Korean J Gastroenterol.
2020 Dec;76(6):304-313. 10.4166/kjg.2020.110.
Effects of the Rome IV Criteria to Functional Dyspepsia Symptoms in Saudi Arabia: Epidemiology and Clinical Practice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Endoscopy Unit, Department of Internal Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Hospital, College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia
- 2Al Kharj, Saudi Arabia; Endoscopy Unit, Department of Internal Medicine, Limassol General Hospital, St George's Medical School, University of Nicosia, Saudi Arabia
- 3Nicosia, Republic of Cyprus; Department of Family Medicine, College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abulaziz University, Saudi Arabia
- 4Al Kharj, Saudi Arabia; Endoscopy Unit, Prince Sultan Military Medical City, Saudi Arabia
- 5Riyadh, Saudi Arabia; Endoscopy Unit, King Khaled Hospital and Prince Sultan Center for Health Care, Saudi Arabia
- 6Al Kharj, Saudi Arabia; Department of Family Medicine, AlKharj Military Hospital, Saudi Arabia
- 7Al Kharj, Saudi Arabia; Department of Internal Medicine, Security Forces Hospital,Saudi Arabia
- 8Riyadh, Saudi Arabia; Ibn Sina National College for Medical Studies, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- 9Jeddah, Saudi Arabia; Almaarefa Medical College, Saudi Arabia
- 10Riyadh, Saudi Arabia; College of Computer and Information Sciences, Al-Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- KMID: 2509707
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2020.110
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Limited data is available in Saudi Arabia (SA) regarding the prevalence of functional dyspepsia (FD) symptoms and its subtypes, as defined by the ROME IV criteria. This study evaluated the burden of self-reported FD symptoms in the adult general population of SA and the current clinical practices.
Methods
A web-based national cross-sectional health survey of the general population of SA was conducted using the Rome IV Diagnostic Questionnaire for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Adults with additional questions on the presence of symptoms compatible with functional heartburn (FH) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The quality of life and somatization questionnaires were also included.
