Prog Med Phys.
2020 Dec;31(4):145-152. 10.14316/pmp.2020.31.4.145.
High-Dose-Rate Electron-Beam Dosimetry Using an Advanced Markus Chamber with Improved IonRecombination Corrections
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research center, Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2510475
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2020.31.4.145
Abstract
- Purpose
In ionization-chamber dosimetry for high-dose-rate electron beams一above 20 mGy/pulse一the ion-recombination correction methods recommended by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and the American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) are not appropriate, because they overestimate the correction factor. In this study, we suggest a practical ion-recombination correction method, based on Boag’s improved model, and apply it to reference dosimetry for electron beams of about 100 mGy/pulse generated from an electron linear accelerator (LINAC).
Methods
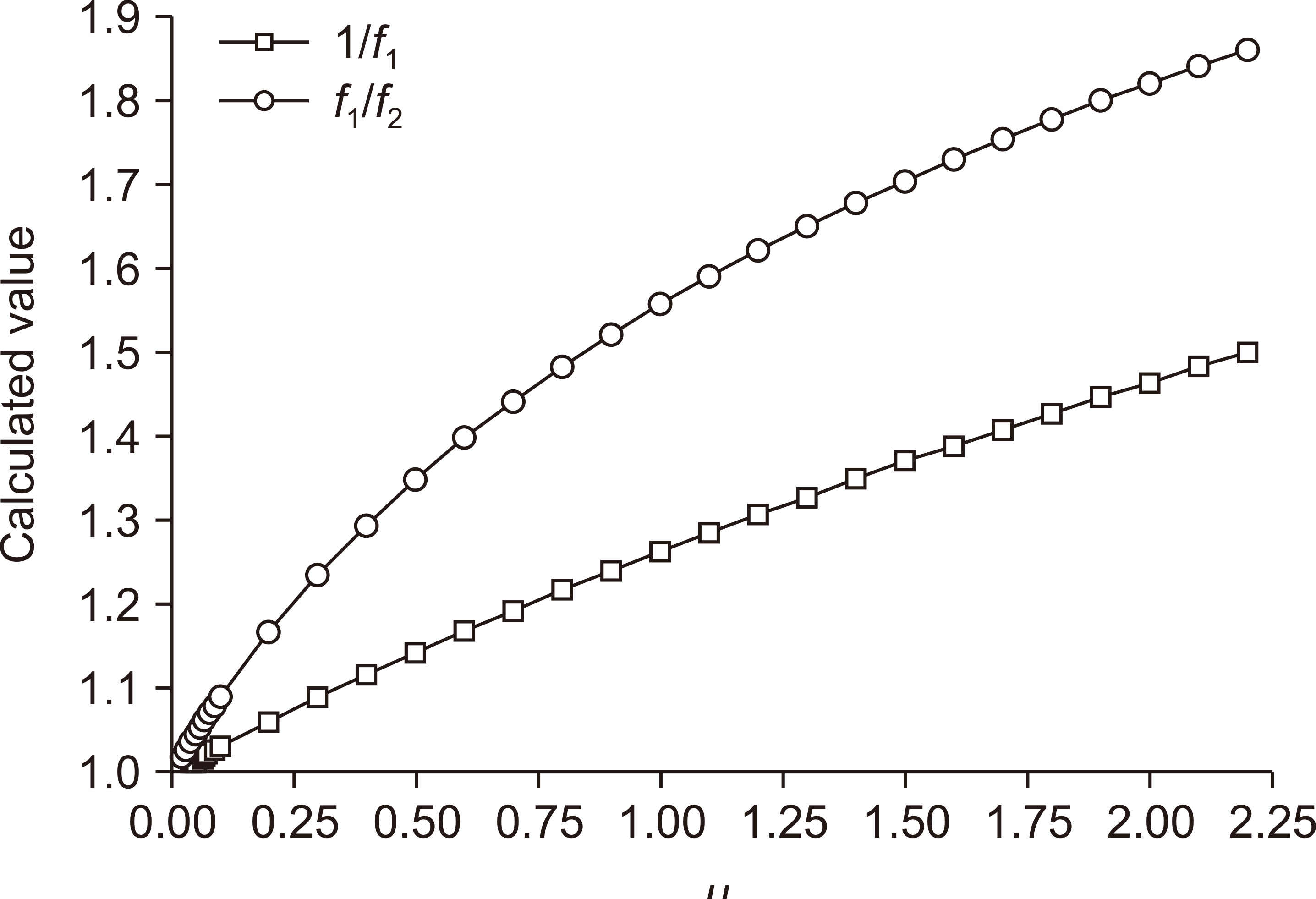
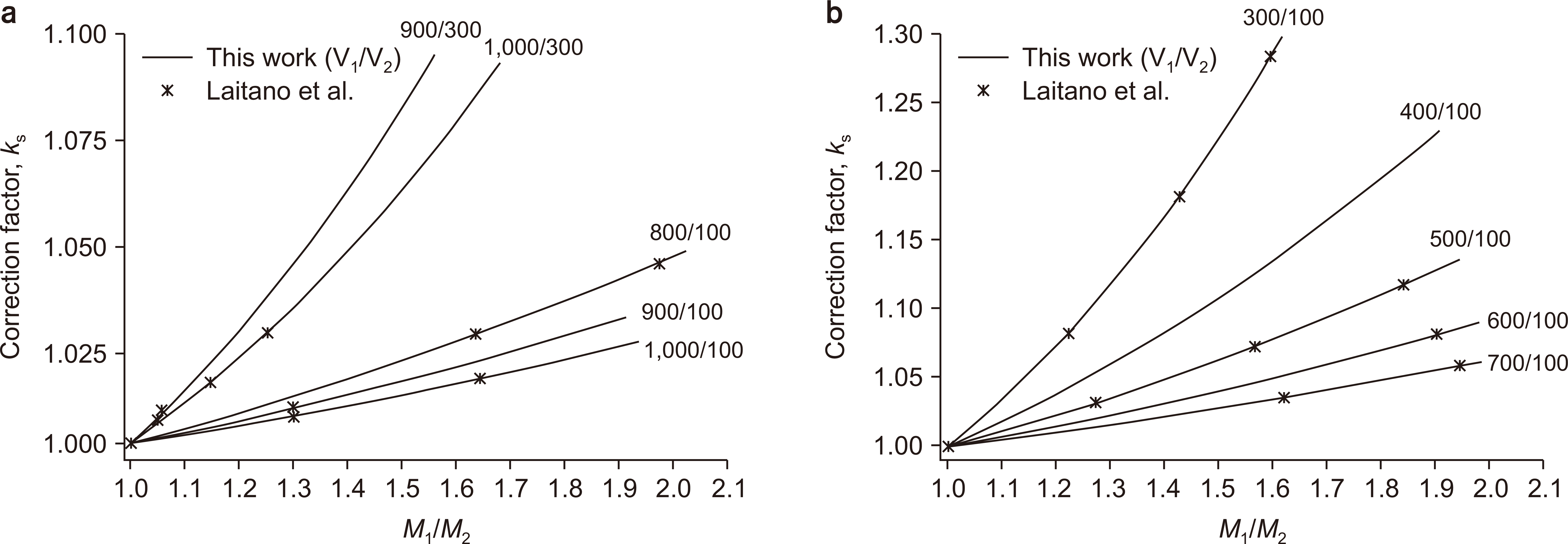
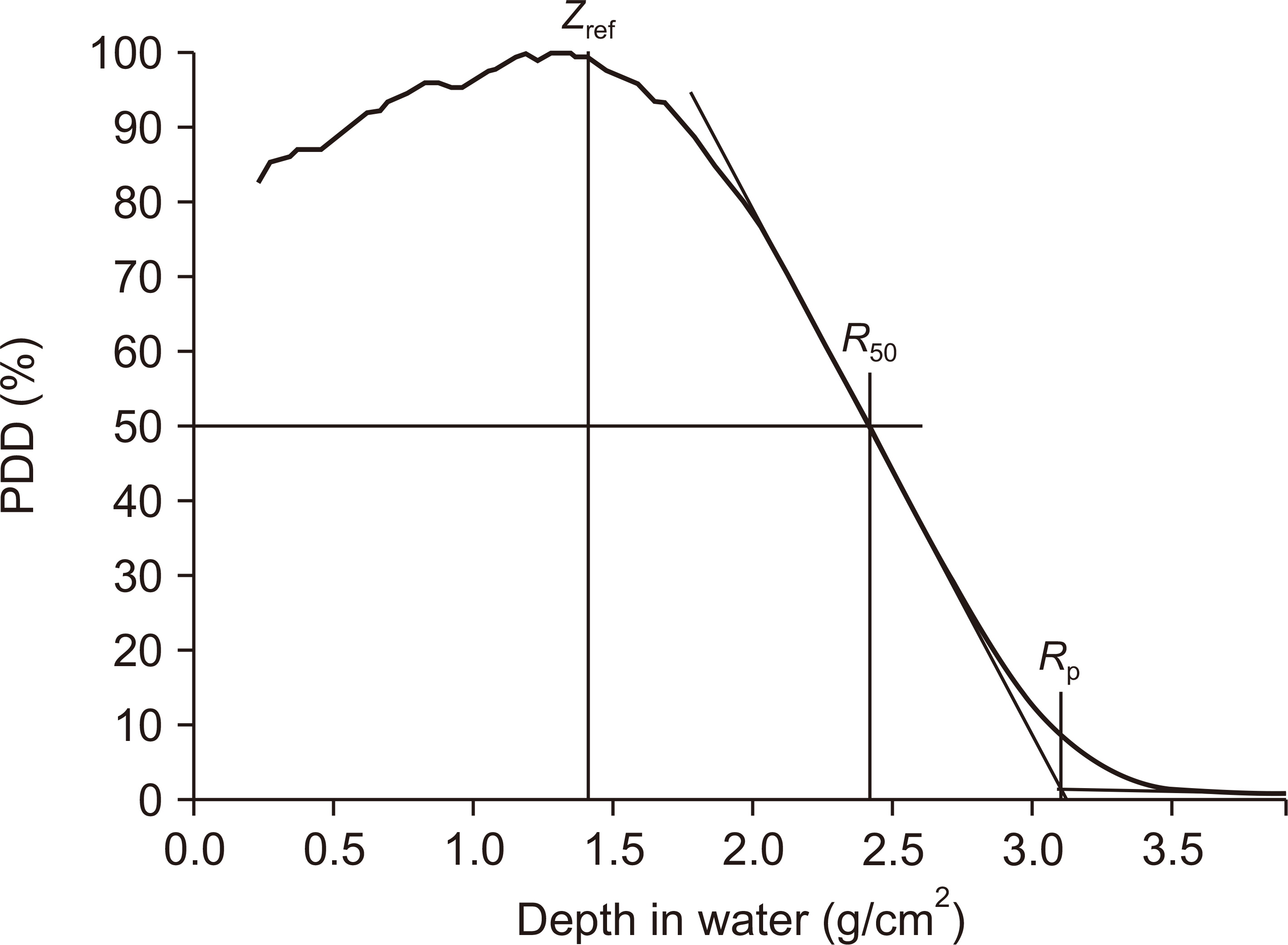
This study employed a theoretical model of the ion-collection efficiency developed by Boag and physical parameters used by Laitano et al. We recalculated the ion-recombination correction factors using two-voltage analysis and obtained an empirical fitting formula to represent the results. Next, we compared the calculated correction factors with published results for the same calculation conditions. Additionally, we performed dosimetry for electron beams from a 6 MeV electron LINAC using an Advanced Markus ® ionization chamber to determine the reference dose in water at the source-to-surface distance (SSD)=100 cm, using the correction factors obtained in this study.
