Int J Stem Cells.
2020 Nov;13(3):312-325. 10.15283/ijsc20097.
The Role and Specific Mechanism of OCT4 in Cancer Stem Cells: A Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Stem Cell and Cancer Center, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
- KMID: 2508905
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc20097
Abstract
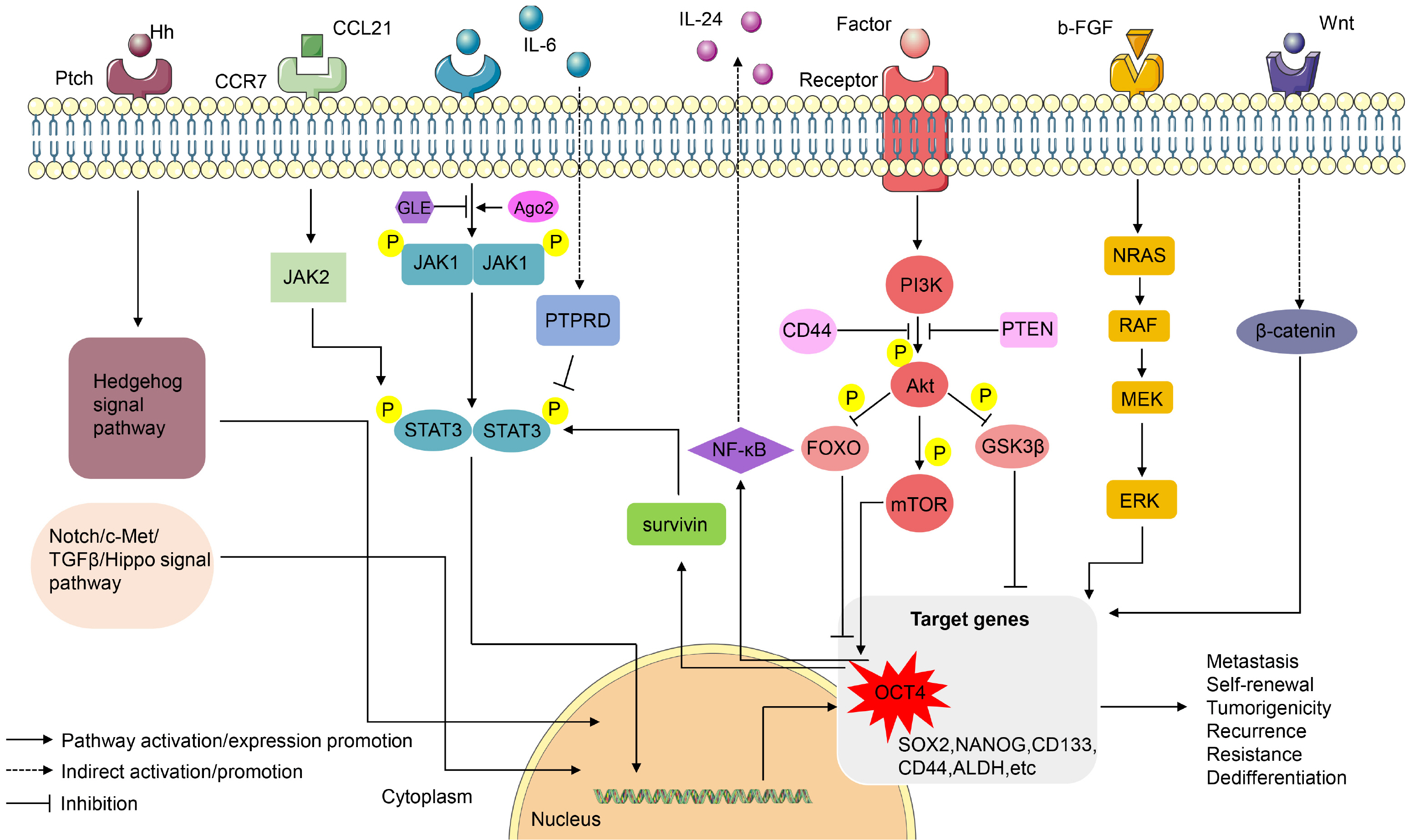
- Recently, evidences show that cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a type of cancer cell group with self-renewal and play a huge role in tumor recurrence, metastasis, and drug resistance. Finding new treatment directions and targets for cancer prognosis and reducing mortality has become a top priority. OCT4, as a transcription factor, participates in maintaining the stem characteristics of CSCs, but the mechanism of OCT4 is often overlooked. In this review, we try to illustrate the mechanism by which OCT4 plays a role in CSCs from the perspective of genetic modification of OCT4, non-coding RNA, complexes and signaling pathways associated with OCT4. Our ultimate goal is to provide new targets for cancer treatment to prolong the survival of cancer patients.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Essential Guidelines for Manufacturing and Application of Organoids
Sun-Ju Ahn, Sungin Lee, Dayeon Kwon, Sejeong Oh, Chihye Park, Sooyeon Jeon, Jin Hee Lee, Tae Sung Kim, Il Ung Oh
Int J Stem Cells. 2024;17(2):102-112. doi: 10.15283/ijsc24047.
Reference
-
References
1. Pozzi V, Salvolini E, Lucarini G, Salvucci A, Campagna R, Rubini C, Sartini D, Emanuelli M. 2020; Cancer stem cell enrichment is associated with enhancement of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase expression. IUBMB Life. 72:1415–1425. DOI: 10.1002/iub.2265. PMID: 32150326.
Article2. Unver N. 2020; Cancer stemness as a target for immunotherapy is shaped by pro-inflammatory stress. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. doi:10.2174/1574888X15666200309145901. [Epub ahead of print]. DOI: 10.2174/1574888X15666200309145901. PMID: 32148202.
Article3. Mortezaee K. 2020; CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in the microenvironment of solid tumors: a critical mediator of metastasis. Life Sci. 249:117534. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117534. PMID: 32156548.
Article4. Tahmasebi E, Alikhani M, Yazdanian A, Yazdanian M, Tebyanian H, Seifalian A. 2020; The current markers of cancer stem cell in oral cancers. Life Sci. 249:117483. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117483. PMID: 32135187.
