Korean J Gastroenterol.
2010 Apr;55(4):256-260. 10.4166/kjg.2010.55.4.256.
Aplastic Anemia with Trisomy 8 and Trisomy 9 in Intestinal Behcet's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. geniushee@yuhs.ac
- 2Division of Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1792777
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2010.55.4.256
Abstract
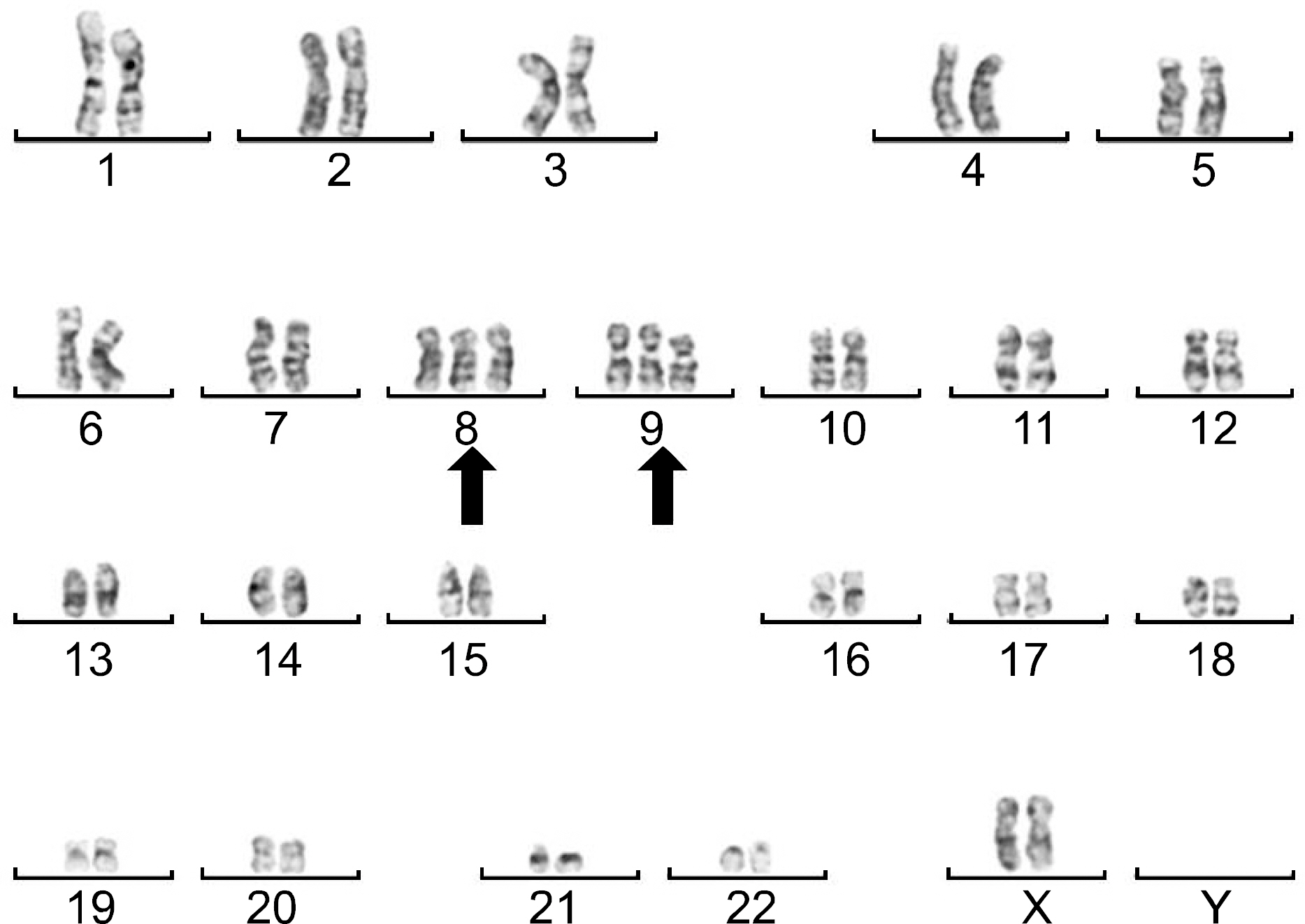
- Behcet's disease is a multisystemic inflammatory disease characterized with recurrent oral ulcer, genital ulcer, and multiple organ involvement. Aplastic anemia is one of the rarest complications of Behcet's disease. There were only several reports about Behcet's disease associated myelodysplatic syndrome worldwide. Moreover, aplastic anemia in intestinal Behcet's disease was rarely reported. Here, we present a case of aplastic anemia with trisomy 8 and trisomy 9 in intestinal Behcet's disease and a review of the literatures. To the authors' knowledge, this is the first case ever reported in Korea.
