Nutr Res Pract.
2020 Dec;14(6):580-592. 10.4162/nrp.2020.14.6.580.
Hypotriglyceridemic effects of brown seaweed consumption via regulation of bile acid excretion and hepatic lipogenesis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Jeju National University, Jeju 63243, Korea
- 2Yerae Elementary School, Jeju 63537, Korea
- 3College of Veterinary Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju 63243, Korea
- 4Department of Animal Nutrition, Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Animal Biotechnology and Disease Control and Prevention, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian 271018, China
- KMID: 2508792
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2020.14.6.580
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
The present study aimed to further investigate the potential health beneficial effects of long-term seaweed supplementation on lipid metabolism and hepatic functions in DIO mice.
MATERIALS/METHODS
Four brown seaweeds (Undaria pinnatifida [UP], Laminaria japonica [LJ], Sargassum fulvellum [SF], or Hizikia fusiforme [HF]) were added to a high fat diet (HFD) at a 5% ratio and supplemented to C57BL/6N mice for 16 weeks. Triglycerides (TGs) and total cholesterol (TC) in the liver, feces, and plasma were measured. Fecal bile acid (BA) levels in feces were monitored. Hepatic insulin signaling- and lipogenesis-related proteins were evaluated by Western blot analysis.
RESULTS
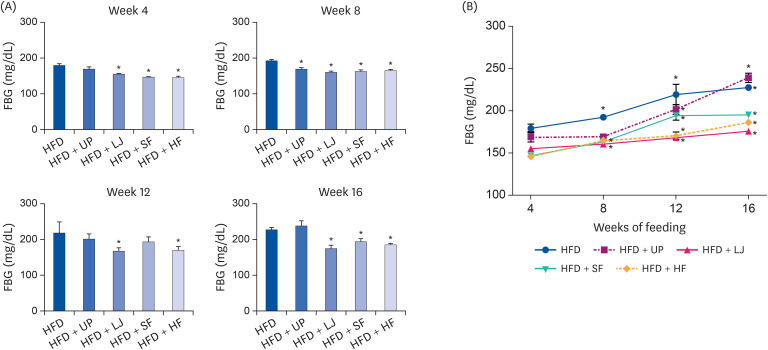
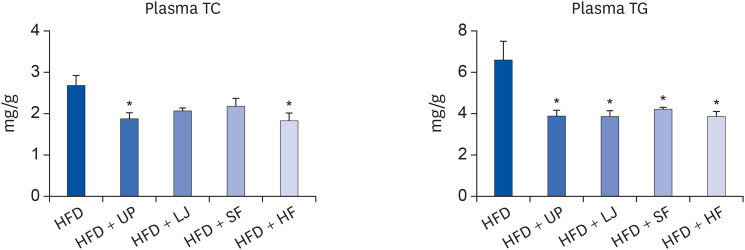
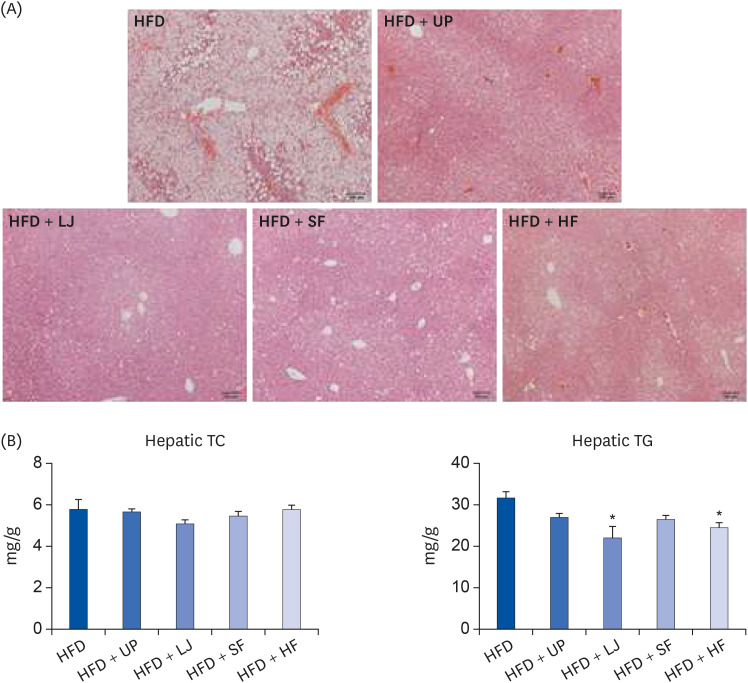
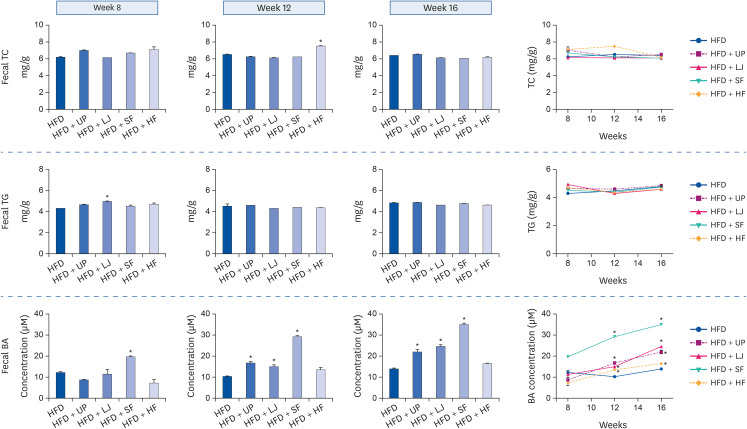
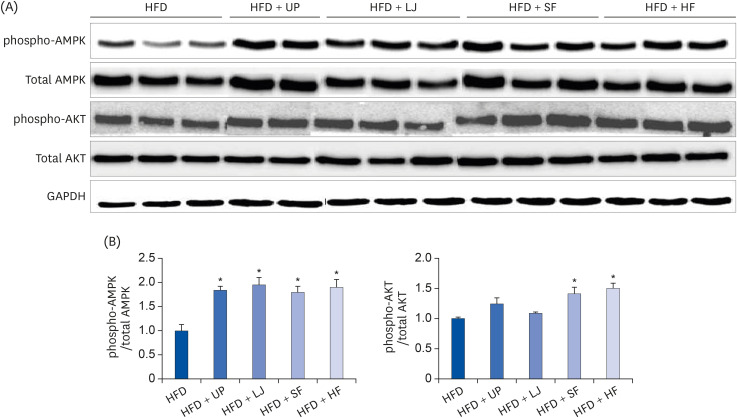
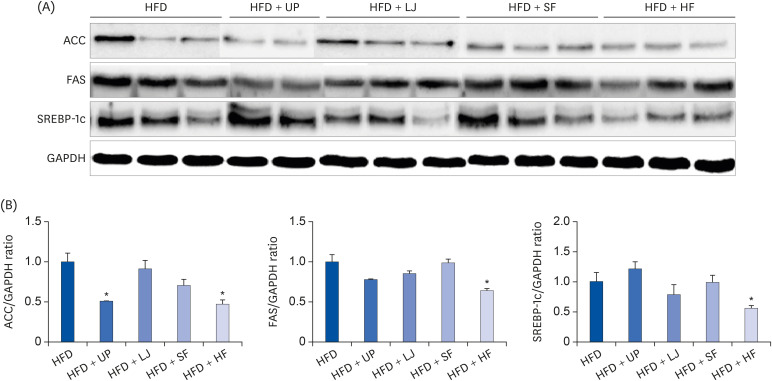
Fasting blood glucose levels were significantly reduced in the LJ, SF, and HF groups compared to the HFD group by the end of 16-week feeding period. Plasma TG levels and hepatic lipid accumulation were significantly reduced in all 4 seaweed supplemented groups, whereas plasma TC levels were only suppressed in the UP and HF groups compared to the HFD group. Fecal BA levels were significantly elevated by UP, LJ, and SF supplementation compared to HFD feeding only. Lastly, regarding hepatic insulin signaling-related proteins, phosphorylation of 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase was significantly up-regulated by all 4 types of seaweed, whereas phosphorylation of protein kinase B was up-regulated only in the SF and HF groups. Lipogenesis-related proteins in the liver were effectively down-regulated by HF supplementation in DIO mice.