Article5. Bigdelou Z, Mortazavi Y, Saltanatpour Z, Asadi Z, Kadivar M, Johari B. 2020; Role of Oct4-Sox2 complex decoy oligodeoxynucleotides strategy on reverse epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) induction in HT29-ShE encompassing enriched cancer stem-like cells. Mol Biol Rep. 47:1859–1869. DOI: 10.1007/s11033-020-05280-2. PMID: 32016633.
Article6. Zhao Y, Li C, Huang L, Niu S, Lu Q, Gong D, Huang S, Yuan Y, Chen H. 2018; Prognostic value of association of OCT4 with LEF1 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and their impact on epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and migration. Cancer Med. 7:3977–3987. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1641. PMID: 29974668. PMCID: PMC6089166.
Article7. Zeineddine D, Hammoud AA, Mortada M, Boeuf H. 2014; The Oct4 protein: more than a magic stemness marker. Am J Stem Cells. 3:74–82. PMID: 25232507. PMCID: PMC4163606.8. van Schaijik B, Davis PF, Wickremesekera AC, Tan ST, Itinteang T. 2018; Subcellular localisation of the stem cell markers OCT4, SOX2, NANOG, KLF4 and c-MYC in cancer: a review. J Clin Pathol. 71:88–91. DOI: 10.1136/jclinpath-2017-204815. PMID: 29180509.
Article9. Shi G, Jin Y. 2010; Role of Oct4 in maintaining and regaining stem cell pluripotency. Stem Cell Res Ther. 1:39. DOI: 10.1186/scrt39. PMID: 21156086. PMCID: PMC3025441.
Article10. Okamoto K, Okazawa H, Okuda A, Sakai M, Muramatsu M, Hamada H. 1990; A novel octamer binding transcription factor is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Cell. 60:461–472. DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90597-8. PMID: 1967980.
Article11. Schöler HR, Ruppert S, Suzuki N, Chowdhury K, Gruss P. 1990; New type of POU domain in germ line-specific protein Oct-4. Nature. 344:435–439. DOI: 10.1038/344435a0. PMID: 1690859.
Article12. Rosner MH, Vigano MA, Ozato K, Timmons PM, Poirier F, Rigby PW, Staudt LM. 1990; A POU-domain transcription factor in early stem cells and germ cells of the mammalian embryo. Nature. 345:686–692. DOI: 10.1038/345686a0. PMID: 1972777.
Article13. Kim JB, Sebastiano V, Wu G, Araúzo-Bravo MJ, Sasse P, Gentile L, Ko K, Ruau D, Ehrich M, van den Boom D, Meyer J, Hübner K, Bernemann C, Ortmeier C, Zenke M, Fleischmann BK, Zaehres H, Schöler HR. 2009; Oct4-induced pluripotency in adult neural stem cells. Cell. 136:411–419. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.023. PMID: 19203577.
Article14. Tai MH, Chang CC, Kiupel M, Webster JD, Olson LK, Trosko JE. 2005; Oct4 expression in adult human stem cells: evidence in support of the stem cell theory of carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 26:495–502. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgh321. PMID: 15513931.
Article15. Shao M, Bi T, Ding W, Yu C, Jiang C, Yang H, Sun X, Yang M. 2018; OCT4 potentiates radio-resistance and migration activity of rectal cancer cells by improving epithelial-mesenchymal transition in a ZEB1 dependent manner. Biomed Res Int. 2018:3424956. DOI: 10.1155/2018/3424956. PMID: 30112378. PMCID: PMC6077687.
Article16. Zhao FQ. 2013; Octamer-binding transcription factors: genomics and functions. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 18:1051–1071. DOI: 10.2741/4162. PMID: 23747866. PMCID: PMC4349413.
Article17. Huertas J, MacCarthy CM, Schöler HR, Cojocaru V. 2020; Nucleosomal DNA dynamics mediate Oct4 pioneer factor binding. Biophys J. 118:2280–2296. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.12.038. PMID: 32027821. PMCID: PMC7202942.
Article18. Medvedev SP, Shevchenko AI, Elisaphenko EA, Nesterova TB, Brockdorff N, Zakian SM. 2008; Structure and expression pattern of Oct4 gene are conserved in vole Microtus rossiaemeridionalis. BMC Genomics. 9:162. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-162. PMID: 18402712. PMCID: PMC2410140.
Article19. Mohiuddin IS, Wei SJ, Kang MH. 2020; Role of OCT4 in cancer stem-like cells and chemotherapy resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1866:165432. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.03.005. PMID: 30904611. PMCID: PMC6754810.
Article20. Wu G, Wilson G, Zhou G, Hebbard L, George J, Qiao L. 2015; Oct4 is a reliable marker of liver tumor propagating cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Discov Med. 20:219–229. PMID: 26562475.21. Hatefi N, Nouraee N, Parvin M, Ziaee SA, Mowla SJ. 2012; Evaluating the expression of oct4 as a prognostic tumor marker in bladder cancer. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 15:1154–1161. PMID: 23653844. PMCID: PMC3646225.22. Chen Y, Li XG. 2006; Epigenetic modification in human leukemia. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 14:635–638. Chinese.23. Juárez-Moreno K, Erices R, Beltran AS, Stolzenburg S, Cuello-Fredes M, Owen GI, Qian H, Blancafort P. 2013; Breaking through an epigenetic wall: re-activation of Oct4 by KRAB-containing designer zinc finger transcription factors. Epi-genetics. 8:164–176. DOI: 10.4161/epi.23503. PMID: 23314702. PMCID: PMC3592902.24. Kristensen DM, Nielsen JE, Kalisz M, Dalgaard MD, Audouze K, Larsen ME, Jacobsen GK, Horn T, Brunak S, Skakkebaek NE, Leffers H. 2010; OCT4 and downstream factors are expressed in human somatic urogenital epithelia and in culture of epididymal spheres. Mol Hum Reprod. 16:835–845. DOI: 10.1093/molehr/gaq008. PMID: 20123703.
Article25. Zhang HJ, Siu MK, Wong ES, Wong KY, Li AS, Chan KY, Ngan HY, Cheung AN. 2008; Oct4 is epigenetically regulated by methylation in normal placenta and gestational trophoblastic disease. Placenta. 29:549–554. DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2008.03.003. PMID: 18440631.
