Ann Clin Microbiol.
2020 Dec;23(4):251-259. 10.5145/ACM.2020.23.4.4.
Causes and Clinical Relevance of Inconclusive SARS-CoV-2 Real-Time Reverse TranscriptionPCR Test Results
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2509644
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2020.23.4.4
Abstract
- Background
Inconclusive SARS-CoV-2 real-time reverse transcription-PCR (rRT-PCR) test results, which are positive for one or more target genes but not all, are problematic in clinical laboratories. In this study, we aimed to investigate the cause and clinical relevance of such inconclusive results.
Methods
rRT-PCR was performed using the Allplex 2019-nCoV assay kit (Seegene Inc., Korea) targeting the following three genes: E, RdRp, and N. For all inconclusive test results reported from March to June 2020, the frequency per kit, lot number, specimen type, cycle threshold (Ct) and peak values of the amplification curves, positive target genes, and results of repeated or consecutive tests were analyzed.
Results
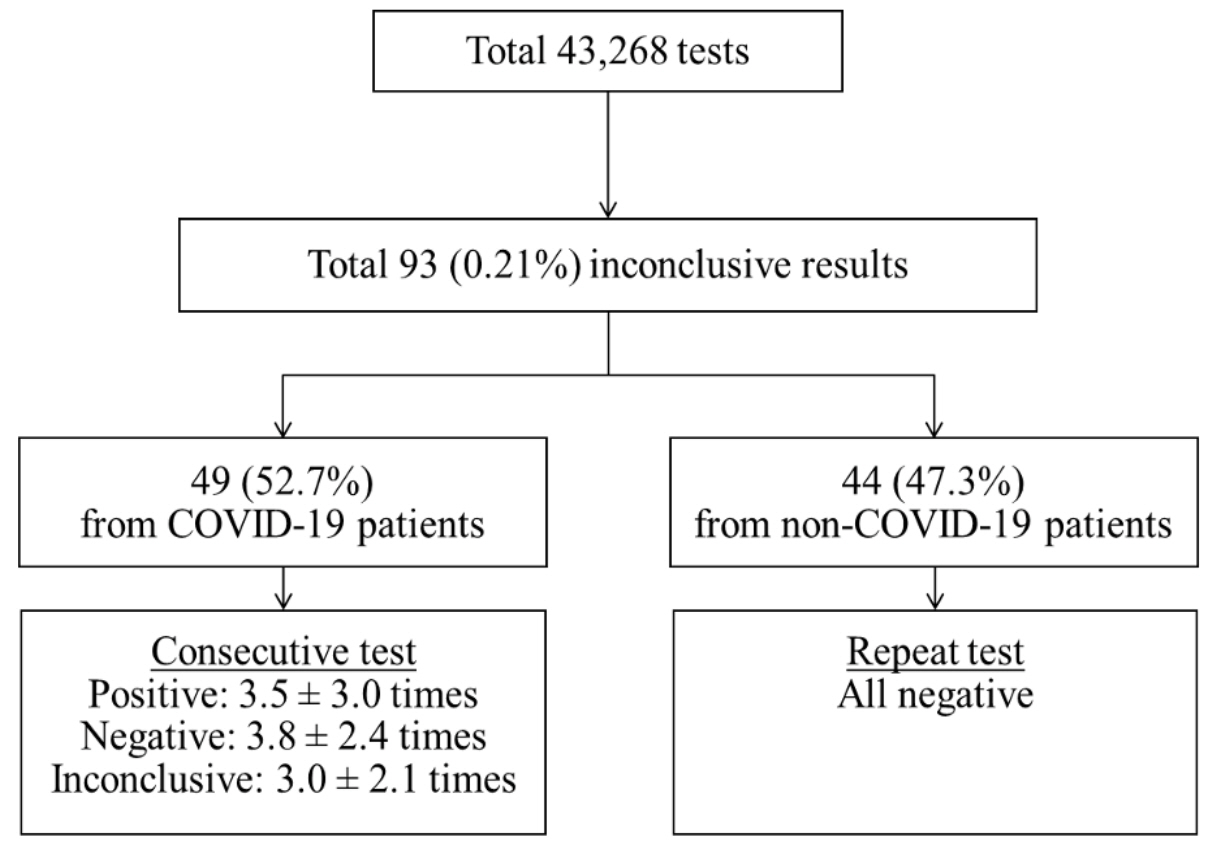
A total of 43,268 tests were conducted, of which 93 (0.21%) were inconclusive—49 from 11 coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients and 44 from non-COVID-19 patients. In COVID-19 patients, the results were inconclusive 11.9 ± 4.7 days after diagnosis and were negative 8.8 ± 5.5 days after the inconclusive results were reported. However, in nonCOVID-19 patients, they were all negative upon retest and 81.8% of them were identified to have yielded in 2 out of 8 lots. The most frequently positive target genes were N (55.4%) in COVID-19 and RdRp (61.2%) in non-COVID-19 patients, respectively. No difference was observed in the Ct or peak values of the amplification curves for inconclusive samples between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 cases.