Results
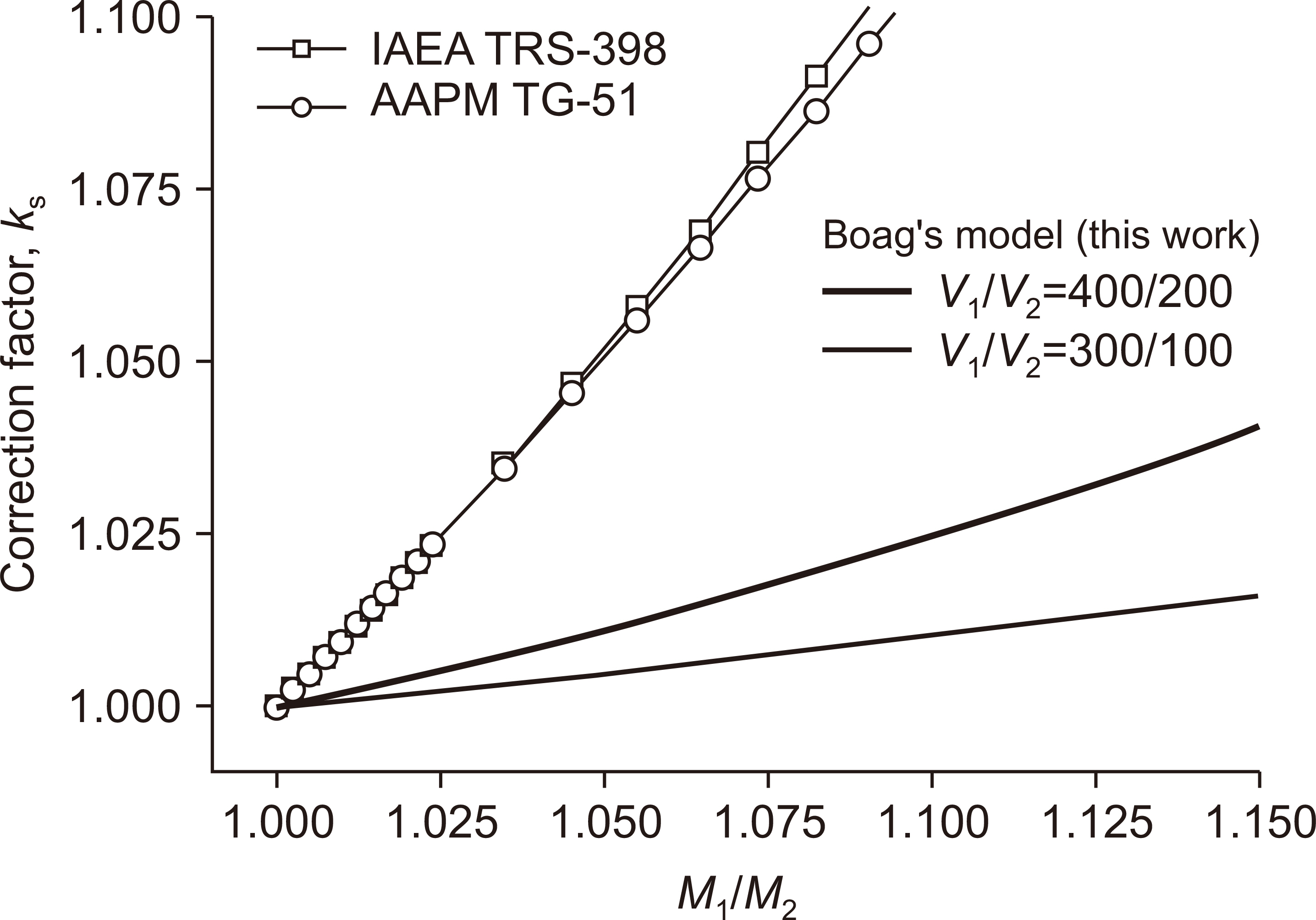
The values of the correction factors obtained in this work are in good agreement with the published data. The measured dose-per-pulse for electron beams at the depth of maximum dose for SSD=100 cm was 115 mGy/pulse, with a standard uncertainty of 2.4%. In contrast, the k s values determined using the IAEA and AAPM methods are, respectively, 8.9% and 8.2% higher than our results.
Conclusions
The new method based on Boag’s improved model provides a practical method of determining the ion-recombination correction factors for high dose-per-pulse radiation beams up to about 120 mGy/pulse. This method can be applied to electron beams with even higher doseper-pulse, subject to independent verification.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Initial Dosimetry of a Prototype Ultra-High Dose Rate Electron-Beam Irradiator for FLASH RT Preclinical Studies
Hyun Kim, Heuijin Lim, Sang Koo Kang, Sang Jin Lee, Tae Woo Kang, Seung Wook Kim, Wung-Hoa Park, Manwoo Lee, Kyoung Won Jang, Dong Hyeok Jeong
Prog Med Phys. 2023;34(3):33-39. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2023.34.3.33.
Reference
-
References
1. Pimpinella M, Andreoli S, De Angelis C, Della Monaca S, D’Arienzo M, Menegotti L. 2019; Output factor measurement in high dose-per-pulse IORT electron beams. Phys Med. 61:94–102. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2019.04.021. PMID: 31151586.