MeSH Terms
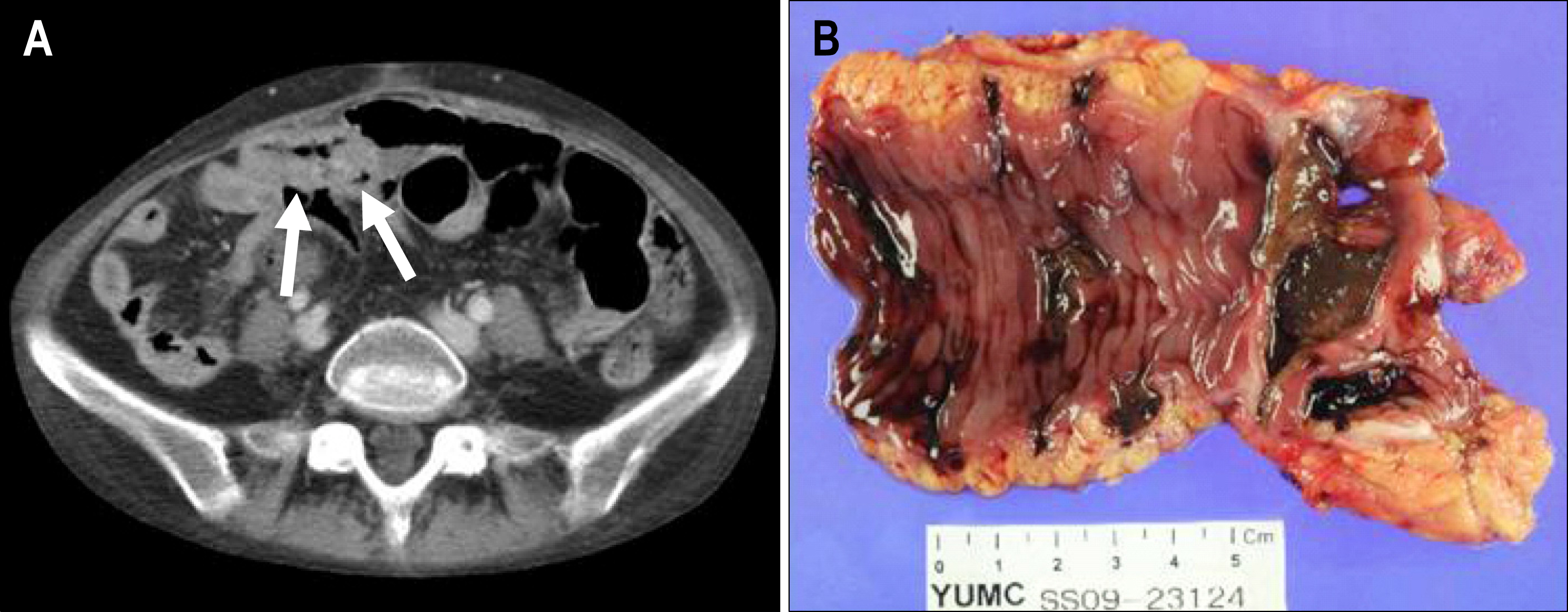
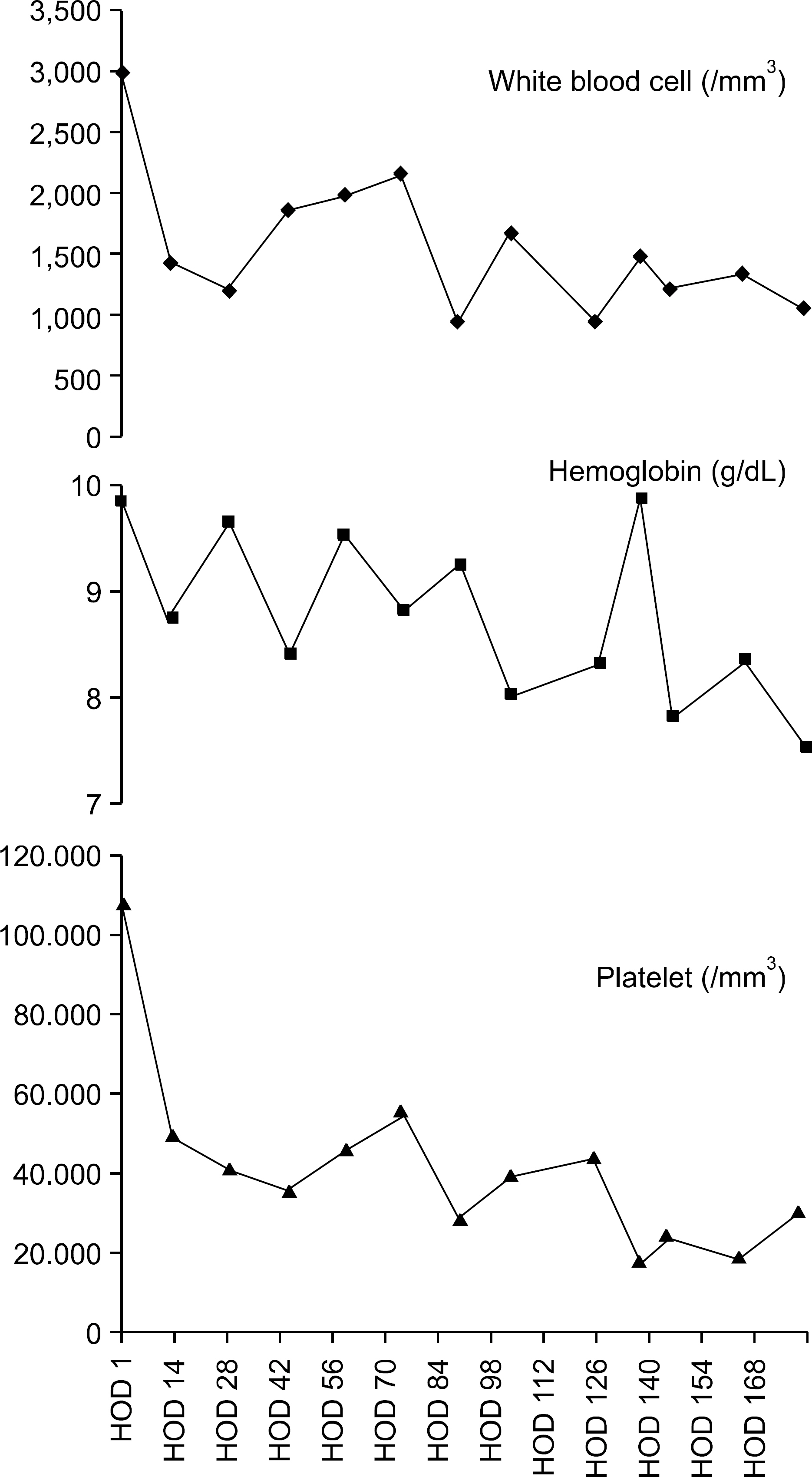
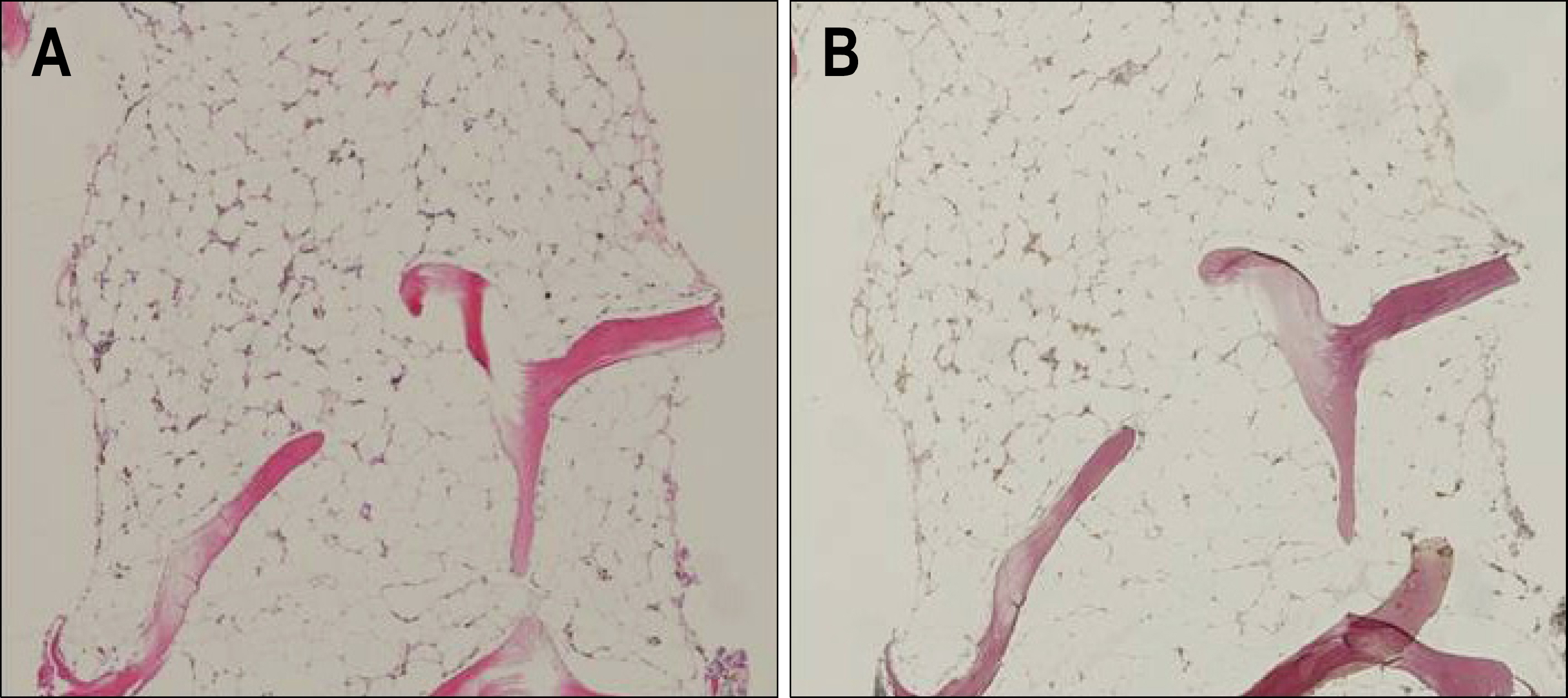
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G. Behç et's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:1284–1291.2. Criteria for diagnosis of Behç et's disease. International Study Group for Behç et's Disease. Lancet. 1990; 335:1078–1080.3. Kaklamani VG, Tzonou A, Kaklamanis PG. Behç et's disease associated with malignancies. Report of two cases and review of the literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005; 23(4 suppl 38):S35–S41.4. Kaloterakis A, Stavrianeas NG, Karagianni IN, et al. Ada-mantiades-Behç et's disease coexisting with acute myeloblastic leukaemia. Br J Dermatol. 1997; 137:317–318.5. Tassies D, Cervantes F, Feliu E, Cabal G, Martinez Orozco F, Rozman C. Behç et's disease with an onset prior to the appearance of chronic myeloid leukemia. Med Clin (Barc). 1992; 99:67–68.6. Abe T, Yachi A, Yabana T, et al. Gastric non-Hodgkin's lymphoma associated with Behç et's disease. Intern Med. 1993; 32:663–667.7. Kawabata H, Sawaki T, Kawanami T, et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome complicated with inflammatory intestinal ulcers: significance of trisomy 8. Intern Med. 2006; 45:1309–1314.
