison of the systems, similar values were found at the coronal and middle levels, without any significant differences (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
These 3 instrumentation systems showed similar shaping abilities, although the OC file achieved a lesser extent of transportation in the apical zone than the OS and PTN files. All 3 file systems were confirmed to be safe for use in mandibular mesial canals.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Peters OA, Schönenberger K, Laib A. Effects of four Ni-Ti preparation techniques on root canal geometry assessed by micro computed tomography. Int Endod J. 2001; 34:221–230. PMID: 12193268.
Article2. Schilder H. Cleaning and shaping the root canal. Dent Clin North Am. 1974; 18:269–296. PMID: 4522570.3. Mittal A, Dadu S, Singh NS, Singh S, Gupta B, Abraham A, Yendrembam B, Kumari S. Comparative assessment of canal transportation and centering ability of Reciproc and One Shape File systems using CBCT-an in vitro study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017; 11:ZC31–ZC34.4. Schäfer E, Tepel J, Hoppe W. Properties of endodontic hand instruments used in rotary motion. Part 2. Instrumentation of curved canals. J Endod. 1995; 21:493–497. PMID: 8596068.
Article5. Celikten B, Uzuntas CF, Kursun S, Orhan AI, Tufenkci P, Orhan K, Demiralp KÖ. Comparative evaluation of shaping ability of two nickel-titanium rotary systems using cone beam computed tomography. BMC Oral Health. 2015; 15:32. PMID: 25887521.
Article6. Thompson SA, Dummer PM. Shaping ability of lightspeed rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals. Part 1. J Endod. 1997; 23:698–702. PMID: 9587312.
Article7. Bergmans L, Van Cleynenbreugel J, Wevers M, Lambrechts P. Mechanical root canal preparation with NiTi rotary instruments: rationale, performance and safety. Status report for the American Journal of Dentistry. Am J Dent. 2001; 14:324–333. PMID: 11803999.8. Duque JA, Vivan RR, Cavenago BC, Amoroso-Silva PA, Bernardes RA, Vasconcelos BC, Duarte MA. Influence of NiTi alloy on the root canal shaping capabilities of the ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Gold rotary instrument systems. J Appl Oral Sci. 2017; 25:27–33. PMID: 28198973.
Article9. Alapati SB, Brantley WA, Iijima M, Clark WA, Kovarik L, Buie C, Liu J, Ben Johnson W. Metallurgical characterization of a new nickel-titanium wire for rotary endodontic instruments. J Endod. 2009; 35:1589–1593. PMID: 19840654.
Article10. Zhou H, Peng B, Zheng YF. An overview of the mechanical properties of nickel titanium endodontic instruments. Endod Topics. 2013; 29:42–54.11. Micro Mega. One Curve, the Endo DNA [Internet]. Besancon: Micro Mega;c2018. updated 2018 Jul 30. cited 2018 Jul 30. Available from: https://micro-mega.com/shaping/one-curve?lang=en.12. Peters OA, Arias A, Paqué F. A micro-computed tomographic assessment of root canal preparation with a novel instrument, TRUShape, in mesial roots of mandibular molars. J Endod. 2015; 41:1545–1550. PMID: 26238528.
Article13. Micro Mega. MM.Tooth, as Real as a Natural Tooth, the Ideal Training Material [Internet]. Besancon: Micro Mega;c2018. cited 2018 Jul 30. updated 2018 Jul 30. Available from: https://micro-mega.com/mm-tooth?lang=en.14. Feldkamp LA, Goldstein SA, Parfitt AM, Jesion G, Kleerekoper M. The direct examination of three-dimensional bone architecture in vitro by computed tomography. J Bone Miner Res. 1989; 4:3–11. PMID: 2718776.15. Gambill JM, Alder M, del Rio CE. Comparison of nickel-titanium and stainless steel hand-file instrumentation using computed tomography. J Endod. 1996; 22:369–375. PMID: 8935064.
Article16. Keskin C, Demiral M, Sarıyılmaz E. Comparison of the shaping ability of novel thermally treated reciprocating instruments. Restor Dent Endod. 2018; 43:e15. PMID: 29765896.
Article17. Bergmans L, Van Cleynenbreugel J, Beullens M, Wevers M, Van Meerbeek B, Lambrechts P. Progressive versus constant tapered shaft design using NiTi rotary instruments. Int Endod J. 2003; 36:288–295. PMID: 12702124.