Article26. Zhao HX, Li Y, Jin HF, Xie L, Liu C, Jiang F, Luo YN, Yin GW, Li Y, Wang J, Li LS, Yao YQ, Wang XH. 2010; Rapid and efficient reprogramming of human amnion-derived cells into pluripotency by three factors OCT4/SOX2/NAN OG. Differentiation. 80:123–129. DOI: 10.1016/j.diff.2010.03.002. PMID: 20510497.
Article27. Hattori N, Nishino K, Ko YG, Hattori N, Ohgane J, Tanaka S, Shiota K. 2004; Epigenetic control of mouse Oct-4 gene expression in embryonic stem cells and trophoblast stem cells. J Biol Chem. 279:17063–17069. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M309002200. PMID: 14761969.
Article28. Liu Q, Chen K, Liu Z, Huang Y, Zhao R, Wei L, Yu X, He J, Liu J, Qi J, Qin Y, Li B. 2017; BORIS up-regulates OCT4 via histone methylation to promote cancer stem cell-like properties in human liver cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 403:165–174. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.06.017. PMID: 28645561.
Article29. Dai X, Liu P, Lau AW, Liu Y, Inuzuka H. 2014; Acetylation-dependent regulation of essential iPS-inducing factors: a regulatory crossroad for pluripotency and tumorigenesis. Cancer Med. 3:1211–1224. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.298. PMID: 25116380. PMCID: PMC4302671.
Article30. Chai S, Xu X, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Zhang C, Yang Y, Yang Y, Xu H, Xu R, Wang K. 2015; Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIγ enhances stem-like traits and tumorigenicity of lung cancer cells. Oncotarget. 6:16069–16083. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3866. PMID: 25965829. PMCID: PMC4599257.
Article31. Tan Y, Xue Y, Song C, Grunstein M. 2013; Acetylated histone H3K56 interacts with Oct4 to promote mouse embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 110:11493–11498. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1309914110. PMID: 23798425. PMCID: PMC3710873.
Article32. Guo L, Zhou Y, Wang S, Wu Y. 2014; Epigenetic changes of mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional (3D) sphe-roids. J Cell Mol Med. 18:2009–2019. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12336. PMID: 25090911. PMCID: PMC4244016.
Article33. Abulaiti X, Zhang H, Wang A, Li N, Li Y, Wang C, Du X, Li L. 2017; Phosphorylation of threonine343 is crucial for OCT4 interaction with SOX2 in the maintenance of mouse embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Stem Cell Reports. 9:1630–1641. DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.09.001. PMID: 28988986. PMCID: PMC5829306.
Article34. Deng L, Meng T, Chen L, Wei W, Wang P. 2020; The role of ubiquitination in tumorigenesis and targeted drug disco-very. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:11. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-020-0107-0. PMID: 32296023. PMCID: PMC7048745.
Article35. Liao B, Zhong X, Xu H, Xiao F, Fang Z, Gu J, Chen Y, Zhao Y, Jin Y. 2013; Itch, an E3 ligase of Oct4, is required for embryonic stem cell self-renewal and pluripotency induction. J Cell Physiol. 228:1443–1451. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.24297. PMID: 23255053.
Article36. Cho Y, Kang HG, Kim SJ, Lee S, Jee S, Ahn SG, Kang MJ, Song JS, Chung JY, Yi EC, Chun KH. 2018; Post-translational modification of OCT4 in breast cancer tumorigene-sis. Cell Death Differ. 25:1781–1795. DOI: 10.1038/s41418-018-0079-6. PMID: 29511337. PMCID: PMC6180041.
Article37. Villodre ES, Kipper FC, Pereira MB, Lenz G. 2016; Roles of OCT4 in tumorigenesis, cancer therapy resistance and prognosis. Cancer Treat Rev. 51:1–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.10.003. PMID: 27788386.
Article38. Jang H, Kim TW, Yoon S, Choi SY, Kang TW, Kim SY, Kwon YW, Cho EJ, Youn HD. 2012; O-GlcNAc regulates pluripotency and reprogramming by directly acting on core components of the pluripotency network. Cell Stem Cell. 11:62–74. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.03.001. PMID: 22608532.
Article39. Lou W, Ding B, Fu P. 2020; Pseudogene-derived lncRNAs and their miRNA sponging mechanism in human cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:85. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00085. PMID: 32185172. PMCID: PMC7058547.
Article40. Chen Q, Zhu C, Jin Y, Si X, Jiao W, He W, Mao W, Li M, Luo G. 2020; Plasma long non-coding RNA RP11-438N5.3 as a novel biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 12:1513–1521. DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S237024. PMID: 32184656. PMCID: PMC7055527.41. Zhu Y, Luo C, Korakkandan AA, Fatma YHA, Tao Y, Yi T, Hu S, Liao Q. 2020; Function and regulation annotation of up-regulated long non-coding RNA LINC01234 in gastric cancer. J Clin Lab Anal. 34:e23210. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23210. PMID: 32011780. PMCID: PMC7246363.
Article42. Guo QS, Wang P, Huang Y, Guo YB, Zhu MY, Xiong YC. 2019; Regulatory effect of miR-30b on migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer stem cells. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 99:3019–3023. Chinese.43. Guo JC, Yang YJ, Zheng JF, Zhang JQ, Guo M, Yang X, Jiang XL, Xiang L, Li Y, Ping H, Zhuo L. 2019; Silencing of long noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS inhibits the Wnt signaling pathway via the upregulation of HOXA11 and thereby inhibits the proliferation, invasion, and self-renewal of hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells. Exp Mol Med. 51:1–20. DOI: 10.1038/s12276-019-0328-x. PMCID: PMC6874533. PMID: 31757938.
Article44. Zhao Y, Zhu Z, Shi S, Wang J, Li N. 2019; Long non-coding RNA MEG3 regulates migration and invasion of lung cancer stem cells via miR-650/SLC34A2 axis. Biomed Phar-macother. 120:109457. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109457. PMID: 31585300.