Conclusion
Inconclusive test results should be reported neither positive nor negative. Such results can be reported as inconclusive without retesting in COVID-19 patients; however, they should certainly be confirmed by a retest in non-COVID-19 patients or newly diagnosed cases.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020;579:270-3.2. WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 [Online] (last visited on 6 August 2020).3. WHO. Laboratory testing for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in suspected human cases. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/10665-331501 [Online] (last visited on 19 March 2020).4. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. List of COVID-19 diagnostic kits authorized for use under emergency use authorizations. http://www.cdc.go.kr/board.es?mid=a20504000000&bid=0014&act=view&list_no=368209 [Online] (last visited on 24 August 2020).5. Corman VM, Landt O, Kaiser M, Molenkamp R, Meijer A, Chu DK, et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill 2020;25:2000045.6. Hong KH, Lee SW, Kim TS, Huh HJ, Lee J, Kim SY, et al. Guidelines for laboratory diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea. Ann Lab Med 2020;40:351-60.7. Sung H, Roh KH, Hong KH, Seong MW, Ryoo N, Kim HS, et al. COVID-19 molecular testing in Korea: practical essentials and answers from experts based on experiences of emergency use authorization assays. Ann Lab Med 2020;40:439-47.8. Hur KH, Park K, Lim Y, Jeong YS, Sung H, Kim MN. Evaluation of four commercial kits for SARS-CoV-2 real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction approved by emergency-use-authorization in Korea. Front Med 2020;7:521.9. Penarrubia L, Ruiz M, Porco R, Rao SN, Juanola-Falgarona M, Manissero D, et al. Multiple assays in a real-time RT-PCR SARS-CoV-2 panel can mitigate the risk of loss of sensitivity by new genomic variants during the COVID-19 outbreak. Int J Infect Dis 2020;97:225-9.10. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Response guidelines against COVID-19 (9th ed). http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/duBoardList.do?brdId=2&brdGubun=24 [Online] (last visited on 9 July 2020).11. Jung J, Oh DK, Ahn JH, Hong SB, Sung H, Kim MN, et al. Re: low-dose corticosteroid therapy does not delay viral clearance in patients with COVID-19. J Infect 2020;81:e79-81.12. Sung H, Han MG, Yoo CK, Lee SW, Chung YS, Park JS, et al. Nationwide external quality assessment of SARS-CoV-2 molecular testing, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis 2020;26:2353.13. Barry A and Eskild P. SARS-CoV-2 shedding and infectivity. Lancet 2020;395:1339-40.14. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Findings from investigation and analysis of re-positive cases. https://www.cdc.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a30402000000&bid=0030 [Online] (last visited on 19 May 2020).15. Lee J, Kim KH, Kang HM, Kim JH. Do we really need to isolate all children with COVID-19 in healthcare facilities? J Korean Med Sci 2020;35:e277.16. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Duration of isolation and precautions for adults with COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/duration-isolation.html?CDC_AA_refVal=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cdc.gov%2Fcoronavirus%2F2019-ncov%2Fcommunity%2Fstrategy-discontinue-isolation.html [Online] (last visited on 22 July 22 2020).17. Moreno JL, Zúñiga S, Enjuanes L, Sola I. Identification of a coronavirus transcription enhancer. J Virol 2008;82:3882-93.18. Chu DKW, Pan Y, Cheng SMS, Hui KPY, Krishnan P, Liu Y, et al. Molecular diagnosis of a novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) causing an outbreak of pneumonia. Clin Chem 2020;66:549-55.19. Nalla AK, Casto AM, Huang MLW, Perchetti GA, Sampoleo R, Shrestha L, et al. Comparative performance of SARS-CoV-2 detection assays using seven different primer-probe sets and one assay kit. J Clin Microbiol 2020;58:e00557-20.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Understandings and Prospects of Laboratory Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2
- Laboratory Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Korea
- Evaluation of the AccuPower® RV1 Real-Time RT-PCR Kit and the AccuPower® RV1 Multiplex Kit for SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza Virus Detection
- Evaluation of the AdvanSure One-Stop COVID-19 Plus Kit for SARS-CoV-2 Detection Using a Streamlined RNA Extraction Method
- Retrospective Validation of Xpert Xpress SARSCoV-2 and Rapid COVID-19 PCR Tests