Article18. Bergmans L, Van Cleynenbreugel J, Wevers M, Lambrechts P. A methodology for quantitative evaluation of root canal instrumentation using microcomputed tomography. Int Endod J. 2001; 34:390–398. PMID: 11482723.
Article19. Peters OA, Laib A, Göhring TN, Barbakow F. Changes in root canal geometry after preparation assessed by high-resolution computed tomography. J Endod. 2001; 27:1–6. PMID: 11487156.
Article20. Versiani MA, Pécora JD, Sousa-Neto MD. The anatomy of two-rooted mandibular canines determined using micro-computed tomography. Int Endod J. 2011; 44:682–687. PMID: 21447139.
Article21. Versiani MA, Leoni GB, Steier L, De-Deus G, Tassani S, Pécora JD, de Sousa-Neto MD. Micro-computed tomography study of oval-shaped canals prepared with the self-adjusting file, Reciproc, WaveOne, and ProTaper Universal systems. J Endod. 2013; 39:1060–1066. PMID: 23880278.
Article22. Zhao D, Shen Y, Peng B, Haapasalo M. Root canal preparation of mandibular molars with 3 nickel-titanium rotary instruments: a micro-computed tomographic study. J Endod. 2014; 40:1860–1864. PMID: 25205262.23. Stern S, Patel S, Foschi F, Sherriff M, Mannocci F. Changes in centring and shaping ability using three nickel–titanium instrumentation techniques analysed by micro-computed tomography (μCT). Int Endod J. 2012; 45:514–523. PMID: 22625863.
Article24. Ertuğrul İF. Effect of sodium hypochlorite on the cyclic fatigue resistance: a scanning electron microscopy evaluation. Microsc Res Tech. 2019; 82:2089–2094. PMID: 31574200.
Article25. Arias A, Singh R, Peters OA. Torque and force induced by ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Next during shaping of large and small root canals in extracted teeth. J Endod. 2014; 40:973–976. PMID: 24935546.
Article26. Ruddle CJ, Machtou P, West JD. The shaping movement: fifth-generation technology. Dent Today. 2013; 32:9496–99.27. Capar ID, Ertas H, Ok E, Arslan H, Ertas ET. Comparative study of different novel nickel-titanium rotary systems for root canal preparation in severely curved root canals. J Endod. 2014; 40:852–856. PMID: 24862716.
Article28. Bürklein S, Poschmann T, Schäfer E. Shaping ability of different nickel-titanium systems in simulated S-shaped canals with and without glide path. J Endod. 2014; 40:1231–1234. PMID: 25069939.
Article29. Wu MK, Fan B, Wesselink PR. Leakage along apical root fillings in curved root canals. Part I: effects of apical transportation on seal of root fillings. J Endod. 2000; 26:210–216. PMID: 11199720.
Article30. Uzunoglu E, Turker SA. Comparison of canal transportation, centering ratio by cone-beam computed tomography after preparation with different file systems. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2015; 16:360–365. PMID: 26162254.31. Hieawy A, Haapasalo M, Zhou H, Wang ZJ, Shen Y. Phase transformation behavior and resistance to bending and cyclic fatigue of ProTaper Gold and ProTaper Universal instruments. J Endod. 2015; 41:1134–1138. PMID: 25841955.
Article32. Hülsmann M, Peters OA, Dummer PMH. Mechanical preparation of root canals: shaping goals, techniques and means. Endod Topics. 2005; 10:30–76.33. Burroughs JR, Bergeron BE, Roberts MD, Hagan JL, Himel VT. Shaping ability of three nickel-titanium endodontic file systems in simulated S-shaped root canals. J Endod. 2012; 38:1618–1621. PMID: 23146648.
Article34. Elnaghy AM. Cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Next nickel-titanium rotary files. Int Endod J. 2014; 47:1034–1039. PMID: 24392730.
Article35. Ninan E, Berzins DW. Torsion and bending properties of shape memory and superelastic nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J Endod. 2013; 39:101–104. PMID: 23228266.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of shaping ability using various Nickel-Titanium rotary files and hybrid technique
- Shaping ability of Ni-Ti rotary files in combination with GT rotary Ni-Ti file
- Shaping ability of four rotary nickel-titanium instruments to prepare root canal at danger zone
- The effect of gutta-percha removal using nickel-titanium rotary instruments
- A comparison of the shaping ability of four rotary nickel-titanium files in simulated root canals