Results
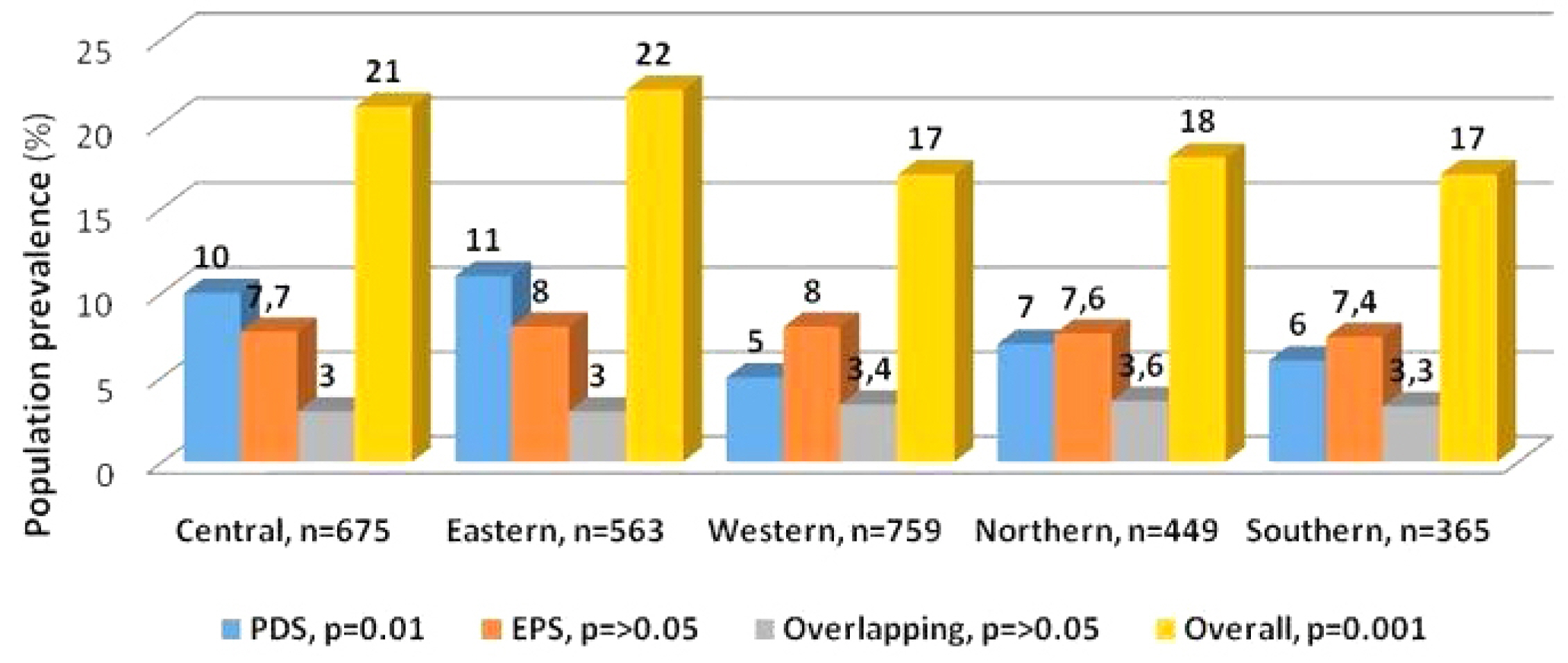
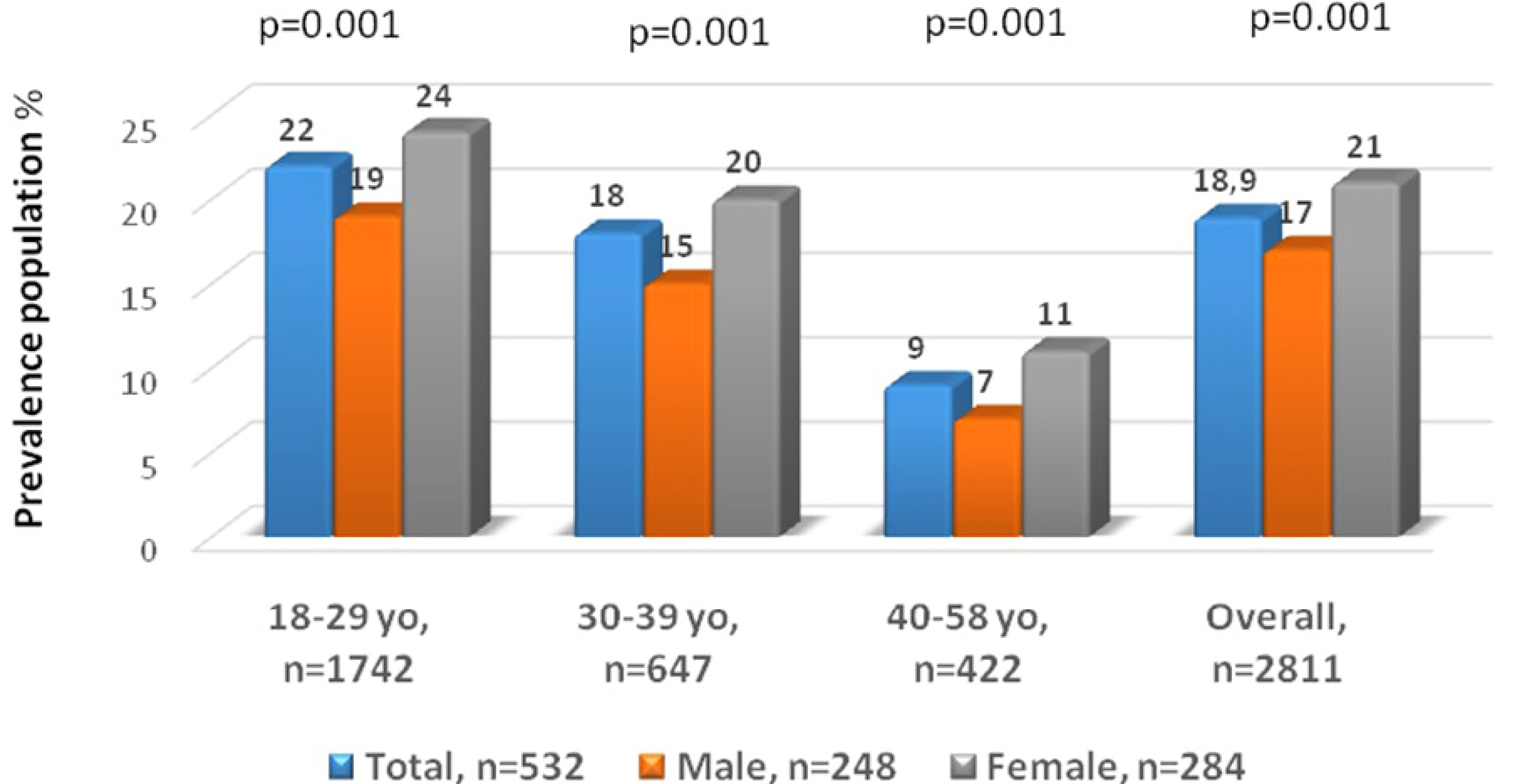
Overall, 3,114 adults completed the questionnaire, but 303 (9.7%) were excluded due to inconsistent responses. Of the 2,811 consistent responders, 532 (18.3%) fulfilled the Rome IV criteria for FD symptoms. These were distributed into the FD subtypes as follows: 208 (7.4%) had postprandial distress syndrome, 228 (8.1%) had epigastric pain syndrome, and 96 (3.4%) had the overlapping variant. IBS-like symptoms were reported in 232 (44%) and FH in 102 (19%) 19% (102) of the subjects with functional dyspepsia. H. pylori-associated dyspepsia was reported by 25% (87/348). High somatization, lower quality of life scores, younger age, and female sex were associated more with the FD symptoms participants than those without. Approximately 1/5 respondents used over-the-counter medications to relieve the FD symptoms.
Conclusions
In this population-based survey, FD affected almost 1/5 of the responding adult population in SA, which was less than previously reported.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Epidemiologic Properties of Functional Dyspepsia in Saudi Arabia
Hyun Jin Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2020;76(6):273-274. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.159.
Reference
-
1. Koduru P, Irani M, Quigley EMM. 2018; Definition, pathogenesis, and management of that cursed dyspepsia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:467–479. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.09.002. PMID: 28899670.2. Tack J, Talley NJ, Camilleri M, et al. 2006; Functional gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology. 130:1466–1479. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.11.059. PMID: 16678560.
Article3. Mearin F, Cucala M, Azpiroz F, Malagelada JR. 1991; The origin of symptoms on the brain-gut axis in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 101:999–1006. DOI: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90726-2.
