Pediatric split liver transplantation using a hyperreduced left lateral segment graft in an infant weighing 4 kg
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2507166
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.2020.34.3.204
Abstract
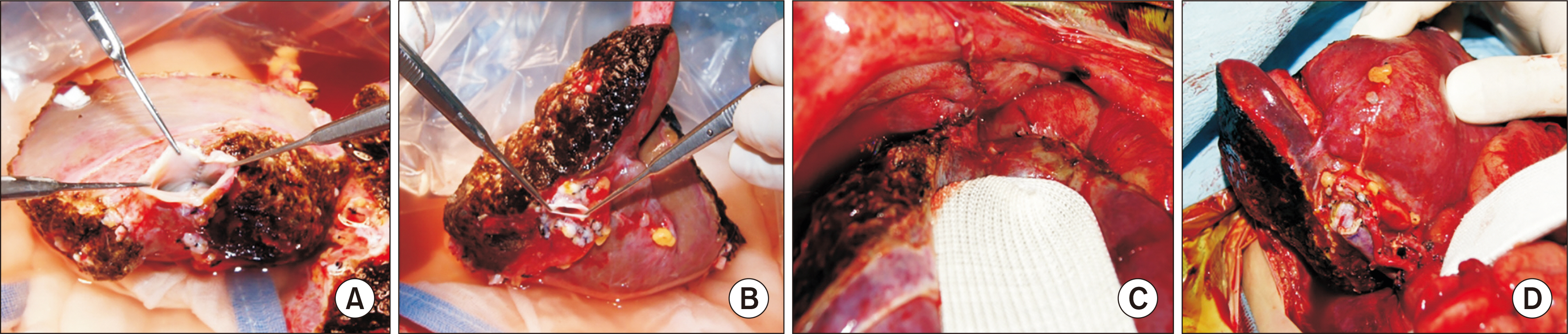
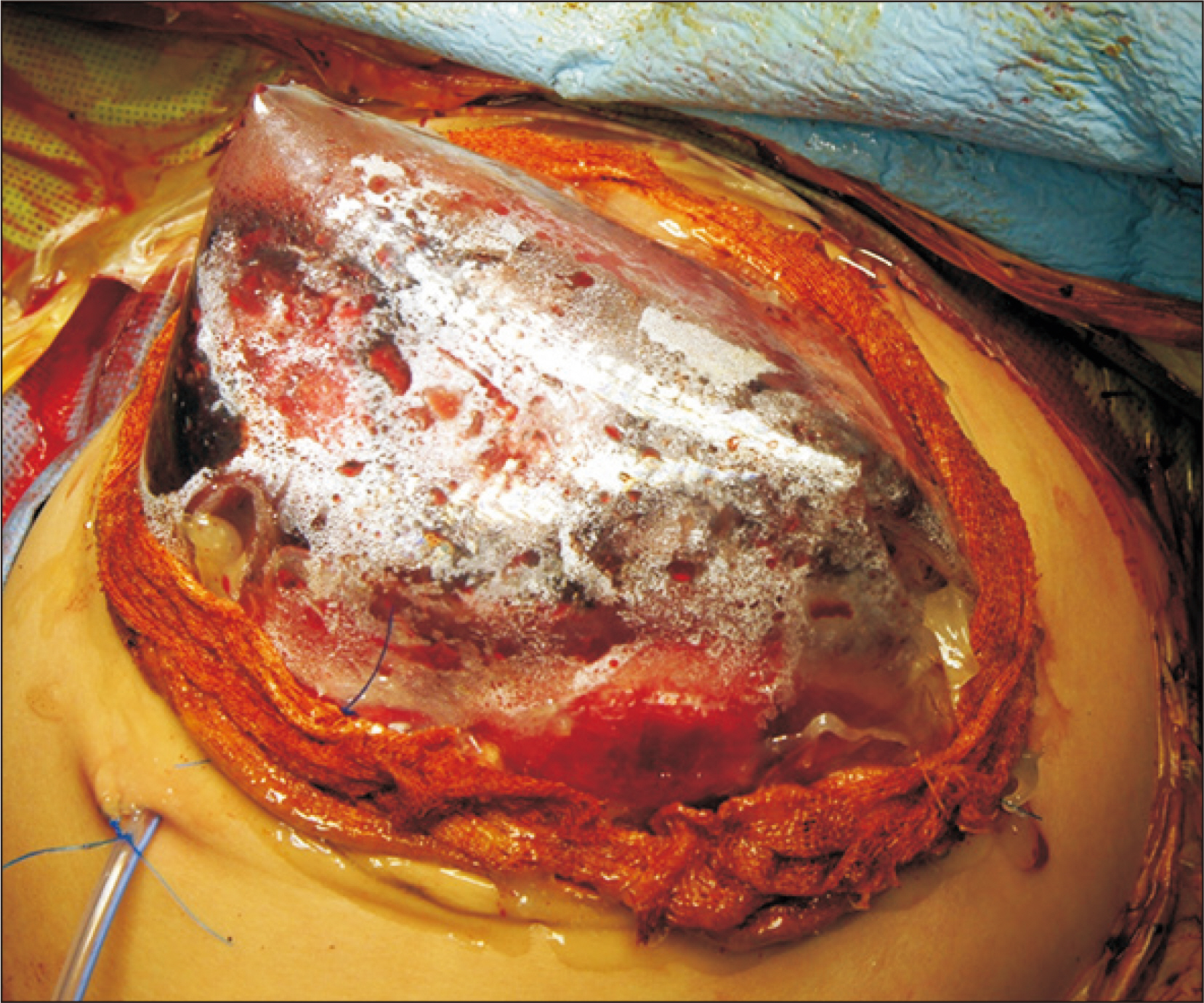
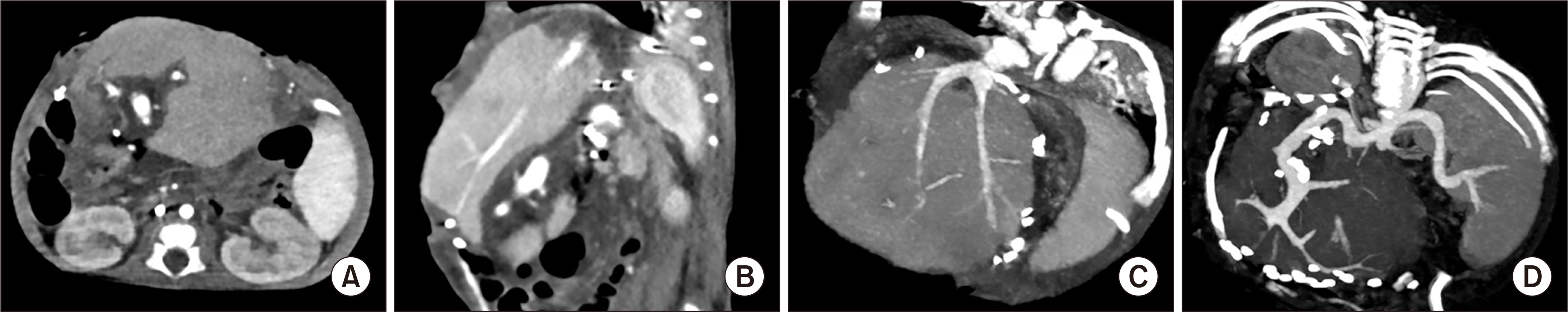
- We present a case of successful split liver transplantation (LT) using a hyperreduced left lateral segment (LLS) graft in a 106-day-old female infant patient weighing 4 kg. The patient was diagnosed with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Her general condition and liver function deteriorated progressively and she was finally allocated for a split LT under status 1. The deceased donor was a 20-year-old female weighing 63.7 kg. We performed in situ liver splitting and in situ size reduction sequentially. The weight of the hyperreduced LLS graft was 225 g, with a graft-recipient weight ratio of 5.5%. We performed recipient hepatectomy and graft implantation according to the standard procedures for pediatric living-donor LT. Since the graft was too large for primary abdomen closure, the abdominal wall was closed in three stages to make a prosthetic silo, temporary closure with a xenograft sheet, and final primary repair over 2 weeks. The