Article45. Zhao W, Li W, Jin X, Niu T, Cao Y, Zhou P, Zheng M. 2019; Silencing long non-coding RNA NEAT1 enhances the suppression of cell growth, invasion, and apoptosis of bladder cancer cells under cisplatin chemotherapy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 12:549–558. PMID: 31933859. PMCID: PMC6945077.46. Xu Z, Liu C, Zhao Q, Lü J, Ding X, Luo A, He J, Wang G, Li Y, Cai Z, Wang Z, Liu J, Liu S, Li W, Yu Z. 2020; Long non-coding RNA CCAT2 promotes oncogenesis in triple-negative breast cancer by regulating stemness of cancer cells. Pharmacol Res. 152:104628. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104628. PMID: 31904506.
Article47. Tang D, Yang Z, Long F, Luo L, Yang B, Zhu R, Sang X, Cao G, Wang K. 2019; Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 mediates stem cell-like properties in human colorectal cancer cells by regulating miR-20b-5p/Oct4 axis. J Cell Physiol. 234:20816–20828. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.28687. PMID: 31012108.
Article48. Fan H, Liu G, Zhao C, Li X, Yang X. 2017; Transcription factor Oct4 promotes osteosarcoma by regulating lncRNA AK055 347. Oncol Lett. 13:396–402. DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.5400. PMID: 28123573. PMCID: PMC5244871.
Article49. Han Q, Xu L, Lin W, Yao X, Jiang M, Zhou R, Sun X, Zhao L. 2019; Long noncoding RNA CRCMSL suppresses tumor invasive and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma through nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of HMGB2. Oncogene. 38:3019–3032. DOI: 10.1038/s41388-018-0614-4. PMID: 30575817.
Article50. Bauderlique-Le Roy H, Vennin C, Brocqueville G, Spruyt N, Adriaenssens E, Bourette RP. 2015; Enrichment of human stem-like prostate cells with s-SHIP promoter activity uncovers a role in stemness for the long noncoding RNA H19. Stem Cells Dev. 24:1252–1262. DOI: 10.1089/scd.2014.0386. PMID: 25567531. PMCID: PMC4425227.
Article51. Zimmerman DL, Boddy CS, Schoenherr CS. 2013; Oct4/Sox2 binding sites contribute to maintaining hypomethylation of the maternal igf2/h19 imprinting control region. PLoS One. 8:e81962. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081962. PMID: 24324735. PMCID: PMC3855764.
Article52. Chen S, Zhu J, Wang F, Guan Z, Ge Y, Yang X, Cai J. 2017; LncRNAs and their role in cancer stem cells. Oncotarget. 8:110685–110692. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.22161. PMID: 29299179. PMCID: PMC5746414.
Article53. Wang Y, Xu Z, Jiang J, Xu C, Kang J, Xiao L, Wu M, Xiong J, Guo X, Liu H. 2013; Endogenous miRNA sponge lincRNA-RoR regulates Oct4, Nanog, and Sox2 in human embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Dev Cell. 25:69–80. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.03.002. PMID: 23541921.
Article54. Sandmaier SE, Telugu BP. 2015; MicroRNA-mediated reprogra-mming of somatic cells into induced pluripotent stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 1330:29–36. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2848-4_3. PMID: 26621586.
Article55. Bräutigam C, Raggioli A, Winter J. 2013; The Wnt/β-catenin pathway regulates the expression of the miR-302 cluster in mouse ESCs and P19 cells. PLoS One. 8:e75315. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075315. PMID: 24040406. PMCID: PMC3769259.56. Hu S, Wilson KD, Ghosh Z, Han L, Wang Y, Lan F, Ransohoff KJ, Burridge P, Wu JC. 2013; MicroRNA-302 increases reprogramming efficiency via repression of NR2F2. Stem Cells. 31:259–268. DOI: 10.1002/stem.1278. PMID: 23136034. PMCID: PMC3572288.
Article57. Wu Y, Liu S, Xin H, Jiang J, Younglai E, Sun S, Wang H. 2011; Up-regulation of microRNA-145 promotes differentia-tion by repressing OCT4 in human endometrial adenocar-cinoma cells. Cancer. 117:3989–3998. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.25944. PMID: 21365617.
Article58. Yang YP, Chien Y, Chiou GY, Cherng JY, Wang ML, Lo WL, Chang YL, Huang PI, Chen YW, Shih YH, Chen MT, Chiou SH. 2012; Inhibition of cancer stem cell-like properties and reduced chemoradioresistance of glioblastoma using microRNA145 with cationic polyurethane-short branch PEI. Biomaterials. 33:1462–1476. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.10.071. PMID: 22098779.
Article59. Jerabek S, Merino F, Schöler HR, Cojocaru V. 2014; OCT4: dynamic DNA binding pioneers stem cell pluripotency. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1839:138–154. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.10.001. PMID: 24145198.
Article60. Gao Y, Zhang Z, Li K, Gong L, Yang Q, Huang X, Hong C, Ding M, Yang H. 2017; Linc-DYNC2H1-4 promotes EMT and CSC phenotypes by acting as a sponge of miR-145 in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 8:e2924. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2017.311. PMID: 28703793. PMCID: PMC5550858.
Article61. Bai M, Yuan M, Liao H, Chen J, Xie B, Yan D, Xi X, Xu X, Zhang Z, Feng Y. 2015; OCT4 pseudogene 5 upregulates OCT4 expression to promote proliferation by competing with miR-145 in endometrial carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 33:1745–1752. DOI: 10.3892/or.2015.3763. PMID: 25634023.
Article62. Wang L, Guo ZY, Zhang R, Xin B, Chen R, Zhao J, Wang T, Wen WH, Jia LT, Yao LB, Yang AG. 2013; Pseudogene OCT4-pg4 functions as a natural micro RNA sponge to regulate OCT4 expression by competing for miR-145 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 34:1773–1781. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgt139. PMID: 23615404.
Article63. Liu T, Chi H, Chen J, Chen C, Huang Y, Xi H, Xue J, Si Y. 2017; Curcumin suppresses proliferation and in vitro invasion of human prostate cancer stem cells by ceRNA effect of miR-145 and lncRNA-ROR. Gene. 631:29–38. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.08.008. PMID: 28843521.
Article64. Chai S, Ng KY, Tong M, Lau EY, Lee TK, Chan KW, Yuan YF, Cheung TT, Cheung ST, Wang XQ, Wong N, Lo CM, Man K, Guan XY, Ma S. 2016; Octamer 4/microRNA-1246 signaling axis drives Wnt/β-catenin activation in liver cancer stem cells. Hepatology. 64:2062–2076. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28821. PMID: 27639189.