Article4. Talley NJ, Hunt RH. 1997; What role does Helicobacter pylori play in dyspepsia and nonulcer dyspepsia? Arguments for and against H. pylori being associated with dyspeptic symptoms. Gastroenterology. 113(Suppl 6):S67–S77. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5085(97)80016-9.
Article5. Tack J, Piessevaux H, Coulie B, Caenepeel P, Janssens J. 1998; Role of impaired gastric accommodation to a meal in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 115:1346–1352. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5085(98)70012-5.
Article6. Walker MM, Talley NJ, Prabhakar M, et al. 2009; Duodenal mastocytosis, eosinophilia and intraepithelial lymphocytosis as possible disease markers in the irritable bowel syndrome and functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 29:765–773. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.03937.x. PMID: 19183150. PMCID: PMC4070654.
Article7. Drossman DA, Creed FH, Olden KW, et al. 1999; Psychosocial aspects of the functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gut. 45(Suppl 2):II25–II30. DOI: 10.1136/gut.45.2008.ii25. PMID: 10457041. PMCID: PMC1766694.
Article8. Vanheel H, Carbone F, Valvekens L, et al. 2017; Pathophysiological abnormalities in functional dyspepsia subgroups according to the Rome III criteria. Am J Gastroenterol. 112:132–140. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2016.499. PMID: 27958284.
Article9. Hammer J. 2018; Identification of individuals with functional dyspepsia with a simple, minimally invasive test: a single center cohort study of the oral capsaicin test. Am J Gastroenterol. 113:584–592. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2018.16. PMID: 29533398.
Article10. Stanghellini V, Chan FK, Hasler WL, et al. 2016; Gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology. 150:1380–1392. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.011. PMID: 27147122.
Article11. Drossman DA, Hasler WL. 2016; Rome IV-functional GI disorders: disorders of gut-brain interaction. Gastroenterology. 150:1257–1261. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.03.035. PMID: 27147121.
Article12. Drossman DA. 2016; Functional gastrointestinal disorders: history, pathophysiology, clinical features, and Rome IV. Gastroenterology. 150:1262–1279. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.032. PMID: 27144617.