CONCLUSIONS
Brown seaweed consumption showed hypotriglyceridemic effects in the prolonged DIO mouse model. Specifically, combinatory regulation of BA excretion and lipogenesis-related proteins in the liver by seaweed supplementation contributed to the reduction of plasma and hepatic TG levels, which inhibited hyperglycemia in DIO mice. Thus, the discrepant and species-specific functions of brown seaweeds provide novel insights for the selection of future targets for therapeutic agents.
Keyword
- Seaweed; liver; lipogenesis; bile; mice
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee HS, Choi MS, Lee YK, Park SH, Kim YJ. A study on the development of high-fiber supplements for the diabetic patients - Effect of seaweed supplementation on the lipid and glucose metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats -. Korean J Nutr. 1996; 29:296–306.2. Cho YJ, Bang MA. Effects of dietary seaweed on blood glucose, lipid and glutathione enzymes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2004; 33:987–994.3. Jang MA, Lee KS, Seo JS, Choi YS. Effects of dietary supplementation of sea tangle extracts on the excretion of neutral steroids and bile acid in diabetic rats. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2002; 31:819–825.4. Khan MN, Choi JS, Lee MC, Kim E, Nam TJ, Fujii H, Hong YK. Anti-inflammatory activities of methanol extracts from various seaweed species. J Environ Biol. 2008; 29:465–469. PMID: 19195382.5. Cumashi A, Ushakova NA, Preobrazhenskaya ME, D'Incecco A, Piccoli A, Totani L, Tinari N, Morozevich GE, Berman AE, Bilan MI, Usov AI, Ustyuzhanina NE, Grachev AA, Sanderson CJ, Kelly M, Rabinovich GA, Iacobelli S, Nifantiev NE. Consorzio Interuniversitario Nazionale per la Bio-Oncologia, Italy. A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology. 2007; 17:541–552. PMID: 17296677.
Article6. Park MJ, Ryu HK, Han JS. Effects of Laminaria japonica extract supplement on blood glucose, serum lipids and antioxidant systems in type II diabetic patients. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2007; 36:1391–1398.7. Park SH, Lee YK, Lee HS. The effect of dietary fiber feeding on gastrointestinal functions and lipid and glucose metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Korean J Nutr. 1994; 27:311–322.8. Jiménez-Escrig A, Sánchez-Muniz F. Dietary fibre from edible seaweeds: chemical structure, physicochemical properties and effects on cholesterol metabolism. Nutr Res. 2000; 20:585–598.
Article9. Choi JS, Bae HJ, Kim YC, Park NH, Kim TB, Choi YJ, Choi EY, Park SM, Choi IS. Nutritional composition and biological activities of the methanol extracts of sea mustard (Undaria pinnatifida) in market. J Life Sci. 2008; 18:387–394.10. Narayan B, Miyashita K, Hosakawa M. Comparative evaluation of fatty acid composition of different Sargassum (Fucales, Phaeophyta) species harvested from temperate and tropical waters. J Aquat Food Prod Technol. 2005; 13:53–70.11. Oh JH, Kim J, Lee Y. Anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic effects of brown seaweeds in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Nutr Res Pract. 2016; 10:42–48. PMID: 26865915.
Article12. Kang SY, Kim E, Kang I, Lee M, Lee Y. Anti-diabetic effects and anti-inflammatory effects of Laminaria japonica and Hizikia fusiforme in skeletal muscle: in vitro and in vivo model. Nutrients. 2018; 10:491.13. Jang WS, Choung SY. Antiobesity effects of the ethanol extract of Laminaria japonica Areshoung in high-fat-diet-induced obese rat. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013; 2013:492807. PMID: 23365609.14. Grasa-López A, Miliar-García Á, Quevedo-Corona L, Paniagua-Castro N, Escalona-Cardoso G, Reyes-Maldonado E, Jaramillo-Flores ME. Undaria pinnatifida and fucoxanthin ameliorate lipogenesis and markers of both inflammation and cardiovascular dysfunction in an animal model of diet-induced obesity. Mar Drugs. 2016; 14:148.15. Kumar SA, Brown L. Seaweeds as potential therapeutic interventions for the metabolic syndrome. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2013; 14:299–308. PMID: 23959342.