Article65. Kim JY, Kim JC, Lee JY, Park MJ. 2018; Oct4 suppresses IR-induced premature senescence in breast cancer cells through STAT3- and NF-κB-mediated IL‑24 production. Int J Oncol. 53:47–58. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4391. PMID: 29749438. PMCID: PMC5958730.66. Lo WL, Chien Y, Chiou GY, Tseng LM, Hsu HS, Chang YL, Lu KH, Chien CS, Wang ML, Chen YW, Huang PI, Hu FW, Yu CC, Chu PY, Chiou SH. 2012; Nuclear localization signal-enhanced RNA interference of EZH2 and Oct4 in the eradication of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma-derived cancer stem cells. Biomaterials. 33:3693–3709. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.01.016. PMID: 22361100.
Article67. Huang JQ. 2011; Small interfering RNA-mediated OCT4 gene silencing inhibits the proliferation and induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cell line PANC1. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 31:860–863. Chinese.68. Huang ZJ, You J, Luo WY, Chen BS, Feng QZ, Wu BL, Jiang L, Luo Q. 2015; Reduced tumorigenicity and drug resistance through the downregulation of octamer-binding protein 4 and Nanog transcriptional factor expression in human breast stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:1647–1654. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2972. PMID: 25405855. PMCID: PMC4270319.
Article69. Mydlikova Z, Gursky J, Pirsel M. 2010; Transcription factor IIH-the protein complex with multiple functions. Neoplasma. 57:287–290. DOI: 10.4149/neo_2010_04_287. PMID: 20429618.70. Whitton B, Okamoto H, Packham G, Crabb SJ. 2018; Vacuolar ATPase as a potential therapeutic target and mediator of treatment resistance in cancer. Cancer Med. 7:3800–3811. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1594. PMID: 29926527. PMCID: PMC6089187.
Article71. Bourguignon LYW, Earle C, Shiina M. 2017; Activation of matrix hyaluronan-mediated CD44 signaling, epigenetic regulation and chemoresistance in head and neck cancer stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 18:1849. DOI: 10.3390/ijms18091849. PMID: 28837080. PMCID: PMC5618498.
Article72. Fu TY, Hsieh IC, Cheng JT, Tsai MH, Hou YY, Lee JH, Liou HH, Huang SF, Chen HC, Yen LM, Tseng HH, Ger LP. 2016; Association of OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG expression with oral squamous cell carcinoma progression. J Oral Pathol Med. 45:89–95. DOI: 10.1111/jop.12335. PMID: 26211876.
Article73. Pan X, Cang X, Dan S, Li J, Cheng J, Kang B, Duan X, Shen B, Wang YJ. 2016; Site-specific disruption of the Oct4/Sox2 protein interaction reveals coordinated mesendodermal differentiation and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem. 291:18353–18369. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.745414. PMID: 27369080. PMCID: PMC5000082.
Article74. Herreros-Villanueva M, Bujanda L, Billadeau DD, Zhang JS. 2014; Embryonic stem cell factors and pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 20:2247–2254. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i9.2247. PMID: 24605024. PMCID: PMC3942830.
Article75. Liang Y, Huimei Hong F, Ganesan P, Jiang S, Jauch R, Stanton LW, Kolatkar PR. 2012; Structural analysis and dimerization profile of the SCAN domain of the pluripotency factor Zfp206. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:8721–8732. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks611. PMID: 22735705. PMCID: PMC3458555.
Article76. Zhao B, Zheng X, Tan X, Ke K, Wang F, Wang Y, Xing X, Zhang C, Hu P, Lan S, Li Q, Huang A, Liu X. 2020; Ku80 negatively regulates the expression of OCT4 via competitive binding to SALL4 and promoting lysosomal degradation of OCT4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 118:105664. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.105664. PMID: 31816404.
Article77. Zhang X, Yuan X, Zhu W, Qian H, Xu W. 2015; SALL4: an emerging cancer biomarker and target. Cancer Lett. 357:55–62. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.11.037. PMID: 25444934.
Article78. Tanimura N, Saito M, Ebisuya M, Nishida E, Ishikawa F. 2013; Stemness-related factor Sall4 interacts with transcription factors Oct-3/4 and Sox2 and occupies Oct-Sox elements in mouse embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem. 288:5027–5038. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.411173. PMID: 23269686. PMCID: PMC3576104.
Article79. Maiuthed A, Bhummaphan N, Luanpitpong S, Mutirangura A, Aporntewan C, Meeprasert A, Rungrotmongkol T, Rojanasakul Y, Chanvorachote P. 2018; Nitric oxide promotes cancer cell dedifferentiation by disrupting an Oct4:caveolin-1 complex: a new regulatory mechanism for cancer stem cell formation. J Biol Chem. 293:13534–13552. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000287. PMID: 29986880. PMCID: PMC6120192.
Article80. Yoon HJ, Kim DH, Kim SJ, Jang JH, Surh YJ. 2019; Src-mediated phosphorylation, ubiquitination and degradation of Caveolin-1 promotes breast cancer cell stemness. Cancer Lett. 449:8–19. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.01.021. PMID: 30673589.
Article81. Yongsanguanchai N, Pongrakhananon V, Mutirangura A, Rojanasakul Y, Chanvorachote P. 2015; Nitric oxide induces cancer stem cell-like phenotypes in human lung cancer cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 308:C89–C100. DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00187.2014. PMID: 25411331.
Article82. Yang YC, Chien MH, Liu HY, Chang YC, Chen CK, Lee WJ, Kuo TC, Hsiao M, Hua KT, Cheng TY. 2018; Nuclear translocation of PKM2/AMPK complex sustains cancer stem cell populations under glucose restriction stress. Cancer Lett. 421:28–40. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.01.075. PMID: 29408265.
Article83. Giannoni E, Taddei ML, Morandi A, Comito G, Calvani M, Bianchini F, Richichi B, Raugei G, Wong N, Tang D, Chiarugi P. 2015; Targeting stromal-induced pyruvate kinase M2 nuclear translocation impairs oxphos and prostate cancer metastatic spread. Oncotarget. 6:24061–24074. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4448. PMID: 26183399. PMCID: PMC4695170.