Article13. Palsson OS, Whitehead WE, van Tilburg MAL, et al. 2016; Development and validation for Rome IV diagnostic questionnaire for adults. Gastroenterology. 150:1481–1491. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.014. PMID: 27144634.14. Ford AC, Marwaha A, Sood R, Moayyedi P. 2015; Global prevalence of, and risk factors for, uninvestigated dyspepsia: a meta-analysis. Gut. 64:1049–1057. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307843. PMID: 25147201.
Article15. Alanazi BG, Alanazi FH, Albriek AZ, et al. 2019; The prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with dyspepsia in the central rural region of Saudi Arabia. IAJPS. 6:1358–1364.16. Akeel M, Elmakki E, Shehata A, et al. 2018; Prevalence and factors associated with H. pylori infection in Saudi patients with dyspepsia. Electron Physician. 10:7279–7286. DOI: 10.19082/7279. PMID: 30258561. PMCID: PMC6140988.
Article17. Masoodi I. 2018; The prevalence and risk factors of non-ulcer dyspepsia in the western region of Saudi Arabia: short form Leads dyspepsia questionnaire revisited. Int J Med Sci Public Health. 7:915–921. DOI: 10.5455/ijmsph.2018.0823617082018.
Article18. Ayoola AE, Ageely HM, Gadour MO, Pathak VP. 2004; Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection among patients with dyspepsia in South-Western Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 25:1433–1438.19. Morad NA, Ahmed ME, Al-Wabel A, et al. 1993; Helicobacter pylori associated dyspepsia in 208 patients from southern Saudi Arabia. Ann Saudi Med. 13:340–343. DOI: 10.5144/0256-4947.1993.340. PMID: 17590697.
Article20. Spiller RC, Humes DJ, Campbell E, et al. 2010; The patient health questionnaire 12 somatic symptom scale as a predictor of symptom severity and consulting behaviour in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and symptomatic diverticular disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 32:811–820. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2010.04402.x. PMID: 20629976.
Article21. Moayyedi P, Lacy BE, Andrews CN, Enns RA, Howden CW, Vakil N. 2017; ACG and CAG clinical guideline: management of dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol. 112:988–1013. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2017.154. PMID: 28631728.
Article22. Enck P, Azpiroz F, Boeckxstaens G, et al. 2017; Functional dyspepsia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:17081. DOI: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.81. PMID: 29099093.
Article23. Ware JE, Kosinski M, Dewey JE, et al. 2001. How to score and interpret single-item health status measures: a manual for users of the SF-8TM Health Survey. Quality Metric Incorporated;Lincoln:24. Aziz I, Palsson OS, Trnblom H, Sperber AD, Whitehead WE, Simrén M. 2018; Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and associations for symptom-based Rome IV functional dyspepsia in adults in the USA, Canada, and the UK: a cross-sectional pop-ulation-based study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3:252–262. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30003-7.
Article25. Zagari RM, Law GR, Fuccio L, et al. 2010; Epidemiology of functional dyspepsia and subgroups in the Italian general population: an endoscopic study. Gastroenterology. 138:1302–1311. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.12.057. PMID: 20074574.
Article26. Bernersen B, Johnsen R, Straume B. 1996; Non-ulcer dyspepsia and peptic ulcer: the distribution in a population and their relation to risk factors. Gut. 38:822–825. DOI: 10.1136/gut.38.6.822. PMID: 8984017. PMCID: PMC1383186.
Article27. Wang A, Liao X, Xiong L, et al. 2008; The clinical overlap between functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome based on Rome III criteria. BMC Gastroenterol. 8:43. DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-8-43. PMID: 18808723. PMCID: PMC2569040.
Article28. van Kerkhoven LA, Laheij RJ, Meineche-Schmidt V, Veldhuyzen-van Zanten SJ, de Wit NJ, Jansen JB. 2009; Functional dyspepsia: not all roads seem to lead to Rome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 43:118–122. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31815591f7. PMID: 18719513.29. Carbone F, Holvoet L, Tack J. 2015; Rome III functional dyspepsia subdivision in PDS and EPS: recognizing postprandial symptoms reduces overlap. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 27:1069–1074. DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12585. PMID: 26220647.
Article30. Pleyer C, Bittner H, Locke GR 3rd, et al. 2014; Overdiagnosis of gastro-esophageal reflux disease and underdiagnosis of functional dyspepsia in a USA community. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 26:1163–1171. DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12377. PMID: 24916517.