Article8. Suk KT, Kim HS, Kim JM, et al. A case of intestinal Behç et's disease associated with myelodysplastic syndrome with chromosomal trisomy 8. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2003; 41:229–233.9. Ahn JK, Cha HS, Koh EM, et al. Behç et's disease associated with bone marrow failure in Korean patients: clinical characteristics and the association of intestinal ulceration and trisomy 8. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008; 47:1228–1230.10. Tada Y, Koarada S, Haruta Y, Mitamura M, Ohta A, Nagasawa K. The association of Behç et's disease with myelodysplastic syndrome in Japan: a review of the literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006; 24(5 suppl 42):S115–S119.11. Voulgarelis M, Giannouli S, Ritis K, Tzioufas AG. Myelody-splasia-associated autoimmunity: clinical and pathophysiologic concepts. Eur J Clin Invest. 2004; 34:690–700.
Article12. Hsu HC, Lee YM, Tsai WH, et al. Circulating levels of thrombopoietic and inflammatory cytokines in patients with acute myeloblastic leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Oncology. 2002; 63:64–69.
Article13. Hadda V, Pandey BD, Gupta R, Goel A. Azathioprine induced pancytopenia: a serious complication. J Postgrad Med. 2009; 55:139–140.
Article14. Desai SB, Furst DE. Problems encountered during anti-tu-mour necrosis factor therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 20:757–790.