Article84. Lei I, Tian S, Chen V, Zhao Y, Wang Z. 2020; SWI/SNF component BAF250a coordinates OCT4 and WNT signaling pathway to control cardiac lineage differentiation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 7:358. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00358. PMID: 32039194. PMCID: PMC6987383.
Article85. Zhu P, Wang Y, He L, Huang G, Du Y, Zhang G, Yan X, Xia P, Ye B, Wang S, Hao L, Wu J, Fan Z. 2015; ZIC2-dependent OCT4 activation drives self-renewal of human liver cancer stem cells. J Clin Invest. 125:3795–3808. DOI: 10.1172/JCI81979. PMID: 26426078. PMCID: PMC4607118.
Article86. Tsai PH, Chien Y, Wang ML, Hsu CH, Laurent B, Chou SJ, Chang WC, Chien CS, Li HY, Lee HC, Huo TI, Hung JH, Chen CH, Chiou SH. 2019; Ash2l interacts with Oct4-stemness circuitry to promote super-enhancer-driven pluripotency network. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:10115–10133. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz801. PMID: 31555818. PMCID: PMC6821267.
Article87. Chen D. 2015; Tumor formation and drug resistance properties of human glioblastoma side population cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:4309–4314. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3279. PMID: 25633829.
Article88. Blum W, Pecze L, Felley-Bosco E, Wu L, de Perrot M, Schwaller B. 2017; Stem cell factor-based identification and functional properties of in vitro-selected subpopulations of malignant mesothelioma cells. Stem Cell Reports. 8:1005–1017. DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.02.005. PMID: 28285878. PMCID: PMC5390099.
Article89. Lee S, Wottrich S, Bonavida B. 2017; Crosstalks between Raf-kinase inhibitor protein and cancer stem cell transcription factors (Oct4, KLF4, Sox2, Nanog). Tumour Biol. 39:1010428317692253. DOI: 10.1177/1010428317692253. PMID: 28378634.
Article90. Yang L, Shi P, Zhao G, Xu J, Peng W, Zhang J, Zhang G, Wang X, Dong Z, Chen F, Cui H. 2020; Targeting cancer stem cell pathways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:8. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-020-0110-5. PMID: 32296030. PMCID: PMC7005297.
Article91. Rios-Fuller TJ, Ortiz-Soto G, Lacourt-Ventura M, Maldonado-Martinez G, Cubano LA, Schneider RJ, Martinez-Montemayor MM. 2018; Ganoderma lucidum extract (GLE) impairs breast cancer stem cells by targeting the STAT3 pathway. Oncotarget. 9:35907–35921. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.26294. PMID: 30542507. PMCID: PMC6267592.
Article92. Wang H, Deng J, Ren HY, Jia P, Zhang W, Li MQ, Li SW, Zhou QH. 2017; STAT3 influences the characteristics of stem cells in cervical carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 14:2131–2136. DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.6454. PMID: 28781654. PMCID: PMC5530137.
Article93. Wang H, Cai HB, Chen LL, Zhao WJ, Li P, Wang ZQ, Li Z. 2015; STAT3 correlates with stem cell-related transcription factors in cervical cancer. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 35:891–897. DOI: 10.1007/s11596-015-1524-0. PMID: 26670442.
Article94. Yang CM, Chiba T, Groner B. 2012; Expression of reprogramming factors in breast cancer cell lines and the regulation by activated Stat3. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 10:241–248. DOI: 10.1515/hmbci-2012-0003. PMID: 25436680.
Article95. Yin X, Zhang BH, Zheng SS, Gao DM, Qiu SJ, Wu WZ, Ren ZG. 2015; Coexpression of gene Oct4 and Nanog initiates stem cell characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of Stat3/Snail signaling. J Hematol Oncol. 8:23. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-015-0119-3. PMID: 25879771. PMCID: PMC4377043.
Article96. Kim SY, Kang JW, Song X, Kim BK, Yoo YD, Kwon YT, Lee YJ. 2013; Role of the IL-6-JAK1-STAT3-Oct-4 pathway in the conversion of non-stem cancer cells into cancer stem-like cells. Cell Signal. 25:961–969. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.01.007. PMID: 23333246. PMCID: PMC3595341.
Article97. Do DV, Ueda J, Messerschmidt DM, Lorthongpanich C, Zhou Y, Feng B, Guo G, Lin PJ, Hossain MZ, Zhang W, Moh A, Wu Q, Robson P, Ng HH, Poellinger L, Knowles BB, Solter D, Fu XY. 2013; A genetic and developmental pathway from STAT3 to the OCT4-NANOG circuit is essential for maintenance of ICM lineages in vivo. Genes Dev. 27:1378–1390. DOI: 10.1101/gad.221176.113. PMID: 23788624. PMCID: PMC3701193.
Article98. Zhao H, Guo Y, Li S, Han R, Ying J, Zhu H, Wang Y, Yin L, Han Y, Sun L, Wang Z, Lin Q, Bi X, Jiao Y, Jia H, Zhao J, Huang Z, Li Z, Zhou J, Song W, Meng K, Cai J. 2015; A novel anti-cancer agent Icaritin suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma initiation and malignant growth through the IL-6/Jak2/Stat3 pathway. Oncotarget. 6:31927–31943. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5578. PMID: 26376676. PMCID: PMC4741651.
Article99. Yu X, Zhang F, Mao J, Lu Y, Li J, Ma W, Fan S, Zhang C, Li Q, Wang B, Song B, Li L. 2017; Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor-type δ acts as a negative regulator suppressing breast cancer. Oncotarget. 8:98798–98811. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.22000. PMID: 29228728. PMCID: PMC5716768.100. Chen Y, Shao Z, Jiang E, Zhou X, Wang L, Wang H, Luo X, Chen Q, Liu K, Shang Z. 2020; CCL21/CCR7 interaction promotes EMT and enhances the stemness of OSCC via a JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 235:5995–6009. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29525. PMID: 32017846.