Article16. Brunt EM. Pathology of fatty liver disease. Mod Pathol. 2007; 20(Suppl 1):S40–S48. PMID: 17486051.
Article17. Samuel VT, Shulman GI. The pathogenesis of insulin resistance: integrating signaling pathways and substrate flux. J Clin Invest. 2016; 126:12–22. PMID: 26727229.
Article18. Gupta S, Abu-Ghannam N. Bioactive potential and possible health effects of edible brown seaweeds. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2011; 22:315–326.
Article19. MacArtain P, Gill CI, Brooks M, Campbell R, Rowland IR. Nutritional value of edible seaweeds. Nutr Rev. 2007; 65:535–543. PMID: 18236692.
Article20. Maeda H, Hosokawa M, Sashima T, Miyashita K. Dietary combination of fucoxanthin and fish oil attenuates the weight gain of white adipose tissue and decreases blood glucose in obese/diabetic KK-Ay mice. J Agric Food Chem. 2007; 55:7701–7706. PMID: 17715888.21. Jia RB, Wu J, Li ZR, Ou ZR, Zhu Q, Sun B, Lin L, Zhao M. Comparison of physicochemical properties and antidiabetic effects of polysaccharides extracted from three seaweed species. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020; 149:81–92. PMID: 31945436.
Article22. Bocanegra A, Benedí J, Sánchez-Muniz FJ. Differential effects of konbu and nori seaweed dietary supplementation on liver glutathione status in normo- and hypercholesterolaemic growing rats. Br J Nutr. 2006; 95:696–702. PMID: 16571148.
Article23. Zha XQ, Xiao JJ, Zhang HN, Wang JH, Pan LH, Yang XF, Luo JP. Polysaccharides in Laminaria japonica (LP): extraction, physicochemical properties and their hypolipidemic activities in diet-induced mouse model of atherosclerosis. Food Chem. 2012; 134:244–252.24. Yang Z, Liu G, Wang Y, Yin J, Wang J, Xia B, Li T, Yang X, Hou P, Hu S, Song W, Guo S. Fucoidan A2 from the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum lowers lipid by improving reverse cholesterol transport in C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat diet. J Agric Food Chem. 2019; 67:5782–5791. PMID: 31055921.25. Horton JD, Goldstein JL, Brown MS. SREBPs: activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest. 2002; 109:1125–1131. PMID: 11994399.
Article26. Jakulj L, van Dijk TH, de Boer JF, Kootte RS, Schonewille M, Paalvast Y, Boer T, Bloks VW, Boverhof R, Nieuwdorp M, Beuers UH, Stroes ES, Groen AK. Transintestinal cholesterol transport is active in mice and humans and controls ezetimibe-induced fecal neutral sterol excretion. Cell Metab. 2016; 24:783–794. PMID: 27818259.
Article27. van der Velde AE, Brufau G, Groen AK. Transintestinal cholesterol efflux. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2010; 21:167–171. PMID: 20410820.
Article28. Kern F Jr, Birkner HJ, Ostrower VS. Binding of bile acids by dietary fiber. Am J Clin Nutr. 1978; 31:S175–9. PMID: 30273.
Article29. Story JA, Kritchevsky D. Comparison of the binding of various bile acids and bile salts in vitro by several types of fiber. J Nutr. 1976; 106:1292–1294. PMID: 956912.30. Wang W, Onnagawa M, Yoshie Y, Suzuki T. Binding of bile salts to soluble and insoluble dietary fibers of seaweeds. Fish Sci. 2001; 67:1169–1173.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic effects of brown seaweeds in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
- Leucrose, a Sucrose Isomer, Suppresses Hepatic Fat Accumulation by Regulating Hepatic Lipogenesis and Fat Oxidation in High-fat Diet-induced Obese Mice
- Effects of Genistein Supplementation on Fatty Liver and Lipid Metabolism in Rats Fed High Fat Diet
- Effects of Calcium and Genistein on Body Fat and Lipid Metabolism in High Fat-induced Obese Mice
- Dietary carnosic acid suppresses hepatic steatosis formation via regulation of hepatic fatty acid metabolism in high-fat diet-fed mice