patient has been doing well for more than 6 years after transplantation. In conclusion, split LT using a hyperreduced LLS graft can be a useful option for treating small infants. However, large-for-size graft-related problems, particularly in terms of graft thickness, still remain to be solved.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Dextroplantation of a reduced left lateral section graft in an infant undergoing living donor liver transplantation
Jung-Man Namgoong, Shin Hwang, Gil-Chun Park, Kyung Mo Kim, Seak Hee Oh, Hyunhee Kwon, Yong Jae Kwon
Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2021;25(3):414-418. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.3.414.Pediatric deceased donor liver transplantation with
in situ size reduction for recipient-graft size matching
Jung-Man Namgoong, Shin Hwang, Dae-Yeon Kim, Tae-Yong Ha, Gi-Won Song, Dong-Hwan Jung, Kyung Mo Kim, Seak Hee Oh
Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2021;25(3):431-435. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.3.431.Living donor liver transplantation with hyperreduced segment II monosegment graft for an infant weighing 3 kilograms
Jung-Man Namgoong, Gil-Chun Park, Shin Hwang, Sang-Hoon Kim, Suhyeon Ha, Kyung Mo Kim, Seak Hee Oh
Ann Liver Transplant. 2023;3(1):50-56. doi: 10.52604/alt.23.0001.