Article31. Hsu YC, Liou JM, Liao SC, et al. 2009; Psychopathology and personality trait in subgroups of functional dyspepsia based on Rome III criteria. Am J Gastroenterol. 104:2534–2542. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2009.328. PMID: 19532128.
Article32. Talley NJ, Locke GR, Saito YA, et al. 2015; Effect of amitriptyline and escitalopram on functional dyspepsia: a multicenter, randomized controlled study. Gastroenterology. 149:340–349. e2. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.020. PMID: 25921377. PMCID: PMC4516571.
Article33. Lacy BE, Parkman HP, Camilleri M. 2018; Chronic nausea and vomiting: evaluation and treatment. Am J Gastroenterol. 113:647–659. DOI: 10.1038/s41395-018-0039-2. PMID: 29545633.
Article34. Herrick LM, Camilleri M, Schleck CD, Zinsmeister AR, Saito YA, Talley NJ. 2018; Effects of amitriptyline and escitalopram on sleep and mood in patients with functional dyspepsia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:401–406. e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.10.021. PMID: 29199141.
Article35. Ford AC, Luthra P, Tack J, Boeckxstaens GE, Moayyedi P, Talley NJ. 2017; Efficacy of psychotropic drugs in functional dyspepsia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut. 66:411–420. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310721. PMID: 26567029.
Article36. Akeel M, Shehata A, Elhafey A, et al. 2019; Helicobacter pylori vacA, cagA and iceA genotypes in dyspeptic patients from southwestern region, Saudi Arabia: distribution and association with clinical outcomes and histopathological changes. BMC Gastroenterol. 19:16. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-019-0934-z. PMID: 30683054. PMCID: PMC6346553.
Article37. Tan VP, Liu KS, Lam FY, Hung IF, Yuen MF, Leung WK. 2017; Randomised clinical trial: rifaximin versus placebo for the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 45:767–776. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13945. PMID: 28112426.
Article38. Al-Karawi MA. 1992; Evaluation of gastro-esophageal reflux disease results in 40 patients. Saudi Med J. 13:407–411.39. Wahass S, Khalil MS, Al Qurain AA, Yasawy MI. 2006; The impact of functional dyspepsia on health-related quality of life in Saudi patients. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 12:123–129. DOI: 10.4103/1319-3767.29752. PMID: 19858598.
Article40. Ford AC, Forman D, Bailey AG, Axon AT, Moayyedi P. 2007; Initial poor quality of life and new onset of dyspepsia: results from a longitudinal 10-year follow-up study. Gut. 56:321–327. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.099846. PMID: 16908511. PMCID: PMC1856829.
Article41. Ford AC, Marwaha A, Lim A, Moayyedi P. 2010; Systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in individuals with dyspepsia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:401–409. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.07.020. PMID: 19631762.
Article42. Locke GR 3rd, Zinsmeister AR, Fett SL, Melton LJ 3rd, Talley NJ. 2005; Overlap of gastrointestinal symptom complexes in a US community. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 17:29–34. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2004.00581.x. PMID: 15670261.43. Fang YJ, Liou JM, Chen CC, et al. 2015; Distinct aetiopathogenesis in subgroups of functional dyspepsia according to the Rome III criteria. Gut. 64:1517–1528. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308114. PMID: 25406127. PMCID: PMC4602241.
Article44. Aro P, Talley NJ, Ronkainen J, et al. 2009; Anxiety is associated with uninvestigated and functional dyspepsia (Rome III criteria) in a Swedish population-based study. Gastroenterology. 137:94–100. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.03.039. PMID: 19328797.
Article45. Zagari RM, Law GR, Fuccio L, et al. 2010; Epidemiology of functional dyspepsia and subgroups in the Italian general population: an endoscopic study. Gastroenterology. 138:1302–1311. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.12.057. PMID: 20074574.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Understanding the Rome IV: Gastroduodenal Disorders
- Understanding the Rome IV: Functional Constipation and Anorectal Disorders
- Understanding the Rome IV: Background to the Rome IV Revision
- The Application of the Rome IV Criteria to Functional Esophagogastroduodenal Disorders in Asia
- Diagnostic approach for dyspepsia: Exclusive diagnosis vs. Rome criteria