Article101. Liu HW, Lee PM, Bamodu OA, Su YK, Fong IH, Yeh CT, Chien MH, Kan IH, Lin CM. 2019; Enhanced hsa-miR-181d/p-STAT3 and hsa-miR-181d/p-STAT5A ratios mediate the anticancer effect of garcinol in STAT3/5A-addicted glio-blastoma. Cancers (Basel). 11:1888. DOI: 10.3390/cancers11121888. PMID: 31783691. PMCID: PMC6966688.
Article102. Wang L, Jiang Z, Huang D, Duan J, Huang C, Sullivan S, Vali K, Yin Y, Zhang M, Wegrzyn J, Tian XC, Tang Y. 2018; JAK/STAT3 regulated global gene expression dynamics during late-stage reprogramming process. BMC Genomics. 19:183. DOI: 10.1186/s12864-018-4507-2. PMID: 29510661. PMCID: PMC5840728.
Article103. Tang Y, Luo Y, Jiang Z, Ma Y, Lin CJ, Kim C, Carter MG, Amano T, Park J, Kish S, Tian XC. 2012; Jak/Stat3 signaling promotes somatic cell reprogramming by epigenetic regulation. Stem Cells. 30:2645–2656. DOI: 10.1002/stem.1225. PMID: 22968989.
Article104. Lin CS, Bamodu OA, Kuo KT, Huang CM, Liu SC, Wang CH, Tzeng YM, Chao TY, Yeh CT. 2018; Investigation of ovatodiolide, a macrocyclic diterpenoid, as a potential inhibitor of oral cancer stem-like cells properties via the inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3/JARID1B signal circuit. Phytomedicine. 46:93–103. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.04.016. PMID: 30097127.
Article105. Su C. 2016; Survivin in survival of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 379:184–190. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.06.016. PMID: 26118774.
Article106. Wang G, Zhou H, Gu Z, Gao Q, Shen G. 2018; Oct4 promotes cancer cell proliferation and migration and leads to poor prognosis associated with the survivin/STAT3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 40:979–987. DOI: 10.3892/or.2018.6491. PMID: 29901157.
Article107. Martinez E, Vazquez N, Lopez A, Fanniel V, Sanchez L, Marks R, Hinojosa L, Cuello V, Cuevas M, Rodriguez A, Tomson C, Salinas A, Abad M, Holguin M, Garza N, Arenas A, Abraham K, Maldonado L, Rojas V, Basdeo A, Schuenzel E, Persans M, Innis-Whitehouse W, Keniry M. 2020; The PI3K pathway impacts stem gene expression in a set of glioblastoma cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 146:593–604. DOI: 10.1007/s00432-020-03133-w. PMID: 32030510.
Article108. Weidinger C, Krause K, Mueller K, Klagge A, Fuhrer D. 2011; FOXO3 is inhibited by oncogenic PI3K/Akt signaling but can be reactivated by the NSAID sulindac sulfide. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:E1361–E1371. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2010-2453. PMID: 21752881.
Article109. Gomes AR, Zhao F, Lam EW. 2013; Role and regulation of the forkhead transcription factors FOXO3a and FOXM1 in carcinogenesis and drug resistance. Chin J Cancer. 32:365–370. DOI: 10.5732/cjc.012.10277. PMID: 23706767. PMCID: PMC3845605.
Article110. Bhummaphan N, Chanvorachote P. 2015; Gigantol suppresses cancer stem cell-like phenotypes in lung cancer cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:836564. DOI: 10.1155/2015/836564. PMID: 26339272. PMCID: PMC4539074.
Article111. Chen B, Xue Z, Yang G, Shi B, Yang B, Yan Y, Wang X, Han D, Huang Y, Dong W. 2013; Akt-signal integration is involved in the differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 8:e64877. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064877. PMID: 23762260. PMCID: PMC3675137.
Article112. Li X, Meng Y, Xie C, Zhu J, Wang X, Li Y, Geng S, Wu J, Zhong C, Li M. 2018; Diallyl Trisulfide inhibits breast cancer stem cells via suppression of Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Cell Biochem. 119:4134–4141. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.26613. PMID: 29243835.
Article113. Chen SM, Lee MS, Chang CY, Lin SZ, Cheng EH, Liu YH, Pan HC, Lee HC, Su HL. 2015; Prerequisite OCT4 maintenance potentiates the neural induction of differentiating human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Transplant. 24:829–844. DOI: 10.3727/096368913X675179. PMID: 24256943.
Article114. Guo Y, Li B, Yan X, Shen X, Ma J, Liu S, Zhang D. 2020; Bisphenol A and polychlorinated biphenyls enhance the cancer stem cell properties of human ovarian cancer cells by activating the WNT signaling pathway. Chemosphere. 246:125775. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125775. PMID: 31918092.
Article115. Simandi Z, Horvath A, Wright LC, Cuaranta-Monroy I, De Luca I, Karolyi K, Sauer S, Deleuze JF, Gudas LJ, Cowley SM, Nagy L. 2016; OCT4 acts as an integrator of pluripotency and signal-induced differentiation. Mol Cell. 63:647–661. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.06.039. PMID: 27499297.
Article116. Davidson KC, Adams AM, Goodson JM, McDonald CE, Potter JC, Berndt JD, Biechele TL, Taylor RJ, Moon RT. 2012; Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes differentiation, not self-renewal, of human embryonic stem cells and is repressed by Oct4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 109:4485–4490. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1118777109. PMID: 22392999. PMCID: PMC3311359.
Article117. Wang Y, Zhong Y, Hou T, Liao J, Zhang C, Sun C, Wang G. 2019; PM2.5 induces EMT and promotes CSC properties by activating Notch pathway in vivo and vitro. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 178:159–167. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.086. PMID: 31002970.
Article118. Zhou ZC, Dong QG, Fu DL, Gong YY, Ni QX. 2013; Characteristics of Notch2+ pancreatic cancer stem-like cells and the relationship with centroacinar cells. Cell Biol Int. 37:805–811. DOI: 10.1002/cbin.10102. PMID: 23536545.
Article119. Jung N, Kwon HJ, Jung HJ. 2018; Downregulation of mitochondrial UQCRB inhibits cancer stem cell-like properties in glioblastoma. Int J Oncol. 52:241–251. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4191. PMCID: PMC5505016. PMID: 29115404.
