Intest Res.
2020 Oct;18(4):469-475. 10.5217/ir.2019.09141.
Long-term outcome after surgery in a patient with intestinal Behçet’s disease complicated by myelodysplastic syndrome and trisomy 8
- Affiliations
-
- 1First Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Yamanashi, Yamanashi, Japan
- 2First Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, University of Yamanashi, Yamanashi, Japan
- KMID: 2508580
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2019.09141
Abstract
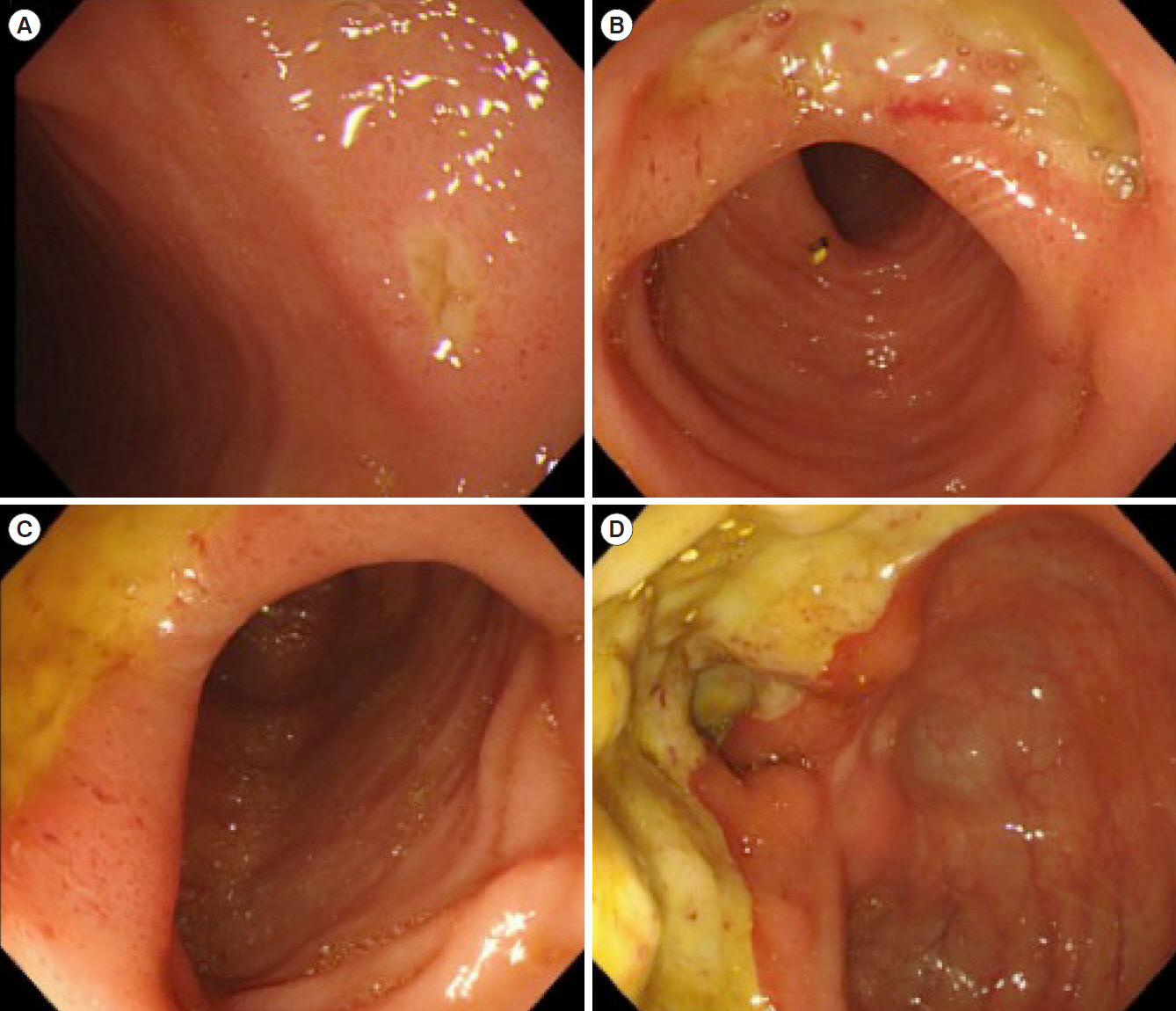
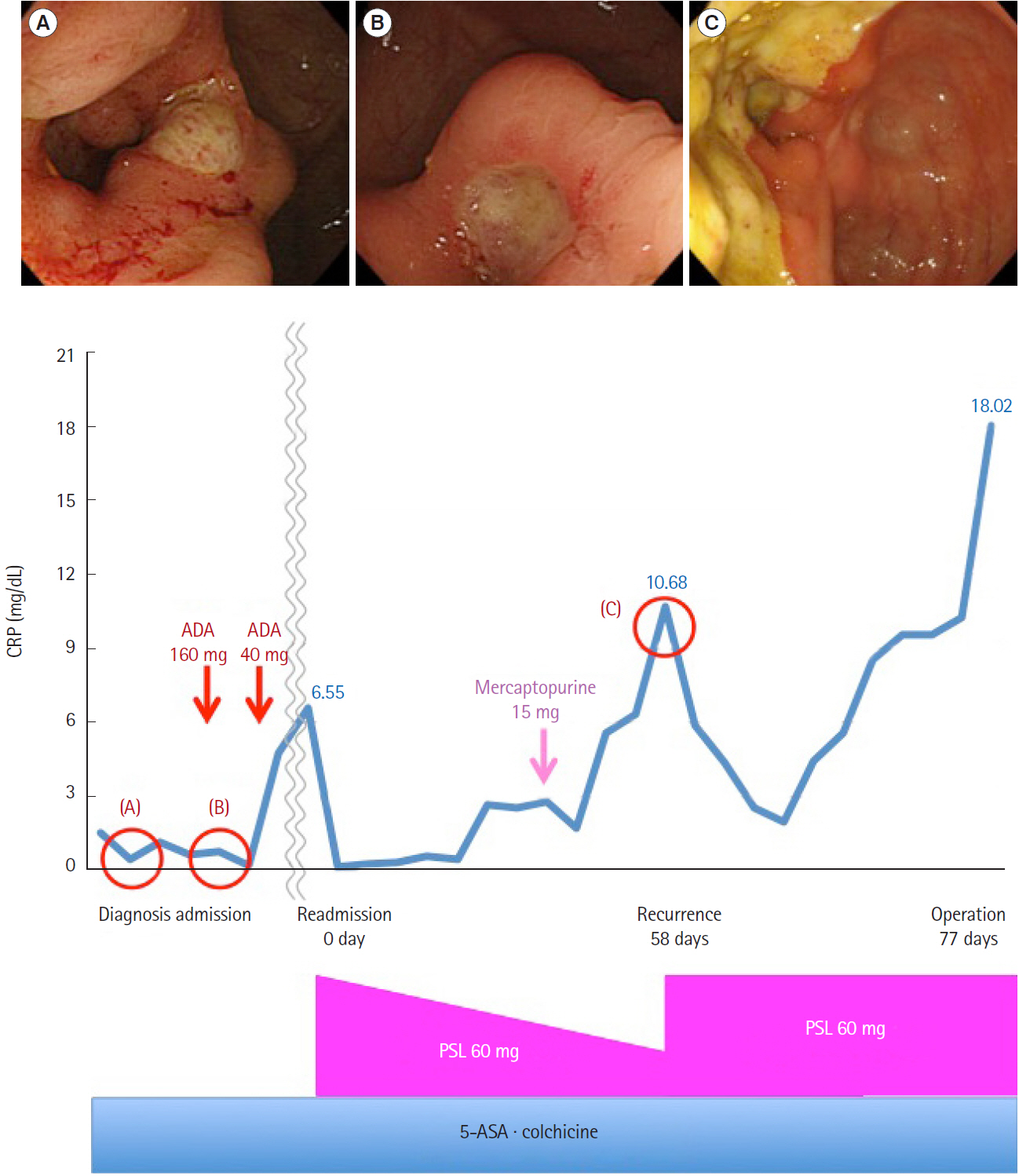
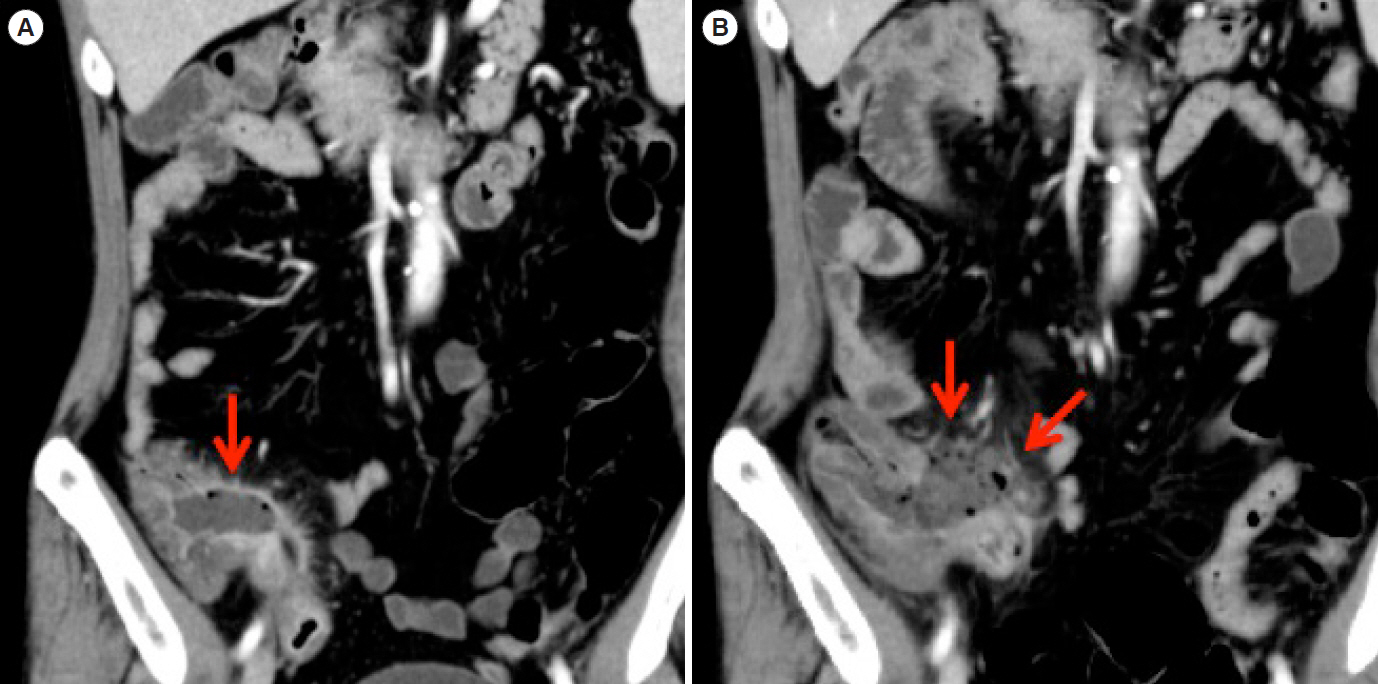
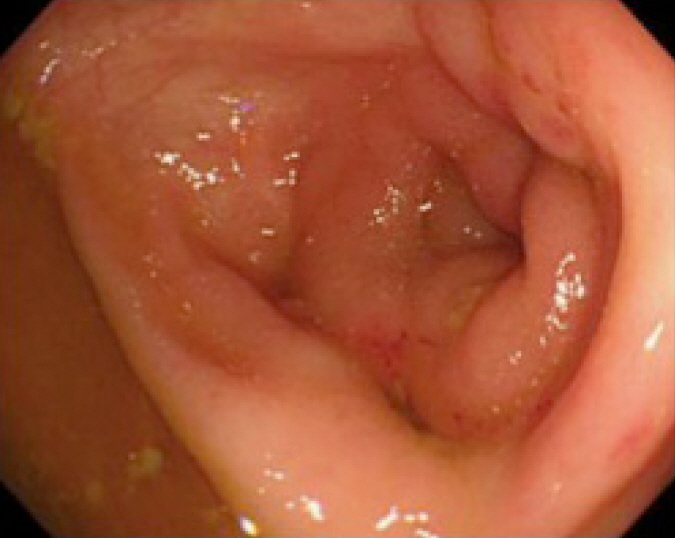
- Behçet’s disease (BD) is a multisystem inflammatory disease of unknown origin. Rarely, BD occurs together with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Interestingly, it is speculated that these are not simple coexistence but that the etiology of intestinal BD is at least partly derived from MDS itself. Furthermore, there is a relationship between MDS in patients with intestinal BD and trisomy 8. Immunosuppressive agents alone are insufficient to control MDS-associated BD, and many of these patients die of infection or hemorrhage. Surgery is considered for intestinal BD patients who are unresponsive to medical treatment or those with bowel complications such as perforation or persistent bleeding. We report a case of intestinal BD associated with MDS and trisomy 8. The patient was unresponsive to oral steroids and immunosuppressive treatment; the patient improved by surgical repair of a bowel perforation. Five years after the surgery, the patient is free of recurrence and not on medication. Our experience suggests that surgery may provide an effective therapeutic option for the treatment of MDS-related BD.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G. Behçet’s disease. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:1284–1291.