Reference
-
1. Kanazawa H, Sakamoto S, Fukuda A, Uchida H, Hamano I, Shigeta T, et al. 2013; Living-donor liver transplantation with hyperreduced left lateral segment grafts: a single-center experience. Transplantation. 95:750–4. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e31827a93b4. PMID: 23503505.2. Shehata MR, Yagi S, Okamura Y, Iida T, Hori T, Yoshizawa A, et al. 2012; Pediatric liver transplantation using reduced and hyper-reduced left lateral segment grafts: a 10-year single-center experience. Am J Transplant. 12:3406–13. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04268.x. PMID: 22994696.
Article3. Ardiles V, Ciardullo MA, D'Agostino D, Pekolj J, Mattera FJ, Boldrini GH, et al. 2013; Transplantation with hyper-reduced liver grafts in children under 10 kg of weight. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 398:79–85. DOI: 10.1007/s00423-012-1020-y. PMID: 23093088.4. Thomas N, Thomas G, Verran D, Stormon M, O'Loughlin E, Shun A. 2010; Liver transplantation in children with hyper-reduced grafts: a single-center experience. Pediatr Transplant. 14:426–30. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2010.01294.x. PMID: 20214746.5. Yamada N, Sanada Y, Hirata Y, Okada N, Wakiya T, Ihara Y, et al. 2015; Selection of living donor liver grafts for patients weighing 6kg or less. Liver Transpl. 21:233–8. DOI: 10.1002/lt.24048. PMID: 25422258.
Article6. Sakuma Y, Sasanuma H, Miki A, Shimizu A, Sata N, Yasuda Y, et al. 2016; Living-donor liver transplantation using segment 2 monosegment graft: a single-center experience. Transplant Proc. 48:1110–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.12.119. PMID: 27320568.
Article7. Hong SK, Suh KS, Kim HS, Yoon KC, Ahn SW, Kim H, et al. 2018; Pediatric living donor liver transplantation using a monosegment procured by pure 3D laparoscopic left lateral sectionectomy and in situ reduction. J Gastrointest Surg. 22:1135–6. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-018-3705-1. PMID: 29435902.
Article8. Srinivasan P, Vilca-Melendez H, Muiesan P, Prachalias A, Heaton ND, Rela M. 1999; Liver transplantation with monosegments. Surgery. 126:10–2. DOI: 10.1067/msy.1999.98686. PMID: 10418586.
Article9. Kiuchi T, Kasahara M, Uryuhara K, Inomata Y, Uemoto S, Asonuma K, et al. 1999; Impact of graft size mismatching on graft prognosis in liver transplantation from living donors. Transplantation. 67:321–7. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-199901270-00024. PMID: 10075602.10. Kasahara M, Fukuda A, Yokoyama S, Sato S, Tanaka H, Kuroda T, et al. 2008; Living donor liver transplantation with hyperreduced left lateral segments. J Pediatr Surg. 43:1575–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2008.02.056. PMID: 18675660.
Article11. Vanatta JM, Esquivel CO. 2007; Status of liver transplantation in infants < 5 kg. Pediatr Transplant. 11:5–9. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2006.00627.x. PMID: 17328158.12. Raices M, Czerwonko ME, Ardiles V, Boldrini G, D'Agostino D, Marcó Del Pont J, et al. 2019; Short- and long-term outcomes after live-donor transplantation with hyper-reduced liver grafts in low-weight pediatric recipients. J Gastrointest Surg. 23:2411–20. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-019-04188-y. PMID: 30887299.
Article13. Houssin D, Soubrane O, Boillot O, Dousset B, Ozier Y, Devictor D, et al. 1992; Orthotopic liver transplantation with a reduced-size graft: an ideal compromise in pediatrics? Surgery. 111:532–42. PMID: 1598673.14. Sakamoto S, Kanazawa H, Shigeta T, Uchida H, Sasaki K, Hamano I, et al. 2014; Technical considerations of living donor hepatectomy of segment 2 grafts for infants. Surgery. 156:1232–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2014.05.003. PMID: 24909347.
Article15. Hwang S, Kim KH, Kim DY, Kim KM, Ahn CS, Moon DB, et al. 2013; Anomalous hepatic vein anatomy of left lateral section grafts and customized unification venoplasty for pediatric living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 19:184–90. DOI: 10.1002/lt.23557. PMID: 23045153.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Living donor liver transplantation with hyperreduced segment II monosegment graft for an infant weighing 3 kilograms
- Pediatric liver transplantation with hyperreduced left lateral segment graft
- Pediatric liver transplantation with hyperreduced left lateral segment graft
- Dextroplantation of a reduced left lateral section graft in an infant undergoing living donor liver transplantation
- Left at right heterotopic implantation of left liver graft in adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation: the technical concern for decision-making