Article120. Au HK, Chang JH, Wu YC, Kuo YC, Chen YH, Lee WC, Chang TS, Lan PC, Kuo HC, Lee KL, Lee MT, Tzeng CR, Huang YH. 2015; TGF-βI regulates cell migration through pluripotent transcription factor OCT4 in endometriosis. PLoS One. 10:e0145256. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145256. PMID: 26675296. PMCID: PMC4682958.121. Yuan F, Zhou W, Zou C, Zhang Z, Hu H, Dai Z, Zhang Y. 2010; Expression of Oct4 in HCC and modulation to wnt/β-catenin and TGF-β signal pathways. Mol Cell Biochem. 343:155–162. DOI: 10.1007/s11010-010-0509-3. PMID: 20549546.
Article122. Liang K, Zhou G, Zhang Q, Li J, Zhang C. 2014; Expression of hippo pathway in colorectal cancer. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 20:188–194. DOI: 10.4103/1319-3767.133025. PMID: 24976283. PMCID: PMC4067916.
Article123. Haghighi F, Dahlmann J, Nakhaei-Rad S, Lang A, Kutschka I, Zenker M, Kensah G, Piekorz RP, Ahmadian MR. 2018; bFGF-mediated pluripotency maintenance in human induced pluripotent stem cells is associated with NRAS-MAPK signaling. Cell Commun Signal. 16:96. DOI: 10.1186/s12964-018-0307-1. PMID: 30518391. PMCID: PMC6282345.
Article124. Jung JS, Jee MK, Cho HT, Choi JI, Im YB, Kwon OH, Kang SK. 2013; MBD6 is a direct target of Oct4 and controls the stemness and differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:711–728. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-012-1157-4. PMID: 23052207.
Article125. Jang JH, Jung JS, Im YB, Kang KS, Choi JI, Kang SK. 2012; Crucial role of nuclear Ago2 for hUCB-MSCs differentiation and self-renewal via stemness control. Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:95–111. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2011.3975. PMID: 21902595.
Article126. Bie Q, Zhang B, Sun C, Ji X, Barnie PA, Qi C, Peng J, Zhang D, Zheng D, Su Z, Wang S, Xu H. 2017; IL-17B activated mesenchymal stem cells enhance proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:18914–18923. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14835. PMID: 28145881. PMCID: PMC5386657.
Article127. Wang D, Xiang T, Zhao Z, Lin K, Yin P, Jiang L, Liang Z, Zhu B. 2016; Autocrine interleukin-23 promotes self-renewal of CD133+ ovarian cancer stem-like cells. Oncotarget. 7:76006–76020. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12579. PMID: 27738346. PMCID: PMC5342794.
Article128. Kim KW, Kim JY, Qiao J, Clark RA, Powers CM, Correa H, Chung DH. 2019; Dual-Targeting AKT2 and ERK in cancer stem-like cells in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget. 10:5645–5659. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.27210. PMID: 31608140. PMCID: PMC6771463.
Article129. Tang J, Li L, Huang W, Sui C, Yang Y, Lin X, Hou G, Chen X, Fu J, Yuan S, Li S, Wen W, Tang S, Cao D, Wu M, Chen L, Wang H. 2015; MiR-429 increases the metastatic capability of HCC via regulating classic Wnt pathway rather than epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 364:33–43. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.04.023. PMID: 25931210.
Article130. Li L, Tang J, Zhang B, Yang W, LiuGao M, Wang R, Tan Y, Fan J, Chang Y, Fu J, Jiang F, Chen C, Yang Y, Gu J, Wu D, Guo L, Cao D, Li H, Cao G, Wu M, Zhang MQ, Chen L, Wang H. 2015; Epigenetic modification of MiR-429 promotes liver tumour-initiating cell properties by targeting Rb binding protein 4. Gut. 64:156–167. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305715. PMID: 24572141.
Article131. Shigeishi H, Biddle A, Gammon L, Emich H, Rodini CO, Gemenetzidis E, Fazil B, Sugiyama M, Kamata N, Mackenzie IC. 2013; Maintenance of stem cell self-renewal in head and neck cancers requires actions of GSK3β influenced by CD44 and RHAMM. Stem Cells. 31:2073–2083. DOI: 10.1002/stem.1418. PMID: 23649588.
Article132. Hu J, Qin K, Zhang Y, Gong J, Li N, Lv D, Xiang R, Tan X. 2011; Downregulation of transcription factor Oct4 induces an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via enhancement of Ca2+ influx in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 411:786–791. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.07.025. PMID: 21798248.
Article133. Xun J, Wang D, Shen L, Gong J, Gao R, Du L, Chang A, Song X, Xiang R, Tan X. 2017; JMJD3 suppresses stem cell-like characteristics in breast cancer cells by downregulation of Oct4 independently of its demethylase activity. Oncotarget. 8:21918–21929. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15747. PMID: 28423536. PMCID: PMC5400634.
Article134. Chen T, Liu K, Xu J, Zhan T, Liu M, Li L, Yang Z, Yuan S, Zou W, Lin G, Carson DA, Wu CCN, Wang X. 2020; Synthetic and immunological studies on the OCT4 immunodominant motif antigen-based anti-cancer vaccine. Cancer Biol Med. 17:132–141. DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2019.0224. PMID: 32296581. PMCID: PMC7142840.
Article135. Yan Y, Liu F, Han L, Zhao L, Chen J, Olopade OI, He M, Wei M. 2018; HIF-2α promotes conversion to a stem cell phenotype and induces chemoresistance in breast cancer cells by activating Wnt and Notch pathways. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:256. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-018-0925-x. PMID: 30340507. PMCID: PMC6194720.136. Asadi MH, Khalifeh K, Mowla SJ. 2016; OCT4 spliced variants are highly expressed in brain cancer tissues and inhibition of OCT4B1 causes G2/M arrest in brain cancer cells. J Neurooncol. 130:455–463. DOI: 10.1007/s11060-016-2255-1. PMID: 27585657.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- OCT4 Expression Enhances Features of Cancer Stem Cells in a Mouse Model of Breast Cancer
- Expression of CD133, CD44, CK7, and OCT4 in Animal Cancers
- The Role of Nkx3.1 in Cancers and Stemness
- The Molecular Nature of Very Small Embryonic-Like Stem Cells in Adult Tissues
- Clinical Implication of Oct4 Expression in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Lung