Article2. Brunning RD, Germing U, Le Beau MM, et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes/neoplasms, overview. In : Swerd Low SH, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon: IARC Press;2008. p. 88–93.3. Castro M, Conn DL, Su WP, Garton JP. Rheumatic manifestations in myelodysplastic syndromes. J Rheumatol. 1991; 18:721–727.4. Ohno E, Ohtsuka E, Watanabe K, et al. Behçet’s disease associated with myelodysplastic syndromes: a case report and a review of the literature. Cancer. 1997; 79:262–268.
Article5. Tada Y, Koarada S, Haruta Y, Mitamura M, Ohta A, Nagasawa K. The association of Behçet’s disease with myelodysplastic syndrome in Japan: a review of the literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006; 24(5 Suppl 42):S115–S119.6. Handa T, Arai Y, Mitani K. Myelodysplastic syndrome associated with intestinal tract-type Behçet disease characterized by an esophageal ulcer. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2004; 45:1135–1137.7. Ahn JK, Cha HS, Koh EM, et al. Behcet’s disease associated with bone marrow failure in Korean patients: clinical characteristics and the association of intestinal ulceration and trisomy 8. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008; 47:1228–1230.
Article8. Handa T, Nakatsue T, Baba M, Takada T, Nakata K, Ishii H. Clinical features of three cases with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis secondary to myelodysplastic syndrome developed during the course of Behçet’s disease. Respir Investig. 2014; 52:75–79.
Article9. Hulscher JB, van den Berg HP, Siegert CE, Steller EP. A Turkish man with Behçet disease and recurrent acute abdomen. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2003; 147:1969–1971.10. Kurata M, Nozue M, Seino K, Murata H, Sumita T, Katashi F. Indications for surgery in intestinal Behçet’s disease. Hepatogastroenterology. 2006; 53:60–63.11. Jung YS, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH, Cheon JH. Early versus late surgery in patients with intestinal Behçet disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 2012; 55:65–71.
Article12. Byeon JS, Choi EK, Heo NY, et al. Antitumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy for early postoperative recurrence of gastrointestinal Behçet’s disease: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 2007; 50:672–676.
Article13. Jung YS, Yoon JY, Lee JH, et al. Prognostic factors and long-term clinical outcomes for surgical patients with intestinal Behcet’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011; 17:1594–1602.
Article14. Iida M, Kobayashi H, Matsumoto T, et al. Postoperative recurrence in patients with intestinal Behçet’s disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1994; 37:16–21.
Article15. Kawano S, Hiraoka S, Okada H, Akita M, Iwamuro M, Yamamoto K. Clinical features of intestinal Behçet’s disease associated with myelodysplastic syndrome and trisomy 8. Acta Med Okayama. 2015; 69:365–369.16. Wada Y, Nakatsue T, Kuroda T, et al. A case of intestinal Behcet’s disease complicated with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) refractory to anti-TNF drug treatment after bone marrow transplantation. J Chubu Rheumatism Association. 2015; 45:45–46.17. Umehara Y, Kudo M, Kawasaki M. Endoscopic findings of intestinal Behçet’s disease complicated with toxic megacolon. Endoscopy. 2010; 42 Suppl 2:E173–E174.
Article18. Nishimura K, Fujiki R, Hirotsu J, et al. A case of hilar bile duct cancer with intestinal Behçet’s disease. Kurume Med J. 2004; 51:169–173.19. Higa A, Uezu Y, Shiohira Y. A case of intestinal Behcet’s disease with perforation early onset. Kyushu J Rheumatology. 2003; 22:110–114.20. Arhan M, Ibiş M, Koklu S, Ozin Y, Oymaci E. Behcet’s disease complicated with descending colon perforation. Dig Surg. 2005; 22:381.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Intestinal Behcet's Disease Associated with Myelodysplastic Syndrome with Chromosomal Trisomy 8
- A Case of Behcet's Disease Associated with Schizophrenia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome with Trisomy 8 and 9
- Usefulness of Adalimumab for Treating a Case of Intestinal Behcet's Disease With Trisomy 8 Myelodysplastic Syndrome
- A Case of Behcet's Disease Associated with Myelodysplastic Syndrome
- Aplastic Anemia with Trisomy 8 and Trisomy 9 in Intestinal Behcet's Disease