Article15. Maciejewski JP, Selleri C. Evolution of clonal cytogenetic abnormalities in aplastic anemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004; 45:433440.
Article16. Maciejewski JP, Risitano A, Sloand EM, Nunez O, Young NS. Distinct clinical outcomes for cytogenetic abnormalities evolving from aplastic anemia. Blood. 2002; 99:3129–3135.
Article17. Chen G, Zeng W, Miyazato A, et al. Distinctive geneexpression profiles of CD34 cells from patients with myelodysplastic syndrome characterized by specific chromosomal abnormalities. Blood. 2004; 104:4210–4218.18. Nonami A, Takenaka K, Sumida C, et al. Successful treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)-related intestinal Behç et's disease by up-front cord blood transplantation. Intern Med. 2007; 46:1753–1756.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cytogenetic Findings in Patients with Acquired Aplastic Anemia
- A Case of Behcet's Disease Associated with Schizophrenia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome with Trisomy 8 and 9
- A Case of Intestinal Behcet's Disease Associated with Myelodysplastic Syndrome with Chromosomal Trisomy 8
- Long-term outcome after surgery in a patient with intestinal Behçet’s disease complicated by myelodysplastic syndrome and trisomy 8
- Usefulness of Adalimumab for Treating a Case of Intestinal Behcet's Disease With Trisomy 8 Myelodysplastic Syndrome