Article2. Montay-Gruel P, Petersson K, Jaccard M, Boivin G, Germond JF, Petit B, et al. 2017; Irradiation in a flash: unique sparing of memory in mice after whole brain irradiation with dose rates above 100Gy/s. Radiother Oncol. 124:365–369. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.05.003. PMID: 28545957.3. Schüler E, Trovati S, King G, Lartey F, Rafat M, Villegas M, et al. 2017; Experimental platform for ultra-high dose rate FLASH irradiation of small animals using a clinical linear accelerator. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 97:195–203. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.09.018. PMID: 27816362.
Article4. Nisbet A, Thwaites DI. 1998; Polarity and ion recombination correction factors for ionization chambers employed in electron beam dosimetry. Phys Med Biol. 43:435–443. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/43/2/016. PMID: 9509537.
Article5. McManus M, Romano F, Lee ND, Farabolini W, Gilardi A, Royle G, et al. 2020; The challenge of ionisation chamber dosimetry in ultra-short pulsed high dose-rate Very High Energy Electron beams. Sci Rep. 10:9089. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-65819-y. PMID: 32493952. PMCID: PMC7270129.
Article6. Boag JW, Hochhäuser E, Balk OA. 1996; The effect of free-electron collection on the recombination correction to ionization measurements of pulsed radiation. Phys Med Biol. 41:885–897. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/41/5/005. PMID: 8735255.
Article7. Laitano RF, Guerra AS, Pimpinella M, Caporali C, Petrucci A. 2006; Charge collection efficiency in ionization chambers exposed to electron beams with high dose per pulse. Phys Med Biol. 51:6419–6436. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/51/24/009. PMID: 17148826.
Article8. Petersson K, Jaccard M, Germond JF, Buchillier T, Bochud F, Bourhis J, et al. 2017; High dose-per-pulse electron beam dosimetry - a model to correct for the ion recombination in the Advanced Markus ionization chamber. Med Phys. 44:1157–1167. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12111. PMID: 28094853.
Article9. Pearce JAD. 2004. Characterisation of two new ionisation chamber types for use in reference electron dosimetry in the UK. National Physical Laboratory;Teddington: NPL Report DQL-RD001.10. Gotz M. 2018. Dosimetry of highly pulsed radiation fields. Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf;Dresden: HZDR-090.11. International Atomic Energy Agency. 2006. Absorbed dose determination in external beam radiotherapy: an international code of practice for dosimetry based on standards of absorbed dose to water. International Atomic Energy Agency;Vienna: IAEA TRS-398.12. Almond PR, Biggs PJ, Coursey BM, Hanson WF, Huq MS, Nath R, et al. 1999; AAPM’s TG-51 protocol for clinical reference dosimetry of high-energy photon and electron beams. Med Phys. 26:1847–1870.
Article13. Kry SF, Popple R, Molineu A, Followill DS. 2012; Ion recombination correction factors (P(ion)) for Varian TrueBeam high-dose-rate therapy beams. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 13:318–325. DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v13i6.3803. PMID: 23149774. PMCID: PMC5718527.
Article14. Lim H, Jo W, Lee DE, Lee M, Kim SH, Shin SW, et al. 2018. Jan. 28-31. Status of the DIRAMS C-band standing-wave accelerator for a radiotherapy machine. Paper presented at: 9th Asia Forum for Accelerators and Detectors. Daejeon, Korea: p. 38.15. Lim H, Lee M, Kim MY, Yi J, Lee M, Kang SK, et al. 2016; Measurement of energy parameters for electron gun heater currents and output dose rate for electron beams from a prototype linac. Prog Med Phys. 27:25–30.
Article16. Jang KW, Lee M, Lim H, Kang SK, Lee SJ, Kim JK, et al. 2020; Development of a wide dose-rate range electron beam irradiation system for pre-clinical studies and multi-purpose applications using a research linear accelerator. Prog Med Phys. 31:9–19.
Article17. Ding GX, Rogers DW. 1996; Mean energy, energy-range relationships and depth-scaling factors for clinical electron beams. Med Phys. 23:361–376. DOI: 10.1118/1.597788. PMID: 8815379.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Determination of Beam Quality Correction Factors for the PTW-Markus Chamber for Electron Beam Qualities R50=1.0 and 1.4 g/cm2
- Measurement of Energy Parameters for Electron Gun Heater Currents and Output Dose Rate for Electron Beams from a Prototype Linac
- Field size and dose distribution of electron beam
- The Study on the Use of a Cylindrical Ionization Chamber for the Calibration of a 6 MeV Electron Beam
- A Study on Electron Beam Dosimetry for Chest Wall Irradiation